Are cannabis abuse and accelerated brain aging linked? This question delves into the complex relationship between cannabis use and potential impacts on brain health. We’ll explore the potential mechanisms through which cannabis might affect the aging brain, examining various usage patterns and the crucial role of confounding factors. Different research methodologies and their limitations will be discussed, along with the potential biological pathways involved.
The cognitive consequences of cannabis use, considering different ages of initiation, will be detailed. Finally, we’ll discuss influencing factors, public health implications, and future research needs.
The potential link between cannabis abuse and accelerated brain aging is a topic of significant debate. While some studies suggest a correlation, others highlight the importance of considering confounding variables. This article will delve into the scientific evidence, examining both the promising findings and the limitations of current research. We will also address the potential impacts on cognitive function, the role of individual differences, and the broader implications for public health.
Introduction to Cannabis and Brain Aging
Cannabis use, particularly chronic and heavy use, has sparked considerable research into potential links with accelerated brain aging. While the exact nature of this relationship remains a subject of ongoing investigation, emerging evidence suggests a correlation between prolonged cannabis use and structural and functional changes in the brain that could be associated with accelerated cognitive decline. This complex interplay warrants a deeper dive into the potential mechanisms and the critical need for careful consideration of confounding factors.The potential mechanisms by which cannabis might impact brain health are multifaceted.
While studies explore if cannabis abuse might accelerate brain aging, it’s a complex area. Interestingly, the question of whether solid foods can help babies sleep better is also a hot topic for parents. For example, can solid food help your baby get sleep ? Ultimately, more research is needed to definitively answer both questions about brain health and baby sleep.
This complexity underscores the importance of careful consideration when evaluating potential links between cannabis and aging.
The primary active compound in cannabis, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), interacts with the brain’s endocannabinoid system, a complex network of receptors and neurotransmitters involved in various cognitive functions. Disruptions to this system might lead to alterations in synaptic plasticity, neurogenesis, and neurotransmitter balance, potentially impacting the structural integrity and functional capacity of the brain over time. Furthermore, the potential for long-term exposure to the cannabinoids and other constituents in cannabis, through repeated use, could also contribute to the potential for accelerated aging effects.
Potential Impacts of Cannabis Use on Brain Aging
The impacts of cannabis use on brain aging are influenced by various factors, including the frequency, duration, and dosage of use. A significant amount of research focuses on chronic, heavy users of cannabis, who may experience more pronounced effects. Light or occasional use might not have the same impact.
- Frequency of Use: Regular or daily use, compared to infrequent or sporadic use, may increase the likelihood of adverse effects on brain structure and function. The more frequent the exposure, the greater the potential for cumulative impact.
- Duration of Use: The duration of cannabis use is also crucial. Long-term users, particularly those who begin use during adolescence or young adulthood, may experience more significant and lasting impacts compared to those who initiate use later in life.
- Dosage: The amount of cannabis consumed also matters. Higher doses may lead to greater exposure to cannabinoids, increasing the potential for disruptions in the endocannabinoid system and cognitive functions.
Importance of Considering Confounding Factors
It is vital to acknowledge the complexity of the relationship between cannabis use and brain aging. Multiple factors, known as confounding factors, can influence the observed outcomes in research studies. These factors need to be carefully considered to avoid misinterpreting the results.
- Genetics: Individual genetic predispositions can influence vulnerability to the effects of cannabis and potentially affect brain development and aging trajectories. Some individuals might be more susceptible to adverse effects than others.
- Lifestyle Factors: Lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, sleep, and stress levels can interact with cannabis use and influence brain health. A healthy lifestyle may mitigate some of the potential negative impacts.
- Other Substance Use: The use of other substances, including alcohol or nicotine, may interact with cannabis use, potentially exacerbating or modifying the effects on brain aging. The cumulative impact of multiple substances can be more significant than the impact of any single substance alone.
Existing Research and Studies
Unraveling the complex relationship between cannabis use and brain aging requires a critical examination of existing research. While anecdotal evidence and personal experiences abound, the scientific community relies on rigorous studies to establish causal links and draw meaningful conclusions. This section delves into the diverse methodologies employed, the characteristics of the samples studied, and the key findings to better understand the current scientific consensus.Existing research on cannabis and brain aging is multifaceted, encompassing a range of study designs and methodologies.
The quality and reliability of the findings are significantly influenced by these approaches, and careful consideration of potential biases and limitations is crucial. The varying degrees of control and observation employed in different studies, along with the characteristics of the participant groups, contribute to the complexity of interpreting the results.
Comparison of Research Studies
Understanding the nuances of different research methodologies is vital for evaluating the robustness of the conclusions drawn. This comparison highlights the strengths and weaknesses of various approaches.
| Study Design | Sample Characteristics | Findings | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Longitudinal study following a cohort of cannabis users over time. | Participants were typically adults, with varying levels of cannabis use and demographics. Specific details on the frequency and duration of cannabis use were recorded. | Some studies found a correlation between heavy cannabis use and decreased performance on cognitive tasks, while others found no significant impact. Longitudinal designs allow for tracking changes over time, but the results may be influenced by confounding factors. | Potential for participant attrition, difficulties in controlling for lifestyle factors, and long study durations. |
| Observational study comparing cognitive function between cannabis users and non-users. | Participants were typically recruited from specific populations, like university students or community members. Data on cannabis use patterns were collected through self-reporting. | Some studies revealed a negative correlation between cannabis use frequency and certain cognitive abilities, while others found no discernible impact. | Observational studies cannot establish causality, as they cannot control for other factors that might influence cognitive function. Selection bias and self-reported data accuracy are potential concerns. |
| Intervention study evaluating the impact of cannabis cessation on cognitive function. | Participants were typically cannabis users who agreed to discontinue use. Baseline cognitive function was assessed before and after cessation. | Some studies showed improvements in certain cognitive domains after cessation, particularly in younger participants. The results are often specific to the type of cognitive test used. | The impact of individual differences in response to cessation, adherence to the cessation protocol, and potential confounding factors (e.g., stress, diet) need to be accounted for. |
Summary of Scientific Consensus
Currently, there’s no definitive scientific consensus on the causal relationship between cannabis use and cognitive function in the long term. While some studies suggest potential negative impacts, particularly with heavy and prolonged use, others report no significant effects. The existing evidence is not strong enough to definitively state a clear correlation.
Potential Biases and Limitations
Several biases and limitations in existing research need careful consideration. These factors can influence the reliability and validity of the conclusions drawn from these studies. Selection bias, where the study participants are not representative of the broader population, can skew results. Self-reported cannabis use, while convenient, may not accurately reflect true usage patterns. The lack of standardization in cognitive testing methods across studies also presents a challenge.
Finally, the interplay of other lifestyle factors (diet, exercise, sleep, stress) complicates the interpretation of results.
Different Research Methods
Various research methods have been employed to investigate the link between cannabis use and brain aging. Longitudinal studies, following individuals over extended periods, allow for the observation of changes over time. Observational studies, comparing groups of users and non-users, can identify potential correlations. Intervention studies, where individuals are encouraged to cease cannabis use, provide insights into potential reversibility of cognitive effects.
Each method offers unique insights, but each also comes with inherent limitations.
Potential Biological Mechanisms
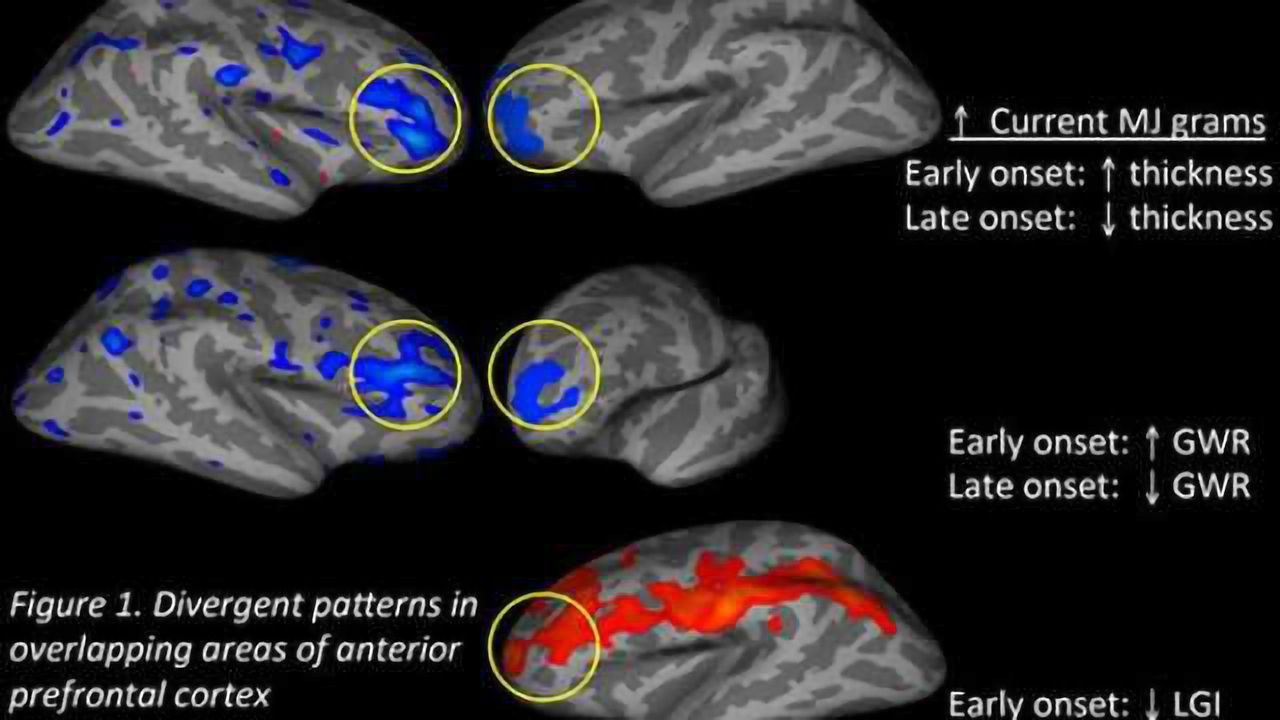
Cannabis use, particularly chronic use, might influence brain aging through several complex neurobiological pathways. Understanding these pathways is crucial for exploring the potential link between cannabis and accelerated brain aging. The effects of cannabinoids on various brain functions, including neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity, and neuroinflammation, are key areas of investigation. This exploration delves into the potential mechanisms by which cannabis could impact brain aging, considering the distinct effects of different cannabinoids like THC and CBD.The intricate interplay between cannabinoid receptors, neurotransmitter systems, and cellular processes within the brain likely plays a role in mediating the impact of cannabis use on brain aging.
Factors like the frequency, duration, and quantity of cannabis use, as well as individual genetic predispositions, can all potentially modify these mechanisms.
Effects of Cannabinoids on Brain Structure and Function
Cannabinoids, particularly THC, exert their effects by interacting with the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex network of receptors and signaling molecules throughout the brain and body. This system plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes, including mood, appetite, pain perception, and memory. THC, the primary psychoactive component of cannabis, directly binds to cannabinoid receptors (CB1 receptors), which are primarily located in the brain.
This binding can influence neuronal activity, potentially affecting brain structure and function over time. Conversely, CBD, a non-psychoactive cannabinoid, also interacts with the ECS but through different pathways, potentially modulating the effects of THC.
Impact on Neurogenesis and Synaptic Plasticity
Neurogenesis, the formation of new neurons, and synaptic plasticity, the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, are crucial for maintaining cognitive function throughout life. Chronic cannabis use may impact these processes in various ways. Some studies suggest that THC can potentially impair neurogenesis in specific brain regions, potentially impacting learning and memory. However, the extent and direction of these effects remain subject to ongoing research.
Furthermore, the impact on synaptic plasticity, which allows the brain to adapt and learn, is not yet fully understood. Changes in synaptic strength or connectivity may contribute to alterations in cognitive function and contribute to accelerated aging in certain individuals.
Impact on Neuroinflammation
Chronic cannabis use may contribute to neuroinflammation, a process characterized by the activation of immune cells in the brain. Neuroinflammation is associated with various age-related neurodegenerative diseases. Cannabinoids can modulate the inflammatory response, and some studies suggest that certain cannabinoids might exert anti-inflammatory effects. However, the long-term impact of chronic cannabis use on neuroinflammation and its potential contribution to accelerated brain aging is a complex and debated topic.
Comparison of THC and CBD Effects
The effects of THC and CBD on brain aging may differ significantly. THC, the psychoactive component, is thought to directly affect neuronal activity and potentially impact neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity, potentially in ways that lead to age-related cognitive decline. Conversely, CBD, the non-psychoactive component, may have a more complex interaction with the ECS, potentially influencing neuroinflammation and other brain processes in ways that might mitigate some of the negative effects of THC.
Further research is needed to fully understand the differential effects of these cannabinoids on brain aging.
Potential Impacts on Cognitive Function: Are Cannabis Abuse And Accelerated Brain Aging Linked
Cannabis use, particularly during crucial developmental periods, can potentially affect cognitive functions. The impact varies significantly depending on factors like the frequency and duration of use, the individual’s genetic predisposition, and the age of initiation. Understanding these nuances is crucial for assessing the potential risks associated with cannabis use.While some studies suggest potential benefits in certain cognitive domains, the overall consensus points towards a more complex and often negative impact on cognitive functions, especially in the long term.
This is particularly concerning when considering the potential for long-term effects, especially during critical periods of brain development.
Cognitive Consequences Across Different Ages of Initiation
The age at which someone begins using cannabis plays a significant role in the potential cognitive consequences. Early initiation, before the brain is fully developed, is often associated with a higher risk of negative effects on various cognitive domains.
- Early Initiation (Adolescence): Adolescence is a critical period for brain development, particularly in areas related to executive function, memory, and learning. Exposure to cannabis during this stage may disrupt normal brain maturation, potentially leading to long-term deficits in these areas. Individuals who initiate cannabis use in adolescence may experience difficulties with tasks requiring sustained attention, working memory, and problem-solving.
- Later Initiation (Adulthood): While the risk of significant cognitive impairment is generally lower for adults who begin using cannabis later in life, there can still be observable effects. Studies have shown that even moderate, chronic cannabis use in adulthood can potentially impact attention span, memory consolidation, and executive functions. The impact might be less pronounced compared to early initiation, but it’s still important to acknowledge the potential for negative effects.
Impact on Memory
Cannabis use can affect various aspects of memory, from short-term recall to long-term memory consolidation. Studies have explored the potential for cannabis use to disrupt the neural pathways crucial for encoding and retrieving memories.
- Short-Term Memory: Some research suggests that cannabis use can negatively affect short-term memory, making it more challenging to retain and process information in the immediate term. This might manifest as difficulty remembering details of conversations or forgetting recent events.
- Long-Term Memory: While short-term memory is often affected, the impact on long-term memory consolidation is a significant concern. Interference with the brain’s ability to create and store long-term memories can have a considerable impact on learning and recall, potentially affecting academic performance and the ability to retain information over time.
Impact on Attention and Executive Functions
Executive functions are a set of higher-order cognitive processes that enable us to plan, organize, and execute tasks. Cannabis use has the potential to disrupt these critical cognitive abilities.
- Attention: Cannabis use can affect attention span and focus. Individuals may experience difficulties maintaining concentration on tasks, leading to decreased productivity and increased errors. This can be seen in academic performance, work productivity, or even driving ability.
- Executive Functions: These functions, including planning, problem-solving, and inhibitory control, can be significantly impacted by cannabis use. Individuals might struggle with organizing their thoughts, making decisions, or controlling impulsive behaviors. This could manifest in difficulty managing daily tasks, or in interpersonal relationships.
Potential Long-Term Effects on Learning and Decision-Making
The long-term effects of cannabis use on learning and decision-making are complex and not fully understood. Studies have shown a potential for negative impacts on these cognitive domains.
- Learning: Chronic cannabis use may impair the brain’s ability to learn and adapt to new information. This can manifest as difficulties acquiring new skills or adjusting to changes in routines. Learning new material may be more challenging.
- Decision-Making: Impaired executive functions and potential changes in reward processing can lead to altered decision-making processes. Individuals may exhibit poor judgment or make impulsive decisions with negative consequences. These consequences can be seen in areas ranging from financial decisions to interpersonal interactions.
Factors Influencing the Relationship
The relationship between cannabis use and brain aging is complex and not fully understood. While some studies suggest a potential link between frequent cannabis use and accelerated brain aging, it’s crucial to recognize that numerous factors can influence this association. Understanding these variables is vital for developing accurate and targeted interventions to promote healthy brain aging, regardless of cannabis use habits.Individual characteristics, lifestyle choices, and even the type of cannabis consumed can all play a significant role in shaping the impact of cannabis on brain health.
This section delves into these influencing factors, highlighting the nuances of this intricate relationship.
Individual Differences
Individual differences significantly impact how cannabis use affects brain aging. Genetics play a critical role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to the effects of cannabis. Some individuals may possess genetic predispositions that make them more or less vulnerable to the neurotoxic effects of certain cannabinoids. Age of initiation also matters; individuals who begin using cannabis at a younger age may experience greater long-term consequences.
Pre-existing conditions, such as mental health issues or other neurological disorders, can interact with cannabis use, potentially exacerbating negative effects on brain aging.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices, such as diet, exercise, and stress levels, can modify the impact of cannabis use on brain aging. A balanced diet rich in antioxidants and essential nutrients may help mitigate some of the potential damage caused by cannabis. Regular physical activity can improve overall brain health, potentially buffering against negative effects of cannabis use. Chronic stress can negatively impact brain health, and the combined effect of cannabis use and high stress levels might lead to more pronounced cognitive decline.
Moderating and Mediating Factors
Various factors can moderate or mediate the relationship between cannabis use and brain aging. Moderating factors can lessen the impact of cannabis use, while mediating factors can explain the link between cannabis use and brain aging. For instance, individuals with high levels of social support might experience fewer negative consequences of cannabis use. Education level or engagement in cognitively stimulating activities could also act as moderating factors.
Mediating factors could include the presence of certain biomarkers associated with inflammation or oxidative stress, which might explain how cannabis use contributes to brain aging.
Cannabis Strain Influence
The specific cannabinoid and terpene profiles of different cannabis strains can influence their impact on brain aging. Some strains may contain higher concentrations of certain cannabinoids, like THC, that are associated with potential negative cognitive effects. Others might contain higher levels of CBD, which may have a protective effect. Research into the specific effects of different strains on brain health is still ongoing, but it’s crucial to recognize that the variety of cannabis strains can contribute to the diverse outcomes associated with cannabis use.
Public Health Implications
The potential link between cannabis abuse and accelerated brain aging raises significant public health concerns. Understanding this connection is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate the risks associated with cannabis use, particularly for vulnerable populations. Public health campaigns must now address the potential long-term cognitive impacts of cannabis use, alongside the well-established short-term effects.This necessitates a multifaceted approach, moving beyond simple warnings to include educational resources and support systems for those who may be at risk.
Recent studies are exploring the potential link between cannabis abuse and accelerated brain aging. It’s a fascinating area, but the complexities are immense. Interestingly, research into the role of fungi in Crohn’s disease, like fungi role in crohns disease , highlights the intricate web of factors influencing human health. Ultimately, understanding the diverse biological pathways involved in both cannabis use and brain aging is crucial for developing effective preventative strategies and treatments.
The potential consequences for public health are substantial, requiring proactive measures to protect individuals and communities.
Public Health Campaigns, Are cannabis abuse and accelerated brain aging linked
Public health campaigns need to move beyond simplistic messaging and incorporate tailored information for different demographics. This includes targeted campaigns for young adults and adolescents, emphasizing the potential long-term effects of cannabis use on brain development. Educational materials should clearly Artikel the potential risks associated with heavy or prolonged cannabis use, and provide accessible resources for those seeking help.
Strategies for Reducing Risks
Strategies for reducing the risks associated with cannabis use and brain aging must consider a comprehensive approach. This includes promoting responsible cannabis use, particularly among young adults. Increased awareness and education campaigns can highlight the importance of moderation and limiting heavy use, particularly during critical developmental periods. Early intervention programs aimed at young adults experimenting with cannabis could be instrumental in mitigating potential negative outcomes.
Need for Further Research and Prevention Strategies
Further research is essential to fully understand the complex interplay between cannabis use, brain aging, and cognitive function. This research should explore the specific mechanisms underlying the potential link, identifying biomarkers and risk factors. Prevention strategies must be developed to address potential disparities in cannabis use patterns across different socioeconomic groups. Public health initiatives should include culturally sensitive and accessible resources for those who might be disproportionately affected by the potential risks.
While research on cannabis abuse and its potential link to accelerated brain aging is ongoing, it’s a complex issue. Understanding the potential effects of substances on our bodies is crucial. This isn’t just about recreational use, but also considering situations like unexpected pregnancies, which can be addressed with birth control emergency contraception options. Ultimately, more research is needed to fully understand the connections between cannabis use, brain health, and overall well-being.
Policy Recommendations
Policy recommendations should consider a range of approaches to regulate and inform cannabis use. These recommendations must balance the need for public health protection with individual autonomy and freedom of choice. Developing clear guidelines for cannabis use, particularly among young adults, is critical. These policies should also address the potential disparities in access to information and support services for different communities.
Regulations on cannabis marketing and advertising should emphasize responsible use and minimize potential negative impacts on vulnerable populations. For example, restricting advertisements targeting youth and highlighting potential long-term risks are vital considerations. This includes clear labelling requirements for cannabis products, highlighting potential risks to cognitive function. This could be in the form of explicit warnings or educational information, alongside warnings about potential risks to brain development.
Ultimately, policies must encourage responsible use and facilitate access to resources for those seeking support.
Future Directions and Research Needs
Unraveling the complex relationship between cannabis use and accelerated brain aging requires a concerted effort to address the current limitations in research. Existing studies often suffer from methodological limitations, leaving crucial gaps in our understanding. Future research must prioritize longitudinal studies, employing advanced neuroimaging techniques, and considering the multifaceted nature of individual experiences to paint a more comprehensive picture.The journey to understanding the long-term effects of cannabis on brain aging is far from over.
Current research, while offering valuable insights, necessitates a shift towards more nuanced and comprehensive approaches. This includes considering individual factors like age at initiation, frequency and duration of use, specific cannabis strains, and co-occurring mental health conditions. These considerations will provide a more precise understanding of the impact of cannabis use on brain health across the lifespan.
Longitudinal Studies with Larger Sample Sizes
Current studies often lack sufficient longitudinal data, limiting our ability to track the progression of brain changes over time in individuals who use cannabis. Studies with larger, more diverse participant groups, tracking their cannabis use patterns and cognitive function over extended periods, are crucial for understanding the long-term effects of cannabis. This will allow for more accurate assessments of the potential relationship between cannabis use and cognitive decline.
For instance, a study following individuals from adolescence into adulthood could offer crucial insights into the potential long-term impact of early cannabis use.
Advanced Neuroimaging Techniques
Employing advanced neuroimaging technologies like fMRI and structural MRI can offer a more in-depth look into the structural and functional changes in the brain associated with cannabis use. These techniques can reveal subtle changes in brain regions associated with memory, executive function, and other cognitive processes. These advanced imaging methods can provide a more detailed understanding of the impact of cannabis on specific neural pathways and networks, allowing researchers to identify specific mechanisms involved.
For example, comparing the brain structures of cannabis users and non-users, tracked longitudinally, can highlight subtle differences in gray matter volume or white matter integrity.
Addressing the Heterogeneity of Cannabis Use
Cannabis use is highly heterogeneous, varying significantly in terms of frequency, duration, and the specific cannabinoids consumed. Future research should consider the diverse ways in which individuals use cannabis and how these factors might interact with the brain’s aging process. This requires categorizing cannabis users into specific groups based on their usage patterns, enabling a more tailored and targeted approach to the study of their impact.
For instance, heavy chronic users, infrequent users, and users who have started in adolescence might exhibit distinct patterns of brain changes.
Ethical Considerations in Cannabis Research
Ethical considerations are paramount in research involving cannabis use. Researchers must ensure informed consent procedures are robust, protect the privacy of participants, and minimize potential harm. These concerns are particularly important when dealing with vulnerable populations, such as adolescents and individuals with pre-existing mental health conditions. Open discussions on the ethical implications of cannabis research, and clear guidelines, are crucial for maintaining public trust and ensuring the responsible conduct of research.
Focus on Specific Brain Regions and Cognitive Functions
Future research should target specific brain regions and cognitive functions known to be affected by aging and potential impacts from cannabis. This involves exploring the impact of cannabis use on areas like the hippocampus (memory), prefrontal cortex (executive function), and the amygdala (emotional processing). For example, studies examining the impact of cannabis use on verbal memory tasks, spatial reasoning, and emotional regulation could provide valuable insights into the nuances of the relationship.
Illustrative Examples
Understanding the potential link between cannabis use and accelerated brain aging requires looking at specific examples. While research is ongoing and complex, examining case scenarios can help illustrate the potential impact of chronic cannabis use on brain health and cognitive function. These examples should not be taken as definitive proof of causality, but rather as potential pathways for future investigation.
Illustrative Case Scenarios
A table below provides examples of potential scenarios, highlighting the interplay between cannabis use, brain aging, and cognitive function. It’s crucial to remember that individual responses vary significantly, and these examples are meant to be illustrative, not exhaustive.
| Case Description | Potential Effects | Further Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| A 25-year-old individual with a history of daily cannabis use for 5 years experiences difficulty with tasks requiring sustained attention, such as studying for exams or following complex instructions at work. | Potential impairment in areas of the brain associated with executive function (prefrontal cortex), potentially leading to difficulties with focus, working memory, and problem-solving. | This individual may also exhibit subtle changes in emotional regulation or impulse control. The duration of use and the frequency of cannabis consumption play a significant role in the extent of the potential effects. |
| A 40-year-old recreational cannabis user notices a gradual decline in their ability to remember recent events or recall information from the past. | Possible impact on the hippocampus, a region crucial for memory formation and retrieval. This could manifest as difficulties with short-term memory, episodic memory, or even the ability to learn new information. | The individual’s overall health, including sleep patterns, diet, and exercise habits, significantly influence the impact of cannabis use on cognitive function. Other factors like stress and pre-existing conditions may also contribute. |
| A 65-year-old individual with a long history of heavy cannabis use reports experiencing confusion and disorientation in familiar environments. | Potential impact on the cerebral cortex and associated areas impacting higher-level cognitive processes like orientation, spatial reasoning, and judgment. This could also be linked to changes in neurotransmitter systems. | This example highlights the possibility of accelerated cognitive decline in older individuals with prolonged cannabis use, especially considering the potential for cumulative effects over time. Pre-existing health conditions and other lifestyle factors must be considered. |
Impact on Brain Regions
The impact of cannabis use on brain aging is not uniform across all regions. Specific brain areas are more vulnerable to the effects of chronic cannabis use. For example, the prefrontal cortex, responsible for executive functions, is a region that may be particularly susceptible. The hippocampus, essential for memory, also appears to be a target. The cerebellum, associated with motor coordination, and the amygdala, related to emotional processing, may also be affected.
Understanding the intricate interactions between these regions is critical to comprehending the broader cognitive consequences.
Influence on Cognitive Domains
Cannabis use can potentially influence various cognitive domains, including memory, attention, executive function, and processing speed. For example, impairments in working memory and sustained attention have been observed in individuals with a history of chronic cannabis use. The impact on specific cognitive domains is likely dependent on factors like the duration and intensity of use, individual susceptibility, and pre-existing conditions.
Impact on Different Age Groups
The potential impact of cannabis use on brain aging varies across different age groups. In adolescents, the developing brain is particularly vulnerable, and cannabis use may interfere with the crucial neural connections forming during this period. Adults may experience subtle cognitive changes that may not be immediately apparent. In older adults, prolonged cannabis use could potentially exacerbate pre-existing cognitive decline or accelerate the onset of age-related cognitive impairment.
Age-specific research is crucial for a complete understanding of the relationship between cannabis use and brain aging.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, the question of whether cannabis abuse accelerates brain aging remains a complex and evolving area of research. While promising research has revealed potential links, confounding factors and limitations in current studies necessitate a cautious interpretation of the evidence. Further longitudinal studies, controlling for these factors, are crucial to a more definitive understanding. Ultimately, this discussion underscores the need for continued research and a nuanced approach to understanding the potential impact of cannabis use on brain health throughout the lifespan.




