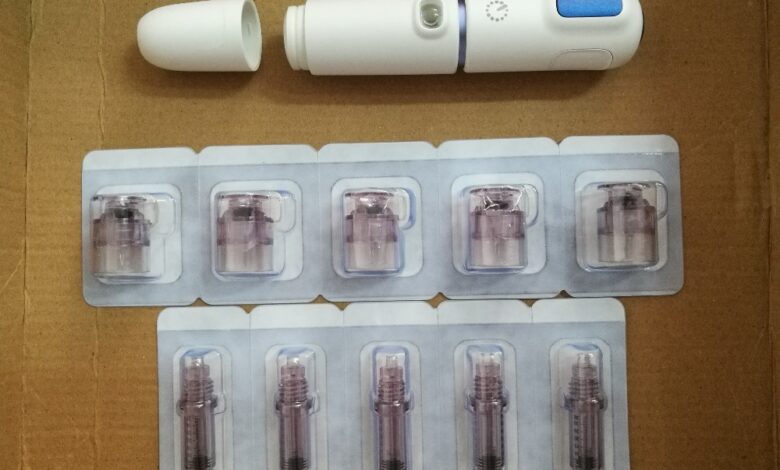
Diabetes needle free injector – Diabetes needle-free injector technology promises a future where injections are painless and easier than ever. This innovative approach is changing the landscape of diabetes management, offering a significant leap forward from traditional needle-based methods. From exploring various injector types and their mechanisms to examining the patient experience and regulatory considerations, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of this groundbreaking technology.
This article will explore the advantages and disadvantages of needle-free injectors, examining their technical aspects, patient perspectives, and safety concerns. We’ll also analyze the regulatory landscape and future trends in this rapidly evolving field, providing a comprehensive overview of this exciting development in diabetes care.
Introduction to Needle-Free Injectors: Diabetes Needle Free Injector
Needle-free injectors represent a significant advancement in diabetes management, aiming to reduce the pain, discomfort, and potential complications associated with traditional needle-based injections. These systems offer a potentially safer and more convenient alternative for patients requiring subcutaneous medication delivery. The evolution of diabetes injection methods has been marked by a gradual shift towards minimizing the need for needles, driven by patient preference and the need for improved injection safety.Historically, diabetes management relied heavily on hypodermic needles.
While effective, these methods presented risks of needle-related injuries, infections, and pain, prompting the development of alternative injection techniques. Needle-free systems offer a solution by employing diverse mechanisms to deliver medications without piercing the skin with needles. This approach is not just about convenience; it also addresses concerns about infection control and patient comfort, particularly for those with sensitive skin or a fear of needles.
Types of Needle-Free Injector Technologies, Diabetes needle free injector
Various technologies underpin needle-free injectors, each with its own design and mechanisms for medication delivery. These technologies vary in complexity, efficiency, and safety profile. A crucial aspect of needle-free injection is ensuring accurate and consistent medication delivery, replicating the precision of needle-based systems.
Comparison of Needle-Free Injector Types
| Injector Type | Mechanism | Injection Speed | Safety Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acoustic Wave Injector | Utilizes high-frequency sound waves to propel the medication through a small aperture in a device. | Generally rapid, allowing for quick delivery. | Relatively low risk of contamination and injury compared to traditional needle injections. |
| Electroporation Injector | Creates temporary pores in the skin using electrical pulses to facilitate medication absorption. | Injection time is generally quick, potentially faster than some other systems. | Potentially higher risk of tissue damage if not carefully controlled; this necessitates rigorous safety testing. |
| Jet Injector | Uses high-pressure pulses to propel medication through a small, precisely-controlled jet. | Fast injection speed, allowing for minimal contact time with the skin. | Requires careful design to prevent clogging and ensure consistent delivery, potentially requiring calibration. |
These varying approaches demonstrate the diverse technological pathways being explored to achieve needle-free injection. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages regarding injection speed, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Careful evaluation of each type’s capabilities and limitations is critical for successful implementation in a clinical setting.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Needle-free injectors represent a significant advancement in drug delivery, promising a more convenient and potentially less painful experience for patients. However, these innovative devices also face challenges that need careful consideration. This section explores the key benefits and drawbacks of needle-free injectors, comparing them to traditional needle-based systems.
Patient Experience and Health Benefits
Needle-free injectors aim to improve patient compliance and reduce the discomfort associated with injections. Studies have shown that the reduced pain and fear associated with needle-free devices can lead to improved adherence to treatment regimens, especially for chronic conditions requiring frequent injections. This translates into better health outcomes, as patients are more likely to maintain their medication schedules. For example, patients with diabetes who struggle with needle-based injections may find needle-free devices significantly easier to use, potentially leading to better blood sugar control and overall well-being.
Technical Challenges and Limitations
While needle-free injectors offer several advantages, they are not without limitations. One key challenge lies in the consistent delivery of medication. The complex mechanisms involved in needle-free injection can sometimes lead to inconsistent dosing, potentially affecting treatment efficacy. Furthermore, certain medications may not be compatible with the materials or processes used in these devices, requiring careful formulation and testing.
Another concern is the potential for clogging or malfunction in the device itself. These technical issues can reduce the reliability and consistency of the treatment process.
Diabetes needle-free injectors are a game-changer, offering a painless alternative to traditional methods. While some might be put off by the idea of a non-invasive injection method, the potential for innovation extends beyond the immediate benefits of comfort. Research into insect-based protein sources, like insect phobe bug protein , suggests a potentially sustainable and nutritious alternative food source.
Ultimately, these advancements in alternative protein sources, like the insect-based ones, could potentially inspire innovative design approaches for needle-free diabetes injectors, creating a more holistic and sustainable solution for managing the condition.
Comparison with Traditional Needle-Based Systems
Traditional needle-based injection systems have been the standard for decades. They are well-established, reliable, and generally effective for delivering medications. However, the associated pain and discomfort can discourage patients from adhering to their treatment plans. Needle-free injectors, in contrast, aim to address this pain issue, although they may still have their own set of technical limitations. The trade-off is between established reliability and the potential for a more patient-friendly experience with needle-free devices.
Pros and Cons Table
| Aspect | Needle-Free Injector | Needle-Based Injector |
|---|---|---|
| Pain | Generally less painful, potentially reducing patient anxiety and improving adherence. | Can be painful, leading to discomfort and potentially reduced patient compliance. |
| Ease of Use | Potentially easier to use, especially for patients with dexterity issues or needle phobia. | May require some practice to master injection technique. |
| Cost | Initial cost of devices can be higher than traditional syringes. | Generally lower initial cost compared to needle-free injectors. |
| Accuracy | Potential for inconsistent dosing, requiring careful monitoring and adjustments. | Generally more accurate in delivering medication. |
| Safety | Potential for device malfunction, requiring thorough maintenance and regular checks. | Established safety profile, with known risks managed through proper usage and technique. |
Technical Aspects and Mechanisms
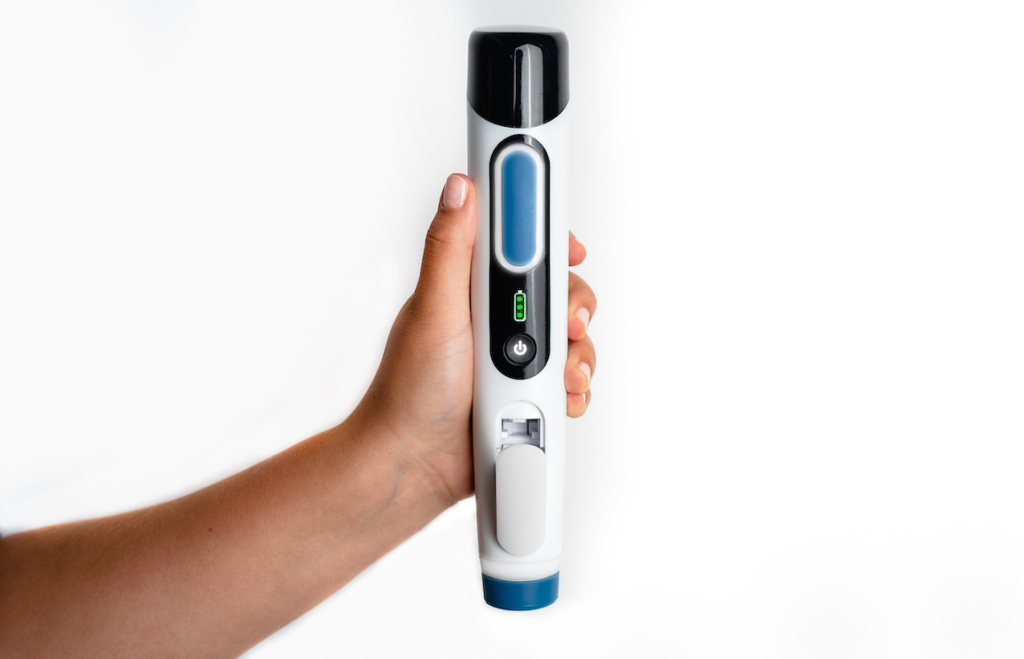
Needle-free injectors, while promising a safer alternative to traditional methods, rely on sophisticated mechanisms to ensure accurate and painless delivery of medication. Understanding the technical intricacies behind these devices is crucial for evaluating their efficacy and potential limitations. The precise steps involved in the injection process, the materials used, and the design principles all contribute to the overall performance and safety of the injector.The injection process in a needle-free injector is meticulously designed to avoid the trauma associated with a traditional needle.
A variety of methods exist, but a common theme is the creation of a controlled pathway for the medication to enter the body. This controlled delivery is essential for minimizing pain and maximizing the effectiveness of the treatment.
Injection Process Steps
The injection process typically involves several carefully orchestrated steps. First, the device is loaded with the medication. Then, a precise amount of pressure is applied to propel the medication through the delivery mechanism. The process concludes with the medication being injected into the desired location. Different injector designs will have slightly varied steps, but the fundamental principle of controlled delivery remains consistent.
Materials and Biocompatibility
The materials used in the construction of a needle-free injector are paramount to its safety and effectiveness. Biocompatibility is a key concern, as the materials must not react negatively with the medication or the recipient’s tissues. Common materials include polymers, such as those derived from polylactic acid (PLA), or biodegradable polymers, which offer biocompatibility and are environmentally friendly.
The choice of materials depends on factors like strength, flexibility, and durability, as well as their biodegradability and potential for allergenic reactions. These considerations are critical for long-term safety and patient well-being.
Design Principles
The design of a needle-free injector is influenced by several critical principles, including the need for accuracy in dosage, the minimization of pain during injection, and the preservation of sterility throughout the process. The device must be ergonomically designed for easy handling and use by patients. Design features, such as the shape and size of the injection port, play a crucial role in patient comfort and the overall efficiency of the injection process.
A well-designed injector will incorporate factors such as the force required to activate the mechanism and the rate of medication delivery.
Injection Mechanism Diagram
A simplified diagram of the injection mechanism would show a barrel containing the medication, a pressure-applying mechanism, and a specialized nozzle or port designed to deliver the medication into the target area. The diagram would clearly label all critical components, including the pressure-applying mechanism, the barrel, the nozzle, and the delivery pathway. The diagram would also indicate the direction of the medication flow. This is essential for understanding how the device functions.
Patient Perspective and User Experience
The transition to needle-free injectors hinges significantly on the patient experience. Comfort, ease of use, and perceived pain are crucial factors influencing adoption rates. Understanding these aspects allows manufacturers to design more effective and user-friendly devices. This, in turn, fosters greater patient compliance and satisfaction with diabetes management.
Pain Levels and Comfort
Patient perception of pain is a critical aspect in evaluating needle-free injectors. Early designs often reported higher pain levels compared to traditional needle injections. However, significant advancements in technology have led to considerable improvements in minimizing discomfort. These improvements are driven by factors like optimized injection pressure, precise targeting mechanisms, and materials with better tissue interaction. Innovations in device design are paramount for improving the patient experience and fostering broader adoption.
Ease of Use and User-Friendly Design
A user-friendly design is vital for needle-free injector adoption. Simplicity in operation, intuitive controls, and clear instructions significantly impact the patient’s experience. A complex or poorly designed device can lead to frustration and reduced compliance. Furthermore, ergonomic design considerations for the device’s form factor and size contribute to user comfort and ease of use.
Psychological and Emotional Impacts
The psychological and emotional aspects of diabetes management are often overlooked. Using a needle-free injector can positively impact patients by reducing the anxiety and fear associated with traditional needle injections. This reduction in stress can translate to improved emotional well-being and better adherence to treatment plans. Conversely, if a patient experiences discomfort or difficulty using the device, it could potentially negatively impact their emotional state and motivation.
User Feedback and Satisfaction Ratings
Gathering user feedback and evaluating satisfaction ratings are essential for improving needle-free injector design. Comprehensive feedback provides valuable insights into areas needing improvement. This data should include specific pain levels, ease of use, and overall satisfaction ratings.
| Injector Type | Ease of Use (Rating) | Pain Level (Rating) | Overall Satisfaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example Type 1 | 4.5/5 | 2.0/5 | 4.2/5 |
| Example Type 2 | 3.8/5 | 2.5/5 | 3.9/5 |
| Example Type 3 | 4.0/5 | 1.8/5 | 4.4/5 |
Note: These are hypothetical ratings for illustrative purposes only. Actual ratings will vary depending on the specific design, user demographics, and clinical trials.
Regulatory and Safety Considerations
Needle-free injectors, while promising, must navigate a complex regulatory landscape and stringent safety protocols. Understanding these factors is crucial for both manufacturers and users to ensure safe and effective administration of medications. This section delves into the regulatory hurdles, safety precautions, potential risks, and preventive measures associated with these devices.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape for needle-free injectors varies across different countries and regions. These devices often undergo rigorous testing and evaluation before approval for use. The process typically involves pre-clinical trials, followed by clinical trials to assess efficacy, safety, and user experience. Successful completion of these trials, often with substantial data collection, is crucial for gaining regulatory approval.
I’ve been researching diabetes needle-free injectors lately, and honestly, it’s fascinating how much progress is being made. It’s all about finding ways to make managing this condition easier and less invasive. But when someone calls me a “patient,” it immediately shifts the conversation to a more clinical space, and honestly, it makes me feel a bit like a lab specimen rather than an individual managing my health.
Check out how I truly feel when you call me a patient here: how i feel when you call me a patient. Ultimately, innovative devices like needle-free injectors are a crucial step towards a more proactive and personal approach to diabetes management.
Different countries and regions have distinct regulatory bodies, each with specific requirements and standards for approval. These bodies usually scrutinize the design, materials, manufacturing process, and potential risks of the device, ensuring it meets safety standards and is fit for its intended use.
Safety Precautions and Guidelines
Adhering to proper safety guidelines is paramount when using needle-free injectors. These guidelines typically cover device handling, storage, and disposal, as well as user training and education. Proper device maintenance is also essential, as malfunctioning components can increase the risk of complications. The guidelines often emphasize the importance of following the manufacturer’s instructions precisely, including specific steps for preparation, administration, and post-injection care.
Failure to adhere to these guidelines can lead to adverse events, so meticulous adherence is crucial.
Needle-free diabetes injectors are a game-changer, offering a less invasive way to manage blood sugar levels. But as we consider innovative medical advancements, we also face tough ethical questions like, “should we save people who overdose drugs?” This crucial discussion highlights the complex considerations surrounding healthcare choices and resource allocation, which ultimately impacts the development and acceptance of new medical technologies like needle-free injectors.
The quest for better diabetes management hinges on responsible decision-making.
Potential Risks and Adverse Events
Needle-free injectors, despite their advantages, are not without potential risks. These include, but are not limited to, injection site reactions, such as pain, redness, swelling, and bruising. The risk of skin damage is a concern, especially in repeated administrations. In certain instances, medication leakage or inaccurate dosing may occur, leading to adverse effects. These potential complications are often evaluated during clinical trials to understand their frequency and severity.
Manufacturers and regulatory bodies must diligently monitor these potential risks to ensure the device is safe for its intended use.
Recommended Safety Measures
Implementing preventative measures can minimize the risk of complications associated with needle-free injectors. A critical aspect is user education and training. Comprehensive training programs should cover proper device handling, injection technique, and potential adverse events. Regular device maintenance is essential to prevent malfunctions that could lead to complications. Strict adherence to recommended injection sites and techniques can also minimize injection site reactions.
Monitoring patients for any adverse reactions post-injection is crucial for early detection and intervention. Finally, proper disposal of used devices according to local guidelines is critical to prevent environmental contamination.
- User Training: Comprehensive training programs are vital to ensure users understand proper injection techniques and recognize potential adverse events. Detailed instructions on device handling, preparation, and administration should be provided.
- Device Maintenance: Regular inspection and maintenance of the device, according to manufacturer instructions, are necessary to prevent malfunctions and ensure optimal performance.
- Injection Site Selection: Using appropriate injection sites and techniques can significantly reduce the risk of injection site reactions. Adhering to recommended guidelines is crucial.
- Post-Injection Monitoring: Careful observation of patients for any adverse reactions after injection is essential for timely intervention and management.
- Disposal Procedures: Proper disposal of used devices, according to local regulations, prevents environmental contamination and promotes safety.
Future Trends and Developments
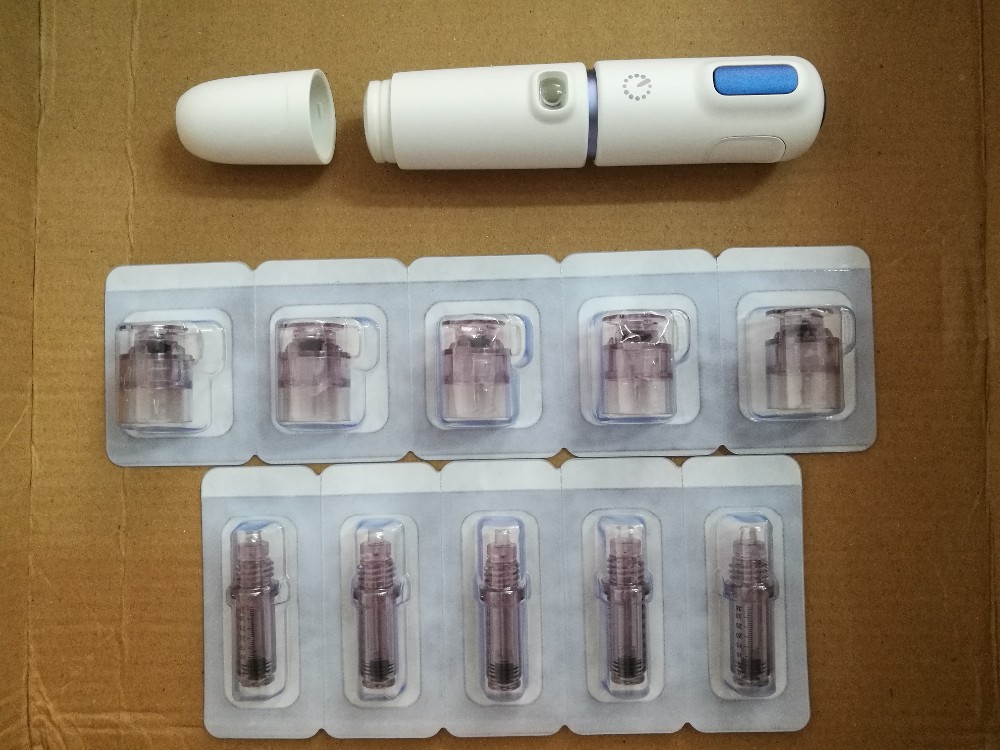
The future of needle-free injectors holds immense promise for revolutionizing diabetes management. Constant innovation in materials science, nanotechnology, and drug delivery systems is paving the way for more efficient, convenient, and potentially less painful administration of insulin and other medications. These advancements aim to address the limitations of current needle-free technologies and enhance the overall patient experience.Current needle-free injector technology faces challenges in terms of dose accuracy, injection depth control, and the need for multiple attempts in some cases.
Further research and development are critical to overcome these obstacles and establish the long-term efficacy and safety of these devices.
Potential Advancements in Materials and Design
Material science plays a crucial role in improving the functionality and safety of needle-free injectors. Future injectors might leverage biocompatible polymers with enhanced mechanical properties for improved durability and ease of use. Researchers are exploring novel materials that can facilitate a more seamless and controlled injection process, minimizing pain and discomfort for patients. This includes the development of materials that mimic the natural body tissues for better biocompatibility.
Nanotechnology Integration
Nanotechnology presents exciting possibilities for enhancing needle-free injection systems. Nanoparticles can be designed to target specific tissues, ensuring optimal drug delivery. For example, targeted delivery of insulin using nanocarriers could lead to more precise blood glucose control. Further, nanotechnology may lead to more compact and user-friendly devices, enhancing portability and overall patient experience. The integration of nanotechnology into needle-free injectors will likely require significant investment in research and development.
Bioprinting and Personalized Medicine
Bioprinting technology is poised to transform personalized medicine, including the development of customized needle-free injectors. This technology allows for the creation of intricate structures tailored to individual patient needs, potentially enabling the development of devices that can precisely deliver medications based on an individual’s specific requirements. This could revolutionize treatment approaches, particularly in managing chronic conditions like diabetes. Early applications of bioprinting are demonstrating the potential for intricate designs, which might improve drug absorption and reduce the need for multiple injections.
Emerging Challenges and Considerations
While the future of needle-free injectors looks promising, several challenges remain. Regulatory hurdles, cost-effectiveness, and long-term safety data will need careful consideration to ensure widespread adoption and positive patient outcomes. Furthermore, the potential impact on existing healthcare infrastructures, including training and support for healthcare professionals, will require careful planning and implementation.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, diabetes needle-free injectors offer a compelling alternative to traditional methods, potentially revolutionizing diabetes management. While challenges remain, the ongoing advancements in technology, coupled with evolving patient preferences, suggest a promising future for these devices. From improved patient comfort and ease of use to potential advancements in injection speed and safety, needle-free injectors could significantly enhance the lives of millions living with diabetes.