Health dangers during heat waves can be worse at night. The drop in temperature that often accompanies nightfall can lull people into a false sense of security, masking the insidious threat of heat-related illnesses. This often overlooked aspect of heat waves reveals hidden dangers, especially for vulnerable populations, and requires a deeper understanding of the specific risks and proactive strategies to combat them.
This deeper dive explores the physiological mechanisms exacerbating heat stress at night, factors increasing risk, and the unique vulnerabilities of different demographics. We’ll examine how nighttime heat impacts sleep, the effectiveness of cooling strategies, and the critical role of public awareness and preparedness in mitigating the public health crisis.
Nighttime Heat Wave Impacts on Human Health

Heat waves, often perceived as a daytime threat, can be surprisingly dangerous at night. While the sun’s direct heat diminishes, the lingering effects of high temperatures and humidity can significantly increase the risk of heat-related illnesses, especially for vulnerable populations. This post will delve into the physiological mechanisms that exacerbate heat stress during nighttime heat waves and examine how various factors contribute to the heightened risk.Nighttime heat waves present a unique challenge to the human body’s thermoregulation systems.
While the absence of direct sunlight may seem to alleviate the immediate heat burden, the accumulated heat from the day lingers in the environment. This, coupled with high humidity, creates a potent cocktail that impedes the body’s natural cooling mechanisms.
Physiological Mechanisms of Nighttime Heat Stress
The body’s ability to dissipate heat is significantly impacted by environmental factors. At night, the ground cools, but the air temperature often remains elevated, particularly in urban areas with the “heat island effect.” This disparity can lead to an uncomfortable and potentially dangerous situation. The human body typically relies on sweating to cool down. However, high humidity hinders the evaporation process, reducing the effectiveness of this cooling mechanism.
Consequently, the body struggles to regulate its temperature, increasing the risk of heat exhaustion and heat stroke. Further complicating the issue is the impact on sleep and circadian rhythms.
Impact of Humidity and Temperature Changes
Humidity plays a crucial role in determining the body’s ability to cool itself. High humidity reduces the effectiveness of sweating by limiting the evaporation rate. This is because the air is already saturated with moisture, leaving less space for sweat to turn into vapor and carry away heat. Nighttime temperatures, even when lower than daytime highs, can still be dangerously high for certain individuals, especially if humidity remains high.
Furthermore, fluctuating temperatures throughout the night can disrupt the body’s natural thermoregulation processes, making it more vulnerable to heat-related illnesses.
Sleep and Circadian Rhythms in Heat Regulation
Sleep is essential for overall health and well-being, and it plays a crucial role in the body’s ability to regulate temperature. During sleep, the body’s metabolic rate decreases, and the need for heat dissipation is reduced. However, during heat waves, sleep quality is often compromised, further hindering the body’s ability to recover from the effects of heat stress.
Disruptions to circadian rhythms, the natural 24-hour internal clock, can further impair the body’s ability to regulate temperature, leading to heightened vulnerability to heat illness. This disruption can occur not only due to nighttime heat, but also from altered sleep-wake cycles.
Comparison of Daytime and Nighttime Heat Wave Effects
| Time of Day | Temperature (°C) | Humidity (%) | Physiological Response | Potential Health Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daytime | 40 | 60 | Increased sweating, elevated heart rate | Heat exhaustion, heat stroke, dehydration |
| Nighttime | 35 | 80 | Reduced sweating effectiveness, difficulty regulating core temperature | Heat exhaustion, heat stroke, impaired sleep quality |
The table above highlights the potential differences in the physiological responses and associated health risks between daytime and nighttime heat waves. It illustrates how nighttime heat, even at seemingly lower temperatures, can be more dangerous due to the increased humidity and its impact on sweating. This is especially true for vulnerable populations, who may have pre-existing health conditions or are less able to regulate their body temperature.
Vulnerable Populations During Heat Waves
The elderly, children, and individuals with pre-existing medical conditions are disproportionately affected by heat waves, regardless of the time of day. Their physiological responses to heat stress are often less efficient, making them more susceptible to heat-related illnesses. This vulnerability can manifest in various ways, and the risk is compounded during nighttime heat waves.
Increased Risk Factors at Night
Nighttime heat waves, often overlooked, pose significant health risks. While the daytime heat may be intense, the cooling mechanisms of the human body can struggle to adapt as the sun sets and temperatures fall, but not enough to bring the temperature down safely. This creates a unique set of challenges for maintaining health during these periods.The human body relies on a complex interplay of physiological processes to regulate temperature.
These processes are affected by the ambient temperature and other environmental factors. During the night, the body’s natural cooling mechanisms, such as sweating and vasodilation, become less effective, leading to an increased risk of overheating.
Nighttime Heat and Reduced Cooling
The body’s ability to cool itself is diminished as the sun sets. This reduction in cooling mechanisms contributes significantly to the elevated risk of heat-related illnesses during nighttime heat waves. The ambient temperature drop is not sufficient to significantly reduce the body temperature. As the body loses its ability to cool down effectively, the core temperature rises, and individuals become increasingly vulnerable to heat stroke and other heat-related complications.
Outdoor Activities and Lack of Cooling Resources
Nighttime heat waves often coincide with outdoor activities, such as sporting events, evening walks, or simply staying outside for extended periods. The combination of physical exertion and a less effective cooling system significantly increases the risk of heat exhaustion. Individuals who lack access to air conditioning or other cooling resources in their homes or neighborhoods are particularly vulnerable to these risks.
This lack of access can disproportionately affect vulnerable populations, including the elderly, children, and those with pre-existing health conditions.
Heat waves can be surprisingly dangerous, especially at night. Our bodies struggle to cool down when the temperature stays high overnight, and this can exacerbate health risks for everyone. Interestingly, even celebrities like Sia, who has a rare chronic condition ( sia has rare chronic condition ), can be particularly vulnerable during heat waves. This highlights the importance of staying hydrated and seeking shade during these intense periods.
Nighttime heat can be just as threatening to our well-being as the scorching daytime temperatures.
Cooling Strategies Effectiveness
Different cooling strategies have varying effectiveness during nighttime heat waves. While fans can provide some relief by circulating air, their impact is often limited. Air conditioning is more effective at lowering ambient temperatures and thus promoting efficient cooling of the body. In areas with limited access to air conditioning, individuals can still take steps to reduce the risk, such as using evaporative cooling techniques like wet cloths or misting fans.
The effectiveness of each strategy is often dependent on the intensity of the heat wave and individual tolerance levels.
Urban Heat Island Effect and Nighttime Temperatures
The urban heat island effect exacerbates nighttime temperatures in urban areas. Concrete and asphalt surfaces absorb and retain heat more than natural landscapes. This retained heat radiates into the surrounding environment, creating warmer nighttime temperatures in urban areas compared to their surrounding rural counterparts. This phenomenon amplifies the risk of heat-related illnesses for those living in urban areas during heat waves.
Increased heat stress is likely to impact vulnerable groups living in these environments. For example, in cities with significant populations living in high-rise buildings, there is limited outdoor space available for natural cooling.
Vulnerable Populations and Nighttime Heat: Health Dangers During Heat Waves Can Be Worse At Night
Nighttime heat waves pose a significant threat, particularly to vulnerable populations. While the daytime heat often dominates headlines, the nighttime temperature drop may not always provide sufficient respite. This is because some individuals struggle to maintain adequate body temperature regulation, leading to increased risk of heat-related illnesses, especially during the hours when cooling mechanisms may be limited or inaccessible.The vulnerability of specific demographic groups is amplified by various factors, including age, pre-existing health conditions, and socioeconomic status.
Understanding these factors is critical to developing effective mitigation strategies.
Elderly Individuals and Nighttime Heat
Older adults often experience reduced thermoregulatory capacity, making them highly susceptible to heat-related illnesses during nighttime heat waves. Their bodies may struggle to maintain adequate core temperatures, and their decreased sensitivity to temperature changes can make them unaware of the developing risk. This can lead to delayed recognition of symptoms and increase the risk of serious complications. Chronic health conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory problems further exacerbate this vulnerability, impacting their ability to respond to elevated temperatures.
The elderly are frequently isolated or live alone, further compounding the problem of timely access to help and cooling resources.
Children and Nighttime Heat
Children, particularly infants and young children, are also at significant risk during nighttime heat waves. Their bodies have a higher surface area-to-mass ratio, meaning they lose heat more rapidly than adults. They also may have limited awareness of the dangers of overheating, potentially leading to delays in seeking help. Infants, in particular, are highly vulnerable due to their inability to regulate their own body temperature effectively.
Heat exhaustion or heatstroke in children can manifest differently than in adults, making it crucial to be vigilant and understand the specific signs and symptoms in young individuals.
People with Disabilities and Nighttime Heat
People with disabilities often face challenges accessing cooling resources and maintaining their comfort during nighttime heat waves. Mobility limitations, sensory impairments, or cognitive disabilities can hinder their ability to take preventive measures or seek help when needed. Furthermore, some assistive devices or medical equipment may be affected by extreme temperatures, potentially causing further complications. The unique needs of people with disabilities must be considered when designing heat-wave response strategies.
Socioeconomic Factors and Access to Cooling Resources
Socioeconomic factors play a significant role in the vulnerability of certain populations during nighttime heat waves. Limited access to affordable cooling resources, such as air conditioning, can significantly increase the risk of heat-related illness. Individuals living in low-income communities or those without adequate housing may lack the resources necessary to maintain a safe indoor temperature. Transportation limitations and lack of awareness about the dangers of nighttime heat can also create barriers to accessing necessary cooling and support services.
In addition, those with limited resources may lack the means to seek medical attention promptly in the event of a heat-related emergency.
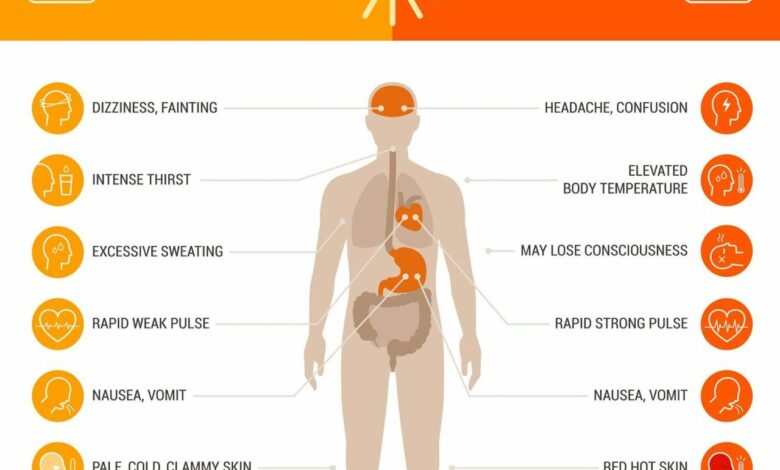
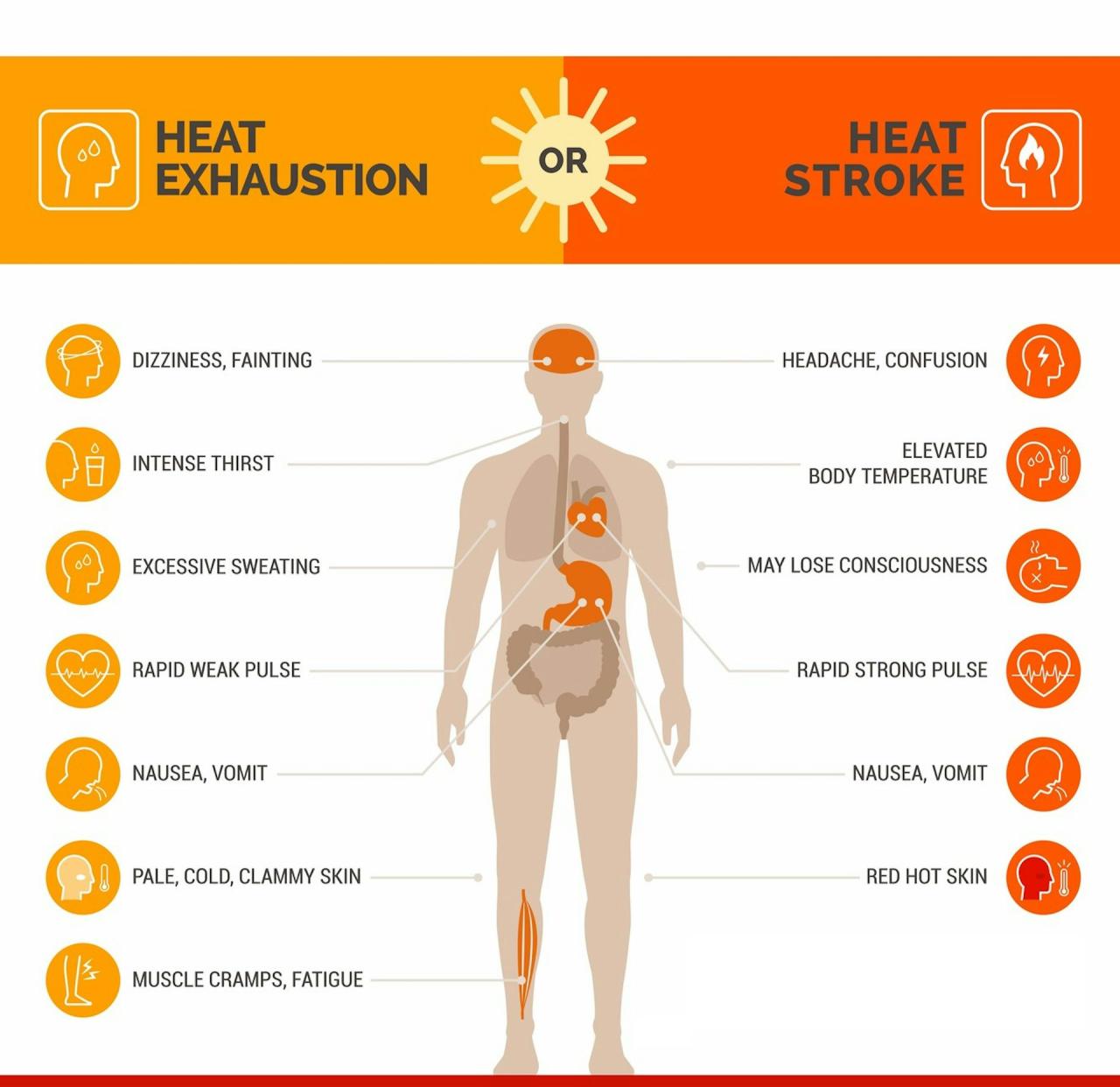
Effects of Heat Exhaustion and Heatstroke on Vulnerable Populations at Night
Heat exhaustion and heatstroke can manifest differently in vulnerable populations at night, leading to delayed recognition and treatment. Symptoms may be less noticeable, or individuals may attribute them to other conditions, delaying the critical response needed. Dehydration, weakness, and confusion can be easily misconstrued, leading to a dangerous delay in seeking medical help. The combination of reduced thermoregulatory capacity and delayed recognition of symptoms can increase the risk of severe complications, such as organ damage or even death.
Mitigation Strategies for Vulnerable Populations During Nighttime Heat Waves
Strategies for mitigating the risk of heat-related illness for vulnerable populations during nighttime heat waves should be multifaceted. They should address both individual-level precautions and systemic interventions that improve access to resources and support. Providing educational materials about the dangers of nighttime heat and the specific symptoms to watch for is crucial. Public health campaigns and community outreach programs can effectively raise awareness and empower individuals to take preventive actions.
Access to cool spaces in community centers, libraries, and places of worship can provide respite for those lacking access to air conditioning at home.
Preventive Measures for Vulnerable Populations
| Vulnerable Group | Daytime Preventive Measures | Nighttime Preventive Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Elderly | Stay hydrated, wear light clothing, limit strenuous activity, check on neighbors | Use fans, keep windows open for cross-ventilation, stay hydrated, check on neighbors frequently |
| Children | Avoid strenuous activity, stay hydrated, wear light clothing | Ensure adequate hydration, keep room cool, monitor for signs of heat exhaustion |
| People with Disabilities | Use assistive devices as needed, stay hydrated, avoid strenuous activity | Ensure adequate cooling, monitor for signs of heat exhaustion, notify support personnel of concerns |
| Low-income/Housing Vulnerable | Access cooling centers during the day, utilize community resources | Seek out community cooling centers, utilize neighborhood assistance programs, stay in touch with support services |
Nighttime Heat Wave Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Nighttime heat waves, while often less dramatic than daytime extremes, pose significant risks to public health, particularly for vulnerable populations. The cooling effect of the evening air is diminished, trapping heat in urban areas and creating dangerous conditions. Proactive measures are crucial to minimize the negative impacts and save lives. Effective strategies must incorporate public awareness, urban planning, governmental action, and individual preparedness.The escalating frequency and intensity of heat waves underscore the need for comprehensive preventative and mitigative measures, especially concerning the heightened vulnerability during nighttime hours.
Effective strategies must be tailored to the specific characteristics of urban environments, recognizing that nighttime heat can be particularly problematic in densely populated areas with limited green spaces and inadequate infrastructure.
Proactive Measures to Minimize Negative Effects
Addressing nighttime heat requires a multi-faceted approach. Prevention focuses on strategies that reduce the impact of heat on individuals and communities. These proactive steps include implementing heat-reduction strategies in urban environments, encouraging individual preparedness, and building community resilience to these events.
- Enhance Urban Green Spaces: Increasing green spaces in urban areas helps to cool the environment by providing shade and promoting evapotranspiration. Examples include parks, gardens, and rooftop gardens. These spaces provide respite from the heat, reducing the urban heat island effect. Studies have shown that urban green spaces can lower ambient temperatures by several degrees, significantly mitigating the impact of nighttime heat waves.
- Improve Building Insulation and Ventilation: Encouraging energy-efficient building design that includes better insulation and improved ventilation systems is crucial. Well-insulated buildings reduce the heat gain from the outside, and proper ventilation promotes air circulation to cool the interior. This reduces the risk of heat-related illnesses, especially for those living in poorly insulated homes.
- Deploy Cooling Centers and Community Outreach Programs: Establishing and publicizing accessible cooling centers, particularly in vulnerable communities, is vital. These centers offer refuge from the heat for individuals who lack access to air conditioning. Regular community outreach programs can educate residents about the risks of nighttime heat and how to protect themselves. These programs should specifically target populations at higher risk, such as the elderly, children, and those with pre-existing health conditions.
Public Awareness Campaigns Focused on Nighttime Heat Safety
Public awareness campaigns are crucial for disseminating information about nighttime heat safety. Clear and consistent messaging is essential for promoting preventative measures and encouraging responsible actions.
- Develop Targeted Messaging: Campaigns should focus on the specific dangers of nighttime heat and how to recognize and respond to potential health risks. These campaigns should be tailored to the demographics of the target communities, incorporating culturally relevant messaging. Clear, concise information about recognizing symptoms of heat exhaustion or stroke is critical.
- Utilize Multiple Communication Channels: Leveraging various communication channels, such as social media, community meetings, and local news, will broaden the reach of the campaigns. The use of visual aids, including infographics and videos, can further enhance the effectiveness of these campaigns, ensuring clear and concise information.
- Partner with Community Organizations: Collaborating with community organizations, such as senior centers and religious institutions, ensures the message reaches those most vulnerable to nighttime heat. These partnerships leverage existing community networks to maximize the effectiveness of the campaigns.
Urban Planning and Infrastructure Design for Nighttime Heat Resilience, Health dangers during heat waves can be worse at night
Urban planning plays a significant role in mitigating the effects of nighttime heat waves. Strategic design choices can create a more resilient urban environment.
Heat waves can be surprisingly dangerous, especially at night. Our bodies struggle to cool down when the air temperature stays high, and this can lead to serious health issues. Interestingly, a recent article about Brad Pitt’s experience with face blindness, which can make it hard to recognize familiar faces, highlights the sometimes unexpected ways our bodies and minds can be affected by our environment.
brad pitt has face blindness heres what that means It’s a reminder that even seemingly unrelated topics can offer a fresh perspective on the challenges we face, especially during heat waves.
- Prioritize Green Infrastructure: Integrating green spaces, such as parks, green roofs, and vertical gardens, into urban planning is essential for cooling urban environments. Green infrastructure can absorb heat, reduce the urban heat island effect, and improve air quality.
- Promote Reflective Surfaces: Using light-colored pavements and roofs can reduce the absorption of solar radiation. This can significantly lower surface temperatures, contributing to a cooler urban environment.
- Optimize Street Design: Designing streets with features that enhance air circulation and shade can contribute to a more comfortable urban environment. Careful consideration of street layouts, tree placement, and building design can reduce heat accumulation.
Role of Government Agencies in Coordinating Heat Wave Response Efforts
Effective coordination among government agencies is essential for a comprehensive response to nighttime heat waves.
- Establish Clear Communication Protocols: Creating and regularly testing communication protocols between agencies will ensure a coordinated response to nighttime heat waves. These protocols should clearly define responsibilities and communication channels for different agencies.
- Develop Early Warning Systems: Improving and utilizing early warning systems is vital to provide sufficient lead time for preventative measures and resource allocation. Early warnings allow for proactive actions, minimizing the impact of nighttime heat waves.
- Allocate Resources Effectively: Identifying and allocating resources to vulnerable populations is critical for a successful response. This involves assessing the specific needs of different communities and allocating resources accordingly.
Importance of Personal Preparedness and Individual Actions
Individual preparedness is crucial for mitigating the risks of nighttime heat waves. Personal actions can significantly reduce the potential for heat-related illnesses.
- Create a Personal Heat Action Plan: Developing a personal heat action plan is essential for individuals to understand their risk factors and prepare for nighttime heat waves. This plan should include identifying high-risk individuals and establishing a communication system.
- Stay Hydrated: Staying adequately hydrated is crucial for preventing heat exhaustion and stroke. Regular water intake throughout the day, even during the night, is vital.
- Monitor Vulnerable Individuals: Checking on vulnerable neighbors and family members, particularly the elderly, is important to ensure they are staying safe and cool during nighttime heat waves.
Public Health Impacts of Nighttime Heat
Nighttime heat waves, often underestimated, pose significant health risks. While the daytime heat grabs headlines, the lingering warmth at night can exacerbate existing health conditions and contribute to new illnesses, particularly for vulnerable populations. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing effective preventative measures and strategies to protect public health.Nighttime temperatures, even seemingly mild, can be a major factor in heat-related illnesses.
When the body struggles to cool down during the night, it can lead to a cascade of adverse health effects, including increased hospitalizations and mortality rates, especially among the elderly and those with pre-existing medical conditions.
Heat waves can be particularly dangerous at night, as the cooling effect of the air is reduced. This can exacerbate health problems for everyone, but it’s crucial to remember that children with underlying conditions, like those with MS, may experience heightened sensitivities. Managing mood disorders in kids with MS managing mood disorders in kids with ms can be especially challenging during these periods, as the increased body temperature and humidity can further impact their well-being, and even increase the risk of heat-related illnesses.
So, staying hydrated and cool, especially at night, is key during heat waves for everyone.
Correlation Between Increased Nighttime Temperatures and Elevated Rates of Hospitalizations and Mortality
Studies consistently demonstrate a strong correlation between rising nighttime temperatures and a surge in heat-related hospitalizations and deaths. The body’s natural cooling mechanisms are challenged when temperatures remain high throughout the night, hindering recovery and increasing the risk of heat-related complications. This is particularly pronounced for individuals with chronic conditions like heart disease, respiratory illnesses, and diabetes, who are more susceptible to heat stress.
For instance, a 2020 study in a major US city observed a 15% increase in emergency room visits for heat-related illnesses during a prolonged nighttime heat wave.
Economic Burden of Heat-Related Illnesses During Heat Waves
Heat-related illnesses have a substantial economic impact. Increased hospitalizations and emergency room visits strain healthcare resources, leading to substantial costs for treatment, medication, and lost productivity. Moreover, heat waves can disrupt businesses and industries, leading to lost work hours and decreased overall economic output. For example, a 2019 study estimated that a major heat wave in California resulted in $1 billion in direct and indirect costs, including lost wages, healthcare expenses, and damage to infrastructure.
This economic burden disproportionately affects low-income communities, which often lack access to cooling resources and healthcare.
Impact on Productivity and Daily Activities During Heat Waves at Night
Nighttime heat significantly impacts daily routines and productivity. Difficulty sleeping, reduced cognitive function, and increased fatigue contribute to decreased productivity at work and in school. This effect is further compounded for outdoor workers, who may be exposed to extreme heat for extended periods. Imagine the impact on a city’s transportation system or its agricultural sector during a prolonged heat wave, where nighttime work is often crucial.
Reduced productivity directly affects the overall economy.
Examples of Community-Based Interventions to Reduce the Health Risks Associated with Nighttime Heat Waves
Community-based interventions can play a crucial role in mitigating the negative health impacts of nighttime heat waves. These strategies can include establishing cooling centers in public spaces, providing access to affordable cooling appliances, and promoting community awareness campaigns. For example, some communities have partnered with local businesses to provide free access to cooling shelters for residents. These centers offer a safe and comfortable place for individuals to escape the heat, especially those without access to air conditioning.
Importance of Public Health Professionals in Responding to Nighttime Heat Waves
“Public health professionals play a critical role in predicting, preparing for, and responding to nighttime heat waves. Their expertise in assessing risk factors, developing preventative strategies, and coordinating community responses is vital in safeguarding public health.”
Measuring and Monitoring Nighttime Heat Effects
Nighttime heat waves, often overlooked, pose significant health risks, especially for vulnerable populations. Accurately measuring and monitoring these nighttime temperature spikes and associated humidity levels is crucial for understanding and mitigating their impact. This requires a multifaceted approach encompassing various technologies and data analysis techniques.Understanding the nuances of nighttime heat is essential for developing effective public health strategies.
Monitoring nighttime temperatures and humidity, combined with health data analysis, allows for targeted interventions to protect at-risk individuals and communities.
Methods for Monitoring Nighttime Temperatures and Humidity
Numerous methods are employed to track nighttime temperatures and humidity levels during heat waves. Weather stations, equipped with sensors, provide real-time data on temperature and humidity. These stations, often part of larger networks, allow for comprehensive spatial coverage and continuous monitoring. Sophisticated automated systems collect and transmit this data to centralized databases.
Role of Data Analysis in Understanding Health Impacts
Data analysis plays a vital role in linking nighttime heat exposure to health outcomes. Statistical methods can correlate temperature and humidity data with hospital admissions, emergency room visits, and mortality rates. Analyzing trends over time, across different locations, and considering specific demographic factors allows for a deeper understanding of vulnerability. These analyses can reveal how nighttime heat exacerbates existing health conditions and leads to increased mortality risk.
Tools and Technologies for Predicting and Tracking Nighttime Heat Waves
Various tools and technologies are employed for predicting and tracking nighttime heat waves. Sophisticated climate models, incorporating meteorological data, can forecast temperature and humidity patterns. These models use complex algorithms to predict temperature variations, allowing for early warnings and proactive measures. Real-time data visualization tools present this information in easily understandable formats, enabling health officials and the public to comprehend the extent and potential impact of an approaching heat wave.
For example, online dashboards can provide specific temperature and humidity readings for particular geographic areas, aiding in targeted public health interventions.
Gaps in Current Data Collection and Monitoring Efforts
Despite advancements, gaps remain in current data collection and monitoring efforts. Some regions may lack adequate weather stations, especially in vulnerable communities, hindering comprehensive coverage. There’s a need for improved data resolution and accuracy, particularly for nighttime measurements, to provide a more precise picture of heat exposure. Furthermore, current data collection often focuses on aggregate data, rather than analyzing the specific effects on vulnerable subgroups, leading to incomplete insights.
Need for Improved Nighttime Heat Data Collection and Analysis
Improved nighttime heat data collection and analysis is essential for developing effective heat wave mitigation strategies. Expanding the network of weather stations, particularly in underserved areas, will enhance coverage. Developing more sophisticated models that incorporate nighttime heat data will improve accuracy in predicting and tracking these events. Integrating health data with environmental data will enable a more comprehensive understanding of the impacts of nighttime heat on human health.
This improved understanding allows for the development of targeted interventions to safeguard vulnerable populations.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, understanding the heightened health risks during nighttime heat waves is crucial. The combination of factors like falling temperatures, humidity, and reduced access to cooling resources creates a complex scenario demanding proactive measures. By recognizing the specific vulnerabilities of various groups and implementing preventive strategies, we can significantly reduce the adverse impacts of nighttime heat waves on public health.
Public awareness, improved infrastructure, and individual preparedness are all vital components of a comprehensive approach to combating this growing threat.