Type 2 diabetes management should include 15 percent weight loss researchers say – Type 2 diabetes management should include 15 percent weight loss, researchers say, highlighting the crucial role of shedding extra pounds in controlling this condition. This isn’t just about aesthetics; it’s about dramatically improving blood sugar levels and potentially preventing or delaying serious complications. We’ll explore the mechanisms behind this, different weight loss strategies, and the factors that can affect success.
Prepare to dive deep into the world of sustainable weight loss and its profound impact on managing type 2 diabetes.
The research suggests a strong link between weight loss and improved blood sugar control. Different approaches to weight loss, like diet, exercise, and medication, each have unique benefits and drawbacks. We’ll examine these in detail, offering practical strategies for those seeking to achieve significant weight loss while managing type 2 diabetes.
Understanding Weight Loss’s Role in Type 2 Diabetes Management
A 15% weight loss is a significant intervention in managing type 2 diabetes, and achieving this goal can lead to substantial improvements in blood sugar control, reduced risk of complications, and improved overall health. This reduction in weight often triggers positive changes in the body’s metabolic processes, making it a crucial strategy in the management of this chronic condition.Weight loss, particularly a 15% reduction in body weight, plays a pivotal role in improving insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
This improvement is achieved through various mechanisms, including reduced visceral fat, improved insulin secretion, and enhanced glucose uptake by tissues. Visceral fat, located around the internal organs, is particularly linked to insulin resistance. Losing this fat can improve the body’s response to insulin, enabling it to regulate blood sugar more effectively.
Mechanisms of Weight Loss Impact on Type 2 Diabetes
Weight loss, especially a 15% reduction, impacts type 2 diabetes management through several mechanisms. Reduced visceral fat leads to decreased inflammation, a key factor in insulin resistance. Furthermore, weight loss often results in improved insulin secretion and enhanced glucose uptake by muscle cells. These combined effects create a more balanced metabolic environment, enabling better blood sugar control.
Comparison of Weight Loss Strategies
Different strategies can facilitate weight loss, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. The effectiveness of these approaches varies depending on individual factors and adherence to the plan.
Researchers are saying that managing type 2 diabetes effectively often involves a 15% weight loss. While drastic measures like some dangerous plastic surgery procedures can sometimes seem appealing for weight loss, they often come with significant risks. It’s crucial to remember that healthy, sustainable weight loss strategies, like diet and exercise, are the most reliable and safest approaches for managing type 2 diabetes.
- Dietary Approaches: Dietary interventions are fundamental in weight loss. Low-calorie diets, such as those emphasizing whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and lean protein, are often recommended. Portion control and mindful eating habits are also essential components. However, strict diets can be challenging to maintain long-term and may lead to nutritional deficiencies if not carefully planned.
- Exercise Regimens: Regular physical activity is crucial for weight management and overall health. Exercise improves insulin sensitivity, enhances glucose utilization, and contributes to calorie expenditure. Aerobic exercises, such as brisk walking, jogging, or swimming, are particularly beneficial for blood sugar control. However, consistent exercise requires dedication and motivation, and proper exercise programs should be tailored to individual needs and abilities.
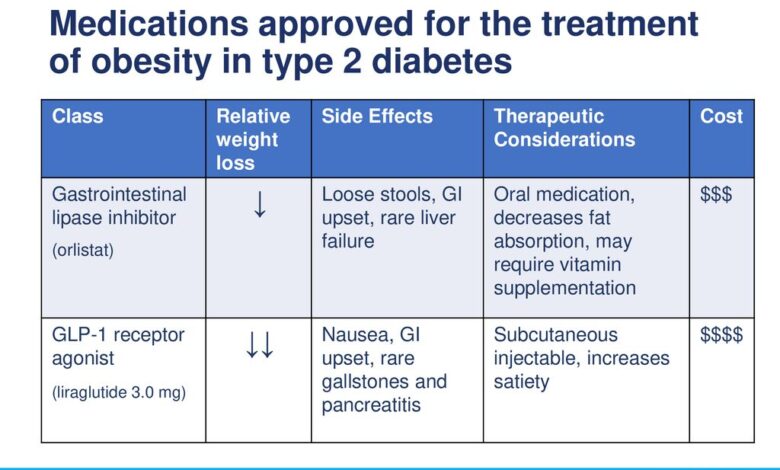
- Pharmacological Interventions: Medications can aid in weight loss by suppressing appetite, increasing metabolism, or promoting fat burning. However, medications are not a standalone solution for weight management. They are typically prescribed in conjunction with lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, to achieve optimal results. Furthermore, these medications may have side effects that need careful consideration.
Long-Term Effects of Weight Loss
Sustained weight loss, particularly a 15% reduction, can significantly impact the long-term health of individuals with type 2 diabetes. It can delay or prevent the development of diabetes-related complications, such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, and kidney problems. Moreover, a healthier weight contributes to improved overall well-being and quality of life.
Importance of Sustainable Weight Loss Strategies
Sustainable weight loss strategies are essential for long-term health benefits. Strategies focused on gradual and consistent lifestyle changes are more likely to be maintained over time. These changes should be personalized to accommodate individual needs and preferences. This personalized approach ensures that the chosen methods are both effective and sustainable, minimizing the risk of relapse and maximizing the benefits of weight loss.
Table Comparing Weight Loss Approaches
| Approach | Benefits | Drawbacks | Example Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dietary Approaches | Improved nutrition, reduced calorie intake, potential for long-term weight management | Requires significant lifestyle changes, potential for nutritional deficiencies if not planned carefully | Mediterranean diet, low-carb diet, calorie-restricted diets |
| Exercise Regimens | Improved insulin sensitivity, increased calorie expenditure, overall health benefits | Requires consistent effort, potential for injuries if not performed properly, time commitment | Walking, jogging, swimming, cycling, strength training |
| Pharmacological Interventions | May accelerate weight loss, can be effective in certain cases | Potential side effects, not a standalone solution, often requires lifestyle changes for sustained success | Appetite suppressants, medications affecting metabolism |
Identifying Factors Affecting Weight Loss Success

Losing 15% of body weight, a crucial target for type 2 diabetes management, presents unique challenges. Success hinges on understanding and addressing the multifaceted factors that influence an individual’s ability to achieve and maintain this significant weight loss. It’s not just about willpower; a holistic approach that acknowledges the interplay of lifestyle, psychology, and demographics is vital.Many factors contribute to the success or failure of weight loss efforts, especially for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Understanding these factors empowers individuals and healthcare professionals to tailor strategies that are more likely to yield lasting results. This involves acknowledging the diverse needs and challenges faced by different demographic groups.
Lifestyle Factors in Weight Loss
Effective weight loss management for type 2 diabetes necessitates a comprehensive approach that integrates lifestyle factors. Diet, exercise, and sleep play crucial roles in achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. Consistent dietary changes are essential, focusing on nutrient-rich foods and portion control. Regular physical activity, tailored to individual abilities and preferences, boosts metabolism and promotes calorie expenditure.
Adequate sleep is equally important, as sleep deprivation can disrupt hormones that regulate appetite and metabolism.
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains provides essential nutrients without excessive calories. Portion control and mindful eating techniques are critical for long-term success. Customized dietary plans should consider individual preferences and cultural backgrounds to enhance adherence.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, including both cardiovascular and strength training, is vital for weight loss and overall health. A gradual increase in activity levels, combined with appropriate exercise intensity and duration, optimizes calorie burning. Finding enjoyable activities that fit into daily routines ensures long-term adherence.
- Sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for weight management. Insufficient sleep disrupts hormones that regulate appetite and metabolism, potentially leading to increased hunger and reduced calorie expenditure. Prioritizing 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night is crucial for successful weight loss efforts.
Psychological and Emotional Aspects of Weight Loss
Weight loss can be emotionally challenging. Psychological and emotional factors can significantly impact adherence to management plans. Addressing potential emotional eating patterns, developing positive coping mechanisms for stress, and building self-esteem are crucial for long-term success. Support systems, such as counseling or support groups, can play a vital role in providing emotional support and guidance.
Demographic Differences in Weight Loss Challenges
Different demographic groups may face unique challenges in achieving and maintaining weight loss. Access to healthy food options, financial constraints, cultural norms, and physical limitations can all influence weight loss outcomes. Tailoring interventions to address specific needs of diverse communities is crucial for equitable and effective weight management. For example, communities with limited access to fresh produce or affordable healthy food options may require targeted solutions to overcome these barriers.
Potential Barriers to 15% Weight Loss, Type 2 diabetes management should include 15 percent weight loss researchers say
| Barrier Category | Example Barriers | Potential Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Dietary Constraints | Limited access to affordable, healthy foods; cultural food preferences; food allergies/intolerances | Food banks, nutrition education programs, meal preparation assistance, personalized dietary plans |
| Financial Constraints | Cost of healthy foods, gym memberships, or other resources; lack of access to affordable transportation | Government subsidies for healthy foods, community gardens, financial assistance programs |
| Lack of Support System | Social pressure to eat certain foods, lack of family or friend support, isolation | Support groups, family involvement, community-based programs, counseling |
| Physical Limitations | Physical disabilities, lack of safe exercise spaces, chronic pain | Modified exercise programs, assistive devices, accessible gyms/parks, pain management |
| Psychological Factors | Emotional eating, stress, low self-esteem, lack of motivation | Therapy, stress management techniques, motivational coaching, mindfulness practices |
| Cultural Factors | Cultural norms around food and portion sizes; beliefs about weight loss | Culturally sensitive interventions, community health workers, education on cultural practices |
Strategies for Achieving and Maintaining 15% Weight Loss
Reaching a 15% weight loss target, crucial for managing type 2 diabetes, requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond temporary fixes. Sustained lifestyle changes are key to achieving and maintaining this significant weight reduction, and it’s essential to acknowledge the challenges and develop strategies for long-term success. This journey demands dedication, understanding, and a personalized plan.Achieving a 15% weight loss is not just about the number on the scale; it’s about improving overall health and well-being.
This substantial reduction in weight can lead to significant improvements in blood sugar control, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels, ultimately reducing the risk of complications associated with type 2 diabetes. Understanding the intricacies of weight management and the role of dietary changes, exercise, and lifestyle modifications is vital for long-term success.
Dietary Recommendations for Healthy Weight Loss
A balanced diet is fundamental for successful weight loss. It’s not about deprivation but rather about making informed choices that support your health goals. A balanced approach, focusing on nutrient-rich foods, will nourish your body and provide the energy needed for daily activities. Avoid fad diets that promise quick results, as they often lead to unsustainable practices.
- Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods:
- Control portion sizes:
- Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats:
- Increase fiber intake:
- Stay hydrated:
Fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains form the foundation of a healthy diet. These foods are packed with essential nutrients, promoting satiety and supporting overall health.
Portion control is crucial for weight management. Using smaller plates and mindful eating techniques can help you consume fewer calories without feeling deprived.
These foods often contribute excess calories and lack essential nutrients. Substituting them with healthier options will positively impact your weight loss journey.
Researchers are saying that managing type 2 diabetes effectively often involves a 15% weight loss. This focus on weight management is crucial for overall health, and it’s important to remember that other conditions, like those associated with Epstein Barr virus, such as epstein barr multiple sclerosis symptoms , can also impact health. Ultimately, a holistic approach to managing type 2 diabetes is key, and weight loss plays a significant role.
Fiber-rich foods promote satiety and aid digestion. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet.
Drinking plenty of water helps with satiety and overall bodily functions.
Effective Exercise Routines for Type 2 Diabetes
Regular physical activity is an integral part of managing type 2 diabetes and achieving weight loss. Exercise not only helps burn calories but also improves insulin sensitivity, aiding in blood sugar control.
- Aerobic exercises:
- Strength training exercises:
- Flexibility and balance exercises:
- Finding activities you enjoy:
Activities like brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling are excellent for cardiovascular health and calorie burning. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
Incorporating strength training exercises, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises, builds muscle mass. Muscle mass is important for burning more calories even at rest.
Yoga, Pilates, or tai chi improve flexibility and balance, crucial for preventing falls and injuries, especially important as you progress in your weight loss journey.
Choose activities that you find enjoyable to make exercise a sustainable part of your routine. This will prevent burnout and ensure long-term adherence.
Sample Weekly Meal Plan
A sample weekly meal plan is a starting point and should be adjusted based on individual needs and preferences. Consulting a registered dietitian or a healthcare professional is highly recommended to create a personalized plan.
| Day | Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner | Snacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | Oatmeal with berries and nuts | Salad with grilled chicken | Baked salmon with roasted vegetables | Apple slices with peanut butter |
| Tuesday | Greek yogurt with fruit | Lentil soup with whole-wheat bread | Lean ground turkey stir-fry | Carrot sticks with hummus |
| Wednesday | Whole-wheat toast with avocado | Quinoa salad with chickpeas | Chicken breast with brown rice and steamed broccoli | Handful of almonds |
| Thursday | Scrambled eggs with spinach and whole-wheat toast | Turkey and vegetable wrap | Vegetarian chili with cornbread | Edamame |
| Friday | Smoothie with protein powder, fruits, and vegetables | Leftover chicken and vegetable stir-fry | Baked cod with steamed asparagus | Mixed fruit |
| Saturday | Breakfast burrito with scrambled eggs, beans, and salsa | Salad with grilled tofu | Lean beef with sweet potato and green beans | Hard-boiled egg |
| Sunday | Pancakes made with whole-wheat flour and fruit | Leftover beef and sweet potato | Vegetarian pasta with marinara sauce | String cheese |
Creating a Sustainable Lifestyle
Creating a sustainable lifestyle that maintains weight loss requires a shift in mindset. It’s about integrating healthy habits into your daily routine, making them a part of your overall well-being, rather than a temporary fix.
- Seek support from a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian:
- Join a support group:
- Focus on gradual changes, rather than drastic ones:
- Track your progress and celebrate milestones:
- Practice self-compassion:
A personalized plan can be tailored to your specific needs and goals.
Connecting with others who share similar goals can provide encouragement and motivation.
Sustainable changes are more likely to stick than quick fixes.
Monitoring your progress and acknowledging achievements can help maintain motivation.
Be kind to yourself and understand that setbacks are part of the process. Learn from them and keep moving forward.
Healthcare Professional’s Role in Weight Management
Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in supporting individuals with type 2 diabetes in achieving and maintaining a 15% weight loss. This involves more than just prescribing medications; it requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the multifaceted nature of weight management and considers the individual’s unique circumstances. Success hinges on fostering a strong patient-provider relationship built on trust, education, and shared decision-making.Effective weight management for individuals with type 2 diabetes necessitates a proactive and supportive role from healthcare professionals.
They are instrumental in guiding patients toward sustainable lifestyle changes and providing ongoing encouragement and support. This extends beyond simply prescribing a diet or exercise regimen; it encompasses a thorough understanding of the patient’s needs, preferences, and challenges.
Importance of Education and Support
Providing comprehensive education about healthy eating, portion control, and physical activity is paramount. This empowers patients to make informed choices and adopt sustainable habits. Regular follow-up appointments, encouragement, and addressing any barriers encountered during the weight loss journey are vital. Furthermore, education should include strategies for managing stress and emotional eating, common factors that can derail weight loss efforts.
Open communication channels and a supportive environment facilitate a positive patient experience, promoting adherence to the treatment plan.
Researchers are saying that managing type 2 diabetes effectively often hinges on a 15 percent weight loss. This is crucial for overall health, and incorporating delicious, healthy recipes like those found in Franco Noriega’s Peruvian cooking can be a fantastic way to reach that goal. Franco Noriega’s Peruvian cooking offers a wealth of inspiration for flavorful, nutrient-rich dishes that support healthy eating habits.
So, when it comes to managing type 2 diabetes, remember that a balanced diet, rich in diverse foods like those featured in Peruvian cuisine, is key.
Individualized Treatment Plans
Individualized treatment plans are essential for successful weight management in type 2 diabetes. No two individuals respond identically to interventions, and a one-size-fits-all approach is rarely effective. Factors like cultural background, socioeconomic status, access to resources, and individual preferences must be considered. This requires a thorough assessment of the patient’s current lifestyle, dietary habits, physical activity levels, and psychological well-being.
Tailoring the plan to address these specific factors increases the likelihood of achieving and maintaining weight loss goals.
Tools and Resources for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare professionals have a range of tools and resources available to support weight management. These include evidence-based weight loss programs, registered dietitians, certified diabetes educators, and support groups. Utilizing technology such as mobile applications and wearable devices can further enhance patient engagement and promote accountability. Collaboration with other healthcare professionals, such as psychologists or psychiatrists, can be beneficial in addressing emotional factors that may influence weight loss.
Approaches to Counseling Patients on Weight Loss
| Approach | Description | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | CBT focuses on identifying and modifying negative thought patterns and behaviors related to eating and exercise. | Effective in addressing underlying psychological factors influencing weight loss, promoting self-efficacy. | Requires trained professionals, potentially time-consuming. |
| Motivational Interviewing (MI) | MI emphasizes patient autonomy and self-motivation by exploring and resolving ambivalence toward weight loss. | Emphasizes patient empowerment and intrinsic motivation, fosters a collaborative relationship. | Requires skilled practitioners, might not address complex psychological issues. |
| Behavioral Strategies | Focuses on practical strategies like meal planning, portion control, and increasing physical activity. | Practical and easily implemented, can address immediate needs and challenges. | May not address underlying psychological factors contributing to weight gain. |
| Nutritional Counseling | Provides tailored dietary guidance considering individual needs and preferences, promoting healthy eating habits. | Addresses nutritional deficiencies, improves overall health, aligns with long-term health goals. | Requires expertise in nutrition, potential difficulty in changing ingrained dietary patterns. |
Illustrative Examples of Successful Weight Loss
Achieving a 15% weight loss and managing type 2 diabetes requires dedication and a personalized approach. Real-life examples demonstrate the transformative power of consistent effort and the importance of tailored support systems. Success stories offer valuable insights into the strategies that work and the positive outcomes that can be achieved.Successfully managing type 2 diabetes often involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes, increased physical activity, and emotional support.
These examples illustrate the impact of these strategies on individuals’ health and well-being. They show how individuals can not only lose weight but also experience significant improvements in their overall health and quality of life.
Successful Weight Loss Journeys and Diabetes Management
Individuals who successfully manage type 2 diabetes through weight loss often demonstrate a profound commitment to their health. Their journeys highlight the importance of tailored plans and consistent support. A crucial aspect of these successful journeys is the integration of these components.
Strategies and Support Systems
A critical component of successful weight loss is a personalized strategy. Tailored approaches consider individual needs, preferences, and health conditions. This approach should include a comprehensive assessment of current lifestyle habits and preferences to determine how to integrate lifestyle changes into existing routines.
Example 1: Sarah’s Journey
Sarah, a 45-year-old woman diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, experienced significant improvements after implementing a multifaceted weight loss plan. She started by working with a registered dietitian to develop a balanced meal plan rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. This involved careful portion control and mindful eating practices. In addition to dietary changes, Sarah actively increased her physical activity.
She joined a local walking group and gradually incorporated more strenuous exercises into her routine. Regular check-ins with her endocrinologist were also critical. This consistent monitoring and support were crucial for maintaining motivation and ensuring the plan aligned with her evolving needs. The result of this comprehensive approach was a 15% weight loss over 12 months.
This significant weight loss enabled her to better manage her blood sugar levels, reduce her medication needs, and experience a notable improvement in her overall health and energy levels.
Example 2: David’s Approach
David, a 62-year-old man with type 2 diabetes, focused on gradual lifestyle changes. He started by making small, sustainable dietary adjustments. He replaced sugary drinks with water and incorporated more whole grains into his diet. He also gradually increased his daily physical activity by incorporating short walks into his routine. A key aspect of David’s success was his active engagement with a support group for people with diabetes.
This group provided encouragement, shared experiences, and practical advice, reinforcing his commitment to the lifestyle changes. David’s approach to weight loss, emphasizing small, manageable changes, contributed to long-term success. His 15% weight loss resulted in a marked improvement in his blood sugar control and a significant reduction in his reliance on medication. This example showcases the importance of finding sustainable strategies.
Positive Outcomes of Weight Loss
The positive outcomes of weight loss extend beyond the reduction in body weight. Significant improvements in blood sugar control, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels were observed in both Sarah and David’s cases. Reduced reliance on diabetes medication was also a common outcome. These improvements led to a heightened quality of life, increased energy levels, and a greater sense of well-being.
Long-Term Health Improvements
Both Sarah and David experienced long-term health improvements. They reported improved mobility, reduced pain, and increased energy levels. The sustained weight loss and improved health management fostered a more optimistic outlook on their overall health. These positive experiences highlight the long-term benefits of consistent weight management strategies.
Challenges and Considerations for 15% Weight Loss
Achieving a 15% weight loss, while a significant goal for managing type 2 diabetes, presents unique challenges. This journey isn’t a one-size-fits-all endeavor. Individual responses to dietary and exercise plans vary greatly, influenced by factors ranging from genetics and metabolism to psychological well-being and underlying health conditions. Understanding these challenges and developing personalized strategies are crucial for success.
Individual Variability in Response to Weight Loss Efforts
Individual responses to weight loss plans differ due to variations in metabolism, genetics, and lifestyle. Some individuals may find it easier to lose weight than others, while some might struggle with maintaining the lost weight. This variability necessitates tailored approaches to weight management. Factors such as age, sex, activity level, and pre-existing health conditions significantly impact how the body responds to interventions.
For example, a sedentary individual may require more intense exercise programs than an active one, while a person with a history of eating disorders might need a more psychologically focused approach.
Psychological Factors Affecting Weight Loss Success
Psychological factors play a significant role in weight loss journeys. Emotional eating, stress, and mental health conditions can all hinder progress. Weight loss can be emotionally challenging, and individuals may experience feelings of frustration, disappointment, or even guilt. A supportive environment, including counseling or therapy, can be crucial for navigating these psychological obstacles. For instance, individuals who use food as a coping mechanism for stress might benefit from stress management techniques alongside a structured diet plan.
Medical Conditions and Their Impact on Weight Loss
Certain medical conditions can complicate weight loss efforts. Underlying health issues like hypothyroidism, sleep apnea, or certain medications can affect metabolism and make weight loss more challenging. Individuals with such conditions should consult their healthcare providers for personalized guidance and strategies to address these specific obstacles. For instance, someone with hypothyroidism might need medication adjustments in conjunction with a carefully monitored diet plan.
Importance of Monitoring Weight Loss Progress and Adjusting Strategies
Regular monitoring of weight loss progress is essential. Tracking weight, body measurements, and dietary intake allows for adjustments to strategies as needed. Progress should be evaluated not just in terms of weight loss but also in terms of overall well-being and adherence to the plan. For example, if a specific exercise routine isn’t yielding results, adjusting it to something more effective and sustainable is important.
Need for Personalized Approaches to Weight Management
A one-size-fits-all approach to weight loss is ineffective. Personalized strategies are crucial for addressing individual needs and maximizing success. This involves considering factors like current health status, dietary preferences, activity levels, and psychological well-being. Healthcare professionals should guide individuals in creating tailored plans that cater to their specific circumstances. This is critical, as one person’s dietary needs may differ significantly from another’s.
Potential Complications to Monitor and Manage
| Potential Complication | Symptoms | Management |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Deficiencies | Fatigue, weakness, hair loss, skin problems | Dietary supplements, balanced diet, regular blood tests |
| Muscle Loss | Weakness, decreased strength, reduced mobility | Resistance training, adequate protein intake, consultation with a physical therapist |
| Gallstones | Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting | Medical evaluation, dietary modifications, medication |
| Kidney Stones | Severe flank pain, nausea, vomiting | Hydration, dietary changes, medical intervention |
| Depression/Anxiety | Persistent sadness, hopelessness, difficulty sleeping, loss of interest in activities | Professional counseling, therapy, medication |
| Orthostatic Hypotension | Lightheadedness, dizziness upon standing | Hydration, gradual changes in activity levels, consultation with a physician |
Final Summary: Type 2 Diabetes Management Should Include 15 Percent Weight Loss Researchers Say
In conclusion, achieving and maintaining a 15% weight loss, as recommended for managing type 2 diabetes, is a multifaceted journey requiring a personalized approach. Success hinges on understanding the role of lifestyle factors, emotional well-being, and the crucial support of healthcare professionals. We’ve explored the science behind this recommendation, the challenges, and the strategies for success. Remember, consistency and personalized plans are key to achieving lasting health improvements.
It’s a journey, not a race, and the support of a healthcare team is invaluable.