What national diabetes commission will try to accomplish is a comprehensive plan to combat the growing diabetes epidemic. This initiative aims to prevent, detect, and treat diabetes effectively, focusing on diverse populations and improving access to quality healthcare. The commission will leverage existing public health programs, partner with healthcare providers, and collect data to track progress and ensure success.
The commission will meticulously Artikel its goals and objectives, encompassing prevention strategies, improved healthcare access, and a robust data collection and analysis plan. It will address the specific needs of different demographics, identifying potential challenges and devising solutions to overcome them. The plan will be built on strong partnerships with healthcare providers and a comprehensive approach to community engagement.
Goals and Objectives of the National Diabetes Commission
The National Diabetes Commission, a crucial initiative, aims to comprehensively address the escalating diabetes burden in the nation. Its establishment reflects a commitment to improving the lives of those affected and preventing further complications. This commission will play a pivotal role in shaping a more robust and effective national response to this prevalent health concern.
Potential Goals and Objectives
The commission will strive to achieve several key goals, primarily focused on prevention, management, and research. These include developing and implementing evidence-based strategies for diabetes prevention, early detection, and management. Crucially, the commission will aim to create a national framework for consistent, high-quality care across diverse communities.
- Enhance Prevention Strategies: The commission will focus on implementing public awareness campaigns, promoting healthy lifestyle choices (diet and exercise), and providing targeted interventions for high-risk populations. These initiatives are expected to significantly reduce the incidence of diabetes.
- Improve Access to Care: The commission will advocate for improved access to affordable and comprehensive diabetes care, including preventative screenings, medication, and ongoing support services. Addressing disparities in access to quality care is a critical objective.
- Strengthen Research and Innovation: The commission will support research initiatives focused on the development of new diagnostic tools, treatments, and preventative measures. This includes fostering collaborations with research institutions and encouraging innovation in the field.
- Develop a National Diabetes Care Standard: The commission will create a national standard for diabetes care, encompassing guidelines for diagnosis, treatment, and management. This standard will aim to ensure consistent quality across all healthcare settings.
- Promote Public Health Initiatives: The commission will champion and support the implementation of public health initiatives to combat diabetes, focusing on educational programs, community outreach, and the creation of supportive environments for healthy living. These efforts will play a crucial role in promoting healthier lifestyles and reducing risk factors.
Expected Impact and Desired Outcomes
The commission’s efforts are expected to lead to significant improvements in diabetes management, reducing the burden of the disease on individuals, families, and the healthcare system. Expected outcomes include reduced rates of diabetes-related complications, improved quality of life for those affected, and reduced healthcare costs associated with the disease.
- Reduced Prevalence of Diabetes-Related Complications: The commission aims to reduce the prevalence of complications like heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage by promoting early diagnosis and effective management.
- Improved Quality of Life for Individuals with Diabetes: The commission seeks to improve the overall quality of life for individuals with diabetes by providing access to comprehensive care, support, and resources.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: By promoting prevention, early detection, and effective management, the commission anticipates a decrease in healthcare costs associated with diabetes-related complications.
Metrics for Measuring Success
The commission’s success will be measured using a range of metrics, including changes in the prevalence of diabetes, improvements in the quality of diabetes care, and reductions in diabetes-related complications and hospitalizations.
- Changes in Diabetes Prevalence: Monitoring the change in the prevalence of diabetes across different demographic groups over time will be a crucial metric for evaluating the commission’s success.
- Improvements in Quality of Diabetes Care: Evaluating the quality of diabetes care provided in various healthcare settings will be crucial for measuring the commission’s effectiveness.
- Reductions in Diabetes-Related Complications: Tracking the reduction in the incidence of diabetes-related complications, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage, will be a critical indicator of the commission’s impact.
Comparison with Existing National Diabetes Strategies
| Goal | Description | Existing National Diabetes Strategy (Example) | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enhance Prevention Strategies | Implement public awareness campaigns, promote healthy lifestyle choices | National Diabetes Prevention Program | Aligned with existing programs, but aims for broader scope and community engagement. |
| Improve Access to Care | Ensure affordable and comprehensive diabetes care | Medicaid expansion programs | Complements existing initiatives by focusing on access across the healthcare spectrum. |
| Strengthen Research and Innovation | Support research in diagnostics, treatments, and prevention | National Institutes of Health (NIH) funding | Leverages existing research infrastructure, aims to prioritize diabetes-related research. |
Expected Impact on Different Demographics
| Demographic | Potential Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Reduce disparities in diabetes management across different age groups. | Tailored interventions for children, adolescents, and older adults. |
| Socioeconomic Status | Increase access to resources for individuals with lower socioeconomic status. | Community health centers, mobile clinics, and financial assistance programs. |
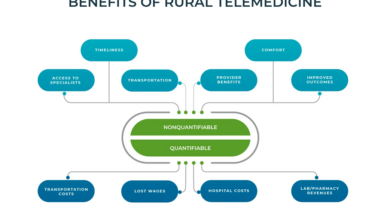
| Geographic Location | Reduce disparities in diabetes care across different geographic areas. | Telemedicine initiatives, rural health clinics. |
Scope and Focus Areas
The National Diabetes Commission will tackle the multifaceted challenge of diabetes with a comprehensive and targeted approach. This involves understanding the full spectrum of the disease, from prevention and early detection to effective treatment and ongoing management. A crucial element will be focusing on the specific needs of different population groups to ensure equitable access to care and resources.This section details the scope and key focus areas of the commission, highlighting the populations it aims to serve, the stakeholders it will engage, and the potential collaborations that will be vital to its success.
A strong emphasis will be placed on evidence-based strategies to optimize outcomes and minimize the impact of diabetes on individuals and the community as a whole.
Potential Scope of the Commission
The commission’s scope encompasses a broad range of activities aimed at improving diabetes outcomes across the nation. This includes developing and implementing comprehensive prevention strategies, enhancing early detection programs, and improving access to high-quality treatment and ongoing care. The commission will also address the social determinants of health, which play a significant role in diabetes development and management.
Focus Areas
The commission will concentrate on several key areas to effectively address the diabetes epidemic. These areas include:
- Prevention and Education: Initiatives will focus on educating the public about diabetes risk factors, promoting healthy lifestyles, and empowering individuals to take proactive steps towards prevention. This will include community outreach programs, school-based education, and accessible online resources.
- Early Detection and Screening: The commission will develop and implement strategies for early detection and screening, particularly targeting high-risk populations. This will include expanding access to affordable and convenient screening services, ensuring accurate diagnosis, and connecting individuals with appropriate support systems early in the process.
- Improved Access to Treatment and Care: Efforts will be made to improve access to affordable and quality diabetes treatment and care, including medication, counseling, and support groups. This will involve working with healthcare providers, insurers, and community organizations to ensure equitable access.
- Research and Innovation: The commission will encourage and support research into new treatments, prevention strategies, and technologies to advance the fight against diabetes. Collaborations with research institutions and funding opportunities will be explored.
- Social Determinants of Health: Recognizing the critical role of socioeconomic factors, the commission will address the social determinants of health, such as food security, access to affordable healthcare, and housing stability. This will involve partnerships with community organizations and policymakers to create supportive environments for diabetes management.
Target Populations
The commission will address the needs of diverse populations, including:
- Individuals with pre-diabetes: Focus on early interventions and lifestyle modifications to prevent progression to type 2 diabetes.
- Individuals with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: Provision of comprehensive care, including treatment, education, and support services.
- Children and adolescents: Addressing the growing incidence of type 2 diabetes in young people, focusing on preventative measures and early detection.
- Rural and underserved communities: Ensuring equitable access to resources and care, considering the unique challenges faced by these communities.
- Minority groups: Acknowledging the disproportionate impact of diabetes on specific racial and ethnic groups, tailored interventions will be developed.
Key Stakeholders
Effective engagement with key stakeholders is crucial for the commission’s success. These include:
- Healthcare providers: Collaborating with physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals to ensure seamless integration of diabetes care into existing systems.
- Public health agencies: Partnering with state and local health departments to leverage existing resources and implement community-based programs.
- Community organizations: Engaging with local groups to address the social determinants of health and promote community engagement.
- Researchers and academic institutions: Collaborating to support research and development of innovative solutions.
- Policymakers: Engaging with legislators to advocate for policies that support diabetes prevention, early detection, and treatment.
Potential Collaborations
The commission will seek collaborations with various organizations to enhance its impact:
- Non-profit organizations: Collaborations with diabetes support groups and other non-profits will expand reach and enhance community support.
- Pharmaceutical companies: Partnerships to provide access to medication and support programs for those who need them.
- Insurance providers: Collaboration to make diabetes care more accessible and affordable through insurance coverage.
- Technology companies: Exploring the use of technology to improve diabetes management, such as telehealth and mobile health applications.
Commission’s Approach
| Area | Prevention | Early Detection | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strategies | Promoting healthy lifestyles, public awareness campaigns, and early interventions for pre-diabetes. | Implementing routine screenings for high-risk individuals, developing accessible diagnostic tools, and improving access to testing facilities. | Providing individualized treatment plans, access to quality care, and ongoing support for managing the condition. |
| Resources | Community health education programs, accessible resources, and partnerships with community organizations. | Partnerships with healthcare providers, expanding screening programs, and promoting awareness campaigns. | Medication support, counseling services, and comprehensive care management programs. |
| Evaluation | Monitoring the effectiveness of prevention programs and adjusting strategies as needed. | Tracking early detection rates, evaluating diagnostic accuracy, and analyzing outcomes for individuals screened. | Assessing treatment efficacy, evaluating patient satisfaction, and identifying areas for improvement. |
Strategies for Addressing Diabetes
Combating diabetes requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing prevention, effective management, and equitable access to care. This section details the strategies the National Diabetes Commission plans to implement, emphasizing community engagement and sustainable solutions. Our goal is to not just treat diabetes, but to empower individuals and communities to lead healthier lives.Our strategies are rooted in the understanding that diabetes is a complex issue requiring a holistic response.
We aim to address the social determinants of health, such as socioeconomic factors, access to healthy food, and education, to create lasting positive change.
Diabetes Prevention Strategies
Proactive measures are crucial to prevent the onset of diabetes. The commission will focus on promoting healthy lifestyle choices through comprehensive public awareness campaigns. These campaigns will target diverse populations, emphasizing the importance of balanced diets, regular physical activity, and stress management techniques. Education initiatives will be tailored to specific communities, taking into account cultural nuances and individual needs.
The National Diabetes Commission aims to improve diabetes management and prevention strategies across the nation. It’s a huge undertaking, but considering the impact of a chronic condition like diabetes, it’s a vital effort. Living with diabetes long-term, or even experiencing the challenges of recovery from a stroke, as detailed in this powerful account of what its like to live for 15 years after a stroke , highlights the importance of comprehensive support systems.
Ultimately, the commission’s work is about fostering healthier communities and better outcomes for everyone.
This includes providing resources like workshops, cooking demonstrations, and community-based exercise programs.
Effective Diabetes Management Strategies
Beyond prevention, effective management is critical for those already diagnosed. The commission will implement programs to improve access to comprehensive care, including early diagnosis, medication adherence support, and ongoing education. We will also encourage the development of diabetes self-management education programs, empowering individuals to take an active role in their health. Partnerships with healthcare providers and community organizations will be essential to ensure seamless transitions between care settings.
Improving Access to Affordable Healthcare
Ensuring access to affordable healthcare is a cornerstone of our approach. The commission will work with insurance providers and government agencies to explore innovative financing mechanisms. This includes negotiating lower drug costs, providing subsidies for preventative care, and increasing the availability of affordable healthcare services in underserved communities. Collaborations with community health centers and non-profit organizations will be vital in reaching those who face barriers to accessing quality care.
Community Engagement Initiatives
Engaging communities in the fight against diabetes is paramount. The commission will establish partnerships with local organizations to create supportive environments. This includes organizing community health fairs, conducting workshops on nutrition and exercise, and providing access to diabetes support groups. These initiatives will focus on culturally appropriate methods to ensure that information reaches diverse communities effectively.
Table of Strategies and Expected Effectiveness
| Strategy | Expected Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Public Awareness Campaigns | Increased knowledge and awareness of diabetes risk factors, leading to early detection and healthier lifestyle choices. |
| Community Health Fairs | Increased access to screenings, education, and resources for diabetes prevention and management. |
| Partnerships with Healthcare Providers | Improved coordination of care, seamless transitions between care settings, and increased access to specialists. |
| Affordable Healthcare Initiatives | Reduced financial barriers to accessing diabetes care, improving adherence to treatment plans, and potentially slowing disease progression. |
| Diabetes Self-Management Education Programs | Increased patient empowerment and self-efficacy, leading to improved management of blood glucose levels, reduced complications, and better quality of life. |
Potential Challenges and Solutions: What National Diabetes Commission Will Try To Accomplish

Navigating the complexities of diabetes requires a multifaceted approach, recognizing the diverse challenges individuals and communities face. This section details potential hurdles the National Diabetes Commission might encounter and Artikels strategic solutions to overcome them. Addressing logistical and financial barriers, along with complex social and cultural factors, is crucial for the commission’s success.
Financial Constraints
Financial limitations can hinder the commission’s ability to implement comprehensive programs. Funding shortages may impact the procurement of essential resources, like equipment for screenings, educational materials, and community outreach initiatives. Insufficient funding could also restrict the commission’s capacity to hire and retain qualified personnel, ultimately compromising program effectiveness.
- Solution: Diversify funding sources. Explore partnerships with private foundations, corporations, and government agencies to supplement the commission’s budget. Seek grants and philanthropic donations. Develop cost-effective strategies for program delivery, like utilizing volunteer support where appropriate and leveraging technology to reduce overhead.
- Example: Collaborate with pharmaceutical companies to provide subsidized medication or diagnostic tools to underserved populations. Develop community-based fundraising initiatives to support local diabetes support groups.
Logistical Barriers
Implementing programs across diverse geographic areas presents logistical hurdles. Accessibility to healthcare services, especially in rural or underserved communities, is a significant concern. Reaching diverse populations and ensuring equitable access to resources requires careful planning and strategic partnerships. Coordinating multiple stakeholders, including healthcare providers, community organizations, and government agencies, is a key logistical challenge.
- Solution: Implement mobile health units and telehealth services to address accessibility issues in remote areas. Develop community partnerships with existing healthcare providers and community centers to create convenient access points. Establish clear communication channels and standardized protocols to facilitate seamless information exchange between stakeholders.
- Example: Partner with local transportation services to provide transportation to screenings and appointments for individuals without reliable transportation. Create bilingual materials to ensure all communities are reached.
Complex Issues Related to Diabetes
Diabetes management often involves complex interplay of social, cultural, and economic factors. Addressing the underlying causes of diabetes, such as socioeconomic disparities, requires a nuanced understanding of community needs and cultural sensitivities. For example, cultural beliefs and practices can affect adherence to treatment plans.
The national diabetes commission is aiming to improve preventative measures and patient support programs. While they focus on diabetes management, it’s important to remember that overall health awareness is key. For example, did you know that ear wax might be a bigger health hazard than you think? ear wax might be a bigger health hazard than you think This underscores the broader need for comprehensive health education and preventative care, a goal the commission is undoubtedly striving for.
- Solution: Conduct thorough needs assessments to understand the unique challenges faced by different communities. Develop culturally sensitive educational materials and support groups tailored to specific cultural needs. Involve community leaders and health workers in program design and implementation to foster trust and ensure cultural appropriateness.
- Example: Create diabetes education programs in different languages and formats, such as videos and community workshops. Recruit community health workers to act as trusted intermediaries between healthcare providers and patients, ensuring cultural sensitivity and trust in the process.
Contingency Plans
| Challenge | Contingency Plan |
|---|---|
| Funding Shortfall | Explore alternative funding sources, optimize resource allocation, and prioritize essential programs. |
| Lack of Community Engagement | Conduct community outreach programs, partner with community leaders, and adapt communication strategies to enhance engagement. |
| Logistical Challenges (Accessibility) | Implement mobile health initiatives, telehealth services, and strategic partnerships with community organizations to overcome accessibility issues. |
| Resistance to Change (Treatment Adherence) | Develop culturally sensitive educational materials and support systems, engage community health workers, and personalize treatment plans. |
| Data Management Issues | Establish secure and standardized data collection systems, train staff on data entry procedures, and implement data quality control measures. |
Role of Public Health Initiatives
Public health initiatives are crucial in the fight against diabetes. They provide a framework for preventative measures, early detection, and ongoing support for individuals at risk or living with the condition. A comprehensive approach that leverages existing resources and builds community capacity is essential to achieving sustainable improvements in diabetes management. This section Artikels the National Diabetes Commission’s commitment to utilizing and enhancing public health programs to foster a healthier nation.
Importance of Public Health Initiatives
Public health initiatives play a vital role in mitigating the impact of diabetes. By promoting healthy lifestyles, early diagnosis, and access to care, these programs can significantly reduce the prevalence and severity of the disease. These initiatives are particularly important in reaching underserved populations and creating a more equitable health landscape.
Leveraging Existing Public Health Programs
The commission will leverage existing public health programs by establishing partnerships and collaborations with relevant organizations. This includes collaborations with schools, community centers, and healthcare providers to integrate diabetes prevention and management into existing initiatives. These collaborations will streamline efforts and maximize the reach of valuable resources.
Promoting Public Awareness and Education
Public awareness and education are fundamental to the commission’s strategy. The commission will actively promote understanding of diabetes risk factors, prevention strategies, and available resources. This includes creating a range of educational materials tailored for diverse audiences. By providing accessible and engaging information, the commission aims to empower individuals to take control of their health.
Examples of Educational Materials, What national diabetes commission will try to accomplish
The commission will develop a variety of educational materials to reach different demographics and learning styles. This will include:
- Interactive online modules: These modules will provide engaging content about diabetes prevention, risk factors, and management strategies. They will be tailored to different age groups and educational levels.
- Informative brochures and pamphlets: These materials will provide concise and easy-to-understand information about diabetes, including risk factors, symptoms, and management techniques.
- Social media campaigns: Engaging social media posts, videos, and infographics will disseminate crucial information about diabetes to a wider audience.
- Community workshops and presentations: These events will provide interactive opportunities for individuals to learn about diabetes, ask questions, and connect with healthcare professionals.
Roles of Different Public Health Sectors in the Commission’s Strategy
The National Diabetes Commission recognizes the diverse roles different public health sectors play in combating diabetes. Effective collaboration and shared responsibility are key to a successful strategy.
| Public Health Sector | Specific Roles |
|---|---|
| Healthcare Providers (Clinics, Hospitals) | Integrating diabetes screening and management into routine care; providing ongoing support and education to patients; participating in community outreach programs. |
| Schools and Community Centers | Implementing health education programs focused on nutrition, physical activity, and diabetes prevention; hosting workshops and seminars on diabetes awareness. |
| Public Health Departments | Developing and implementing statewide diabetes prevention programs; coordinating with healthcare providers and community organizations; monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of interventions. |
| Nonprofit Organizations | Providing community-based support services; organizing support groups for individuals with diabetes; facilitating access to resources and information. |
Collaboration with Healthcare Providers

The National Diabetes Commission recognizes the critical role healthcare providers play in preventing and managing diabetes. Effective collaboration with these professionals is paramount to the success of our initiatives. This section details the commission’s approach to fostering partnerships and empowering providers to deliver optimal care.The commission aims to create a supportive ecosystem for healthcare providers, enabling them to integrate diabetes management into their routine practices.
This includes offering comprehensive training, establishing clear guidelines, and providing incentives for participation. By working hand-in-hand with providers, the commission seeks to improve patient outcomes and ultimately reduce the burden of diabetes within our communities.
Approach to Collaboration
The commission will employ a multi-pronged approach to collaboration, encompassing direct engagement, knowledge sharing, and ongoing support. We will focus on building strong relationships with various healthcare settings, from primary care clinics to specialized diabetes centers. This involves regular communication channels, joint workshops, and collaborative research initiatives.
Training and Education for Healthcare Professionals
To ensure providers are equipped with the latest knowledge and best practices, the commission will implement targeted training programs. These programs will cover various aspects of diabetes management, including:
- Advanced diagnostic techniques and early detection strategies.
- Personalized treatment plans and management strategies for diverse patient populations.
- Effective communication and counseling skills for patients with diabetes.
- Integration of diabetes self-management education programs into routine care.
These programs will be designed to be flexible and adaptable, catering to the specific needs of different healthcare settings and professional backgrounds.
Supporting the Development of Diabetes Care Guidelines
The commission will actively participate in the development and dissemination of updated diabetes care guidelines. This involves:
- Collaboration with leading diabetes experts and researchers.
- Reviewing and analyzing the latest clinical trials and research findings.
- Ensuring guidelines are practical, accessible, and tailored to the diverse needs of patients and healthcare settings.
- Facilitating the translation of guidelines into actionable strategies for healthcare professionals.
This will help ensure consistency and quality in diabetes care across the nation.
Incentives for Healthcare Provider Participation
The commission recognizes the importance of incentivizing healthcare providers’ participation in its efforts. Strategies include:
- Providing continuing medical education (CME) credits for participation in training programs.
- Offering financial incentives for implementing evidence-based diabetes care protocols.
- Recognizing and rewarding providers who demonstrate excellence in diabetes management.
- Providing access to specialized resources and tools to support diabetes care.
These incentives will foster a positive and supportive environment for healthcare providers to actively participate in the commission’s initiatives.
Communication Channels with Healthcare Providers
The following table Artikels the structure of the commission’s communication channels with healthcare providers.
The National Diabetes Commission is aiming to improve diabetes prevention and management strategies across the country. They’re looking at innovative ways to boost early detection and encourage healthier lifestyles, which are crucial for overall well-being. Considering the link between chronic conditions and pain management, it’s important to explore doctors’ ideas on how to reduce opioid prescriptions, such as doctors ideas on how to reduce opioid prescriptions , to reduce reliance on potentially addictive medications.
Ultimately, the commission aims to create a comprehensive approach to diabetes care, one that prioritizes holistic patient health and addresses related pain management issues.
| Communication Channel | Frequency | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Quarterly Newsletters | Quarterly | Dissemination of updates, resources, and best practices |
| Webinars and Online Forums | Monthly | Interactive knowledge sharing, Q&A sessions, and expert presentations |
| Regional Workshops | Semi-annually | Face-to-face training, networking opportunities, and practical application of guidelines |
| Dedicated Hotline | 24/7 | Direct support and guidance for healthcare providers on complex cases |
Data Collection and Analysis
Understanding diabetes prevalence and its impact requires a robust data collection and analysis strategy. This crucial component of the National Diabetes Commission will inform effective interventions and track progress towards our goals. Data-driven insights are essential for tailoring prevention programs, resource allocation, and evaluating the effectiveness of implemented strategies.
Methods for Collecting Relevant Data
The commission will employ a multi-faceted approach to gather comprehensive data on diabetes prevalence and outcomes. This includes surveys, which can provide a broad overview of the population’s health status, and health records analysis. By examining existing medical records, we can gain valuable insights into individual patient experiences and the effectiveness of current treatments. Furthermore, collaborations with local health organizations will provide valuable local context.
Data Sources for Analysis and Reporting
A variety of data sources will be utilized for comprehensive analysis and reporting. National health surveys, such as the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), will provide valuable baseline data on diabetes prevalence. Data from hospital discharge summaries, electronic health records, and insurance claims will offer a more granular view of the disease’s impact. Furthermore, data from community health centers, including local surveys, will provide critical local context.
Data Security and Privacy
Protecting patient data is paramount. The commission adheres to the highest standards of data security and privacy. All data collection and analysis will comply with relevant privacy regulations, such as HIPAA in the United States. Data will be anonymized and de-identified whenever possible to ensure confidentiality. Strict access controls will be implemented to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Presenting Findings to the Public and Stakeholders
The commission will present its findings in a transparent and accessible manner to the public and stakeholders. Clear and concise reports, infographics, and presentations will be utilized to communicate key findings and insights. Interactive online dashboards will allow for real-time monitoring of trends and progress. Regular public forums and presentations at relevant conferences will facilitate engagement and dialogue.
Data Collection Tools and Methods
| Data Collection Tool | Method | Data Type | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| National Health Surveys | Structured questionnaires, interviews | Prevalence rates, risk factors | Government agencies, academic institutions |
| Hospital Discharge Summaries | Review of medical records | Patient demographics, diagnoses, treatment details | Hospitals, clinics |
| Electronic Health Records (EHRs) | Data extraction from EHR systems | Patient history, medication use, treatment outcomes | Clinics, hospitals |
| Insurance Claims Data | Analysis of insurance claims | Treatment costs, utilization rates | Insurance providers |
| Community Health Center Surveys | Local surveys, community outreach | Local prevalence, community needs | Local health organizations |
Implementation Timeline and Budget
Successfully tackling diabetes requires a well-defined roadmap and a realistic budget. This section Artikels the proposed timeline for implementing the National Diabetes Commission’s strategies, coupled with a detailed budget breakdown and potential funding sources. A clear understanding of these factors is crucial for ensuring the commission’s effectiveness and sustainability.
Implementation Timeline
The implementation timeline is structured around key milestones, each with specific deliverables and timelines. This phased approach ensures manageable progress and allows for adjustments based on feedback and emerging data. It aims to achieve a balance between speed and thoroughness, which are essential for lasting impact.
- Phase 1 (Year 1): Foundation Building (Q1-Q4). This phase focuses on establishing the commission’s structure, staffing, and initial data analysis. This includes recruitment of key personnel, development of internal processes, and gathering baseline data on diabetes prevalence and related factors within the target population. Budget allocated to this phase would cover salaries, operational costs, and initial research funding.
- Phase 2 (Year 2): Strategic Program Development (Q1-Q4). The second year is dedicated to developing comprehensive strategies for diabetes prevention and management. This involves collaborating with stakeholders, identifying key interventions, and creating detailed action plans for each initiative. Budget will be allocated to expert consultations, stakeholder meetings, and the creation of project documents.
- Phase 3 (Year 3): Pilot Program Implementation (Q1-Q4). The commission will implement pilot programs in selected communities to test and refine strategies. This phase will gather crucial data on program effectiveness and gather community feedback. Budget for this phase will cover program materials, personnel support, and initial evaluation resources.
- Phase 4 (Year 4): Scaling Up and Sustainability (Q1-Q4). Based on the results of the pilot programs, the commission will scale up successful initiatives to reach a broader population. This phase will focus on building sustainable partnerships and long-term support systems. Budget will be allocated to expansion of program delivery, training of healthcare providers, and community engagement activities.
- Phase 5 (Year 5+): Ongoing Evaluation and Refinement. This phase ensures the commission’s strategies remain relevant and effective in the long term. It involves continuous monitoring of program impact, evaluation of outcomes, and adaptation to emerging challenges and best practices. Budget for this phase would be allocated to ongoing data analysis, evaluation research, and personnel for the maintenance of long-term programs.
Budget Allocation
The budget is structured to align with the phased implementation timeline. This detailed breakdown ensures transparency and accountability. It is designed to be flexible, allowing for adjustments based on actual costs and program needs.
| Phase | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Phase 1 | Foundation Building | $1,500,000 |
| Phase 2 | Strategic Program Development | $2,000,000 |
| Phase 3 | Pilot Program Implementation | $3,000,000 |
| Phase 4 | Scaling Up and Sustainability | $4,000,000 |
| Phase 5 | Ongoing Evaluation and Refinement | $1,000,000/year |
| Total Estimated Cost | $13,500,000 |
Funding Sources
The commission will seek funding from a variety of sources to ensure the sustainability of its programs. This multifaceted approach helps secure resources to support the program over the long term.
- Government Grants: Applications for grants will be submitted to relevant government agencies. Past success stories from similar organizations will be reviewed to inform grant writing strategies.
- Private Foundations: Reaching out to foundations that have demonstrated support for health initiatives will be crucial. Their investment can play a vital role in long-term funding.
- Corporate Partnerships: Collaborating with corporations that align with the commission’s goals and have a strong commitment to community well-being will provide vital support.
- Public Donations: Engaging the public through awareness campaigns can encourage individual contributions. Transparency and accountability in the use of funds are essential.
Evaluation Plan
The commission’s effectiveness will be evaluated regularly to ensure the strategies are producing the desired outcomes. This includes both quantitative and qualitative measurements.
- Data Collection: Regular monitoring of key metrics, such as diabetes prevalence rates, hospitalizations, and lifestyle changes, will provide valuable insights into the program’s impact.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Gathering feedback from participants and stakeholders through surveys and focus groups will allow for continuous improvement and adaptation.
- Comparative Analysis: Comparing the commission’s outcomes with those of similar programs in other regions will provide valuable context and insights.
- Independent Audits: Periodic audits conducted by independent organizations will ensure transparency and accountability.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, the national diabetes commission’s multifaceted approach promises to significantly impact the fight against diabetes. By combining evidence-based strategies, strong partnerships, and a commitment to data-driven decision-making, the commission is poised to create a lasting and positive change in the lives of individuals affected by this pervasive health issue. The commission’s success will be measured not only by improved outcomes but also by the strengthened public health infrastructure and awareness it fosters.