Young adults with high cholesterol not given statins is a complex issue with significant implications for their long-term health. This exploration delves into the reasons behind this practice, examining potential side effects and alternative treatments. We’ll explore the unique characteristics of this demographic and the prevalence of high cholesterol in young adults. Further, we’ll discuss the potential impacts on lifestyle choices and the importance of alternative management strategies, such as lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and potential underlying conditions.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the challenges faced by young adults with high cholesterol who are not prescribed statins. It explores the factors influencing this decision, the potential risks and benefits of various treatment options, and the crucial role of lifestyle interventions in managing the condition effectively.
Defining the Population
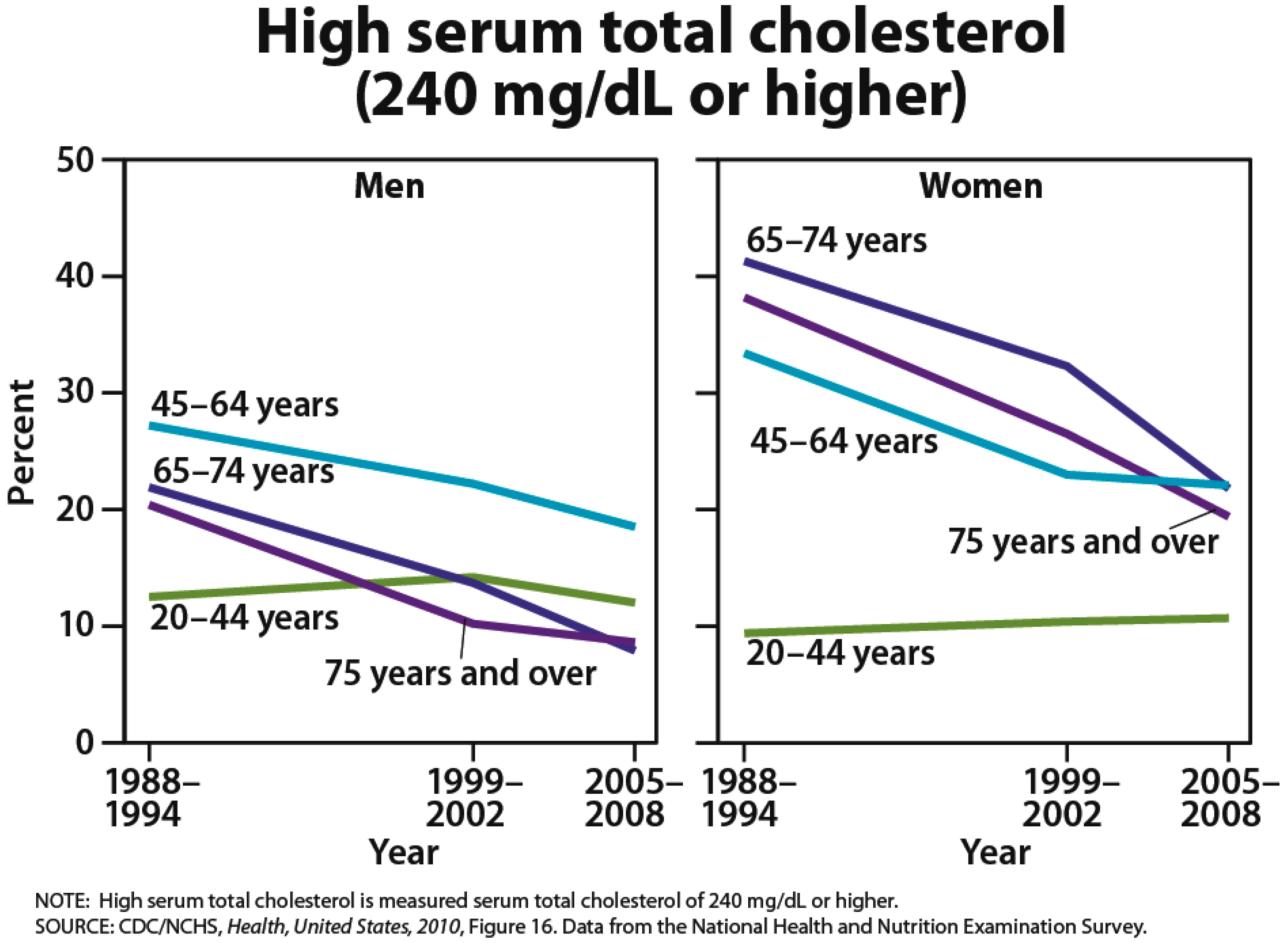
High cholesterol, a prevalent health concern, often receives significant attention, particularly in older adults. However, young adults can also experience high cholesterol, which requires careful consideration. Understanding this population is crucial for early detection and effective management. This segment delves into the characteristics, prevalence, and potential long-term consequences of untreated high cholesterol in young adults.
Young Adult Characteristics
Young adults, typically aged 18-40, are characterized by various lifestyle factors. This demographic often experiences significant life transitions, including career changes, relationship milestones, and financial responsibilities. These transitions frequently impact dietary habits, exercise routines, and stress levels. The demanding nature of these periods can sometimes lead to unhealthy choices, contributing to high cholesterol risk. For example, stress-induced poor dietary choices and a lack of regular exercise are common.
Types of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol encompasses several forms. The most common types are elevated low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, and reduced high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, or “good” cholesterol. Elevated LDL cholesterol can contribute to plaque buildup in the arteries, potentially leading to cardiovascular disease. Reduced HDL cholesterol, conversely, can hinder the body’s ability to remove excess cholesterol from the arteries.
Prevalence of High Cholesterol in Young Adults
High cholesterol prevalence in young adults varies, depending on factors such as genetic predisposition, dietary habits, and lifestyle choices. While the exact prevalence figures are subject to ongoing research and regional variations, studies suggest that high cholesterol is not uncommon in this demographic. Factors like family history, genetics, and dietary patterns play a crucial role in the development of high cholesterol in young adults.
This underscores the importance of early screening and lifestyle interventions.
Common Misconceptions about High Cholesterol in Young Adults
A common misconception is that high cholesterol primarily affects older individuals. However, genetics, unhealthy diets, and lack of physical activity can lead to high cholesterol in young adults. Another misconception is that high cholesterol symptoms are always obvious. Often, the symptoms are subtle or absent entirely, making early detection crucial. Consequently, preventative measures and lifestyle changes are vital for this age group.
Potential Long-Term Health Consequences of Untreated High Cholesterol
Untreated high cholesterol in young adults can lead to significant health issues in later life. Elevated LDL cholesterol can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque builds up in the arteries, potentially leading to heart disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. These conditions can significantly impact quality of life and lead to severe complications, even premature death.
It’s interesting how some young adults with high cholesterol aren’t prescribed statins right away. Maybe there are parallels to how a breast cancer survivor might approach the COVID vaccine – weighing potential benefits and risks, especially when considering long-term health implications. Ultimately, the decision to prescribe statins to young adults with high cholesterol still needs to be carefully evaluated on a case-by-case basis, taking into account individual factors and potential side effects, similar to navigating vaccination choices after a significant health event like breast cancer.
breast cancer survivor and covid vaccine is a good resource for exploring the complexities of health decisions.
For example, individuals with untreated high cholesterol in their twenties and thirties are more likely to experience heart attacks and strokes in middle age.
Health Characteristics Comparison
| Characteristic | Young Adults with High Cholesterol | Young Adults without High Cholesterol |
|---|---|---|
| Dietary Habits | Often include high-fat foods, processed foods, and limited fruits and vegetables. | Typically include a balanced diet with adequate fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. |
| Physical Activity | Generally engage in less physical activity and exercise. | Regularly engage in physical activity and exercise. |
| Stress Levels | Tend to experience higher levels of stress and anxiety. | Typically manage stress effectively and maintain lower stress levels. |
| Blood Lipid Profiles | Show elevated LDL cholesterol and/or reduced HDL cholesterol. | Maintain healthy LDL and HDL cholesterol levels. |
| Cardiovascular Risk | Higher risk of developing cardiovascular diseases and related complications later in life. | Lower risk of developing cardiovascular diseases and related complications later in life. |
Reasons for Not Prescribing Statins: Young Adults With High Cholesterol Not Given Statins
High cholesterol, while often a concern, doesn’t always necessitate immediate statin prescription, especially for young adults. This decision involves a careful consideration of potential benefits and drawbacks, weighing the risk of high cholesterol against the potential side effects of statins. Understanding the reasons behind this approach is crucial for informed decision-making regarding cholesterol management.The decision to prescribe statins to young adults with high cholesterol isn’t a simple yes or no.
Factors like the severity of the high cholesterol, family history, lifestyle choices, and overall health play a critical role in the decision-making process.
Potential Reasons for Not Prescribing Statins
Statins, while effective for many, aren’t suitable for everyone. There are instances where the potential risks outweigh the benefits, especially for young adults. These include concerns about the medication’s potential side effects, the individual’s overall health, and their willingness to commit to a lifestyle change. Furthermore, the long-term implications of statin use need to be assessed against the short-term benefits.
Potential Side Effects of Statins and Their Impact on Young Adults
Statins, while generally safe, can cause various side effects. Muscle pain (myalgia) and liver damage are potential concerns. These effects can be particularly problematic for young adults, impacting their physical activity and overall well-being. Furthermore, some young adults may experience cognitive side effects, affecting their academic performance or daily tasks.
Long-Term Risks and Benefits of Statins for Young Adults
The long-term risks of statins in young adults need careful consideration. While statins can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease in the long term, the long-term side effects of continuous statin use must be carefully weighed. The potential benefits of lowering cholesterol are balanced against the potential for long-term side effects, such as muscle damage, liver dysfunction, and cognitive issues.
The decision to initiate statin therapy requires careful monitoring and evaluation of the individual’s specific situation.
Alternative Treatments for High Cholesterol in Young Adults
Lifestyle modifications are often the first line of treatment for high cholesterol in young adults. These modifications include dietary changes, increased physical activity, and stress management techniques. Nutritional counseling and exercise programs can significantly improve cholesterol levels. Other alternative therapies, like dietary supplements, are sometimes used in conjunction with lifestyle changes. However, the effectiveness of these alternative therapies in lowering cholesterol needs to be assessed carefully and compared with the results of statin use.
Comparison of Statins and Alternative Treatments
The effectiveness of statins and alternative treatments in young adults varies depending on the individual’s health status and adherence to treatment plans. Lifestyle modifications, such as a heart-healthy diet and regular exercise, can often effectively lower cholesterol levels in young adults. However, if lifestyle changes alone aren’t sufficient, alternative treatments, such as dietary supplements, may be considered. A comparison of the effectiveness of these treatments requires considering individual responses, potential side effects, and long-term implications.
Table of Pros and Cons of Statins and Alternative Treatments
| Treatment | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Statins | Effective in lowering cholesterol; proven track record; potentially significant reduction in cardiovascular risk. | Potential side effects (muscle pain, liver damage, cognitive issues); long-term use may require ongoing monitoring; potential for drug interactions. |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Generally safe; no significant side effects; promotes overall health; cost-effective. | May not be sufficient to significantly lower cholesterol in all cases; requires sustained commitment and discipline; may not provide immediate results. |
| Dietary Supplements | Potential to support cholesterol management; often affordable. | Limited scientific evidence on effectiveness; may interact with other medications; potential for adverse effects; not always regulated. |
Impact on Lifestyle and Treatment
Choosing not to take statins for high cholesterol in young adulthood can significantly impact lifestyle choices and overall health management. This approach often necessitates a more proactive and disciplined approach to maintaining a healthy lifestyle, as cholesterol-lowering medications are a crucial component of comprehensive treatment plans for many. It emphasizes the crucial role of diet and exercise in mitigating the risks associated with high cholesterol.High cholesterol, when left unmanaged with statins, can lead to a greater focus on lifestyle modifications to maintain health.
This includes a profound awareness of dietary choices, increased physical activity, and a heightened commitment to overall well-being. It’s important to remember that lifestyle changes alone might not be sufficient to fully manage high cholesterol in all cases, and medical advice should always be sought.
Impact on Lifestyle Choices
Young adults without statin prescriptions face a greater emphasis on dietary control and regular physical activity to manage their cholesterol. This necessitates conscious choices in food selection and consistent exercise routines. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular exercise becomes even more critical.
Effect on Overall Health Management
Without statins, young adults with high cholesterol need to prioritize and closely monitor their health. This proactive approach involves frequent checkups with healthcare providers to track cholesterol levels and overall well-being. This proactive health management is crucial for early detection and prevention of potential complications.
Importance of Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications are paramount in managing high cholesterol, especially for young adults not on statins. These modifications include not just diet and exercise, but also stress management and sleep hygiene. This comprehensive approach to health is crucial for long-term well-being and can significantly improve cholesterol levels over time.
Role of Diet and Exercise
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, coupled with regular physical activity, plays a pivotal role in managing high cholesterol. Regular exercise helps improve cardiovascular health, reduce body weight, and increase the body’s ability to utilize cholesterol effectively.
Healthy Lifestyle Recommendations
- Prioritize a balanced diet: Focus on whole foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit saturated and trans fats, processed foods, and excessive sugar intake. This includes choosing lean meats, poultry without skin, and fish. For instance, opting for baked salmon over fried chicken can significantly impact cholesterol levels.
- Engage in regular physical activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week. This could include brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling. Consistency is key for effective results.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly improve cholesterol levels. Consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized guidance.
- Manage stress effectively: Chronic stress can negatively impact cholesterol levels. Engage in stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature.
- Prioritize adequate sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for overall health and well-being, which indirectly influences cholesterol levels.
Impact of Lifestyle Changes on Cholesterol Levels
Implementing these lifestyle modifications can lead to measurable improvements in cholesterol levels over time. By reducing saturated and trans fats, increasing fiber intake, and incorporating regular exercise, young adults can actively lower their cholesterol levels. Consistent adherence to these changes is crucial for sustained results.
Dietary Changes and Their Impact on Cholesterol Levels
| Dietary Change | Impact on Cholesterol Levels |
|---|---|
| Increase soluble fiber intake (e.g., oats, beans, fruits) | Reduces LDL (“bad”) cholesterol |
| Limit saturated and trans fats (e.g., red meat, processed foods) | Reduces LDL cholesterol and raises HDL (“good”) cholesterol |
| Increase unsaturated fats (e.g., avocados, nuts, olive oil) | Improves overall cholesterol profile |
| Include foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (e.g., fatty fish) | Reduces triglycerides and raises HDL cholesterol |
| Control portion sizes and calorie intake | Maintains a healthy weight, which contributes to better cholesterol management |
Potential Underlying Conditions
High cholesterol in young adults can sometimes be a symptom of an underlying medical condition. While lifestyle factors are often implicated, it’s crucial to consider the possibility of other contributing factors. A thorough evaluation is essential to pinpoint the root cause and develop a personalized treatment plan.
It’s frustrating when young adults with high cholesterol aren’t given statins, right? Sometimes, navigating health decisions feels like a toxic relationship – you need to carefully consider your options and prioritize your well-being. Learning how to get out of a toxic relationship, whether it’s with a doctor, a friend, or a situation, can be a valuable skill to apply in such situations.
For a helpful guide on breaking free from unhealthy dynamics, check out this article on how to get out of toxic relationship. Ultimately, finding the right support and resources for managing your health is crucial, just as it is in other aspects of life.
Genetic Predispositions
Genetic factors play a significant role in determining cholesterol levels. Individuals with a family history of high cholesterol, particularly at a young age, are more likely to inherit genes that increase their risk. Identifying these genetic predispositions is vital for early intervention and management. This is particularly true for young adults, as lifestyle changes may not be sufficient to address the underlying genetic issue.
Early diagnosis allows for proactive measures to be taken, potentially preventing long-term health complications.
Family History’s Role
Family history is a critical indicator of potential genetic predispositions to high cholesterol. A family history of early-onset high cholesterol or other cardiovascular diseases significantly increases the likelihood of a young adult inheriting genes that affect cholesterol metabolism. This understanding underscores the importance of detailed family health history assessments during medical evaluations. By understanding the family history, healthcare professionals can better assess the individual’s risk and tailor preventive strategies accordingly.
Importance of Regular Health Checkups and Screenings
Regular health checkups and screenings are vital for young adults, regardless of their cholesterol levels. Early detection of underlying conditions, including those that may contribute to high cholesterol, can be achieved through routine screenings. This proactive approach allows for timely interventions and potentially prevents the development of more severe health problems. For example, a routine lipid panel, blood pressure check, and physical examination can identify potential issues early on.
Specific Medical Conditions
Several medical conditions can lead to elevated cholesterol levels in young adults. These conditions often disrupt the body’s natural cholesterol regulation processes. Examples include hypothyroidism, certain kidney diseases, and some forms of liver disease. Early detection of these conditions through appropriate medical evaluations is critical for managing high cholesterol and associated risks. In addition, some medications, such as corticosteroids, can also elevate cholesterol levels.
Thorough Medical Evaluations
A thorough medical evaluation is essential for young adults with high cholesterol. This evaluation should encompass a comprehensive review of medical history, including family history, lifestyle factors, and any symptoms. Physical examinations, blood tests, and potentially imaging studies can help identify any underlying conditions. The goal is to identify the specific cause of the elevated cholesterol to develop a tailored treatment plan.
Comparison of Medical Conditions
| Medical Condition | Potential Impact on Cholesterol | Other Relevant Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Hypothyroidism | Increased LDL cholesterol, decreased HDL cholesterol | Fatigue, weight gain, constipation, cold intolerance |
| Kidney Disease | Increased LDL cholesterol, decreased HDL cholesterol | Swelling, frequent urination, fatigue, high blood pressure |
| Liver Disease | Increased LDL cholesterol, decreased HDL cholesterol | Jaundice, abdominal pain, fatigue, nausea |
| Certain Medications | Increased LDL cholesterol, decreased HDL cholesterol | Depends on the medication, may include specific side effects |
The table above highlights potential links between various medical conditions and cholesterol levels. Note that this is not an exhaustive list, and many other conditions may contribute. Always consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and personalized recommendations.
Alternative Management Strategies
High cholesterol in young adults, while often manageable with lifestyle changes, can sometimes necessitate alternative strategies. These strategies, when combined with a doctor’s guidance, can help individuals achieve optimal cholesterol levels without resorting to statins. Understanding the nuances of these approaches is crucial for proactive health management.Alternative management strategies offer avenues beyond statins for effectively managing high cholesterol in young adults.
Young adults with high cholesterol sometimes aren’t prescribed statins, which can be a tricky situation. Scientists are exploring innovative solutions like “human on a chip technology can test cancer treatments” here , potentially leading to personalized treatments for various health conditions, including cholesterol management in younger populations. This could pave the way for more effective and tailored approaches to treating high cholesterol in young adults.
These approaches are tailored to individual needs and preferences, emphasizing a holistic approach to health. They should always be discussed and implemented in conjunction with a healthcare professional to ensure safety and efficacy.
Dietary Modifications
Dietary modifications play a pivotal role in managing high cholesterol. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can contribute significantly to lower cholesterol levels. Reducing saturated and trans fats, which are often found in processed foods and some animal products, is essential.
- Focus on foods rich in soluble fiber, such as oats, barley, and beans. Soluble fiber helps to bind cholesterol in the digestive tract, preventing its absorption into the bloodstream.
- Increase consumption of omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel. Omega-3s have been shown to improve cholesterol profiles and reduce inflammation.
- Limit intake of red meat and processed foods. These often contain high levels of saturated fat, which can raise cholesterol.
- Choose lean protein sources, such as poultry without skin and fish.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Beyond dietary changes, lifestyle adjustments can significantly impact cholesterol levels. Regular physical activity and stress management techniques are often recommended. Incorporating these elements can lead to overall well-being.
- Regular exercise is crucial. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities twice a week.
- Stress management is vital. Practices like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels, which can indirectly influence cholesterol.
- Adequate sleep is essential. Getting enough sleep (7-9 hours per night) is often overlooked but crucial for overall health, including cholesterol management.
Supplements
Certain supplements, when used under medical supervision, may help manage cholesterol. However, the efficacy and safety of these supplements vary. It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional before incorporating any supplements into a regimen.
- Some individuals find that supplements like plant sterols or stanols can reduce cholesterol absorption. However, individual responses to these supplements vary greatly.
- CoQ10 is another supplement sometimes used in managing cholesterol, but its efficacy in lowering cholesterol needs further research and confirmation.
Monitoring Cholesterol Levels
Regular monitoring of cholesterol levels is crucial for assessing the effectiveness of alternative management strategies. Blood tests play a critical role in this process.
- Blood tests are essential for measuring cholesterol levels. These tests typically measure total cholesterol, LDL (“bad”) cholesterol, HDL (“good”) cholesterol, and triglycerides.
- Monitoring cholesterol levels over time provides valuable data on the effectiveness of different management strategies.
- Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional are necessary to track progress and adjust strategies as needed.
Comparison of Monitoring Methods
Various methods exist for tracking cholesterol levels. These methods differ in terms of frequency, cost, and convenience. The choice of method should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional.
| Monitoring Method | Frequency | Cost | Convenience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Home cholesterol test kits | Variable | Low | High |
| Doctor’s office blood tests | Regular | Moderate | Moderate |
| Specialized lipid panels | Regular | High | Moderate |
Potential Limitations
Alternative management strategies may not be as effective for all individuals. Factors such as adherence to the plan and underlying conditions can impact outcomes. Individual responses to dietary modifications and supplements can vary.
“Success in managing high cholesterol through alternative strategies depends significantly on consistent lifestyle changes and regular monitoring.”
Future Research Directions
High cholesterol in young adults presents a complex challenge, demanding proactive research to understand the long-term implications and optimal management strategies. While current understanding provides a solid foundation, further investigation is crucial to refine our approach and ensure the best possible health outcomes for this demographic. This includes exploring the unique physiological factors influencing cholesterol levels in younger individuals and evaluating the long-term effects of alternative management strategies.
Long-Term Effects of Not Prescribing Statins
Research needs to delve deeper into the long-term cardiovascular consequences of not prescribing statins to young adults with high cholesterol. This includes examining the development of atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease, and other cardiovascular complications over extended periods. Observational studies and large-scale cohort analyses are necessary to track the progression of these conditions in individuals with high cholesterol who do not receive statin therapy.
Understanding the potential impact on life expectancy and quality of life is also essential. This research should also consider lifestyle factors, as these can influence the trajectory of the disease.
Unique Needs of Young Adults, Young adults with high cholesterol not given statins
Young adults often have different lifestyle factors and health priorities than older populations. Research should focus on understanding how these factors impact cholesterol levels and the efficacy of various management strategies. This includes exploring the influence of diet, exercise, stress levels, and sleep patterns on cholesterol regulation in young adults. Specific research should also address the potential impact of mental health conditions and social determinants of health on cholesterol levels in this demographic.
Effectiveness of Alternative Management Strategies
Alternative management strategies for high cholesterol, such as dietary modifications, exercise programs, and lifestyle interventions, warrant further investigation. Studies should assess the effectiveness of these strategies in reducing cholesterol levels and improving cardiovascular health in young adults. Comparative trials comparing the effectiveness of various dietary approaches, exercise regimens, and lifestyle modifications are essential to guide clinical practice. The specific needs of different young adult populations (e.g., athletes, students, those with specific dietary restrictions) should be addressed in these studies.
Potential Research Collaborations and Partnerships
Multidisciplinary collaborations are vital to advancing research on high cholesterol in young adults. Collaborations between cardiologists, nutritionists, endocrinologists, and public health professionals can provide a comprehensive approach to addressing this issue. Partnerships with healthcare organizations, universities, and research institutions can facilitate the implementation of large-scale studies and the dissemination of research findings. This can include collaborations with technology companies to develop innovative diagnostic tools and personalized treatment plans.
Innovative Research Approaches
Innovative research approaches, such as using advanced imaging techniques, genetic analysis, and large-scale observational studies, are needed to gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms underlying high cholesterol in young adults. For example, using wearable technology to monitor lifestyle factors in real-time and analyzing their impact on cholesterol levels. Utilizing artificial intelligence and machine learning to identify risk factors and personalize treatment strategies for young adults.
Potential Research Questions and Relevance
| Research Question | Relevance to Young Adults with High Cholesterol |
|---|---|
| What is the long-term impact of lifestyle interventions on cardiovascular health in young adults with high cholesterol who do not receive statins? | Understanding the potential risks and benefits of alternative approaches is crucial for guiding treatment decisions. |
| How do social determinants of health influence cholesterol levels and treatment adherence in young adults? | Recognizing the impact of social factors allows for tailored interventions and supports. |
| What are the most effective dietary and exercise interventions for reducing cholesterol levels in young adults with specific dietary needs or lifestyles? | Developing tailored strategies for specific groups will maximize efficacy and patient compliance. |
| What is the role of genetics in determining cholesterol levels and response to different management strategies in young adults? | Genetic information can personalize treatment and predict individual responses. |
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, the decision to withhold statins from young adults with high cholesterol raises crucial questions about optimal treatment strategies. The discussion highlights the need for personalized approaches, considering the unique needs and potential side effects of various interventions. While statins remain a cornerstone of treatment for many, alternative approaches, combined with lifestyle changes, can be vital in managing this condition.
Further research is essential to refine our understanding and develop optimal strategies for young adults.
