Vitamin D and prostate cancer: a complex relationship demanding exploration. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate connection between vitamin D levels and the development, progression, and potential treatment of prostate cancer. We’ll examine current research, explore potential mechanisms of action, and discuss the role of vitamin D intake, sunlight exposure, and existing treatment strategies. From observational studies to clinical trials, we’ll uncover the nuances of this vital connection.
Understanding the interplay between vitamin D and prostate cancer is crucial for both prevention and treatment. This exploration will examine the evidence linking vitamin D intake to prostate cancer risk, discuss potential mechanisms of action, and analyze current treatment strategies. The exploration of this complex relationship will also highlight the limitations of current research and potential avenues for future investigation.
Introduction to Vitamin D and Prostate Cancer
Vitamin D, a crucial nutrient for human health, plays a vital role in calcium absorption, bone health, and immune function. Its influence extends beyond these well-established roles, with ongoing research exploring its potential impact on various diseases, including cancer. Understanding the intricacies of vitamin D’s action in the body is essential to assess its potential relationship with prostate cancer.Prostate cancer, a prevalent malignancy in men, is characterized by the uncontrolled growth of cells within the prostate gland.
Its development and progression are complex processes influenced by a multitude of factors, including genetics, lifestyle choices, and environmental exposures. The disease often progresses through distinct stages, from localized to metastatic forms, impacting treatment strategies and prognosis. A key challenge in cancer research lies in identifying early warning signs and preventative measures to reduce the risk of developing or progressing the disease.
Recent studies on vitamin D and prostate cancer are fascinating, but I’ve been equally intrigued by advancements in diagnosing and predicting MS progression. For example, MRI tests are becoming increasingly valuable in helping doctors predict how multiple sclerosis might progress in patients, as detailed in this insightful article mri tests help doctors predict ms progression in patients.
While the exact mechanisms aren’t fully understood, these breakthroughs offer hope for better treatment strategies. Ultimately, I’m keen to see how this type of technology can further inform our understanding of vitamin D’s role in prostate cancer prevention.
Vitamin D’s Role in the Body
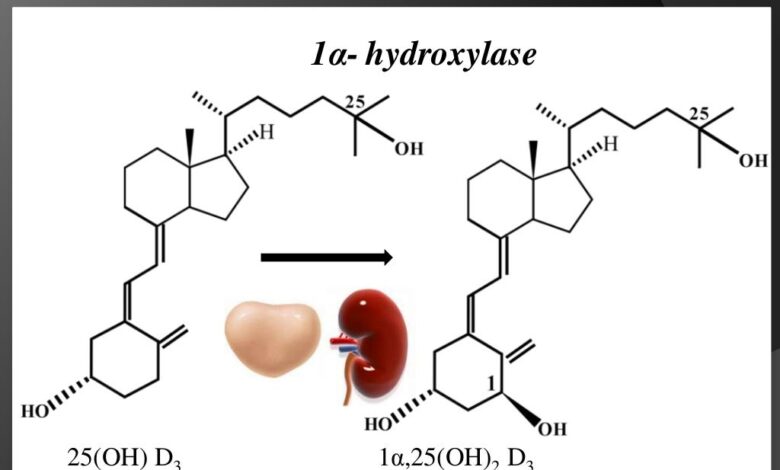
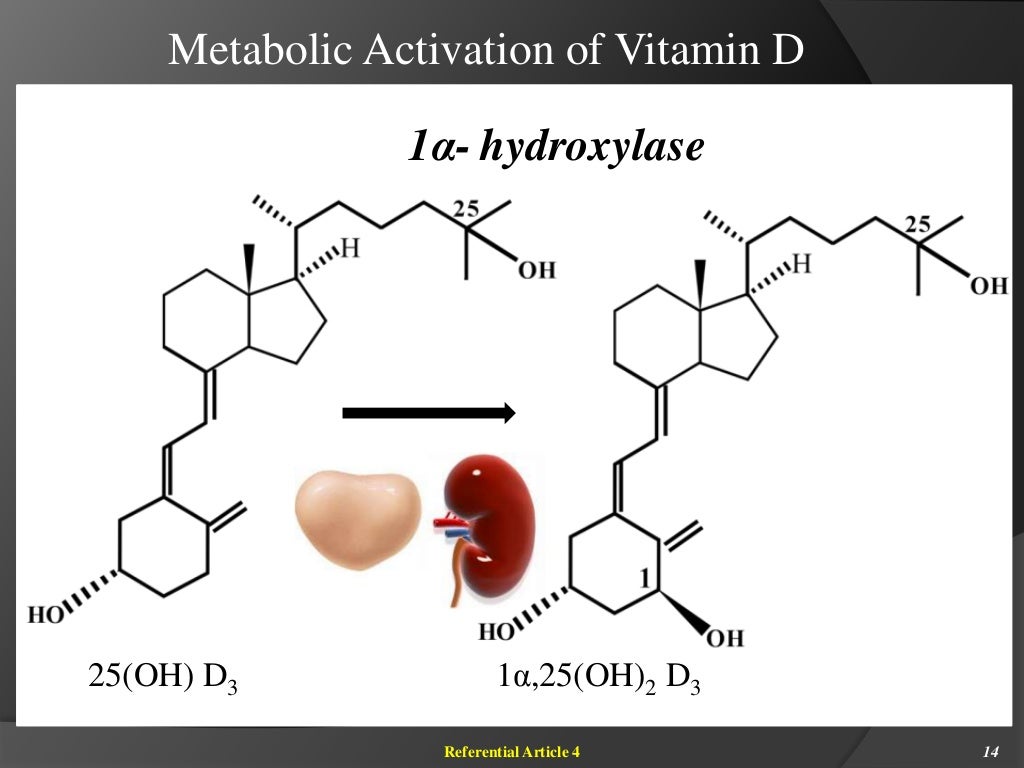
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that exists in two main forms: D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol). The body can synthesize vitamin D3 from exposure to sunlight, while dietary sources and supplements provide D2 and D3. Vitamin D’s primary function involves regulating calcium and phosphate levels, crucial for bone health and overall body function. It also plays a role in immune function, cell growth, and differentiation.
Furthermore, emerging evidence suggests a possible involvement in modulating inflammation and cell cycle control.
Prostate Cancer Development and Progression
Prostate cancer’s development typically involves several stages. Initially, benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH) can occur, leading to enlarged prostate tissue. This can sometimes progress to pre-cancerous lesions, and ultimately, to cancerous cells. Factors like genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalances, and dietary habits can influence the progression of the disease. Understanding the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying these stages is critical for developing effective diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
Recent research suggests a potential link between vitamin D levels and prostate cancer risk. While more studies are needed, some studies show a correlation. This is exciting news, especially considering the advancements in targeted therapies, such as the innovative work being done by a company developing a pill that would replace injected drugs, a potential game-changer for cancer treatments.
This company is pushing the boundaries of pharmaceutical innovation, and this could translate to more effective and accessible treatments for prostate cancer patients in the future. Ultimately, more research is needed to fully understand the role of vitamin D in prostate cancer prevention and treatment.
Potential Link Between Vitamin D and Prostate Cancer Risk
Some studies suggest a correlation between low vitamin D levels and an increased risk of prostate cancer. However, the precise mechanisms linking vitamin D to prostate cancer remain unclear. Possible pathways include vitamin D’s potential to influence cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis (programmed cell death). This suggests that maintaining adequate vitamin D levels might have a protective effect against prostate cancer development.
Existing Research on the Topic, Vitamin d and prostate cancer
Research on the relationship between vitamin D and prostate cancer is ongoing, with varying results. Observational studies, which analyze existing data, have shown potential links, but they often cannot definitively prove causation. Intervention studies, where participants are given vitamin D supplements, have yielded more mixed results.
Summary of Studies on Vitamin D and Prostate Cancer
| Study Type | Methodology | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Observational Studies | Analyze existing data on vitamin D levels and prostate cancer diagnoses in large populations. | Some studies indicate an inverse relationship between vitamin D levels and prostate cancer risk, but results are not consistent across all studies. |
| Intervention Studies (Supplementation) | Randomly assign participants to receive vitamin D supplements or a placebo. Monitor prostate cancer incidence over time. | Results are varied, with some studies showing no significant effect of vitamin D supplementation on prostate cancer risk, while others suggest a possible benefit, but more research is needed to confirm these findings. |
Vitamin D Intake and Prostate Cancer Risk

The link between vitamin D and prostate health has garnered significant attention. While a definitive cause-and-effect relationship hasn’t been established, observational studies and some clinical trials suggest a potential correlation between vitamin D intake and prostate cancer incidence. This exploration delves into the evidence surrounding this connection, focusing on sunlight exposure, dietary sources, and optimal vitamin D levels for prostate health.Vitamin D’s role in the body extends beyond bone health.
Emerging research suggests a possible impact on prostate cancer development. This impact is likely multifaceted, potentially involving vitamin D’s influence on cell growth, immune function, and inflammation. Understanding the relationship between vitamin D intake and prostate cancer risk is crucial for developing preventive strategies.
Sunlight Exposure and Vitamin D Synthesis
Sunlight plays a critical role in vitamin D production in the body. UVB rays from sunlight trigger the synthesis of vitamin D3 in the skin. Geographic location, time of day, and skin pigmentation influence the amount of vitamin D produced. Individuals living in higher latitudes or with darker skin may require more time in the sun to achieve sufficient levels.
Understanding how sunlight exposure impacts vitamin D synthesis is important for personalized recommendations regarding vitamin D intake.
Dietary Sources of Vitamin D
Dietary sources of vitamin D are limited. Fatty fish, egg yolks, and some fortified foods are notable sources. The bioavailability of vitamin D from dietary sources can vary. For example, the vitamin D content in fortified foods may differ depending on the specific product. Therefore, dietary sources alone may not be sufficient for maintaining optimal vitamin D levels, particularly for those with limited sun exposure.
Observational Studies and Clinical Trials
Numerous observational studies have investigated the correlation between vitamin D intake and prostate cancer risk. These studies often report an inverse association, meaning higher vitamin D levels might be linked to a lower risk of prostate cancer. However, these studies are correlational, meaning they cannot definitively prove a causal relationship. Clinical trials, which directly test interventions, are crucial to confirm these associations.
Several clinical trials are underway to investigate the effect of vitamin D supplementation on prostate cancer risk and progression.
Optimal Vitamin D Levels for Prostate Health
Establishing optimal vitamin D levels for prostate health is an ongoing area of research. While there isn’t a universally agreed-upon level, maintaining adequate vitamin D levels is crucial. Blood tests can measure vitamin D levels, and supplementation may be necessary for individuals with deficiencies. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to determine appropriate vitamin D levels for individual needs.
Impact of Vitamin D Intake on Prostate Cancer Risk
| Vitamin D Intake Level | Potential Effect on Prostate Cancer Risk |
|---|---|
| Low | Potentially increased risk. |
| Adequate | Potentially reduced risk, but more research needed. |
| High | Limited evidence regarding impact, but generally considered safe. |
This table provides a general overview. Individual responses may vary, and further research is needed to definitively establish the optimal vitamin D intake levels for prostate cancer prevention. Further studies are essential to establish a clear link between vitamin D intake and prostate cancer risk.
Recent research suggests a potential link between vitamin D levels and prostate cancer risk. While the exact mechanisms are still being explored, maintaining healthy vitamin D intake might play a role in prostate health. However, it’s crucial to remember that other lifestyle factors, like the rising use of flavored tobacco among teens (see flavored tobacco use rising again among teens ), also significantly impact overall health, potentially increasing the risk of various diseases.
Ultimately, a balanced approach to diet and lifestyle, including sufficient vitamin D intake, remains key for prostate health.
Mechanisms of Action
Vitamin D’s potential role in prostate cancer prevention and treatment hinges on its intricate effects on various cellular processes within the prostate. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial to evaluating its efficacy and potential therapeutic applications. The interplay between vitamin D and prostate cells is complex, involving multiple pathways and interactions.Vitamin D exerts its influence on prostate cells through a variety of mechanisms, primarily by binding to vitamin D receptors (VDRs).
These receptors, once activated by vitamin D, initiate a cascade of events that can influence cell growth, differentiation, and programmed cell death (apoptosis). This complex interaction is a subject of ongoing research, but emerging evidence suggests a significant role for vitamin D in regulating prostate cancer progression.
Potential Effects on Cell Growth
Vitamin D’s interaction with VDRs can modulate the expression of genes involved in cell proliferation. This modulation can either stimulate or inhibit cell growth, depending on the specific cellular context and the presence of other signaling pathways. For example, in some studies, vitamin D has been shown to suppress the proliferation of prostate cancer cells by influencing the expression of growth factors and cyclins, molecules that regulate the cell cycle.
Conversely, in certain circumstances, vitamin D might potentially promote cell growth in healthy prostate cells, contributing to their normal function.
Influence on Cell Differentiation
Vitamin D plays a role in regulating the differentiation of prostate cells. Differentiation is a crucial process in normal tissue development and function. In the context of prostate cancer, maintaining proper differentiation is vital for preventing uncontrolled cell growth. Vitamin D may influence the differentiation of both healthy and cancerous prostate cells, potentially altering the expression of genes involved in this process.
The specific outcome, whether promotion or suppression of differentiation, depends on the intricate interplay of various factors.
Role in Apoptosis
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a natural process that eliminates damaged or unwanted cells. Vitamin D’s influence on apoptosis in prostate cells is an area of active investigation. Studies suggest that vitamin D can induce apoptosis in prostate cancer cells by modulating the expression of proteins involved in this process. This apoptotic effect could be a crucial mechanism by which vitamin D inhibits prostate cancer development and progression.
In contrast, vitamin D might also affect apoptosis in healthy prostate cells, but the specific outcomes are still being studied.
Involvement of Vitamin D Receptors (VDRs)
Vitamin D receptors (VDRs) are essential in mediating vitamin D’s effects on prostate cells. Once vitamin D binds to VDRs, a complex is formed that initiates intracellular signaling pathways. These pathways can then influence the expression of genes involved in cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. The activation of VDRs can have different consequences in healthy versus cancerous cells, potentially contributing to the selective targeting of cancerous cells.
Cellular Pathways Affected by Vitamin D
| Cellular Pathway | Potential Effect on Prostate Cancer Cells | Potential Effect on Healthy Prostate Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Cycle Regulation | Inhibition of cell proliferation | Regulation of normal cell growth |
| Differentiation Pathways | Alteration of differentiation markers | Maintenance of normal differentiation |
| Apoptosis Pathways | Induction of apoptosis | Regulation of apoptosis (potential roles still being studied) |
| Inflammation Pathways | Modulation of inflammatory response | Modulation of inflammatory response (potential roles still being studied) |
| Growth Factor Signaling | Inhibition of growth factor signaling | Regulation of growth factor signaling |
Existing Treatment Strategies
Prostate cancer, a prevalent malignancy, necessitates a multifaceted approach to treatment. Effective strategies encompass a range of interventions, from surgical removal to targeted therapies, all tailored to the individual patient’s specific circumstances. Understanding these approaches is crucial for comprehending the potential role of vitamin D supplementation in conjunction with existing treatments.Current treatments for prostate cancer aim to eliminate or control the disease’s progression, often employing a combination of therapies.
These treatments vary depending on the stage and grade of the cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health.
Surgical Removal
Surgical removal, or prostatectomy, involves the complete or partial removal of the prostate gland. This procedure is often considered for localized prostate cancer, where the cancer is confined to the prostate. Open prostatectomy involves a larger incision, while laparoscopic or robotic-assisted procedures offer less invasive options. The choice of surgical approach depends on the specific circumstances of each patient.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells. External beam radiation therapy directs radiation from a machine outside the body, while brachytherapy involves implanting radioactive seeds directly into the prostate. The choice between these methods depends on factors such as the stage of the cancer and the patient’s overall health. Precise targeting and dose delivery are crucial to minimize side effects.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It is often used for advanced prostate cancer, particularly when the disease has spread beyond the prostate. Chemotherapy drugs may be administered intravenously or orally, and the specific regimen depends on the type and stage of cancer. The effectiveness and potential side effects of chemotherapy vary considerably depending on the individual patient.
Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy is frequently employed in prostate cancer management. It works by reducing the production of hormones, such as testosterone, that fuel prostate cancer growth. This approach is particularly effective for advanced prostate cancer, and it may be used in conjunction with other treatments. Common methods include androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), which blocks testosterone production, and other hormonal manipulations.
The efficacy of hormone therapy can vary, and its long-term impact needs careful monitoring.
Integration of Vitamin D Supplementation
The integration of vitamin D supplementation into existing treatment protocols for prostate cancer remains an area of active research. While preliminary studies suggest a potential role for vitamin D in modulating the growth and spread of prostate cancer cells, more robust clinical trials are necessary to validate these findings and establish optimal dosages.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks
Vitamin D supplementation, when combined with standard treatments, may offer potential benefits, such as reducing the risk of recurrence or improving treatment response. However, potential drawbacks, such as adverse effects and interactions with other medications, need careful consideration. The interplay between vitamin D, other therapies, and individual patient characteristics necessitates a personalized approach.
Importance of Personalized Approaches
Personalized approaches to treatment are crucial in managing prostate cancer. These approaches consider the specific characteristics of each patient’s cancer, including its stage, grade, and genetic profile. This personalized strategy optimizes treatment outcomes while minimizing potential side effects. For example, a patient with a specific genetic predisposition might benefit from a treatment plan that emphasizes targeted therapies, while another patient might respond better to a combination of surgery and radiation.
Limitations and Future Research
Unraveling the intricate relationship between vitamin D and prostate cancer is a complex endeavor. While studies have shown promising correlations, definitive conclusions remain elusive. The challenges lie in the multifaceted nature of the disease, the difficulty in isolating vitamin D’s precise role, and the inherent limitations of observational studies. Addressing these limitations requires meticulous research strategies and innovative approaches to truly understand the mechanisms at play.The current body of research predominantly relies on observational studies, which are prone to confounding factors.
For example, individuals with higher vitamin D levels might also have healthier lifestyles, including better diets and more physical activity, potentially skewing the results. This difficulty in establishing a direct cause-and-effect relationship between vitamin D and prostate cancer risk is a significant hurdle. Further research needs to incorporate rigorous experimental designs to overcome these challenges.
Challenges in Establishing Cause-and-Effect
Establishing a definitive cause-and-effect relationship between vitamin D intake and prostate cancer risk is complicated by several confounding variables. Dietary habits, lifestyle choices, genetic predispositions, and other environmental factors can all influence both vitamin D levels and prostate cancer risk. The intricate interplay of these factors makes it challenging to isolate the precise role of vitamin D. Observational studies, while valuable for identifying correlations, cannot definitively prove causation.
Robust experimental designs are crucial to overcome these limitations.
Potential Areas for Future Research
Future research should delve deeper into the specific mechanisms by which vitamin D might influence prostate cancer risk. The exact pathways involved, including the interactions with other nutrients, hormones, and genetic factors, require further investigation. For instance, exploring how vitamin D interacts with other dietary components like calcium and magnesium, or how it affects cellular processes within the prostate gland, could yield significant insights.
Developing targeted therapies that leverage vitamin D’s potential role in prostate cancer prevention or treatment is another promising avenue.
Need for More Robust Clinical Trials
Large-scale, well-controlled clinical trials are essential to validate the observational findings and determine the optimal vitamin D intake for prostate cancer prevention. These trials should meticulously monitor participants’ vitamin D levels, dietary habits, lifestyle factors, and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) markers over extended periods. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are particularly valuable for isolating the effect of vitamin D supplementation on prostate cancer risk.
The long-term follow-up of participants is critical to assess the long-term impact of vitamin D interventions.
Promising Avenues for Future Research
| Research Area | Specific Focus | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D Receptor (VDR) Interactions | Investigating the intricate interactions between vitamin D and the vitamin D receptor (VDR) within prostate cells. | Potentially uncover new targets for therapeutic interventions, leading to improved treatments. |
| Vitamin D and Inflammation | Exploring the relationship between vitamin D levels and inflammation in the prostate. | Identify the potential role of inflammation in prostate cancer development and how vitamin D might modulate this process. |
| Vitamin D and Other Nutrients | Examining the combined effects of vitamin D with other nutrients, such as calcium and magnesium, on prostate health. | Understanding the synergistic or antagonistic effects of different nutrients in the context of prostate cancer risk. |
| Personalized Medicine Approaches | Developing personalized strategies based on genetic profiles, lifestyle factors, and vitamin D levels to predict individual risk and tailor interventions. | Improving the precision and effectiveness of preventive strategies. |
Public Health Implications
Understanding the potential link between vitamin D and prostate cancer has significant implications for public health. This knowledge allows for the development of proactive strategies to potentially reduce the risk of prostate cancer. The focus on lifestyle choices and vitamin D intake becomes crucial in promoting overall health and well-being. A comprehensive approach encompassing dietary recommendations and awareness campaigns can be instrumental in preventing this disease.The potential for preventive strategies hinges on our ability to identify populations at risk and implement targeted interventions.
If vitamin D deficiency is indeed a contributing factor to prostate cancer development, preventive measures focused on ensuring adequate vitamin D intake can significantly impact public health outcomes. This includes promoting awareness of the importance of vitamin D and providing practical guidance on achieving optimal levels.
Potential Preventive Strategies
Promoting vitamin D intake as a preventive measure against prostate cancer necessitates a multi-faceted approach. Educational campaigns can highlight the importance of vitamin D in maintaining overall health, including bone health, immune function, and potentially prostate health. These campaigns should target diverse populations, considering variations in dietary habits and geographical factors that may influence vitamin D levels. Dietary supplements, particularly in individuals at risk of deficiency, could be a part of a preventative strategy.
Importance of Healthy Lifestyle Choices
A healthy lifestyle encompassing a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and avoidance of tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption plays a crucial role in preventing prostate cancer. These lifestyle choices, in conjunction with sufficient vitamin D intake, contribute to a reduced risk of developing the disease. Encouraging regular check-ups and screenings for prostate cancer are equally essential components of a comprehensive public health strategy.
Optimizing Vitamin D Levels in the General Population
Achieving optimal vitamin D levels requires a combination of dietary intake, sunlight exposure, and potentially supplementation. Individuals should aim for a balanced diet rich in vitamin D-containing foods, along with regular exposure to sunlight (within safe limits). However, specific dietary needs may vary, necessitating personalized recommendations based on individual factors like age, geographical location, and skin tone. For instance, individuals living in areas with limited sunlight exposure might require additional supplementation.
Dietary Recommendations for Vitamin D Intake
Adequate vitamin D intake is crucial for maintaining overall health and potentially reducing the risk of prostate cancer. The following table provides dietary recommendations for vitamin D intake, highlighting various food sources. It’s important to remember that these are general guidelines, and individual needs may vary.
| Food Source | Vitamin D Content (approximate) |
|---|---|
| Fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel) | High |
| Egg yolks | Moderate |
| Fortified milk and dairy products | High (varies by product) |
| Fortified cereals | Moderate (varies by product) |
| Mushrooms (exposed to UV light) | Moderate |
| Beef liver | Moderate |
Note: These values are approximate and can vary depending on the specific food and preparation methods. Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized dietary advice.
Case Studies and Examples: Vitamin D And Prostate Cancer
Understanding the complex interplay between vitamin D and prostate cancer requires examining real-world scenarios. Individual experiences vary significantly, influenced by factors like age, genetics, lifestyle, and existing health conditions. This section presents hypothetical case studies to illustrate potential benefits and challenges associated with vitamin D supplementation in prostate cancer management.
Diverse Experiences with Prostate Cancer and Vitamin D
Individual responses to vitamin D supplementation for prostate cancer vary greatly. Factors like pre-existing vitamin D levels, the stage of prostate cancer, and concomitant health issues significantly influence the outcomes. Some individuals might experience symptom mitigation, while others might not observe any notable changes. This highlights the need for personalized approaches to vitamin D supplementation.
Potential Benefits of Vitamin D in Mitigating Prostate Cancer Symptoms
Vitamin D may play a role in reducing certain symptoms associated with prostate cancer. These potential benefits can range from improved bone health to reduced inflammation, contributing to a better quality of life for affected individuals. Clinical trials and observational studies are crucial for further exploring these potential benefits.
Importance of Patient-Specific Considerations
Prostate cancer, like many other diseases, is highly individualistic. Factors such as the patient’s baseline health, existing medications, and specific type of prostate cancer should always be considered when evaluating vitamin D’s role. A personalized approach is essential for maximizing the potential benefits and minimizing risks.
Clinical Scenarios Where Vitamin D May Play a Role
Vitamin D supplementation might be considered in various clinical scenarios involving prostate cancer. These scenarios include patients with low vitamin D levels, those undergoing hormone therapy, and those experiencing bone-related complications. Furthermore, its role in preventing recurrence and improving overall well-being warrants further investigation.
Table of Hypothetical Case Studies
| Case Study | Patient Characteristics | Vitamin D Status | Prostate Cancer Stage | Intervention | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 55-year-old male, obese, with type 2 diabetes, low vitamin D levels. | Deficient | Early-stage | Vitamin D supplementation (oral) | Improved bone density, reduced inflammation markers, no significant impact on tumor growth. |
| Case 2 | 68-year-old male, history of osteoporosis, advanced prostate cancer. | Severely deficient | Advanced | Vitamin D supplementation (oral & intravenous), combined with conventional therapies. | Reduced bone pain, improved quality of life, but no significant impact on tumor progression. |
| Case 3 | 72-year-old male, diagnosed with early prostate cancer, normal vitamin D levels. | Normal | Early | Vitamin D supplementation (oral) | No significant change in prostate cancer progression or symptoms. |
Closing Summary
In conclusion, the link between vitamin D and prostate cancer remains a topic of active research. While promising correlations exist, definitive cause-and-effect relationships are still under investigation. Further robust clinical trials and a deeper understanding of the mechanisms involved are crucial to fully grasp the complex interplay between vitamin D, lifestyle factors, and prostate cancer. Ultimately, personalized approaches and continued research are vital to harnessing the potential benefits of vitamin D in prostate cancer prevention and management.