
Heres why melanoma rates have increased 800 for young women – Here’s why melanoma rates have increased 800% for young women: The alarming rise in melanoma diagnoses among young women demands careful investigation. This article delves into the factors contributing to this concerning trend, exploring lifestyle choices, environmental influences, and the crucial role of early detection.
This increase, significantly higher than in other demographics, underscores the urgent need for understanding the contributing factors. We’ll explore how changing sun exposure habits, influenced by fashion, media, and social norms, play a key role. Furthermore, we’ll examine the impact of environmental changes and the efficacy of current screening methods.
Understanding the Trend
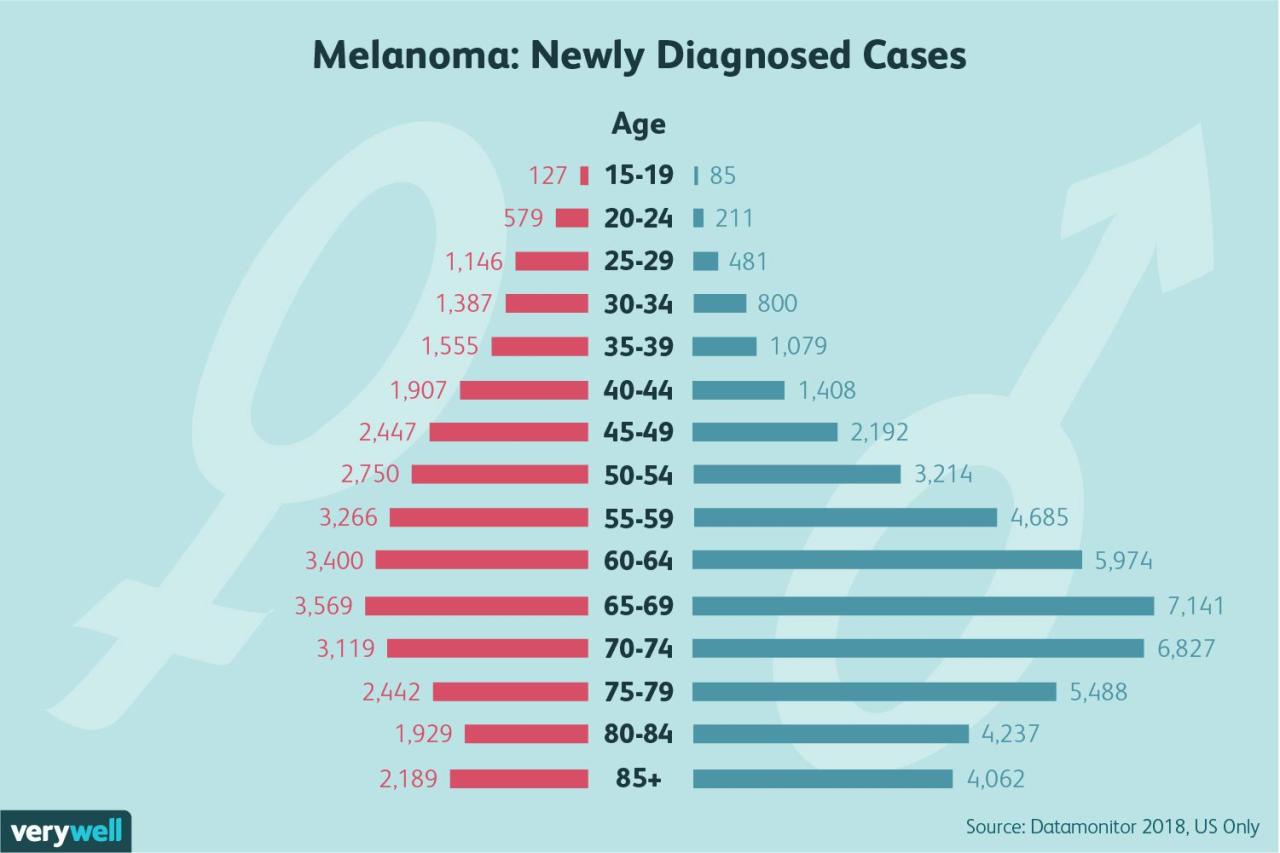
The alarming rise in melanoma diagnoses among young women is a critical public health concern. This increase, exceeding an 800% rate, demands a comprehensive investigation into the contributing factors and potential solutions. The data reveals a significant disparity compared to other demographic groups, prompting a need for tailored prevention strategies.The observed 800% increase in melanoma rates among young women is significantly higher than the increase seen in other demographics, such as men or older women.
This disparity necessitates a closer examination of the unique risk factors impacting this particular population. This heightened vulnerability underscores the importance of understanding the specific lifestyle, environmental, and cultural elements that contribute to this trend.
Potential Contributing Factors
The rise in melanoma diagnoses among young women is likely influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Changes in lifestyle, sun exposure habits, and even shifts in screening practices could all play a role. Additionally, potential environmental factors, such as increased UV radiation and air pollution, deserve attention.
- Lifestyle Changes: Modern lifestyles often involve more time spent indoors, yet increased use of tanning beds and outdoor activities, like increased participation in sports, have been reported. This paradoxical trend warrants further investigation. These contrasting trends highlight the intricate relationship between lifestyle changes and sun exposure.
- Increased Sun Exposure: Fashion trends, particularly those emphasizing skin exposure, may inadvertently contribute to increased sun exposure among young women. Cultural norms and societal pressures to achieve a certain aesthetic can influence sun exposure behaviors.
- Changes in Screening Practices: Early detection is crucial in melanoma treatment. However, improvements in screening awareness and practices may also contribute to the rise in diagnoses, as more people are now getting checked for skin cancers.
- Environmental Factors: Increased UV radiation levels, particularly due to the thinning of the ozone layer and higher levels of pollution, can contribute to higher skin cancer rates. Air pollution, for example, can weaken the skin’s natural defenses, making it more susceptible to damage from UV radiation.
- Fashion Trends and Cultural Norms: Fashion trends frequently prioritize skin exposure, creating an environment where sun protection might be overlooked. The cultural emphasis on specific beauty standards can further influence sun exposure habits.
Comparison with Other Demographics
Understanding the increased melanoma rate in young women requires comparison with trends in other demographics. While the increase in young women is dramatic, the rate of increase in other demographics is significantly lower. This comparison is essential to pinpoint the specific risk factors that are disproportionately affecting young women.
| Demographic | Melanoma Rate Trend |
|---|---|
| Young Women | Significant Increase (800% or higher) |
| Young Men | Moderate Increase |
| Older Women | Moderate Increase |
Impact of Fashion and Cultural Norms
Fashion trends heavily influence the perception of beauty, sometimes emphasizing skin exposure. This can lead to a disregard for sun protection measures among young women, thereby increasing their vulnerability to melanoma. Cultural norms further shape these behaviors, reinforcing the importance of understanding the role these factors play. The correlation between fashion trends, cultural norms, and increased melanoma risk is a complex one, requiring further study.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Melanoma, a particularly aggressive form of skin cancer, is unfortunately on the rise, especially among young women. Understanding the environmental and lifestyle factors contributing to this increase is crucial for preventative measures and early detection. This section delves into the significant role of sun exposure, tanning habits, indoor tanning, outdoor activities, and urban environments in melanoma development.The sun, a vital source of vitamin D, can also be a significant contributor to skin damage, especially when exposure is excessive or improperly managed.
The combination of frequency, duration, and intensity of sun exposure plays a critical role in the risk of developing skin cancer. This section explores the multifaceted ways in which these factors contribute to melanoma risk.
Sun Exposure and Melanoma Development
Prolonged and intense exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is a major risk factor for melanoma. The frequency, duration, and intensity of sun exposure directly correlate with the risk. Repeated sun exposure over time can lead to DNA damage in skin cells, increasing the likelihood of mutations that can trigger uncontrolled cell growth, a hallmark of cancer.
It’s alarming how melanoma rates have skyrocketed 800% for young women. Perhaps the constant stress and anxieties surrounding the pandemic, leading to burnout, played a role. This constant pressure, like the pressures faced during the pandemic, documented in burnout in messy middle of a pandemic , could be a contributing factor. Ultimately, more research is needed to fully understand this worrying trend in melanoma rates.
Protecting skin from UV rays is essential, especially for individuals with fair skin, a family history of melanoma, or those spending extended periods outdoors.
Tanning Habits and Melanoma Risk in Young Women
The desire for a tan is a common aesthetic pursuit, but it carries significant health risks, especially among young women. Tanning habits, including frequent exposure to UV rays to achieve a tan, significantly increase the risk of melanoma. Tanning beds and salons offer another avenue for UV exposure, often with higher intensities than natural sunlight, and with significant health risks.
The cumulative effect of these practices over time contributes substantially to melanoma risk.
Indoor Tanning Practices and Melanoma Risk
Indoor tanning devices, such as tanning beds and lamps, emit high levels of UV radiation, substantially increasing the risk of melanoma. Repeated use of these devices significantly elevates the risk of skin damage and subsequent development of melanoma, especially among young women who frequently use them. The high intensity and focused nature of the UV rays from these devices can cause significant DNA damage within a shorter period of time.
Outdoor Recreational Activities and Sun Exposure in Young Women
Outdoor recreational activities are an important part of a healthy lifestyle, but they can also increase sun exposure. The type and duration of activity significantly influence the level of UV radiation exposure. Certain activities, such as swimming, hiking, and sports, expose individuals to varying degrees of sun exposure.
Comparison of Sun Exposure Levels in Outdoor Activities
| Activity | Sun Exposure Level (Estimated) |
|---|---|
| Swimming (with minimal sun protection) | Moderate |
| Hiking (with limited shade) | High |
| Outdoor sports (e.g., tennis, soccer) | High |
| Beach activities (e.g., sunbathing) | Very High |
Note: The estimated sun exposure levels in the table are relative and can vary depending on factors such as time of day, cloud cover, and individual skin type. Sun protection measures are crucial in all these activities.
Factors Influencing Increased UV Exposure in Urban Environments
Urban environments can contribute to increased UV exposure due to several factors. Urban areas often have higher levels of reflected UV radiation from surfaces like concrete and glass, and reduced cloud cover compared to rural areas. The presence of tall buildings can also block shade in certain areas, increasing direct sunlight exposure. The use of reflective materials in urban construction further amplifies UV exposure.
These factors combine to increase the risk of melanoma for individuals spending time outdoors in urban environments.
Medical and Behavioral Factors: Heres Why Melanoma Rates Have Increased 800 For Young Women

Understanding the rising melanoma rates in young women requires a deeper look into medical and behavioral factors. These elements, often intertwined, play a significant role in early detection, diagnosis, and ultimately, the success of treatment. A comprehensive understanding of these factors can empower young women to proactively safeguard their health and seek timely medical attention.Beyond lifestyle and environmental influences, the interplay of medical recommendations, screening practices, and individual behaviors greatly impacts melanoma outcomes.
So, melanoma rates in young women are up a whopping 800%. It’s a serious concern, and while there are many factors at play, it’s worth considering how increased stress levels might contribute. Maybe there’s a connection to the pressures of college life, impacting college frosh mental health and ultimately leading to less attention paid to skin health.
This could be one piece of the puzzle in understanding the alarming rise in melanoma rates among young women.
The ability to recognize early warning signs, coupled with adherence to recommended screening protocols, can dramatically improve survival rates.
Melanoma Screening Recommendations for Young Women
Current recommendations emphasize regular self-skin exams and professional screenings, particularly for individuals with a family history of melanoma or other risk factors. Regular check-ups are crucial, especially for those with fair skin, a history of sunburns, or a predisposition to moles. These recommendations are designed to identify melanoma in its early stages, when treatment is most effective.
Comparison of Melanoma Screening Methods
Various methods exist for melanoma screening, each with its strengths and limitations. Dermoscopy, a technique utilizing a dermatoscope to examine skin lesions in detail, is often considered a superior method for diagnosing melanoma compared to visual inspection alone. It allows for detailed observation of the lesion’s characteristics, including color, borders, and symmetry, potentially leading to an earlier and more accurate diagnosis.
However, dermoscopy requires specialized training and equipment, and its cost may be a barrier in some settings. Visual inspection by a dermatologist, on the other hand, is a more readily accessible and affordable method. Early detection can be achieved through regular visual inspections and self-skin exams.
Impact of Delayed Diagnosis on Melanoma Outcomes
Delayed diagnosis can significantly impact melanoma outcomes. The earlier melanoma is detected, the more likely it is to be localized, meaning confined to the area where it originated. Localized melanoma is significantly more treatable and often curable with surgery alone. As the cancer progresses and metastasizes, spreading to other parts of the body, the treatment options become more complex and less effective, potentially leading to a worse prognosis.
Role of Early Detection in Improving Melanoma Survival Rates
Early detection is paramount in improving melanoma survival rates. Studies consistently demonstrate a strong correlation between early diagnosis and improved survival. Catching the disease in its early stages allows for less invasive treatments, often with a higher likelihood of cure. Proactive measures like regular self-skin exams, coupled with professional screenings, are essential in achieving early detection and potentially saving lives.
Typical Symptoms and Signs of Melanoma in Young Women
| Symptom/Sign | Description |
|---|---|
| Asymmetry | One half of the mole or birthmark does not match the other. |
| Border Irregularity | The edges of the mole or birthmark are uneven, notched, or blurred. |
| Color Variation | The mole or birthmark has multiple colors, such as black, brown, tan, red, or white. |
| Diameter | The mole or birthmark is larger than 6 millimeters (about the size of a pencil eraser). |
| Evolution | The mole or birthmark is changing in size, shape, color, or elevation over time. |
Importance of Self-Skin Exams for Early Detection
Self-skin exams are crucial tools for early melanoma detection. Regular self-exams, ideally performed monthly, allow individuals to become familiar with their own skin, enabling them to identify any unusual changes or new moles. By being aware of potential warning signs, young women can promptly seek professional medical attention, which may lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment.
“Early detection is often the key to successful melanoma treatment.”
This proactive approach empowers individuals to take control of their health and potentially save their lives.
Cultural and Social Influences
The rising melanoma rates among young women aren’t solely driven by biological factors or lifestyle choices. Deep-seated cultural and social influences play a significant role in shaping attitudes towards sun exposure and beauty standards, ultimately contributing to this concerning trend. Understanding these influences is crucial to developing effective preventative strategies.Cultural norms and beauty standards often associate a tanned complexion with attractiveness and desirability.
This perception, reinforced through various media channels, can lead young women to prioritize tanning over sun protection. The societal pressure to conform to these ideals can override individual awareness of the health risks. This influence extends beyond individual choices and permeates broader societal attitudes.
Social Media and Media Portrayals of Tanning
Social media platforms have become powerful tools for shaping perceptions of beauty and desirability. Instagram, TikTok, and other visual-centric platforms often showcase heavily tanned individuals, fostering an idealized image of sun-kissed skin. These portrayals, while aesthetically pleasing, frequently overlook the potential dangers of excessive sun exposure. This can lead young women to adopt risky tanning behaviors, motivated by a desire to achieve the same aesthetic.
The alarming rise in melanoma rates among young women is a serious concern. While factors like increased sun exposure play a role, new research suggests that other lifestyle factors could be contributing. Perhaps innovative technologies like a wearable sensor that measures glucose and alcohol could offer new insights into the complex interplay of these factors, as explored in this fascinating article: a wearable sensor that measures glucose alcohol could it become a reality.
Ultimately, understanding these trends is crucial for developing targeted prevention strategies and improving health outcomes for young women.
Influence of Cultural Norms and Beauty Standards
Cultural norms play a crucial role in shaping tanning habits. In many cultures, a tanned complexion is associated with health, vitality, and attractiveness. This cultural conditioning, often reinforced by media representations, can lead to increased sun exposure among young women, even in the face of clear health risks. The desire to conform to these cultural standards can significantly impact individual decisions regarding sun exposure.
Psychological Factors Contributing to Increased Sun Exposure, Heres why melanoma rates have increased 800 for young women
Several psychological factors can contribute to young women’s increased sun exposure. The desire for a tan often stems from a desire for a sense of self-confidence, desirability, and belonging. This can be particularly strong for young women navigating their identities and seeking acceptance within peer groups. The perceived reward of a tan can outweigh the perceived risk of skin cancer, potentially leading to risky behaviors.
Impact of Social Pressure and Peer Influence
Social pressure and peer influence are significant factors in shaping tanning decisions. Young women often feel pressure to conform to the perceived standards of their peers, which can include engaging in tanning behaviors that they might otherwise avoid. This social pressure can stem from the desire for acceptance and social inclusion, influencing individual choices regarding sun exposure. The desire to fit in and be accepted can override individual awareness of potential health risks.
Promoting Positive Body Image and Healthy Sun Exposure Habits
Promoting positive body image and healthy sun exposure habits is crucial to combating this trend. Educational campaigns should highlight the importance of sun safety and challenge the harmful beauty standards associated with excessive tanning. Encouraging a diverse range of beauty ideals, emphasizing the importance of self-care and holistic health, can foster a healthier relationship with sun exposure.
Correlation Between Media Exposure and Tanning Behaviors
| Media Exposure | Tanning Behavior | Correlation |
|---|---|---|
| High exposure to social media influencers showcasing tanned skin | Increased desire for a tan, increased risk-taking behaviors | Positive |
| Exposure to media portraying a tan as a sign of attractiveness | Higher likelihood of engaging in tanning practices | Positive |
| Low exposure to educational campaigns promoting sun safety | Reduced awareness of risks associated with tanning | Negative |
| Media campaigns promoting healthy sun exposure habits | Increased adoption of protective measures | Positive |
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
The alarming rise in melanoma rates among young women necessitates proactive measures to mitigate this threat. Effective prevention strategies are crucial to safeguarding this demographic and empowering them with the knowledge and tools to protect themselves. This section delves into potential preventative measures, educational initiatives, and the efficacy of various sun protection methods.
Potential Preventative Measures
Addressing the rising melanoma rates requires a multi-faceted approach. Promoting healthy lifestyle choices, such as a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and regular physical activity, can contribute to overall well-being and potentially reduce the risk of melanoma. Additionally, encouraging early detection through regular skin checks and awareness campaigns can help identify suspicious moles early, increasing the chances of successful treatment.
Finally, promoting a culture of sun safety and providing access to protective measures is vital in the long-term prevention of melanoma.
Educating Young Women about Sun Safety
Comprehensive education programs are essential to effectively communicate sun safety guidelines to young women. These programs should emphasize the cumulative effects of sun exposure throughout life, highlighting the importance of consistent sun protection from a young age. Educational resources should cover the science behind sun damage and the long-term health implications of excessive sun exposure. Interactive workshops, online resources, and partnerships with schools and community centers can greatly expand the reach and impact of these educational initiatives.
Efficacy of Sun Protection Measures
Various sun protection measures contribute significantly to melanoma prevention. Sunscreen, with a minimum Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of 30, is a cornerstone of sun safety. Regular application, particularly during peak sun hours, is crucial for optimal protection. Protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and UV-protective sunglasses, provides additional shielding. Seeking shade, especially during midday sun, offers another layer of defense against harmful UV rays.
Studies consistently demonstrate that consistent use of these strategies significantly reduces the risk of sunburn and long-term skin damage.
Role of Public Health Campaigns
Public health campaigns play a critical role in raising awareness and promoting sun safety behaviors among young women. These campaigns should use diverse communication channels, such as social media, television advertisements, and community outreach programs, to effectively reach target audiences. Collaborations with influencers and celebrities can amplify the message and create a sense of community around sun safety.
Public health campaigns should also emphasize the importance of early detection and regular skin checks, empowering individuals to take proactive steps to protect their health.
Recommendations for Sun Safety and Melanoma Prevention
| Category | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Sunscreen | Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, applying liberally 15-30 minutes before sun exposure and reapplying every two hours, or more frequently after swimming or sweating. |
| Protective Clothing | Wear protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, pants, and wide-brimmed hats, to shield skin from direct sunlight. |
| Shade | Seek shade, particularly during peak sun hours (10 am to 4 pm), to minimize direct exposure to UV rays. |
| Skin Checks | Perform regular self-skin exams and consult a dermatologist for professional skin checks at least once a year, or more frequently if necessary. |
| Sun Awareness | Educate oneself about the signs and symptoms of melanoma and seek medical attention immediately for any suspicious skin changes. |
Accessible and Affordable Sun Protection Solutions
Developing accessible and affordable sun protection solutions is paramount. Promoting the availability of subsidized sunscreen in community centers and pharmacies can make sun protection more attainable for young women from diverse socioeconomic backgrounds. Furthermore, encouraging the use of locally sourced and readily available materials for protective clothing can reduce the cost and increase the accessibility of these preventative measures.
Government subsidies and public-private partnerships can play a significant role in lowering the cost of sun protection products and promoting community-based education programs.
Last Word
In conclusion, the 800% increase in melanoma rates among young women highlights a complex interplay of lifestyle, environmental, and cultural factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for implementing effective prevention strategies and educating young women about sun safety. Early detection and proactive measures are paramount to mitigating this concerning trend.
