New sub variants of omicron detected what to know about ba 4 and ba 5. These newly identified Omicron subvariants, BA.4 and BA.5, are sparking concern and prompting questions about their impact on the ongoing pandemic. Understanding their emergence, transmission, potential severity, and the public health response is crucial for navigating this evolving situation. How do these new variants differ from previous iterations of Omicron?
Are they more transmissible? What does this mean for our existing immunity and vaccination efforts?
This in-depth look delves into the specifics of BA.4 and BA.5, exploring their characteristics, comparing them to earlier Omicron versions, and examining the potential long-term consequences. We’ll also analyze the public health response and the crucial role of vaccination and ongoing research.
Introduction to BA.4 and BA.5

The recent emergence of BA.4 and BA.5, subvariants of the Omicron variant of COVID-19, has sparked global health concerns. These new subvariants are characterized by specific mutations in their genetic makeup, which might influence their transmissibility, severity, and immune evasion capabilities compared to earlier Omicron subvariants. Understanding their origins and characteristics is crucial for informed public health responses.BA.4 and BA.5 evolved from the original Omicron variant (BA.1).
This evolutionary relationship, stemming from shared genetic ancestry, highlights the ongoing adaptation of the virus. The process of viral evolution, driven by natural selection, allows the virus to potentially overcome existing immunity and spread more efficiently. Tracking their emergence and spread is vital to predict potential impacts and formulate appropriate countermeasures.
Timeline of Identification and Spread
BA.4 and BA.5 were initially identified in South Africa and subsequently detected in other parts of the world. The timeline of their identification and spread is crucial for understanding their impact. The initial identification and subsequent reports of these subvariants highlight the importance of ongoing surveillance efforts. Global reporting systems and scientific collaboration are essential for monitoring and responding to evolving viral threats.
Relationship to BA.1
The emergence of BA.4 and BA.5 from the BA.1 subvariant underscores the continuous evolution of the virus. This evolutionary process, driven by natural selection, allows the virus to adapt to changing environments and overcome existing immunity. Understanding this dynamic relationship between different subvariants is critical for developing effective strategies to combat the virus.
Key Differences in Genomic Makeup
Comparative analysis of the genomic makeup of BA.4 and BA.5 with earlier Omicron subvariants, like BA.1, reveals specific mutations that distinguish them. These mutations are crucial for understanding the virus’s evolution and its potential impact on infection patterns. The following table illustrates the key differences:
| Characteristic | BA.1 | BA.4 | BA.5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spike Protein Mutations | Specific mutations present in the spike protein | Specific mutations in the spike protein, potentially impacting immune evasion | Specific mutations in the spike protein, potentially differing from BA.4 |
| Other Mutations | Specific mutations in other parts of the genome | Specific mutations in other parts of the genome, possibly related to transmission or disease severity | Specific mutations in other parts of the genome, possibly differing from BA.4 |
| Overall Impact | Characteristic features associated with the BA.1 subvariant | Potential impact on transmissibility, immune evasion, or disease severity compared to BA.1 | Potential impact on transmissibility, immune evasion, or disease severity compared to BA.1 and BA.4 |
Symptoms and Transmission
BA.4 and BA.5, two Omicron subvariants, have sparked considerable interest due to their potential impact on public health. Understanding their symptoms, transmissibility, and immune evasion characteristics is crucial for informed public health responses. These subvariants, while sharing similarities with other Omicron strains, may also exhibit subtle differences in their presentation.The observed symptoms of BA.4 and BA.5 infections generally align with those seen in other Omicron subvariants.
However, subtle differences in symptom prevalence and severity might exist. Early reports suggest a potential increase in gastrointestinal symptoms like diarrhea and nausea, but more research is needed to confirm this trend definitively.
Symptoms of BA.4 and BA.5
Early data suggests that BA.4 and BA.5 infections often manifest with symptoms similar to those seen in previous Omicron subvariants. Common symptoms include fatigue, headache, runny nose, and sore throat. However, there might be a slightly increased frequency of gastrointestinal symptoms, such as diarrhea and nausea, compared to other Omicron strains. It’s essential to note that these are preliminary observations, and further research is required to establish definitive patterns.
New Omicron subvariants BA.4 and BA.5 are making headlines, but let’s be honest, sometimes it’s the less flashy issues that need more attention. Just like navigating the complexities of new virus variants, understanding teen dietary habits, particularly emotional eating and gateway foods, can be tricky. Learning how to approach these issues with teens can be a challenge, and understanding the role of emotional eating and gateway foods is key.
For more on this, check out this insightful piece on teen dietary habits what parents should know about emotional eating and gateway foods. Ultimately, understanding these factors can help us all better navigate the health landscape, whether it’s viral variants or adolescent development.
Transmission Rates of BA.4 and BA.5
BA.4 and BA.5 have demonstrated a higher transmissibility compared to earlier variants of concern. This enhanced transmissibility is likely due to several factors, including potential mutations that improve the virus’s ability to bind to human cells. While precise transmission rates are still under investigation, early epidemiological data suggest that BA.4 and BA.5 spread more rapidly than previous variants.
Immune Evasion Potential
BA.4 and BA.5 possess the potential to evade pre-existing immunity. Scientists are investigating how mutations in these subvariants might influence their ability to bind to the human immune system’s antibodies. This potential for immune evasion could contribute to their observed increased transmissibility. Understanding the specific mechanisms of immune evasion will be critical for developing effective preventative measures and treatments.
Comparison of Transmission Rates
| Variant | Estimated Transmission Rate (compared to earlier Omicron variants) | Supporting Data |
|---|---|---|
| BA.4 | Potentially higher | Early epidemiological studies and genomic sequencing data. |
| BA.5 | Potentially higher | Early epidemiological studies and genomic sequencing data. |
| Earlier Omicron variants | Lower (relative to BA.4 and BA.5) | Available epidemiological data and studies. |
Note: Transmission rates are estimates and may vary based on factors like vaccination status, social distancing, and environmental conditions. Further research is necessary to establish precise transmission rates for BA.4 and BA.5.
Severity of Illness
BA.4 and BA.5, the latest Omicron subvariants, have raised concerns about their potential impact on public health. While early data suggests a similar infection trajectory to previous Omicron subvariants, a nuanced understanding of their severity is crucial for effective public health responses. This analysis will delve into the current data on hospitalization and mortality rates, as well as explore potential risk factors.Understanding the severity of illness associated with BA.4 and BA.5 is essential for healthcare providers and public health officials to make informed decisions about resource allocation and preventative measures.
Comparing these subvariants to previous variants and identifying potential risk factors can help predict and mitigate potential health impacts.
Hospitalization Rates
Hospitalization rates are a key indicator of the severity of a variant. Early data suggests that BA.4 and BA.5, while causing illness, may lead to lower hospitalization rates compared to some earlier variants of concern, like Delta. However, it’s important to acknowledge that the data is still developing, and longer-term trends need further observation.
Mortality Rates
Mortality rates associated with BA.4 and BA.5 infections are currently under investigation. Early reports suggest that these subvariants are not associated with significantly higher mortality rates compared to other Omicron subvariants. However, rigorous epidemiological studies are necessary to confirm these trends over time and across different populations.
New Omicron subvariants BA.4 and BA.5 are making headlines, and rightfully so. While understanding their potential impact on overall health is crucial, it’s also important to remember that conditions like acromegaly can significantly increase the risk of heart failure, as detailed in this article on acromegaly and heart failure. So, while we track these new variants, it’s a good reminder to prioritize general health, especially if you have pre-existing conditions.
Risk Factors for Severe Illness
Several factors can influence the severity of illness from BA.4 and BA.5 infections. Pre-existing health conditions, particularly those affecting the respiratory or cardiovascular systems, are potential risk factors. Age is another significant risk factor, with older adults and individuals with compromised immune systems being more vulnerable to severe outcomes.
Impact of Pre-existing Health Conditions
Individuals with pre-existing health conditions like diabetes, chronic lung disease, heart conditions, or weakened immune systems are at a higher risk of developing severe illness from BA.4 and BA.5 infections. These conditions can exacerbate the impact of the virus on the body, increasing the likelihood of hospitalization or complications.
Comparison to Other Variants
A comparison of hospitalization and mortality rates between BA.4/5 and other variants is crucial for understanding the overall severity. Data is still emerging, but early reports indicate lower hospitalization rates than some earlier variants, such as Delta. However, ongoing monitoring and analysis are essential to draw definitive conclusions.
Public Health Response
The emergence of BA.4 and BA.5 omicron subvariants has prompted a global public health response, requiring adjustments to existing strategies and a nuanced understanding of their unique characteristics. This response involves a multifaceted approach, encompassing vaccination efforts, public awareness campaigns, and the monitoring of infection trends. The effectiveness of these strategies will be crucial in mitigating the impact of these new variants.A comparative analysis of public health measures across various regions highlights the adaptability and diversity in global approaches.
Factors like healthcare infrastructure, population density, and pre-existing health conditions influence the specific strategies employed in different areas. Despite these differences, a common thread runs through these approaches – the prioritization of public health measures to safeguard the well-being of their citizens.
Public Health Measures to Address BA.4 and BA.5
Public health authorities are employing various measures to address the spread of BA.4 and BA.5, including enhanced surveillance of infection rates, updated guidance on masking and social distancing, and increased testing capacity. These proactive measures aim to minimize transmission and prevent overwhelming healthcare systems.
- Enhanced Surveillance: Real-time monitoring of infection rates, hospitalization trends, and variant prevalence is crucial for assessing the impact of BA.4 and BA.5. This data allows for informed decision-making and the tailoring of public health responses to the evolving situation.
- Updated Guidance: Public health agencies are providing updated recommendations on masking, social distancing, and hygiene practices, aiming to reduce transmission. This includes advice on the effectiveness of different types of masks and the importance of handwashing.
- Increased Testing Capacity: Expanding testing capabilities enables faster identification of cases, facilitating contact tracing and isolation, and limiting the spread of infection.
Comparative Analysis of Public Health Strategies
Different regions employ diverse public health strategies, reflecting their unique circumstances. For example, some regions prioritize widespread masking mandates, while others rely more on vaccination campaigns. The effectiveness of these strategies will depend on factors such as the local healthcare infrastructure, population density, and public compliance.
So, the new Omicron subvariants BA.4 and BA.5 are making headlines. While the details are still emerging, it’s important to stay informed. Knowing that if you received the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines, expect to get a booster starting this fall here , it’s a good reminder that vaccination remains a crucial tool in our arsenal against these variants.
This means staying vigilant and up-to-date on the latest information about these new subvariants is more important than ever.
- Varying Masking Policies: Some regions have maintained or re-implemented mask mandates in public spaces, while others have opted for more relaxed recommendations. These differing approaches demonstrate the multifaceted nature of the response and the need for adaptability based on local circumstances.
- Vaccination Prioritization: Regions with robust vaccination programs may focus on booster shots for vulnerable populations, aiming to maximize immunity against BA.4 and BA.5. Other regions may emphasize broader vaccination campaigns to increase population immunity.
- Testing Strategies: Some areas are prioritizing rapid antigen tests, while others emphasize PCR testing for more accurate identification and confirmation of cases. The choice of testing strategy influences the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of infection control measures.
Role of Vaccination in Mitigating BA.4 and BA.5 Infections
Vaccination remains a cornerstone of public health efforts in mitigating the impact of BA.4 and BA.5 infections. Studies show that vaccination can significantly reduce the severity of illness and the risk of hospitalization, particularly for individuals with pre-existing health conditions.
Potential Impact of Booster Shots on Immunity
Booster shots can play a significant role in boosting immunity against BA.4 and BA.5. The potential impact of these shots on immunity will depend on the specific vaccine type and the timing of administration relative to infection. Booster shots can be crucial in enhancing protection against severe illness and hospitalization.
Vaccination Effectiveness Against BA.4 and BA.5
The effectiveness of vaccination against BA.4 and BA.5 is still under investigation. However, initial data suggests that vaccination provides some protection against infection, particularly in preventing severe outcomes.
| Vaccine Type | Effectiveness against BA.4/BA.5 (Estimated) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| mRNA vaccines (e.g., Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna) | Moderately reduced infection risk, potentially reduced severity | Further data is needed for precise estimations |
| Other vaccine types | Data on effectiveness is limited | Specific data will vary by vaccine type |
Evolutionary Considerations: New Sub Variants Of Omicron Detected What To Know About Ba 4 And Ba 5
The emergence of BA.4 and BA.5, subvariants of the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2, highlights the virus’s ongoing evolution. Understanding the genetic changes driving these new variants is crucial for predicting future developments and tailoring public health responses. This evolution is a complex process, but understanding the underlying mechanisms can help us anticipate and prepare for future challenges.Understanding the genetic mutations in these new variants and the evolutionary mechanisms behind their emergence is essential for developing effective strategies to combat the ongoing pandemic.
This includes monitoring the virus’s genetic changes, identifying patterns in its evolution, and anticipating potential future challenges. The study of SARS-CoV-2 evolution, including the emergence of subvariants, is a crucial element in mitigating the impact of the pandemic.
Genetic Mutations Contributing to Immune Evasion, New sub variants of omicron detected what to know about ba 4 and ba 5
SARS-CoV-2 constantly mutates, and these mutations can affect the virus’s ability to bind to host cells and evade the immune system. BA.4 and BA.5 have accumulated specific mutations that are hypothesized to contribute to immune evasion. These mutations likely alter the virus’s surface proteins, particularly the spike protein, reducing the effectiveness of pre-existing immunity developed from prior infections or vaccinations.
This allows the virus to more easily infect individuals previously exposed.
Evolutionary Mechanisms Driving Emergence
Several evolutionary mechanisms contribute to the emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants. Natural selection plays a critical role, favoring mutations that enhance the virus’s transmissibility and ability to evade the immune response. High viral loads and rapid replication rates within a population can accelerate the selection of advantageous mutations. Recombination between different SARS-CoV-2 lineages can also introduce new genetic material, potentially leading to novel variants.
Current Understanding of SARS-CoV-2 Evolution
The SARS-CoV-2 virus demonstrates a remarkable capacity for adaptation. The emergence of subvariants like BA.4 and BA.5 illustrates the virus’s ongoing evolution. This evolution is not linear; the virus’s genetic makeup changes based on various factors. The virus adapts to the changing environment, finding ways to outmaneuver host defenses.
Methods for Tracking Viral Evolution
Scientists use several methods to track the evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Genomic sequencing is a critical tool, allowing researchers to identify and analyze the genetic makeup of the virus. Phylogenetic analysis compares the genetic sequences of different virus samples to understand their evolutionary relationships and track the spread of new variants. This data is collected globally, providing a comprehensive view of the virus’s evolution and spread.
Key Mutations in BA.4 and BA.5 Compared to BA.1
| Mutation | BA.4 | BA.5 | BA.1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spike Protein – N501Y | Present | Present | Present |
| Spike Protein – Q498R | Present | Present | Absent |
| Spike Protein – G446S | Present | Present | Absent |
| Spike Protein – E484A | Absent | Absent | Present |
| Other mutations | Various | Various | Various |
The table above highlights key mutations found in BA.4 and BA.5 compared to BA.1. Note that BA.4 and BA.5 share many mutations, but subtle differences may alter their transmissibility and immune evasion capabilities. This is crucial for ongoing monitoring. These variations highlight the dynamic nature of viral evolution.
Future Implications
The emergence of BA.4 and BA.5, while causing concern, also presents an opportunity to refine our understanding of viral evolution and improve pandemic preparedness. Their characteristics, including transmissibility and potential immune escape, necessitate a careful examination of their long-term implications for the pandemic trajectory. This analysis considers ongoing research, potential future subvariants, and critical knowledge gaps.The pandemic’s trajectory is influenced by factors beyond the virus itself, including public health responses, vaccination efforts, and the virus’s own evolution.
The long-term impact of BA.4 and BA.5 will be intertwined with these external elements. Predicting the precise future course is challenging, but by analyzing historical trends and current research, we can better understand the potential outcomes.
Potential Long-Term Impact on the Pandemic
The long-term impact of BA.4 and BA.5 will depend on several factors, including the effectiveness of ongoing vaccination campaigns, the development of new treatments, and the overall response of the global community. These variants might lead to a more protracted, but potentially less severe, pandemic. The sustained presence of the virus could also lead to a more endemic state, where the virus remains a seasonal threat but with milder symptoms.
The emergence of variants with different characteristics can lead to repeated waves of infections. However, the severity of these waves will likely be less compared to the initial stages of the pandemic due to increasing immunity in the population.
Ongoing Research Efforts
Extensive research is being conducted to understand the mechanisms behind the evolution of these variants. Scientists are analyzing viral genetic sequences to identify mutations and their potential effects on infectivity, transmissibility, and immune evasion. These efforts are crucial for predicting the behavior of future variants. Sequencing data from across the globe is crucial in tracking the emergence of new variants and analyzing their mutations.
This allows researchers to understand how the virus evolves and adapt in real time. Studies on antibody responses and immune system reactions to these variants are crucial to developing effective strategies for future outbreaks.
Potential for Further Subvariants to Emerge
The nature of viral evolution suggests that further subvariants will likely emerge. The virus’s inherent capacity for mutation, coupled with the ongoing transmission, provides fertile ground for new variants. This is not an unprecedented event; throughout history, viruses have demonstrated an ability to evolve and adapt to new environments. The emergence of new variants is a natural process.
Strategies for managing future outbreaks must consider this dynamic nature of viral evolution. Public health agencies are working on systems to detect and monitor the evolution of the virus.
Current Knowledge Gaps Regarding BA.4 and BA.5
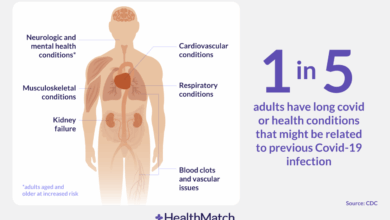
While significant progress has been made, critical gaps in our knowledge regarding BA.4 and BA.5 remain. One major area is understanding the long-term impact on human health, including the potential for long COVID. Further research is needed to assess the overall health effects beyond the acute infection phase. The impact on vulnerable populations, such as the elderly and those with pre-existing conditions, is another important area requiring investigation.
The development of new and effective treatments for BA.4 and BA.5 remains a critical area of research. This includes exploring strategies for reducing the severity of illness and improving outcomes for individuals infected. Understanding the interaction between BA.4 and BA.5 and other viruses circulating in the community is also crucial.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the emergence of BA.4 and BA.5 subvariants presents a dynamic challenge to public health. While significant questions remain, the ongoing research, evolving data, and public health measures offer hope for mitigating the impact of these variants. Continued vigilance, informed decision-making, and a focus on collective action will be essential in navigating this stage of the pandemic.