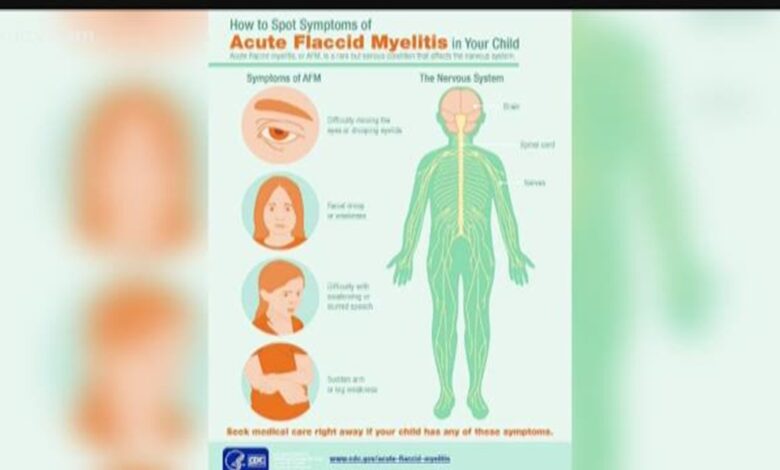
Detecting polio like disease is difficult for doctors – Detecting polio-like disease is difficult for doctors, posing a significant diagnostic hurdle. Pinpointing these illnesses requires careful consideration of symptoms, a thorough understanding of similar conditions, and access to advanced diagnostic tools. Misdiagnosis can lead to delayed treatment and potentially severe complications. Understanding the complexities involved in distinguishing these diseases is crucial for effective patient care.
This intricate challenge highlights the need for accurate and rapid diagnostic methods. Variability in symptom presentation across patients, coupled with the potential for similar symptoms in other conditions, underscores the importance of a multi-faceted approach. From detailed patient histories to advanced imaging techniques and sophisticated laboratory tests, a comprehensive diagnostic strategy is essential.
Introduction to Polio-like Disease Diagnosis Challenges
Diagnosing diseases that mimic polio presents a significant challenge for medical professionals. The subtlety of symptoms and the potential for overlap with other neurological conditions often lead to delays in accurate identification and treatment. Prompt and precise diagnosis is crucial for effective management and to prevent severe complications. The difficulty stems from various factors, including the subtle presentation of symptoms, the lack of readily available and specific diagnostic tools, and the necessity to rule out other conditions with similar manifestations.
Difficulties in Distinguishing Similar Symptoms
Differentiating polio-like symptoms from those of other neurological illnesses requires careful consideration of patient history, physical examination findings, and supporting laboratory tests. Conditions like transverse myelitis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and other viral infections can present with similar weakness and paralysis. The nuanced variations in symptom presentation and progression often necessitate a comprehensive diagnostic approach that involves multiple specialists and extended observation periods.
Importance of Accurate and Rapid Diagnosis
Early and accurate diagnosis is paramount in managing polio-like illnesses. Prompt initiation of appropriate treatment can significantly reduce the severity of the disease and improve patient outcomes. Delays in diagnosis can lead to irreversible neurological damage and long-term disability. The complexity of differentiating between various neurological conditions underscores the importance of specialized expertise and the availability of advanced diagnostic tools.
Factors Contributing to Diagnostic Challenges
Several factors contribute to the difficulty in diagnosing polio-like diseases. The subtle nature of initial symptoms, the potential for symptom overlap with other conditions, and the limited availability of specific diagnostic tests all play a role. Additionally, geographic location and access to specialized healthcare facilities can significantly impact diagnostic capabilities. The evolving nature of viral infections and the potential for emerging strains of pathogens further complicate the process.
Comparison of Symptoms: Polio vs. Similar Diseases
| Characteristic | Polio | Transverse Myelitis | Guillain-Barré Syndrome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Onset | Gradual or sudden, often following a viral illness | Acute, often without a preceding illness | Gradual, typically starting with sensory symptoms |
| Symptoms | Muscle weakness, paralysis, fever, headache | Severe back pain, weakness in limbs, sensory disturbances | Progressive muscle weakness, sensory changes, areflexia |
| Muscle Involvement | Symmetrical muscle weakness, flaccid paralysis | Focal or asymmetrical muscle weakness, spastic paralysis | Distal muscle weakness, ascending paralysis |
| Diagnosis | Requires laboratory confirmation (e.g., viral isolation) | Often relies on MRI scans and clinical presentation | Diagnosis typically based on neurological examination and CSF analysis |
Diagnostic Methods and Limitations
Pinpointing polio-like illnesses can be challenging for medical professionals, as symptoms often overlap with other neurological conditions. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and preventing potential complications. This necessitates a robust understanding of the diagnostic methods available and their inherent limitations.Diagnostic methods for polio-like illnesses often rely on a combination of clinical assessments, laboratory tests, and imaging techniques.
Each method has strengths and weaknesses, impacting the accuracy and reliability of the diagnosis. The sensitivity and specificity of these tests vary depending on the specific polio-like condition suspected, the stage of the illness, and the individual patient’s characteristics.
Common Diagnostic Methods
A variety of methods are employed to diagnose polio-like illnesses. These include thorough physical examinations, neurological assessments, and various laboratory investigations. The initial evaluation involves a careful examination of symptoms, medical history, and physical signs.
- Clinical Evaluation: A detailed history, including onset of symptoms, their progression, and associated factors, is essential. Physical examination, including neurological assessments to evaluate muscle strength, reflexes, and sensation, provides crucial insights into the potential cause of the symptoms. However, the reliability of a clinical diagnosis alone is often limited by the subtle and overlapping nature of symptoms in various neurological conditions.
- Laboratory Tests: These tests aim to identify specific markers or indicators associated with the suspected condition. Examples include cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis to check for viral or bacterial infections, which can sometimes mimic polio-like syndromes. However, these tests might not always be conclusive or readily available, leading to delays in diagnosis. Additionally, false positives and negatives can occur, potentially impacting the accuracy of the results.
Doctors often face challenges in diagnosing polio-like illnesses, requiring meticulous testing and observation. Thankfully, innovative solutions are emerging in other health areas, like the new app helps type 2 diabetes community , which could potentially inspire similar advancements in the field of detecting polio-like diseases. However, the complexities of accurately diagnosing these conditions remain a crucial hurdle for medical professionals.
- Neuroimaging Techniques: Methods like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can reveal structural abnormalities in the brain and spinal cord. These scans can aid in distinguishing polio-like illnesses from other conditions, such as tumors or multiple sclerosis. However, MRI findings are not always specific to polio-like syndromes, and the presence or absence of abnormalities may not always correlate with the severity or type of the condition.
Limitations of Diagnostic Methods
Diagnostic tools often fall short in accurately identifying polio-like illnesses due to overlapping symptoms with other neurological conditions. This leads to difficulties in differentiating between these diseases.
- Overlapping Symptoms: Many neurological conditions share similar symptoms, making it challenging to pinpoint the precise cause. For instance, some viral infections, autoimmune disorders, and even nutritional deficiencies can produce symptoms that mimic polio. This overlapping symptom profile can lead to misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis.
- Sensitivity and Specificity: The sensitivity and specificity of different diagnostic tests vary. Sensitivity refers to the test’s ability to correctly identify those with the condition, while specificity indicates its ability to correctly identify those without the condition. A test with high sensitivity but low specificity might yield many false positives, while a test with high specificity but low sensitivity might miss some cases.
- Development of Diagnostic Tools: Developing accurate and reliable diagnostic tools for polio-like illnesses presents a significant challenge. This is partly due to the complex nature of these conditions and the lack of readily available and specific markers. Furthermore, the limited availability of standardized diagnostic protocols and guidelines can impact the consistency of the diagnostic process.
Comparative Analysis of Diagnostic Tests
Comparing the sensitivity and specificity of various diagnostic tests for similar conditions is crucial for selecting the most appropriate approach.
| Diagnostic Technique | Sensitivity | Specificity | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Evaluation | Moderate | Low | Relies on subjective assessment; highly dependent on experience of clinician |
| CSF Analysis | Variable | Variable | May reveal markers but not always specific; may yield false positives/negatives |
| Neuroimaging (MRI) | High | Moderate | Useful for identifying structural abnormalities but not always conclusive |
| Molecular Testing | High | High | Specific for certain pathogens but may not be available in all settings |
Need for Improved Diagnostic Tools
The development of more sophisticated and specific diagnostic tools is crucial for enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of diagnosing polio-like illnesses.The need for improved diagnostic tools and procedures is underscored by the limitations of existing methods. This necessitates further research and development to create tests that are more sensitive, specific, and readily accessible in diverse healthcare settings.
Clinical Presentation and Symptoms: Detecting Polio Like Disease Is Difficult For Doctors
Pinpointing polio-like diseases relies heavily on recognizing the subtle yet diverse array of symptoms. The complexity arises from the significant overlap between these illnesses and other neurological conditions, making accurate diagnosis a challenge. Distinguishing polio from similar conditions necessitates a thorough understanding of symptom variability, patient history, and the importance of a complete physical examination.
Common Symptoms Associated with Polio-like Diseases
The symptoms of polio-like diseases often present in a manner that mimics other viral infections. Early indicators can include flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache, and muscle aches. These symptoms can be misleading and lead to misdiagnosis, emphasizing the crucial role of careful observation and comprehensive medical evaluation.
Variability in Symptom Presentation
Individual responses to these illnesses vary considerably. Some patients may experience only mild, flu-like symptoms, while others develop more severe neurological manifestations. The severity and duration of symptoms can also fluctuate, complicating the diagnostic process. Factors like age, pre-existing conditions, and the specific causative agent contribute to this variability. For instance, a child might present with fever and mild lethargy, whereas an adult might exhibit severe muscle weakness and paralysis.
Importance of Patient History and Clinical Context
Understanding the patient’s medical history is paramount. Factors such as recent travel, exposure to individuals with similar illnesses, and prior medical conditions provide crucial context. A detailed history can help identify potential risk factors and pinpoint possible causes. A thorough understanding of the patient’s history, including family history of neurological disorders, and any exposure to contaminated water or food, provides critical clues to the diagnosis.
Symptoms Mimicking Polio
Several symptoms can mimic polio, further complicating the diagnosis. These symptoms include:
- Muscle weakness, especially in the limbs, is a hallmark symptom that can be mistaken for polio.
- Paralysis, often affecting one or more limbs, can also indicate a polio-like illness.
- Pain in the muscles and joints, a common feature of various viral infections, can be mistaken for polio.
- Headache and fever are frequently associated with viral infections, potentially mimicking polio.
These symptoms require further investigation to differentiate from polio. It is crucial to remember that these symptoms can occur in other neurological conditions, emphasizing the necessity for thorough diagnostic evaluation.
Importance of Thorough Physical Examinations
Physical examinations play a vital role in the diagnostic process. A neurologist can assess muscle strength, reflexes, and sensory function. The physical examination aids in identifying specific patterns of weakness or paralysis that may suggest a particular diagnosis. A thorough neurological examination is crucial to assess reflexes, muscle tone, and coordination, aiding in the differential diagnosis of polio-like conditions.
Table of Common Symptoms and Possible Causes
| Symptom | Possible Causes |
|---|---|
| Fever | Viral infections, bacterial infections, inflammatory conditions |
| Headache | Viral infections, bacterial infections, meningitis, migraine |
| Muscle weakness | Polio, Guillain-Barré syndrome, other neurological disorders, myositis |
| Paralysis | Polio, Guillain-Barré syndrome, spinal cord injury, transverse myelitis |
| Pain in muscles and joints | Viral infections, bacterial infections, musculoskeletal injuries, inflammatory conditions |
This table illustrates the diverse range of conditions that can present with similar symptoms. Careful consideration of the complete clinical picture is essential for accurate diagnosis.
Role of Imaging Techniques in Diagnosis
Imaging techniques play a crucial role in the diagnostic process of polio-like diseases, especially when distinguishing them from other neurological conditions with overlapping symptoms. While clinical evaluation and laboratory tests are essential, imaging can provide crucial anatomical information, helping to identify potential neurological involvement and pinpoint the location and extent of any damage. This information is vital in guiding treatment decisions and monitoring disease progression.Imaging modalities can reveal subtle changes in the central nervous system (CNS) that might not be apparent through physical examination alone.
These changes, such as inflammation or structural abnormalities, can offer valuable insights into the underlying pathology, potentially differentiating polio-like conditions from other causes of paralysis or neurological dysfunction.
Imaging Techniques Used in Polio-like Disease Diagnosis
Various imaging techniques are employed to assess neurological involvement in suspected polio-like diseases. These techniques offer different levels of detail and insights into the structure and function of the brain and spinal cord.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI is a powerful non-invasive technique that produces detailed images of the brain and spinal cord. It excels at visualizing soft tissues, allowing for the identification of edema, inflammation, and lesions in the CNS. The high resolution and multiplanar capabilities of MRI make it a valuable tool for assessing the extent and location of neurological damage.
MRI is particularly useful in detecting abnormalities in the grey and white matter, characteristic of certain neurological conditions that might mimic polio. Furthermore, MRI can show evidence of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) abnormalities, which can be indicators of specific pathologies.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: CT scans provide cross-sectional images of the brain and spinal cord. While not as detailed as MRI, CT scans are valuable for detecting bony abnormalities, calcifications, or large hemorrhages that might be associated with certain neurological conditions. CT scans are often used as an initial imaging modality to rule out more severe structural issues, such as fractures or tumors, before proceeding to MRI for a more detailed analysis.
The speed of CT scanning makes it useful in emergency situations, providing rapid assessment of possible neurological damage.
- Electroencephalography (EEG): EEG measures the electrical activity of the brain. Although not a structural imaging technique, EEG can be helpful in assessing the function of the brain and identifying abnormal electrical patterns. These abnormal patterns might indicate seizures or other neurological disturbances that could accompany or mimic polio-like symptoms. This helps in differentiating the conditions based on their electrophysiological characteristics.
Limitations of Imaging in Differentiating Polio and Similar Conditions
Imaging techniques, while valuable, have limitations in definitively distinguishing polio from other conditions with similar presentations. The specific patterns of neurological involvement can overlap, and the images themselves might not always provide conclusive evidence of the exact cause of the observed abnormalities. Furthermore, the presence of similar findings in imaging does not definitively confirm polio.
- Overlap in Imaging Findings: Certain imaging findings, such as inflammation or lesions in the spinal cord, can be observed in various neurological conditions. This overlap makes it challenging to definitively identify polio based solely on imaging results.
- Non-Specificity of Imaging: Imaging findings may not be specific enough to pinpoint the precise nature of the neurological condition. Similar patterns of abnormalities can be seen in different conditions, requiring a comprehensive clinical evaluation in conjunction with laboratory tests.
- Severity of Disease: In some instances, the initial imaging findings might not reflect the full extent of the disease. This is particularly relevant in the early stages of certain conditions, when subtle abnormalities may not be readily apparent on imaging.
Comparison of Imaging Modalities
| Imaging Modality | Suitability for Polio-like Diseases | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| MRI | High | Excellent soft tissue detail, multiplanar imaging, identification of subtle changes | Can be expensive, longer scan times |
| CT | Moderate | Fast acquisition, good for bony structures, detects large abnormalities | Limited soft tissue detail, potentially less sensitive for subtle changes |
| EEG | Low | Assesses brain electrical activity, helpful in identifying seizures | Does not provide anatomical information, not specific for polio |
Laboratory Tests and Their Interpretations
Pinpointing a polio-like illness requires a multi-faceted approach, and laboratory tests play a crucial role in differentiating it from other neurological conditions. These tests can reveal specific markers or patterns that point towards a possible polio-like etiology, but it’s essential to remember that no single test can definitively diagnose polio. The interpretation of results must always consider the patient’s clinical presentation, medical history, and epidemiological context.
Types of Laboratory Tests
A battery of laboratory tests is often employed to investigate suspected polio-like illnesses. These tests aim to identify specific indicators of viral infection, nerve damage, or other potential causes. Commonly used tests include:
- Viral Culture: This method involves isolating and cultivating the suspected virus in a laboratory setting. If a poliovirus is isolated, it confirms the diagnosis. However, this process can be time-consuming and may not be successful for all viruses. This is crucial because a definitive viral identification helps differentiate between different polio-like conditions.
- Molecular Testing (PCR): Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a highly sensitive technique that detects the genetic material of a virus. It’s used to identify the presence of poliovirus RNA or other potential pathogens. This method is quicker than viral culture and often more sensitive for detecting viral infections.
- Serological Testing: These tests examine the patient’s blood serum for antibodies against specific viruses, including poliovirus. The presence or absence of these antibodies can suggest a past or current infection. Antibody titers, or levels, can provide clues about the severity and duration of the infection. For example, a significantly elevated antibody titer against poliovirus might indicate a recent infection or vaccination.
- CSF Analysis (Cerebrospinal Fluid): Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis is used to evaluate the composition of the fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Elevated levels of specific proteins, such as immunoglobulin G (IgG), can suggest inflammation in the central nervous system, which is sometimes seen in polio-like illnesses.
Interpreting Laboratory Findings
Interpreting laboratory results is crucial to differentiating polio-like conditions from similar neurological disorders. For example, a positive PCR test for poliovirus, coupled with clinical symptoms like flaccid paralysis, would strongly suggest polio. However, similar symptoms can arise from other viral infections, such as enteroviruses. Distinguishing between these possibilities often requires a combination of laboratory tests and a comprehensive clinical evaluation.
Limitations of Laboratory Tests
While laboratory tests are valuable tools, they have limitations. Sometimes, the results may be inconclusive or nonspecific, requiring further investigation. For instance, a negative PCR test for poliovirus does not definitively rule out the disease, especially in the early stages of infection. Moreover, the sensitivity and specificity of laboratory tests can vary depending on the method used and the presence of other co-infections.
Comprehensive Testing Protocols
A comprehensive testing protocol is essential for accurate diagnosis. It involves a combination of laboratory tests, imaging studies, and detailed clinical evaluation. This approach is crucial because a single test might not always provide enough evidence for a definitive diagnosis, especially given the complexity of neurological conditions that may mimic polio-like symptoms. The testing strategy must adapt to the specific clinical presentation of the patient.
Table of Possible Laboratory Results and Their Implications
| Laboratory Result | Possible Implications |
|---|---|
| Positive PCR for poliovirus | Strong indication of polio infection. |
| Negative PCR for poliovirus, but positive for other enteroviruses | Possible enteroviral infection mimicking polio. Further testing may be required. |
| Elevated CSF protein levels | Suggests inflammation in the central nervous system. |
| Low antibody titers against poliovirus | May indicate a past infection or recent exposure, but more data needed to rule out other factors. |
| No specific markers found | Possible other neurological condition or infection, further investigations needed. |
Differential Diagnosis Considerations
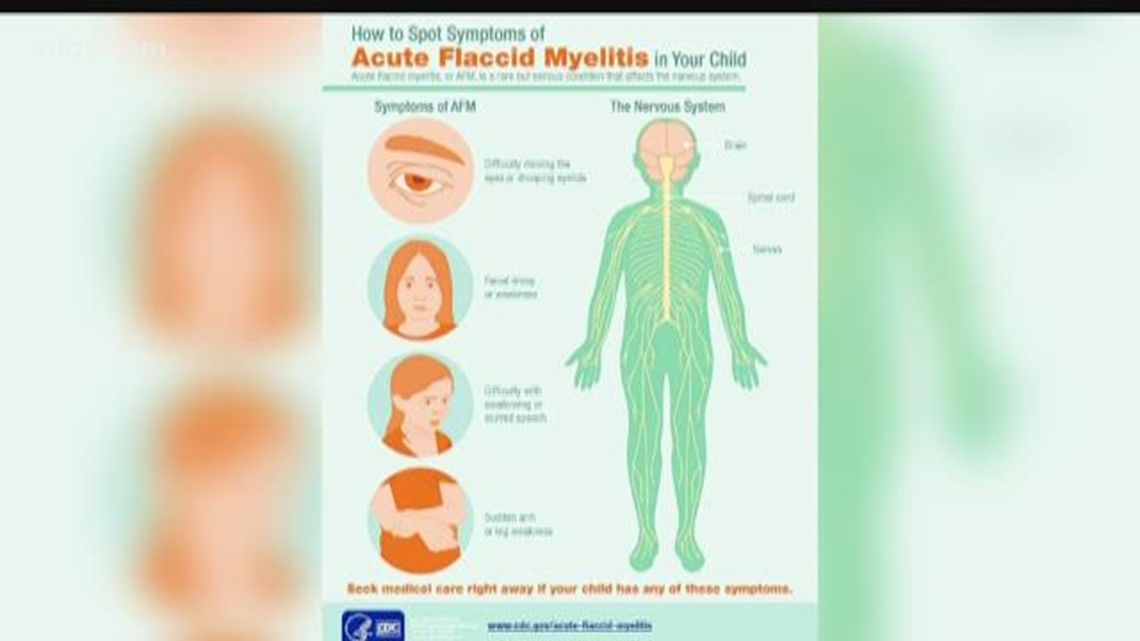
Pinpointing the precise cause of polio-like symptoms is crucial for effective treatment. Many neurological conditions can mimic polio’s characteristic muscle weakness and paralysis. Accurately differentiating polio from these other possibilities is vital for ensuring the correct course of action is taken. Misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate interventions and delay the appropriate treatment for the actual underlying condition.The diagnostic process often involves a comprehensive evaluation, meticulously comparing the patient’s symptoms and clinical presentation to those of other potential diseases.
This process necessitates a multidisciplinary approach, drawing on the expertise of neurologists, infectious disease specialists, and other relevant medical professionals.
Identifying Mimicking Conditions, Detecting polio like disease is difficult for doctors
Several diseases can present with symptoms similar to polio, making accurate diagnosis challenging. These conditions include, but are not limited to, Guillain-Barré syndrome, transverse myelitis, and various types of viral or bacterial infections affecting the nervous system. Other potential causes include metabolic disorders, certain types of cancers, and adverse drug reactions. Differentiating polio from these conditions is paramount to ensuring appropriate treatment.
Importance of Ruling Out Alternative Diagnoses
Correctly ruling out other potential causes is essential to prevent misdiagnosis and to initiate the most effective treatment. A thorough understanding of the symptoms and characteristics of various neurological conditions is vital in this process. This is because treatment approaches differ significantly based on the underlying condition. Incorrectly identifying the cause of the symptoms could lead to inappropriate treatments or delays in receiving the right intervention.
Comparing Clinical Presentations
The clinical presentations of polio and other conditions can overlap. However, subtle differences in the progression of symptoms, associated symptoms, and the patient’s medical history can provide crucial clues. For instance, Guillain-Barré syndrome typically presents with ascending paralysis, whereas polio can manifest with flaccid paralysis. Careful observation of the pattern and location of muscle weakness is essential.
Detailed analysis of the patient’s history is equally important in distinguishing polio from other conditions.
Steps in Differentiating Polio from Other Diseases
A multi-step process is involved in differentiating polio from other conditions. This process involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging techniques. First, a detailed patient history is obtained, including the onset, progression, and distribution of symptoms. Neurological examination is critical to assess the level and extent of muscle weakness, reflexes, and sensory changes. Specific laboratory tests, like cerebrospinal fluid analysis, can help identify specific markers associated with different diseases.
Imaging techniques, such as MRI, may reveal structural abnormalities in the spinal cord or brain. The results of these tests are crucial for forming a differential diagnosis.
Doctors face a tough challenge in diagnosing polio-like illnesses. Symptoms can be vague and mimic other conditions, making early detection tricky. This difficulty highlights just how hard self-care is self care is hard when it comes to something as serious as a potential polio-like disease. Ultimately, the complex nature of the disease makes early detection a real hurdle for medical professionals.
The Need for a Multidisciplinary Approach
Given the complexity of the differential diagnosis, a multidisciplinary approach is crucial. Neurologists, infectious disease specialists, and other relevant medical professionals should collaborate to analyze the patient’s case comprehensively. Combining different perspectives and expertise allows for a more thorough evaluation and minimizes the risk of misdiagnosis. The combined knowledge of these specialists is critical for reaching an accurate diagnosis.
Doctors face a tough challenge in spotting polio-like illnesses. It’s tricky to distinguish them from other ailments, which is why knowing how to tell if the hand sanitizer you’re buying is safe here is important too, as proper hygiene plays a role in preventing potential health issues. Ultimately, diagnosing such conditions accurately still requires careful observation and testing by medical professionals.
Differential Diagnosis Table
| Condition | Key Symptoms | Distinguishing Features |
|---|---|---|
| Polio | Flaccid paralysis, muscle weakness, fever | Often preceded by a viral infection; paralysis typically affects one limb or one side of the body |
| Guillain-Barré Syndrome | Ascending paralysis, sensory changes | Often follows a viral infection; characterized by rapidly progressing weakness |
| Transverse Myelitis | Paralysis, sensory loss, pain | Inflammation of the spinal cord; symptoms can appear abruptly |
| Other Viral Infections | Fever, muscle aches, headache | Varying symptoms depending on the specific virus |
Public Health Implications
Diagnosing polio-like illnesses can be a complex challenge, impacting public health responses in various ways. Difficulties in distinguishing these illnesses from other conditions can lead to delays in appropriate treatment and potentially hinder efforts to contain outbreaks. This delay in diagnosis can have severe consequences, both for individual patients and for the broader community.The consequences of delayed diagnosis and intervention extend beyond individual suffering.
Early diagnosis and intervention are critical in preventing complications and long-term disability. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the overall burden of the disease on healthcare systems and communities.
Impact on Public Health Measures
Effective public health measures rely heavily on accurate and timely diagnoses. When diagnoses are uncertain or delayed, the ability to implement targeted interventions, such as contact tracing and vaccination campaigns, is compromised. This can result in a slower response to outbreaks, allowing the disease to spread further.
Significance of Rapid and Accurate Diagnosis in Managing Outbreaks
Rapid and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effectively managing polio-like disease outbreaks. A swift and accurate diagnosis allows for immediate isolation of cases, contact tracing to identify and isolate potential secondary cases, and the implementation of targeted preventive measures. This proactive approach can dramatically reduce the spread of the disease and prevent widespread complications.For instance, a rapid diagnosis of a polio-like illness in a community setting allows for immediate contact tracing, potentially preventing dozens of secondary cases.
This rapid response is vital in containing the outbreak and limiting the overall impact on the community.
Examples of How Diagnostic Challenges Impact Public Health Responses
Diagnostic challenges can lead to delays in implementing appropriate public health measures. Consider a situation where a cluster of neurological symptoms resembling polio is reported in a school. If the diagnosis is delayed due to difficulty distinguishing the symptoms from other conditions, the school might not be immediately quarantined, potentially leading to further spread of the disease. This highlights the importance of clear diagnostic criteria and readily available testing methods.
Public Health Measures for Managing Polio-like Disease Outbreaks
The table below Artikels key public health measures to be implemented during polio-like disease outbreaks. These measures are designed to limit the spread of the illness, protect vulnerable populations, and prevent long-term complications.
| Public Health Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Rapid and accurate diagnosis | Implementing diagnostic protocols that prioritize speed and accuracy in identifying suspected cases is crucial. This involves using readily available and reliable diagnostic tools and ensuring well-trained personnel are available to conduct these tests. |
| Contact tracing | Identifying and monitoring individuals who have been in contact with confirmed cases is essential for interrupting transmission. This involves rigorous contact tracing procedures to ensure prompt identification and isolation of potentially infected individuals. |
| Quarantine and isolation | Restricting the movement of confirmed cases and their contacts is vital to prevent further transmission. This includes appropriate isolation and quarantine procedures to limit the risk of spread to the wider community. |
| Vaccination campaigns | Implementing targeted vaccination campaigns for susceptible populations, including those in close contact with confirmed cases, is a key preventive measure. These campaigns should be tailored to the specific circumstances and risks posed by the outbreak. |
| Public awareness and education | Educating the public about the symptoms, prevention, and importance of reporting suspected cases is essential. This can encourage early reporting and prompt response to potential outbreaks. |
Future Directions in Diagnosis
The quest for a more accurate and rapid diagnosis of polio-like diseases continues to drive research and innovation. Current methods, while valuable, often present challenges in timely and definitive identification. This necessitates a proactive approach to developing cutting-edge diagnostic tools and strategies.
Current Research Efforts
Researchers are actively exploring various avenues to enhance diagnostic capabilities. This includes leveraging advancements in molecular biology, developing point-of-care tests, and improving imaging techniques. A multi-faceted approach is crucial to address the complexity of diagnosing polio-like diseases.
Novel Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
Numerous innovative tools are emerging in the field of medical diagnostics. These include rapid molecular assays capable of detecting specific viral or bacterial signatures associated with polio-like illnesses. These advancements are crucial for providing faster diagnoses, allowing for timely interventions and better patient outcomes.
Advancements in Molecular Diagnostics
Molecular diagnostics are experiencing significant progress. Techniques like real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) are becoming more sophisticated and sensitive, enabling the detection of minute amounts of viral or bacterial genetic material. This allows for faster and more accurate identification of the causative agent.
Rapid and Accurate Diagnostic Tests
The development of rapid and accurate diagnostic tests is paramount. These tests should be readily available, easy to perform, and provide results within a short timeframe, preferably in the hours, rather than days. This is essential for timely treatment initiation and disease containment.
Improving Diagnostic Accuracy
Further research is needed to refine the diagnostic accuracy of existing methods and improve the specificity of tests. This requires a thorough understanding of the diverse clinical presentations and subtle symptoms associated with polio-like illnesses. Developing comprehensive diagnostic panels that can distinguish between various causes of paralysis is critical.
Promising Areas of Research and Development
| Area of Research | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Rapid Molecular Assays | Development of tests based on CRISPR-Cas systems or loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for faster detection of pathogens. | Faster turnaround time for diagnoses, enabling prompt treatment initiation and disease control. |
| Point-of-Care Diagnostics | Development of portable, user-friendly devices for on-site testing, particularly in resource-limited settings. | Improved accessibility to diagnostics, especially in remote areas, leading to quicker intervention and better patient outcomes. |
| Multiplex Diagnostics | Simultaneous detection of multiple pathogens using advanced technologies, including microfluidic platforms. | Precise identification of the causative agent, aiding in targeted therapy and potentially reducing misdiagnosis. |
| Integration of Imaging Techniques | Combining imaging modalities with molecular diagnostics to provide a more comprehensive evaluation of the disease process. | Improved understanding of disease progression, allowing for more accurate staging and personalized treatment plans. |
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Utilizing AI algorithms to analyze patient data, including clinical symptoms, imaging results, and laboratory findings, to assist in diagnostic decision-making. | Improved diagnostic accuracy and efficiency by identifying subtle patterns in data that might be missed by human clinicians. |
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, the difficulty in diagnosing polio-like diseases underscores the critical need for improved diagnostic tools and procedures. A multidisciplinary approach, incorporating clinical expertise, advanced imaging, and comprehensive laboratory testing, is essential. Further research into novel diagnostic techniques and a heightened awareness of the nuances in symptom presentation will ultimately lead to more accurate and timely diagnoses, improving patient outcomes and public health measures.
