Viral nurse things you can do to avoid flu, from hand hygiene to vaccination strategies, offer crucial insights for staying healthy. This guide explores various preventive measures, equipping you with the knowledge to protect yourself and your community.
This article delves into practical steps you can take to combat the flu. We’ll examine essential preventive measures, including handwashing techniques, vaccination strategies, and environmental hygiene practices, empowering you to make informed decisions about your well-being.
Introduction to Flu Prevention
The flu, or influenza, is a contagious respiratory illness that can range from mild to severe. It’s caused by influenza viruses and spreads easily through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. While often seasonal, the flu can occur year-round, posing a significant public health concern. Preventing its spread is crucial, especially within vulnerable populations.Nurses play a pivotal role in community flu prevention.
They educate individuals about preventative measures, administer vaccinations, and provide care to those who contract the virus. Their proactive approach to health promotion ensures the well-being of their communities. Effective communication and education are key to empowering individuals to take preventative actions. Misconceptions about the flu and its prevention can lead to preventable illnesses. A proactive approach to flu prevention is essential to minimize the impact of this virus.
Understanding the Flu
The flu is a highly contagious respiratory illness, primarily transmitted through airborne droplets released when infected individuals cough, sneeze, or talk. This transmission method makes it highly contagious in enclosed spaces. The virus can survive on surfaces for a period of time, further increasing the risk of transmission. It’s important to understand the transmission process to effectively implement preventative measures.
Importance of Prevention
Proactive measures are crucial in mitigating the impact of the flu on individuals and communities. Preventive strategies can significantly reduce the incidence of the flu, limiting its spread and associated complications. Preventive measures include vaccination, hand hygiene, and maintaining good respiratory hygiene. These simple steps can significantly reduce the risk of infection. Proactive measures are particularly vital for high-risk populations.
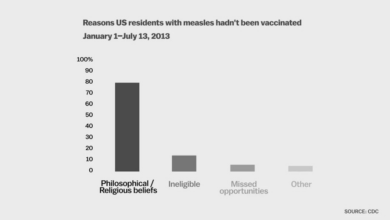
Common Misconceptions about the Flu
Many misconceptions surround the flu and its prevention. Some people believe that the flu is just a bad cold, failing to recognize the severity of the virus. Others believe that only certain people are susceptible, ignoring the fact that everyone is at risk. Another common misconception is that the flu only affects children and the elderly, which is inaccurate.
Role of Nurses in Flu Prevention
Nurses are essential in educating communities about flu prevention. They can provide information about vaccination schedules, hand hygiene techniques, and the importance of respiratory etiquette. Their direct interaction with individuals allows for personalized advice tailored to specific needs. Effective communication is critical for successfully promoting flu prevention strategies. Through education, nurses empower individuals to take control of their health and the health of their communities.
Proactive Approach to Flu Prevention
A proactive approach to flu prevention is paramount. This involves taking steps to protect yourself and others from the virus. This includes regular handwashing, covering coughs and sneezes, and getting vaccinated. Regular cleaning of frequently touched surfaces is also a crucial part of this approach. By taking these precautions, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of infection and protect those around them.
This proactive approach encompasses not just individual actions but also community-wide efforts.
Hand Hygiene Practices
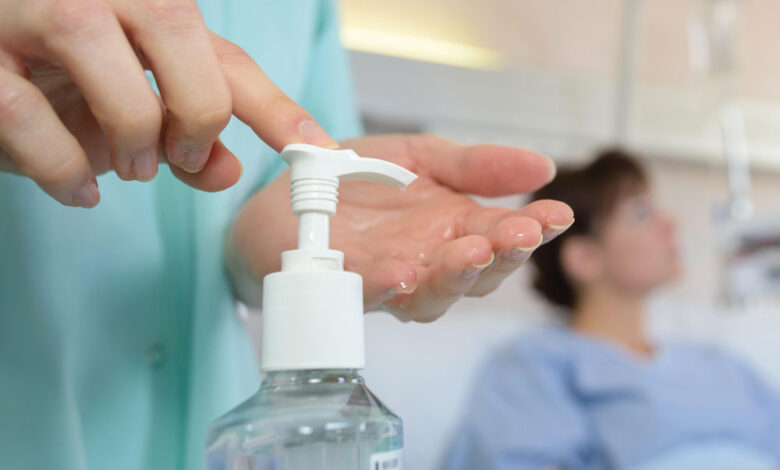
Proper hand hygiene is the cornerstone of preventing the spread of influenza and other contagious illnesses. By diligently practicing effective handwashing and using hand sanitizer, we significantly reduce the risk of contracting and transmitting the flu virus. This proactive approach protects individuals and safeguards communities from outbreaks.Handwashing and hand sanitizer use are crucial barriers against the flu virus.
Flu viruses can survive on surfaces for hours, and transmission often occurs through contact with contaminated hands. Consistent hand hygiene practices, especially in high-traffic areas or during flu season, are vital in preventing the spread of this highly contagious virus.
The Crucial Role of Hand Hygiene
Hand hygiene plays a critical role in preventing the transmission of the flu virus. The flu virus is easily transmitted through direct contact with contaminated surfaces or through the exchange of respiratory droplets. Frequent and thorough handwashing, and the use of hand sanitizer when soap and water aren’t readily available, drastically reduce the risk of transmission. This simple practice can be a powerful tool in protecting individuals and communities from the flu.
Effective Handwashing Procedures
Proper handwashing is a fundamental step in preventing the spread of infectious diseases. Follow these steps for effective handwashing:
- Wet your hands thoroughly with clean, running water (warm or cold). Using warm water can improve the effectiveness of handwashing, especially if it is used in conjunction with soap.
- Apply enough liquid soap to cover all surfaces of your hands.
- Rub your hands together vigorously for at least 20 seconds. Focus on all areas, including the backs of your hands, between your fingers, and under your fingernails. A good way to track time is by singing “Happy Birthday” twice.
- Rinse your hands thoroughly under running water.
- Dry your hands completely with a clean towel or air dryer. Drying thoroughly prevents the spread of bacteria and viruses.
Effective Hand Sanitizer Use
Hand sanitizer is a valuable alternative to handwashing when soap and water are unavailable. To use hand sanitizer effectively:
- Ensure the sanitizer contains at least 60% alcohol. This is the minimum concentration needed to effectively kill most flu viruses.
- Apply a generous amount of sanitizer to cover all surfaces of your hands.
- Rub your hands together until they are completely dry. This usually takes about 15-30 seconds.
Comparing Hand Hygiene Methods
While both handwashing and hand sanitizer use are effective, they differ in their effectiveness and suitability in various situations. Handwashing with soap and water is generally more effective at removing visible dirt and germs. Hand sanitizer is more convenient in situations where water isn’t available, but it’s less effective at removing dirt and grease. Using hand sanitizer is ideal in between activities when you cannot wash your hands with soap and water.
Hand Hygiene for Healthcare Workers
For healthcare workers, particularly nurses, meticulous hand hygiene is paramount. Nurses are often exposed to patients with infectious diseases, and proper hand hygiene practices are essential to prevent the spread of illnesses, including the flu, among patients and staff. Strict adherence to hand hygiene protocols minimizes the risk of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). Maintaining a high standard of hand hygiene is critical to safeguarding the health of both patients and healthcare professionals.
Hand Hygiene Scenarios and Appropriate Responses
| Scenario | Appropriate Response |
|---|---|
| Patient with suspected flu symptoms approaches the nurse’s station. | Immediately sanitize hands with hand sanitizer. If possible, wear a mask and/or gloves. |
| Nurse is assisting a patient with a wound. | Thoroughly wash hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds before and after the procedure. |
| Nurse is in a public area and water/soap isn’t available. | Use hand sanitizer immediately. |
| Nurse has just touched a frequently touched surface in a hospital. | Immediately sanitize hands with hand sanitizer. |
Vaccination Strategies

Influenza vaccination is a cornerstone of flu prevention, offering significant protection against the virus. Understanding the various vaccine types, their effectiveness, and appropriate scheduling is crucial for maximizing individual and community health benefits. This section delves into the details of vaccination strategies, aiming to empower readers with the knowledge to make informed decisions about protecting themselves and their loved ones.
Effectiveness of Influenza Vaccines
Influenza vaccines are highly effective in reducing the risk of contracting the flu, particularly severe cases. Studies consistently demonstrate a substantial reduction in influenza-related hospitalizations and deaths among vaccinated individuals. The effectiveness varies annually, depending on the specific strains circulating and the degree of immune response in the population. Factors such as age, underlying health conditions, and the specific vaccine formulation also play a role in individual responses to vaccination.
Overall, vaccination remains a critical strategy in mitigating the impact of influenza outbreaks.
Types of Influenza Vaccines and Target Groups
Several types of influenza vaccines are available, each with varying compositions and target groups. The most common types include inactivated influenza vaccines (IIVs), live attenuated influenza vaccines (LAIVs), and recombinant influenza vaccines (RIVs).
- Inactivated Influenza Vaccines (IIVs): These vaccines contain inactivated influenza viruses, making them safe for most individuals, including pregnant women and those with weakened immune systems. They are generally recommended for individuals aged 6 months and older.
- Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccines (LAIVs): These vaccines contain live, weakened influenza viruses. While highly effective, they are not suitable for individuals with compromised immune systems or certain medical conditions. They are generally recommended for healthy individuals aged 2 to 49 years.
- Recombinant Influenza Vaccines (RIVs): These vaccines utilize a specific protein from the influenza virus to stimulate an immune response. They are generally well-tolerated and are often recommended for individuals with egg allergies, as they are produced without egg-based ingredients.
Vaccine Scheduling and Recommendations
Annual influenza vaccination is highly recommended for most individuals, particularly those at higher risk of complications. Vaccination schedules typically begin in the fall, aligning with the flu season’s onset. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and other health organizations provide specific recommendations based on age, health conditions, and other factors. Adhering to recommended vaccination schedules ensures optimal protection throughout the influenza season.
Benefits and Potential Side Effects of Influenza Vaccines
Influenza vaccination offers significant benefits, including reduced risk of influenza illness, hospitalization, and death. Vaccination also protects individuals from spreading the virus to others. While generally safe, some individuals may experience mild side effects such as soreness, redness, or swelling at the injection site. Rarely, more serious side effects may occur, but these are typically uncommon. Consulting a healthcare provider can help address any concerns or questions about potential side effects.
Successful Vaccination Campaigns and Their Impact
Numerous successful influenza vaccination campaigns have demonstrated the significant public health impact of widespread vaccination efforts. These campaigns often target vulnerable populations, like the elderly and those with chronic health conditions, to maximize protection. Increased vaccination rates in these groups contribute to a significant decrease in influenza-related illnesses and hospitalizations. The successful implementation of vaccination campaigns demonstrates the critical role of proactive public health strategies in mitigating the impact of influenza outbreaks.
Comparison of Vaccine Options
| Vaccine Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Inactivated Influenza Vaccine (IIV) | Safe for most individuals, including those with weakened immune systems, and pregnant women. Widely available. | Generally less effective than live attenuated vaccines in some individuals, may require annual booster shots. |
| Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccine (LAIV) | Potentially higher effectiveness in some individuals. | Not suitable for immunocompromised individuals or those with certain medical conditions. May cause mild side effects in some. |
| Recombinant Influenza Vaccine (RIV) | Suitable for individuals with egg allergies. Generally well-tolerated. | May be less effective than other types in some cases. |
Environmental Hygiene Measures: Viral Nurse Things You Can Do To Avoid Flu
Protecting yourself and others from the flu isn’t just about personal hygiene; it’s also about maintaining a healthy environment. Proper environmental hygiene plays a crucial role in minimizing the spread of influenza viruses. By focusing on cleaning and disinfecting frequently touched surfaces, we can significantly reduce the risk of infection.Environmental hygiene involves proactive measures to eliminate or reduce the presence of pathogens in the environment.
This is especially important in healthcare settings and other areas where large numbers of people congregate, as these environments can harbor and spread influenza viruses. By consistently practicing proper cleaning and disinfection techniques, we can safeguard the health of individuals and prevent the spread of illness.
Washing your hands frequently is a key viral nurse tip for avoiding the flu, but did you know that similar mental health strategies can help manage conditions like mania in bipolar? Understanding the triggers and symptoms of mania in bipolar, as outlined in this helpful guide, what is mania in bipolar , can be just as crucial as practicing good hygiene.
So, next time you’re feeling under the weather, remember these simple but effective viral nurse strategies to stay healthy!
Cleaning and Disinfecting Frequently Touched Surfaces
Regular cleaning and disinfection of surfaces are essential for preventing the spread of influenza viruses. These surfaces, often used by multiple people, act as reservoirs for the virus, potentially transmitting it to others. The goal is to remove visible dirt, debris, and germs from these surfaces, followed by a disinfectant application to kill any remaining pathogens.
- High-traffic areas like doorknobs, light switches, countertops, and handrails are prime targets for contamination. Cleaning and disinfecting these areas frequently can significantly reduce the risk of spreading the flu.
- Focus on regularly touched surfaces in common areas. This includes shared equipment, such as phones, keyboards, and desks, in workplaces, classrooms, and public spaces.
Use of Disinfectants and Dilution Ratios
Proper disinfectant use is critical for effective flu prevention. Different disinfectants have varying efficacy and require specific dilution ratios for optimal performance. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the correct dilution. Using the wrong concentration may compromise the disinfectant’s effectiveness.
Using a diluted bleach solution (1/10 dilution) is effective for some surfaces. Always check the product label for specific instructions. Never mix disinfectants or use them in ways not specified by the manufacturer.
- Using a bleach solution (1:10 dilution) can be effective on some hard, non-porous surfaces. A dilution of 1 part bleach to 10 parts water is usually recommended. However, always follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Choose disinfectants specifically registered by the EPA for use against influenza viruses.
Crucial Areas Requiring Regular Disinfection in Healthcare Settings
Healthcare settings are particularly susceptible to influenza virus transmission due to the close contact between patients and staff. Therefore, rigorous disinfection protocols are crucial.
- Exam rooms, waiting areas, and restrooms in hospitals and clinics require regular cleaning and disinfection to prevent the spread of viruses.
- Equipment frequently touched by patients, such as stethoscopes, blood pressure cuffs, and bedside tables, should be disinfected after each use. This is a vital practice to prevent cross-contamination.
Effective Environmental Hygiene Practices in Various Settings
Implementing effective environmental hygiene practices is crucial across various settings. The methods should be adjusted based on the specific environment and the type of surfaces present.
- Schools: Regular cleaning and disinfection of classrooms, restrooms, and common areas, with particular attention to high-touch surfaces, are essential. Frequent handwashing stations and reminders about hygiene practices are vital.
- Offices: Cleaning and disinfecting frequently touched surfaces like keyboards, desks, and telephones is essential. Promoting hand hygiene and encouraging employees to stay home when ill are crucial.
Recommended Cleaning Schedules for Different Areas
A well-defined cleaning schedule helps maintain a sanitary environment. The frequency should be based on the level of use and the potential for contamination.
| Area | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Exam rooms (healthcare) | After each patient use |
| Waiting areas (healthcare) | Twice daily |
| Restrooms (healthcare) | Every 2-4 hours |
| Classrooms (schools) | Once daily |
| Common areas (offices) | Twice daily |
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Protecting yourself and others from the flu is crucial, and a key component of this protection involves the strategic use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). Proper use of PPE significantly reduces the risk of transmission, especially in high-risk environments. This section delves into the various types of PPE, their appropriate application, and the importance of following correct procedures for donning and doffing.Understanding the different types of PPE, their correct use, and the specific situations where they are necessary is vital in preventing flu transmission.
Properly selected and used PPE acts as a crucial barrier against the spread of the virus, safeguarding both individuals and the community.
Knowing viral nurse tips to dodge the flu is crucial, but regular health check-ups are just as important. Taking preventative measures like frequent handwashing and getting enough rest are great, but understanding your overall health is key. For example, knowing your blood pressure or cholesterol levels through 5 important health tests can help you make informed decisions about your well-being, even if you’re diligently following viral nurse advice for flu prevention.
Ultimately, a holistic approach to health, combining preventative measures with regular check-ups, is the best way to stay healthy.
Types of PPE for Flu Prevention
Proper selection of PPE is essential for effective flu prevention. Different types of PPE offer varying levels of protection, and the choice depends on the specific situation and potential exposure risks. A critical aspect of using PPE effectively is understanding when and how to apply it correctly.
Washing your hands regularly and getting enough sleep are key viral nurse tips for avoiding the flu, but it’s also worth considering how broader policies, like trump policies could harm your health , might indirectly affect your well-being. Prioritizing good hygiene, along with vaccinations and healthy lifestyle choices, are still the best ways to protect yourself from illness.
Masks
Masks are a fundamental form of PPE for flu prevention. They act as a physical barrier, preventing the spread of respiratory droplets containing the flu virus. Surgical masks are often used in healthcare settings, while N95 respirators offer a higher level of filtration. Different situations call for different types of masks. For example, a surgical mask might suffice in a general office environment, whereas an N95 respirator might be necessary in a hospital or other high-risk area.
Gloves
Gloves, like masks, provide a barrier against the spread of infectious agents. Medical examination gloves and disposable nitrile gloves are commonly used to protect against contamination. Gloves are especially important when handling potentially contaminated surfaces or when caring for someone with the flu. The proper selection and use of gloves are essential to prevent the transmission of the virus.
Proper Donning and Doffing Procedures
Correct procedures for putting on (donning) and taking off (doffing) PPE are crucial for ensuring effective protection and preventing contamination. Incorrect procedures can lead to the spread of the virus. Thorough and consistent adherence to these procedures is essential to maintain safety.
Selecting the Appropriate PPE
The selection of the correct PPE depends on the specific situation. For example, in a healthcare setting, a healthcare worker might need an N95 respirator and gloves. In a public setting, a simple surgical mask might suffice. The key is to consider the potential risk of exposure.
Situations Requiring PPE
Various situations necessitate the use of PPE for flu prevention. Healthcare workers, individuals caring for someone with the flu, and those working in close proximity to potentially infected individuals should prioritize using appropriate PPE. This practice helps to prevent the spread of the virus. For example, during a flu outbreak, using masks in public transportation or crowded areas is a preventive measure.
Table: Types of PPE, Uses, and Precautions
| Type of PPE | Use | Precautions |
|---|---|---|
| Surgical Masks | General protection against respiratory droplets | Change masks frequently, proper donning and doffing |
| N95 Respirators | High-level filtration of airborne particles | Fit-tested for proper seal, change frequently |
| Gloves (Medical Examination or Nitrile) | Protection against contamination from surfaces and bodily fluids | Change gloves frequently, proper donning and doffing, avoid touching face |
Respiratory Hygiene Practices
Proper respiratory hygiene is crucial in preventing the spread of the flu and other respiratory illnesses. By practicing good coughing and sneezing etiquette, we significantly reduce the risk of transmitting infectious droplets containing the virus to others. This simple yet effective measure is a cornerstone of preventing the spread of respiratory infections in communal settings.
Importance of Respiratory Hygiene
Respiratory hygiene practices are essential for preventing the transmission of respiratory viruses, including influenza. These practices involve proper coughing and sneezing techniques, the use of tissues, and the disposal of used tissues. By following these guidelines, individuals minimize the release of infectious droplets into the air, thus reducing the risk of exposure to others.
Proper Coughing and Sneezing Etiquette
Proper coughing and sneezing etiquette involves covering the mouth and nose with a tissue or the crook of the elbow. This prevents the spread of respiratory droplets, which can carry viruses. When coughing or sneezing, individuals should try to contain the expulsion of these droplets.
Use of Tissues and Their Disposal
Using a tissue when coughing or sneezing is a crucial component of respiratory hygiene. Used tissues should be disposed of promptly and properly. This prevents the spread of germs and promotes a hygienic environment. Individuals should always have tissues readily available, especially in high-traffic areas.
Covering Coughs and Sneezes with the Elbow, Viral nurse things you can do to avoid flu
Covering coughs and sneezes with the elbow is an effective alternative to using a tissue. This method is particularly useful when tissues are unavailable. The inner elbow area is less susceptible to germs and minimizes the spread of respiratory droplets. Individuals should ensure they cover their mouth and nose effectively.
Examples of Effective Respiratory Hygiene Practices
Effective respiratory hygiene practices include maintaining a distance from those who are coughing or sneezing, frequently washing hands with soap and water, and wearing a mask in public settings when necessary. By combining these practices, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of acquiring and spreading respiratory infections.
Table Comparing and Contrasting Respiratory Hygiene Methods
| Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Using a tissue | Covering the mouth and nose with a tissue when coughing or sneezing. | Effective at containing droplets, readily available in many situations. | Requires having a tissue readily available, disposal can be a problem if not handled properly. |
| Elbow covering | Covering the mouth and nose with the inner elbow when coughing or sneezing. | Effective alternative when tissues are not available, can be more practical in certain situations. | Less effective than a tissue in containing droplets, may not be as convenient in all situations. |
Social Distancing and Quarantine
Social distancing and quarantine are crucial strategies in preventing the spread of contagious illnesses like the flu. These measures significantly reduce exposure to infected individuals, thereby limiting the virus’s transmission and mitigating the severity of outbreaks. Understanding the importance and appropriate application of these measures is vital for personal safety and community health.Maintaining a safe distance from others and adhering to quarantine protocols can help control the spread of infectious diseases.
This proactive approach minimizes the risk of transmission, protects vulnerable populations, and helps to prevent the escalation of outbreaks.
Importance of Social Distancing
Social distancing involves maintaining a physical separation from others to reduce the risk of transmitting infectious agents. This strategy is particularly important during flu season, when the virus circulates more readily. By keeping a safe distance, individuals can significantly decrease the likelihood of contracting or spreading the flu. The effectiveness of social distancing hinges on consistent and appropriate application in various settings.
Appropriate Distance in Public Spaces
The optimal distance for social distancing in public spaces is generally 6 feet (approximately 1.8 meters). This distance provides a buffer, reducing the likelihood of airborne transmission through respiratory droplets. However, in densely populated areas or situations with poor ventilation, a greater distance may be necessary.
Role of Quarantine in Containing Flu Outbreaks
Quarantine involves isolating individuals who have been exposed to a contagious illness, preventing further transmission. This measure is particularly effective in containing outbreaks and limiting the spread of the flu. Quarantine protocols typically involve restricting movement and contact to prevent the spread of the virus. The duration of quarantine is determined by health authorities based on the specific situation.
Situations Requiring Social Distancing
Social distancing is critical in various situations to prevent the spread of contagious illnesses. Examples include crowded public transportation, indoor gatherings, and community events. Maintaining a safe distance in these settings is crucial for preventing the transmission of the virus.
- Public transportation: Maintaining a distance from others on buses, trains, and subways is vital, especially during peak hours. Avoiding close contact and practicing good hygiene are essential.
- Indoor gatherings: In enclosed spaces, such as restaurants, offices, and community centers, maintaining a safe distance from others is important to reduce the risk of transmission.
- Community events: At large community events or gatherings, social distancing can be challenging but remains important. Promoting physical separation and encouraging hygiene practices can mitigate the risk of spreading illness.
Importance of Self-Isolation
Self-isolation is critical for individuals experiencing flu symptoms. This practice involves isolating oneself from others to prevent the spread of the virus. Early identification and self-isolation are crucial to limit the duration and severity of the illness, thereby reducing the risk of transmission.
Summary Table of Social Distancing and Quarantine Scenarios
| Scenario | Social Distancing Measures | Quarantine Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Public Transportation | Maintain at least 6 feet distance from others; avoid close contact; frequent handwashing | If exposed to a confirmed flu case, follow isolation guidelines set by health authorities. |
| Indoor Gatherings | Maintain 6 feet distance; use appropriate ventilation; avoid prolonged close contact | If symptomatic, self-isolate; if exposed to a confirmed case, follow isolation guidelines set by health authorities. |
| Community Events | Maintain distance; encourage hand hygiene; wear a mask if possible; consider virtual participation | If symptomatic, self-isolate; if exposed to a confirmed case, follow isolation guidelines set by health authorities. |
| Household Exposure | If a household member is symptomatic, separate living areas; increase ventilation; practice frequent hand hygiene | If a confirmed case in a household, follow isolation guidelines set by health authorities; potentially restrict travel. |
Promoting Healthy Habits
A strong immune system is your first line of defense against the flu. This isn’t just about avoiding germs; it’s about bolstering your body’s natural ability to fight off infections. By cultivating healthy habits, you can significantly reduce your risk of contracting the flu and experiencing its debilitating effects. This involves a multifaceted approach that encompasses sleep, nutrition, exercise, hydration, and stress management.A well-functioning immune system, fueled by healthy habits, is crucial in preventing flu infections.
This proactive approach to health significantly reduces the likelihood of succumbing to the virus and its accompanying symptoms. It’s not just about preventing illness; it’s about cultivating overall well-being.
The Link Between Healthy Habits and Flu Prevention
Healthy habits are directly correlated with a robust immune system. A well-nourished body with adequate rest and regular exercise is better equipped to combat viral infections like the flu. Conversely, poor habits can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to illness.
The Importance of Sufficient Sleep
Adequate sleep is paramount for immune function. During sleep, your body repairs and strengthens its cells, including those crucial for fighting off pathogens. Chronic sleep deprivation weakens the immune response, increasing the risk of infection. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night for optimal immune function.
Proper Nutrition for a Healthy Immune System
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein provides the essential vitamins, minerals, and nutrients your body needs to function optimally. Nutrients like Vitamin C, Zinc, and Vitamin D are particularly important for immune health. Choose whole foods over processed options for maximum benefit.
Regular Exercise and Its Impact on Immunity
Regular physical activity can significantly boost your immune system. Exercise increases blood flow, delivering oxygen and nutrients to your cells, including those involved in immune responses. Moderate-intensity exercise, like brisk walking or cycling, can contribute to a healthier immune system. However, excessive or strenuous exercise can temporarily suppress the immune response, so maintaining a balanced routine is key.
Healthy Habits that Boost the Immune System
Several lifestyle choices can actively strengthen your immune system. These include a balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, stress management, and hydration.
- Hydration: Drinking enough water is essential for numerous bodily functions, including immune response. Dehydration can weaken the immune system, making you more susceptible to illness. Maintain adequate fluid intake throughout the day.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can significantly impair immune function. Effective stress management techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature, can help maintain a healthy immune response. Finding healthy ways to cope with stress is crucial for overall well-being and immune system strength.
The Role of Hydration and Stress Management
Hydration plays a crucial role in overall health and immune function. Water helps transport nutrients and remove waste products from the body. Stress, on the other hand, can negatively impact the immune system. Effective stress management techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature, can help maintain a healthy immune response.
Relationship Between Healthy Habits and Flu Prevention
| Healthy Habit | Impact on Flu Prevention |
|---|---|
| Sufficient Sleep (7-9 hours) | Strengthens immune response, reduces susceptibility to infection. |
| Proper Nutrition (Balanced Diet) | Provides essential nutrients for immune cell function. |
| Regular Exercise (Moderate Intensity) | Enhances blood flow, boosts immune system function. |
| Stress Management | Reduces stress hormones, improves immune function. |
| Hydration (Adequate Water Intake) | Supports bodily functions, maintains immune system strength. |
Last Word
In conclusion, a proactive approach to flu prevention involves a combination of factors. By prioritizing hand hygiene, vaccinations, environmental cleanliness, and healthy habits, you can significantly reduce your risk of contracting the flu. Remember that prevention is key to protecting yourself and those around you.