UK diabetes advocate DIY technology is empowering individuals to take control of their health. This exploration delves into the burgeoning community of UK-based individuals creating and utilizing their own diabetes management tools. We’ll examine the diverse range of DIY projects, their motivations, and the potential impact on both individuals and the healthcare system. From accessibility and affordability to safety and regulatory considerations, we’ll cover the crucial aspects of this innovative approach to diabetes management.
The UK diabetes community is actively exploring DIY technology solutions, driven by a desire for greater control and personalized care. Existing tools and resources are analyzed, and successful examples of UK-based DIY projects are highlighted. The motivations behind this trend are discussed, along with a comparison table of different DIY technologies. This discussion also touches on the critical considerations of safety, regulations, and the possible integration of these technologies into the mainstream healthcare system.
Introduction to DIY Diabetes Technology in the UK
The UK diabetes community demonstrates a growing interest in DIY technology solutions for managing their condition. This interest stems from a desire for greater control over personal health, cost-effectiveness, and access to potentially faster innovation. Individuals are increasingly seeking to personalize their diabetes management strategies, often finding limitations in commercially available products. This desire for customization and control is particularly evident in the growing community of UK-based individuals who are designing and implementing their own solutions.DIY diabetes technology in the UK is currently a diverse landscape.
While commercially available continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and insulin pumps are widely used, individuals are actively exploring alternative methods for blood glucose monitoring, insulin delivery, and even creating personalized educational resources. Open-source projects and online forums are facilitating knowledge sharing and collaboration among these individuals.
Successful UK-Based DIY Diabetes Projects
Several UK-based individuals have successfully developed and implemented DIY projects to enhance their diabetes management. These projects often involve repurposing existing technologies or creating custom-designed solutions using readily available components. Examples include modifications to existing blood glucose meters, the development of home-brew insulin delivery systems, and the creation of personalized diabetes management apps. The successful implementation of these projects demonstrates a commitment to personal innovation and problem-solving.
Motivations Behind DIY Diabetes Technology
Individuals are driven by various motivations for engaging in DIY diabetes technology projects. Some are seeking more affordable solutions compared to commercially available products. Others are motivated by a desire for greater personalization and control over their diabetes management, adjusting parameters to suit their individual needs. A significant portion of individuals are also motivated by the potential for faster innovation and the possibility of developing solutions that address unmet needs in the current market.
Comparison of DIY Diabetes Technologies
This table provides a comparison of different types of DIY diabetes technologies currently being explored in the UK. This is not an exhaustive list, but it aims to highlight the diversity of approaches.
| Technology Type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modified Blood Glucose Meters | Existing blood glucose meters are adapted for enhanced accuracy or features, often involving custom calibration or data logging. | Potentially lower cost, personalized calibration, and potentially more frequent readings. | May require significant technical expertise, accuracy can be variable, and calibration needs to be done meticulously. |
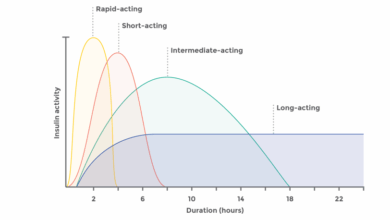
| Home-Brewed Insulin Delivery Systems | Custom-built systems for insulin delivery, often using syringes or other components, designed for more precise control. | Potentially lower cost, more personalized control over insulin dosage, and potential for enhanced flexibility. | Requires significant technical expertise, poses potential safety risks if not implemented correctly, and regulatory approvals are often absent. |
| Personalized Diabetes Management Apps | Apps created to track glucose levels, medication, and other diabetes-related data, often with customized features. | Increased awareness, personalized data tracking, and potential for early detection of patterns. | Data security concerns, potential for errors in data entry, and limited support from regulatory bodies. |
Accessibility and Affordability
DIY diabetes technology holds immense potential for improving access and affordability of care in the UK. However, its practical implementation faces significant hurdles related to equitable access for diverse populations and the cost-effectiveness of these solutions compared to traditional medical interventions. Addressing these challenges is crucial for ensuring that this technology benefits all individuals living with diabetes.
Accessibility for Diverse Populations
The UK’s diverse population requires tailored strategies to ensure equitable access to DIY diabetes technology resources. This includes language support, culturally sensitive educational materials, and accessible digital platforms. Recognizing the varying levels of digital literacy among different groups is essential to create effective training programs. Further, support for individuals with disabilities is critical, requiring accessible interfaces and assistive technologies.
Providing these resources across various socioeconomic backgrounds is vital to maximizing the reach and impact of DIY diabetes solutions.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Comparing the cost-effectiveness of DIY solutions with traditional medical interventions is crucial. DIY technology can potentially reduce healthcare costs in the long run through preventative measures and self-management, which can lower the need for expensive hospital visits and treatments. However, initial costs for equipment and supplies must be considered alongside ongoing maintenance and potential technical support. A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis needs to account for factors like time savings, improved quality of life, and reduced long-term health complications.
For example, a well-designed DIY monitoring system could prevent costly emergency room visits and hospitalizations.
Barriers to Access and Affordability
Several barriers hinder access to and affordability of DIY diabetes technology. These include the initial cost of purchasing equipment, ongoing maintenance fees, and the potential need for technical support. Access to reliable internet connectivity, especially in underserved communities, is also a critical consideration. Furthermore, a lack of awareness and understanding of DIY diabetes technologies among healthcare professionals and patients can create obstacles.
Finally, the availability of quality training and support materials plays a key role in successful implementation.
Funding Sources and Support Programs
Several potential funding sources and support programs can foster DIY diabetes technology projects in the UK. Government grants, charitable donations, and private sector investments are all viable options. Partnerships between healthcare organizations, technology companies, and community groups can also be instrumental in driving innovation and accessibility. Establishing dedicated funding streams specifically for DIY diabetes technology development and implementation would greatly benefit the field.
Furthermore, the development of innovative funding models that incentivize cost-effective solutions and encourage widespread adoption is needed.
Funding Opportunities Table
| Funding Source | Description | Eligibility Criteria | Contact Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) | Provides funding for research and development in healthcare. | Research projects aligned with NIHR priorities, typically involving rigorous methodology and clear outcomes. | https://www.nihr.ac.uk/ |
| Wellcome Trust | Focuses on biomedical research with a broad scope. | Projects addressing health challenges with a strong scientific rationale. | https://wellcome.org/ |
| Diabetes UK | Provides funding for research, support, and awareness campaigns related to diabetes. | Projects directly impacting diabetes care and improving patient outcomes. | https://www.diabetes.org.uk/ |
| Innovate UK | Supports innovation and technological advancement in the UK. | Projects demonstrating commercial viability and potential impact on society. | https://www.innovateuk.org/ |
Safety and Regulatory Considerations: UK Diabetes Advocate DIY Technology
DIY diabetes technology offers potential benefits, but careful consideration of safety and regulation is crucial. Ensuring user safety and adherence to standards is paramount to prevent harm and maintain public trust. The UK, like other countries, faces challenges in balancing innovation with stringent safety protocols.The UK regulatory landscape for DIY diabetes technology is still developing. Existing frameworks for medical devices and general health technologies provide a foundation, but the specific needs of DIY systems require tailored approaches.
This includes defining appropriate standards for device design, manufacturing, and user training.
Safety Standards and Regulations
The UK regulatory framework for medical devices, largely governed by the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA), plays a key role. While not explicitly focused on DIY diabetes technologies, existing regulations regarding medical devices and health technologies provide a basis for assessing safety and efficacy. This includes standards for materials, manufacturing processes, and performance testing. However, specific guidelines for DIY diabetes technologies are still under development, requiring ongoing dialogue and collaboration between developers, users, and regulatory bodies.
Potential Risks and Complications
Several potential risks and complications are associated with DIY diabetes technologies. These include inaccuracies in readings, incorrect interpretation of results, improper device usage, and the potential for psychological stress or anxiety if the technology malfunctions. Furthermore, inadequate user training and insufficient support could lead to incorrect glucose management practices. Carefully designed user interfaces, comprehensive instructions, and ongoing user support are essential to mitigating these risks.
Importance of Proper Training and Guidance
Comprehensive training and ongoing support are essential for safe and effective use of DIY diabetes technology. Training should cover device operation, troubleshooting, data interpretation, and the recognition of potential complications. Clear, concise, and accessible information materials, including user manuals and online resources, should be provided. Support services, such as helplines or online forums, can also play a critical role in addressing user concerns and providing guidance.
The training should be tailored to individual user needs and experience levels.
Regulatory Frameworks for Similar Technologies
The UK has regulatory frameworks for similar DIY health technologies, such as home blood pressure monitors and at-home diagnostic tests. These frameworks often focus on accuracy, safety, and user instructions. These existing regulations offer valuable insights into establishing safety standards for DIY diabetes technologies. Lessons learned from these frameworks can be adapted and applied to ensure user safety and the reliability of the devices.
UK diabetes advocates are impressively resourceful, often creating their own tech solutions. This DIY approach highlights a crucial need for innovative healthcare solutions, particularly for those with obesity. Telemedicine is playing a significant role in making healthcare more accessible for people with obesity, as it allows for remote consultations and monitoring, bridging geographical barriers and potentially leading to better outcomes.
how telemedicine makes healthcare more accessible for people with obesity. Ultimately, these DIY tech solutions, alongside broader advancements in telemedicine, are empowering individuals to manage their health conditions effectively.
Comparison with Other Countries’ Regulatory Environments
Different countries have varying approaches to regulating DIY health technologies. Some countries may have more stringent regulations, while others might be more permissive. Comparing and contrasting these approaches can offer valuable insights for developing a robust regulatory framework in the UK. This comparison can help identify best practices and areas for improvement in the UK’s regulatory environment.
Such comparison might involve examining the regulatory landscape in countries with advanced experience in DIY health technologies, such as the US or European nations.
Impact on Healthcare Systems

DIY diabetes technology has the potential to significantly reshape the UK healthcare system, offering a new paradigm for managing the condition. It’s not simply about individual empowerment; it’s about potentially redistributing resources and fostering a more proactive approach to patient care. The key lies in understanding both the benefits and the challenges inherent in this shift.The traditional model of diabetes care often involves frequent consultations, laboratory tests, and potentially expensive medications.
DIY technology, if effectively integrated, could streamline these processes, allowing for more targeted interventions and reducing the burden on NHS resources. Early detection and prompt adjustments to treatment plans, enabled by DIY monitoring, could help prevent complications and hospitalizations, ultimately saving the NHS money in the long run.
UK diabetes advocates are amazing, often creating their own tech solutions. This DIY approach is inspiring, but it’s important to consider the broader context of chronic conditions like arthritis and IBS, which research shows are often linked to depression. Understanding these connections, as explored in this insightful article why common conditions like arthritis and IBS are linked to depression , helps us appreciate the holistic needs of those with diabetes and similar conditions.
Ultimately, these DIY tech solutions need to be considered within a support network that addresses the whole person, not just the disease itself.
Potential Benefits in Reducing Healthcare Costs
The potential cost savings from DIY diabetes technology are significant. By enabling patients to actively manage their condition, the need for frequent doctor visits and expensive tests might decrease. Early detection of trends, through DIY monitoring, could also lead to earlier intervention, reducing the risk of serious complications and hospital admissions. This preventative approach, combined with improved patient engagement, can result in long-term cost savings for the NHS.
For example, studies in other countries have shown that patients actively involved in their diabetes management require fewer hospital visits and have lower treatment costs.
Examples of Improved Patient Engagement and Self-Management
DIY diabetes technology empowers patients by providing real-time data and personalized insights. This data allows patients to track their progress, identify patterns, and adjust their lifestyle choices accordingly. Mobile apps and connected devices can offer support and guidance, facilitating a sense of ownership and responsibility in managing the condition. Furthermore, shared data with healthcare professionals can facilitate more efficient communication and tailored treatment plans.
UK diabetes advocates are pushing the boundaries of DIY tech, creating innovative tools to manage their condition. However, the challenges of diagnosis extend beyond just diabetes, affecting women disproportionately. Issues like conditions women hard diagnose often present unique symptoms, leading to delayed or inaccurate diagnoses. These DIY tools are a testament to the drive and resourcefulness of those affected by these difficult-to-diagnose conditions, and they hold potential to improve healthcare access and outcomes for everyone.
For instance, continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) allow patients to identify patterns in their glucose levels, leading to more informed discussions with their doctors and better adherence to treatment plans.
Challenges to Integrating DIY Technology into Mainstream Healthcare
Integrating DIY technology into the UK’s healthcare system will not be without hurdles. One major concern is the need for robust regulatory frameworks to ensure the safety and accuracy of these devices. Ensuring data security and interoperability between different DIY technologies and existing NHS systems is also crucial. Furthermore, training healthcare professionals to effectively utilize and interpret data from these devices is vital for seamless integration.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for the successful implementation of DIY technology within the NHS. For example, a lack of clear guidelines for the use of certain DIY devices in conjunction with NHS care could lead to confusion and inconsistencies in treatment.
Potential Future Applications of DIY Diabetes Technology in UK Healthcare
| Application | Description | Potential Benefits | Potential Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Personalized Treatment Plans | AI-powered platforms analyze patient data to generate tailored treatment plans, considering individual factors and preferences. | Improved treatment outcomes, reduced complications, enhanced patient satisfaction. | Data privacy concerns, need for robust AI algorithms, potential for bias in algorithms. |
| Remote Monitoring and Support | Continuous monitoring of vital signs and data transmission to healthcare providers for remote consultations and support. | Increased accessibility to care, timely intervention for emerging issues, reduced travel costs for patients. | Reliable internet connectivity, ensuring data security, potential for over-reliance on technology. |
| Early Detection of Complications | DIY devices that can detect subtle signs of complications like neuropathy or retinopathy, enabling early interventions. | Improved outcomes, reduced severity of complications, potential for preventing severe health events. | Validation of the devices’ accuracy in detecting complications, interpretation of data by healthcare professionals. |
Community Support and Education
DIY diabetes technology offers exciting potential for better self-management, but navigating this new landscape requires strong community support and education. Online communities and resources play a vital role in empowering users, ensuring safe practices, and fostering a supportive network for individuals using these technologies. Proper guidance and accessible information are crucial for successful implementation.Understanding the intricacies of DIY technologies and their potential risks is essential for responsible use.
This necessitates robust educational materials and readily available support systems to equip individuals with the knowledge and confidence to make informed decisions about their health. The UK’s diverse population and varying levels of digital literacy also need to be considered in the design of these support systems.
Online Communities and Support Groups
Online communities and support groups are invaluable resources for individuals using DIY diabetes technology. These platforms provide a space for sharing experiences, asking questions, and receiving peer-to-peer support. They allow users to connect with others facing similar challenges, build trust, and gain insights from diverse perspectives.
Educational Resources
Educational resources are paramount for promoting safe and effective use of DIY diabetes technologies. Comprehensive information, including potential risks and benefits, should be readily accessible to all users. Clear, concise, and engaging materials, tailored to various learning styles, can significantly improve user understanding and adherence to safety protocols.
Resources Available to Support Users
Numerous organizations and platforms provide valuable support for users of DIY diabetes technology in the UK. These include diabetes charities, online forums, and dedicated support groups. Access to these resources, often free or low-cost, can empower individuals to manage their condition effectively. Local community health centers may also offer resources and support programs for individuals.
Examples of Online Communities/Forums
While specific UK-based, dedicated forums for DIY diabetes technology may be limited, existing diabetes support groups and online forums often feature discussions about self-testing and monitoring methods. Engaging with these broader communities can be beneficial for accessing information and connecting with others navigating similar situations. Active participation in these online spaces can foster a sense of community and provide practical insights from experienced users.
Creating an Educational Infographic
An infographic about the risks and benefits of DIY diabetes technology should present information in a clear and visually appealing manner. It should address both the potential advantages, such as greater autonomy and cost-effectiveness, and the risks, such as the potential for errors in self-testing and the importance of adhering to strict safety guidelines.A well-designed infographic could include:
- Benefits: Increased flexibility in managing diabetes, potentially reduced healthcare costs, enhanced self-reliance, and personal control over treatment.
- Risks: Potential for errors in testing and inaccurate results, need for careful adherence to safety procedures, and the importance of seeking professional medical advice.
- Safety Tips: Strict adherence to manufacturer instructions, proper storage of equipment, and regular calibration of devices.
- Troubleshooting: Guidance on handling common problems and knowing when to consult a healthcare professional.
- Accessing Support: Information on readily available support networks, including diabetes charities, online forums, and healthcare professionals.
The infographic should use clear visuals, concise text, and a user-friendly layout to effectively communicate complex information to a wide audience. Consider using a color-coded system, icons, and simple diagrams to enhance understanding and engagement.
Future Trends and Innovations
DIY diabetes technology is rapidly evolving, promising greater autonomy and personalized management for individuals with diabetes in the UK. This evolution is driven by advancements in sensor technology, data analysis, and user-friendly interfaces. As the field progresses, accessibility and affordability will become increasingly crucial factors in shaping its impact on the UK diabetes community.
Potential Developments in Sensor Technology, UK diabetes advocate DIY technology
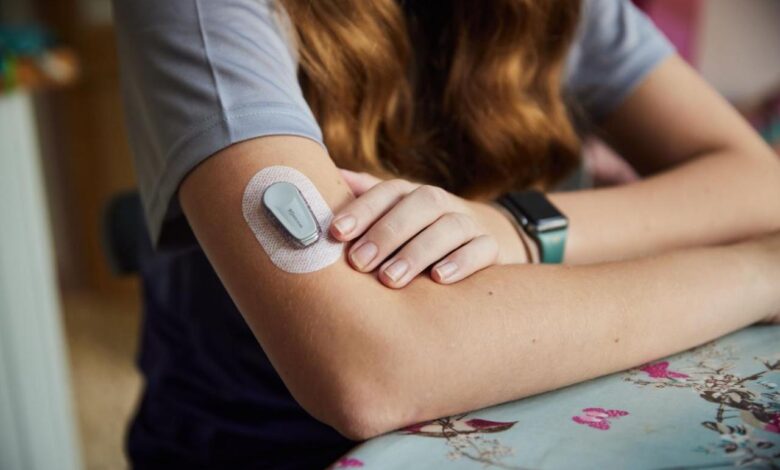
Emerging technologies are poised to revolutionize DIY diabetes monitoring. Miniaturization of glucose sensors, coupled with advancements in continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology, is expected to lead to smaller, more discreet devices with longer operational durations. These advancements would significantly improve the user experience, potentially reducing the burden of frequent finger-pricks associated with traditional blood glucose monitoring.
Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
The increasing volume of data generated by DIY diabetes devices creates an opportunity for AI-driven analysis. Algorithms can identify patterns and trends in individual glucose readings, enabling the prediction of potential hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic events. This predictive capability could allow for proactive interventions and personalized adjustments to treatment plans, empowering individuals with a more proactive approach to managing their condition.
Examples of AI applications include automated insulin dose adjustments based on real-time glucose data and lifestyle factors.
Personalized Diabetes Management Platforms
The future of DIY diabetes management envisions the development of user-friendly, personalized platforms that integrate data from various devices. These platforms would act as central hubs for collecting, analyzing, and visualizing individual data, offering personalized recommendations and insights. This personalized approach will be critical for improving adherence to treatment plans and long-term health outcomes.
Innovative DIY Solutions for Monitoring and Management
Innovative DIY solutions are emerging to address specific needs within the diabetes community. These include innovative patches or implantable sensors that continuously monitor glucose levels, reducing the need for frequent blood tests. Additionally, mobile apps are being developed that provide real-time data analysis, personalized recommendations, and connect users with support groups, fostering a sense of community and shared learning.
Global Landscape of DIY Diabetes Technology
The global landscape of DIY diabetes technology is marked by a diverse range of solutions. Different countries have unique regulatory environments and societal needs, impacting the types of devices and services available. The UK, with its emphasis on patient empowerment and access to healthcare, is expected to adopt and adapt innovations from the global market, fostering a dynamic and evolving landscape of DIY diabetes solutions.
Areas for Future Research and Innovation
Further research is needed to improve the accuracy, reliability, and long-term safety of DIY diabetes technologies. Areas for potential focus include developing non-invasive methods for continuous glucose monitoring, refining AI algorithms for personalized predictions, and enhancing the user experience of DIY devices for better adherence. These advancements will be critical for ensuring the successful integration of DIY diabetes technology into the UK healthcare system.
Closure
In conclusion, UK diabetes advocate DIY technology represents a significant development in self-management. While offering potential benefits in terms of accessibility, affordability, and patient empowerment, it also presents safety and regulatory challenges. The evolving landscape of DIY technology in the UK is closely intertwined with community support and education, ensuring safe and effective implementation. The future of this technology hinges on continued innovation, collaboration, and careful consideration of the regulatory framework.
The ongoing discussion regarding its integration into mainstream healthcare services is crucial for realizing its full potential.