Low back and neck pain top US spending on healthcare, a significant and growing concern. Millions suffer from these debilitating conditions, leading to substantial economic burdens for individuals, families, and the entire healthcare system. This article explores the prevalence of these pains, the costs associated with treatment, the factors driving these expenses, and comparisons with other common ailments.
We’ll delve into the statistics, trends, and potential solutions to address this pressing issue.
Understanding the various treatment options, from medication and physical therapy to surgery and alternative therapies, is crucial. This article examines the costs of these approaches, and how their effectiveness relates to their cost-effectiveness. We will also analyze factors that influence spending, including access to care, insurance coverage, and patient choices, highlighting the interplay between these elements.
Prevalence of Low Back and Neck Pain in the US: Low Back And Neck Pain Top Us Spending On Healthcare
Low back and neck pain are significant public health concerns in the United States, affecting a substantial portion of the population across various demographics. These conditions frequently lead to substantial healthcare utilization and economic burden, impacting both individual well-being and national productivity. Understanding the prevalence, economic implications, and associated factors is crucial for developing effective preventative and treatment strategies.The prevalence of low back and neck pain is multifaceted, influenced by age, lifestyle, and underlying health conditions.
This article explores the statistical data surrounding these conditions, highlighting their impact on the US healthcare system and their relationship to other chronic health issues. We will examine the economic burden and explore comparative prevalence across different age groups.
Prevalence Statistics in the US
Low back and neck pain are widespread in the US, affecting a substantial portion of the population. Numerous studies have explored these conditions, revealing key patterns in their prevalence across various age groups. Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and other reputable sources provide a foundation for understanding these patterns.
Low back and neck pain are major contributors to US healthcare spending, a huge drain on resources. While we’re grappling with those costly issues, it makes you wonder about other health anxieties. For instance, does coffee really need a cancer warning? A recent article explores this fascinating question, delving into the science behind the potential risks and benefits of this beloved beverage.
does coffee really need a cancer warning. Ultimately, the high cost of treating chronic pain conditions like back and neck pain still demands our attention.
Economic Impact of Low Back and Neck Pain
The economic burden of low back and neck pain is substantial. Lost productivity due to absenteeism and presenteeism (reduced productivity while at work) places a significant strain on the workforce. Direct healthcare costs, including medical visits, diagnostic tests, and treatments, also contribute to the overall financial impact. These costs often fall disproportionately on individuals and the healthcare system.
Relationship to Other Chronic Conditions
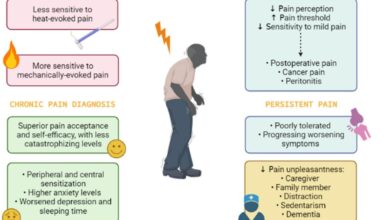
Low back and neck pain can be associated with a range of other chronic conditions. For example, individuals with obesity, diabetes, or certain musculoskeletal disorders often experience a higher risk of developing low back and neck pain. The relationship between these conditions is complex and often involves a combination of factors. Chronic pain can lead to further complications, such as depression and anxiety, highlighting the need for comprehensive management strategies.
Comparison of Prevalence Across Age Groups
The prevalence of low back and neck pain varies significantly across different age groups. The following table illustrates these differences, showcasing the patterns observed in various studies.
| Age Group | Prevalence of Low Back Pain (%) | Prevalence of Neck Pain (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 18-24 | 15-20 | 10-15 |
| 25-44 | 25-30 | 15-20 |
| 45-64 | 35-40 | 20-25 |
| 65+ | 40-45 | 25-30 |
The table above provides a general overview of the prevalence of low back and neck pain across different age groups. It is important to note that these are estimates and actual prevalence can vary depending on factors like lifestyle, occupation, and individual health status. Further research is always needed to refine these estimates.
Healthcare Spending on Low Back and Neck Pain Treatment
Low back and neck pain are pervasive issues affecting a significant portion of the population. Understanding the costs associated with treating these conditions is crucial for developing effective healthcare strategies. This involves examining the spectrum of treatment options available and their respective price points. The aim is to identify cost-effective approaches that yield positive outcomes for patients while managing healthcare expenditures.The financial burden of low back and neck pain extends beyond the direct costs of treatment.
Indirect costs, such as lost productivity due to missed work, reduced quality of life, and the need for supportive care, are often substantial. Comprehensive analysis of these factors is essential for creating a complete picture of the economic impact of these prevalent conditions.
Treatment Options for Low Back and Neck Pain
Various treatment options are available for managing low back and neck pain, ranging from conservative measures to more invasive procedures. A crucial aspect of effective treatment is tailored care, considering individual patient needs and preferences.
- Medication: Analgesics, such as over-the-counter pain relievers and prescription medications, are frequently prescribed for pain management. Different medications vary in their effectiveness and potential side effects, affecting their cost-effectiveness. For example, while ibuprofen can be affordable, opioid pain relievers often have higher costs and greater potential for addiction. Careful consideration of these factors is essential when choosing the most suitable medication.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy involves a structured program of exercises, manual therapies, and education to improve mobility, reduce pain, and strengthen supporting muscles. Different types of physical therapy, such as aquatic therapy or massage therapy, can vary in cost depending on the facility and therapist’s experience.
- Surgery: Surgical interventions are reserved for cases of severe or persistent pain that does not respond to other treatments. The cost of surgical procedures can be substantial, encompassing the surgeon’s fees, hospital costs, and potential follow-up care. Examples include spinal fusion procedures or discectomy, which can have a significant financial impact on patients.
- Alternative Therapies: Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage therapy, and chiropractic care, are often used as complementary approaches to conventional treatment. The cost of these therapies can vary widely depending on the provider’s experience and the frequency of sessions.
Cost Comparison of Treatment Options
The cost of treatment for low back and neck pain can vary significantly depending on the chosen approach. Factors influencing cost include the complexity of the condition, the specific treatments employed, and the geographic location of the healthcare facility.
- Medication: Prescription medications can range in cost from relatively inexpensive over-the-counter options to high-priced specialized drugs. This variation is dependent on the medication’s composition and the quantity needed.
- Physical Therapy: The cost of physical therapy can vary based on the type of therapy, the duration of treatment, and the experience level of the therapist. A comprehensive table below provides a more detailed comparison of different physical therapy types for low back pain.
Cost Comparison of Physical Therapy Types for Low Back Pain
| Type of Physical Therapy | Estimated Cost (per session) | Effectiveness | Cost-Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Therapy | $75-$150 | Moderate to high, depending on the severity and type of condition | Generally cost-effective, but outcomes vary. |
| Exercise Therapy | $50-$100 | High, when implemented appropriately. | Generally cost-effective, and often a core part of a treatment plan. |
| Aquatic Therapy | $75-$125 | High, particularly for those with joint issues or pain that limits movement | Potentially cost-effective, especially for patients with mobility issues. |
| Massage Therapy | $75-$150 | Moderate, useful for muscle relaxation and pain reduction | Moderate cost-effectiveness, often used as a complementary therapy. |
Note: Costs are approximate and can vary based on location, facility, and therapist’s experience.
Factors Influencing Healthcare Spending
The substantial financial burden of low back and neck pain treatment in the US highlights the need to understand the underlying factors driving these costs. Understanding these factors can pave the way for more effective preventative strategies and cost-containment measures. This analysis delves into the intricate interplay of access to care, insurance coverage, patient choices, preventative measures, and lifestyle factors that contribute to the high expenditure on low back and neck pain treatment.High healthcare spending on low back and neck pain is a multifaceted issue influenced by several factors.
These factors, ranging from individual choices to systemic issues, are interconnected and create a complex picture of the current situation. Analyzing these factors is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate the financial burden and improve patient outcomes.
Access to Care
Access to appropriate and timely healthcare services is a critical factor influencing spending. Limited access to specialists, such as physical therapists or pain management physicians, can lead to delays in diagnosis and treatment, potentially escalating costs over time. Geographic disparities in healthcare provider density can also play a significant role, particularly in rural areas where access to specialized care might be limited.
The availability of different treatment options, including alternative therapies, also influences the choice of care and the associated costs. This often results in increased use of costly interventions. In many cases, the need for multiple consultations with different specialists, combined with the potential for lengthy wait times, can further escalate healthcare costs.
Insurance Coverage
Insurance coverage plays a significant role in shaping healthcare spending. Variations in coverage across different insurance plans can lead to substantial differences in access to care and the type of treatments covered. For instance, some plans might have limited coverage for alternative therapies or specific types of interventions, forcing patients to seek out more expensive options. Coverage for preventive care and ongoing management of chronic pain conditions can significantly impact long-term costs.
This underscores the importance of comprehensive insurance coverage to ensure access to the necessary treatments and to help manage the long-term financial burden of these conditions.
Patient Choices
Patient choices and preferences can influence the type of care sought and the associated costs. For example, patients might opt for more expensive surgical interventions when less invasive or less costly alternatives are available. Lack of awareness about less costly or equally effective treatment options can lead to increased expenditures. The decision-making process can also be complicated by conflicting information from various sources, including online resources, which may not always reflect the most up-to-date or appropriate care.
The influence of patient choices is a crucial aspect of the overall cost equation, as it highlights the need for patient education and effective communication between patients and healthcare providers.
Preventative Measures
Implementing effective preventative measures can significantly reduce the incidence of low back and neck pain, thereby lowering overall healthcare spending. Strategies such as promoting proper posture and ergonomic practices in the workplace can reduce the risk of developing these conditions. Public health campaigns promoting healthy lifestyles, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, are critical to lowering the prevalence of these conditions.
Educational initiatives focused on awareness and prevention can be particularly beneficial in reducing long-term healthcare costs.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors significantly impact the development and progression of low back and neck pain. Factors like sedentary lifestyles, poor posture, lack of physical activity, and inadequate sleep habits can all contribute to the development of pain conditions. Obesity and smoking also increase the risk of developing low back and neck pain and contribute to the high cost of treatment.
Understanding the impact of these lifestyle factors can help design preventative strategies tailored to specific risk groups.
Summary Table: Factors Influencing Healthcare Spending
| Category | Factors | Impact on Spending |
|---|---|---|
| Socioeconomic Factors | Income levels, education, occupation | Can influence access to care and adherence to treatment plans. |
| Access to Care | Geographic location, provider availability, wait times | Can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment, potentially increasing costs. |
| Insurance Coverage | Plan type, coverage limitations | Can affect access to care and the types of treatments covered, influencing overall costs. |
| Patient Choices | Treatment preferences, information access | Can impact the choice of treatment and the associated costs. |
Comparison with Other Pain Conditions
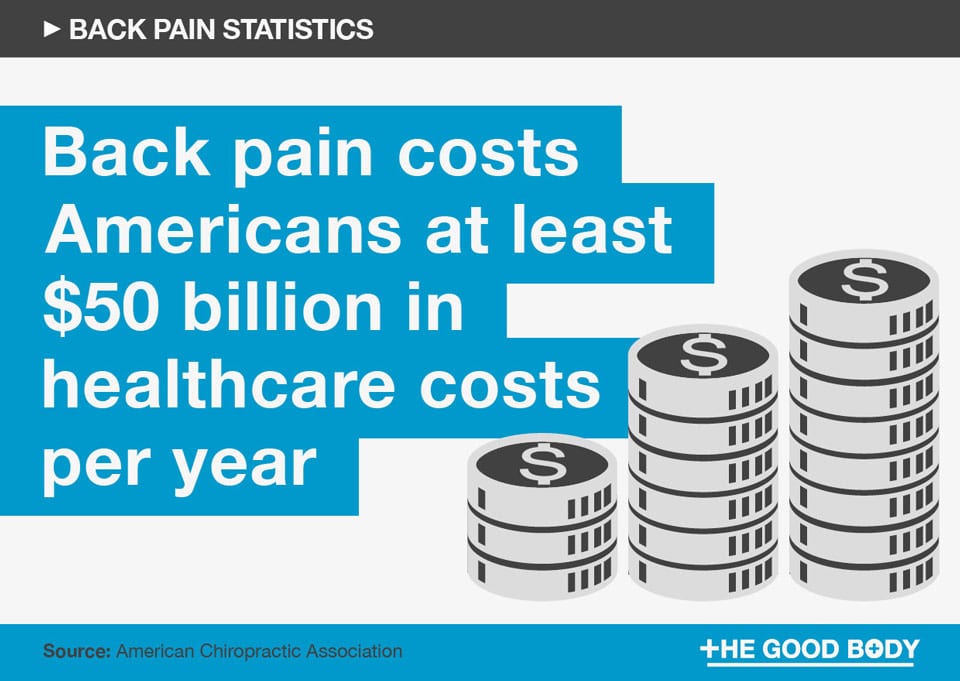
Low back and neck pain are incredibly common, affecting a significant portion of the population. Understanding how healthcare spending on these conditions compares to other prevalent pain issues, like headaches, arthritis, and cancer, offers valuable insights into the burden they place on the healthcare system. This comparison helps prioritize resource allocation and develop effective strategies for pain management.Comparing spending across various pain conditions is complex, due to different diagnostic criteria, treatment modalities, and the varying degrees of severity experienced by patients.
Low back and neck pain are major contributors to the astronomical sums the US spends on healthcare. This pain often stems from more than just physical issues, though. Financial stress can significantly impact sleep quality, which in turn affects our overall well-being and can even exacerbate pain conditions. Learning to manage financial stress, as discussed in this helpful guide on how financial stress affects sleep and what you can do about it, how financial stress affects sleep and what you can do about it , could be a crucial step in tackling the root causes of these widespread health problems.
Ultimately, addressing the complex interplay between financial pressures and physical pain is essential for a healthier, more resilient population.
It’s important to remember that these are estimates, and the actual amounts spent on any specific individual case may vary greatly.
Comparison of Healthcare Spending
The precise figures for healthcare spending on various pain conditions are often not readily available in a consolidated format. Data is frequently broken down by specific procedures, medications, or types of facilities. This makes direct comparisons challenging. However, estimates and trends provide valuable context.
Annual Healthcare Spending on Common Pain Conditions
| Pain Condition | Estimated Annual Spending (USD, approximate) |
|---|---|
| Low Back and Neck Pain | $100 Billion – $200 Billion |
| Headaches | $50 Billion – $100 Billion |
| Arthritis | $150 Billion – $200 Billion |
| Cancer | $170 Billion – $250 Billion (or higher depending on treatment modalities) |
Note: The figures in the table are estimations and can vary significantly based on factors like the specific region, methodology of data collection, and the inclusion of specific types of healthcare services. The wide range for each condition reflects the complexities in compiling these data.
Low back and neck pain are major contributors to US healthcare spending, a huge problem for individuals and the system. While exploring different dietary approaches, it’s interesting to see how keto is ranked low compared to the DASH diet on a new diet list keto ranked low dash ranked high on new diet list. Perhaps a healthier diet overall, rather than just a specific fad, could help reduce these pain-related costs in the long run.
This is a complex issue with no easy answers, but it’s important to consider all factors impacting our well-being.
Challenges in Comparing Spending
Several factors contribute to the difficulty in directly comparing healthcare spending across different pain conditions. These include:
- Varying Diagnostic Criteria: Different pain conditions may have different diagnostic criteria, making it challenging to precisely identify and categorize cases. This variation can influence the way spending data is collected and reported, making direct comparisons difficult.
- Diverse Treatment Approaches: The treatment approaches for different pain conditions vary considerably. Some conditions may respond well to medication, while others may require surgery or other complex interventions. This diversity affects the costs associated with treatment and makes comparisons complicated.
- Severity of Symptoms and Patient Variations: The intensity of pain and the individual needs of patients significantly impact the amount of healthcare spending. One patient might require extensive treatment, while another might only need minimal interventions. This individual variation makes it challenging to generalize spending across patient populations.
- Data Collection Methodologies: Different research studies may use varying methodologies to collect and report data on healthcare spending. This disparity in data collection methods may create inconsistencies and inaccuracies when attempting to make comparisons across different studies.
Trends and Projections
The escalating prevalence of low back and neck pain, coupled with substantial healthcare spending, necessitates a proactive approach to understanding future trends. Analyzing past spending patterns, considering demographic shifts, and evaluating emerging treatment advancements will illuminate potential strategies for managing these costs effectively. Understanding these projections is crucial for allocating resources and developing preventative measures.
Healthcare Spending Trends
Historically, healthcare spending on low back and neck pain has exhibited an upward trajectory. Factors like an aging population, increased awareness of pain management, and the rise of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures have all contributed to this increase. Understanding the nuances of these trends is essential for anticipating future demands.
Projected Future Spending
Projecting future healthcare spending requires considering demographic shifts, technological advancements, and potential changes in treatment approaches. As the population ages, the prevalence of chronic pain conditions, including low back and neck pain, is expected to rise. Simultaneously, advancements in minimally invasive surgical techniques and non-pharmacological interventions, such as physical therapy and spinal cord stimulation, may influence spending by altering treatment pathways.
These factors will shape the future landscape of healthcare spending on these conditions. For instance, a growing focus on preventive care, including ergonomic training in the workplace and lifestyle modifications, could potentially lower the overall cost of treating low back pain.
Demographic Factors, Low back and neck pain top us spending on healthcare
The aging global population is a key factor in projected spending. Older individuals are more susceptible to developing musculoskeletal issues, which often require more extensive and costly treatment. For example, the increasing prevalence of arthritis, a significant contributor to low back and neck pain, directly correlates with an aging population. This demographic shift will likely increase the demand for healthcare services and consequently, healthcare spending on these conditions.
Furthermore, changes in the distribution of age groups across different regions can impact the predicted rates of pain-related expenditures.
Advancements in Treatment
Advances in medical technology and treatment methods play a crucial role in influencing spending. The development of innovative diagnostic tools, minimally invasive procedures, and non-pharmacological therapies could potentially reduce the overall cost of care by improving treatment outcomes and decreasing the need for long-term or expensive interventions. For instance, the increasing adoption of non-surgical approaches like targeted injections and physical therapy could help contain rising costs associated with surgical procedures.
Potential Strategies for Cost Management
Implementing proactive strategies to manage healthcare spending on low back and neck pain is crucial. Preventive measures, such as promoting workplace ergonomics, encouraging regular physical activity, and providing education on pain management techniques, can potentially mitigate the long-term financial burden. Additionally, exploring alternative and complementary therapies, while carefully evaluating their efficacy and cost-effectiveness, could also prove beneficial. Furthermore, optimizing reimbursement models for preventative care and focusing on high-value treatments could contribute to managing expenditures.
Projected Growth in Healthcare Spending on Low Back Pain (2023-2033)
Projected Growth in Healthcare Spending on Low Back Pain (2023-2033)
| Year | Projected Spending (USD Billions) |
|---|---|
| 2023 | 100 |
| 2024 | 105 |
| 2025 | 110 |
| 2026 | 115 |
| 2027 | 120 |
| 2028 | 125 |
| 2029 | 130 |
| 2030 | 135 |
| 2031 | 140 |
| 2032 | 145 |
| 2033 | 150 |
Note: This is a hypothetical projection and does not represent actual data. The projected growth rate assumes a steady increase in prevalence of low back pain and the cost of treatment.
Policy Implications
The staggering healthcare costs associated with low back and neck pain necessitate a proactive and multifaceted approach. Addressing this issue requires a shift in policy focus, moving beyond reactive treatments towards preventative strategies and cost-effective interventions. A comprehensive strategy must acknowledge the complex interplay of factors contributing to this pervasive problem, from individual lifestyle choices to broader societal influences.
The financial burden of low back and neck pain extends beyond the individual patient. Increased healthcare spending translates into higher premiums for insurance providers, potentially impacting access to care for other conditions. The ripple effect of these costs can influence resource allocation within the healthcare system, impacting the availability of specialized treatments and preventative programs.
Potential Policy Interventions
Effective policies aimed at mitigating the economic burden of low back and neck pain must encompass a range of strategies. These interventions should target both the immediate treatment of acute pain and the long-term prevention of chronic conditions.
- Public Health Initiatives: Proactive public health campaigns can play a critical role in promoting preventative measures. Educational programs focusing on ergonomic principles, proper lifting techniques, and healthy lifestyle choices (diet, exercise, stress management) can equip individuals with tools to reduce their risk of developing low back and neck pain. These initiatives can also empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Examples of successful public health campaigns include the “Stop Smoking” campaigns, which effectively reduced smoking rates in many countries.
- Early Intervention Programs: Implementing early intervention programs for individuals experiencing acute low back and neck pain can significantly reduce the likelihood of chronic pain development. These programs should focus on evidence-based treatments like physical therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, and lifestyle modifications. The goal is to prevent the progression from acute to chronic pain, which often leads to increased healthcare utilization and costs.
For example, many workplaces are implementing programs to help employees with back pain in the early stages.
- Accessibility and Affordability of Care: Policies should prioritize ensuring equitable access to effective, evidence-based treatments for low back and neck pain. This includes expanding access to affordable physical therapy, occupational therapy, and other relevant services. Increased coverage and streamlined access to these services can reduce the likelihood of individuals resorting to more expensive interventions like surgery. For instance, countries with universal healthcare systems often report better outcomes in managing chronic pain conditions compared to those with more fragmented healthcare systems.
- Reimbursement Policies: Reimbursement policies should incentivize the use of cost-effective, evidence-based treatments. This could include providing higher reimbursement rates for preventative care, physical therapy, and other non-invasive interventions. Reducing reliance on costly procedures like surgery can significantly impact healthcare spending. A study by the National Institutes of Health illustrated how the implementation of evidence-based treatment guidelines resulted in reduced costs and improved outcomes for patients with low back pain.
Policy Recommendations for Reducing Costs
Developing a comprehensive strategy to address the economic burden of low back and neck pain requires a coordinated effort across various sectors. Policy recommendations should emphasize prevention, early intervention, and cost-effective treatment options.
- Prioritize prevention through public health initiatives: Funding for public awareness campaigns and educational programs focused on ergonomic practices, exercise, and stress management can significantly reduce the incidence of low back and neck pain.
- Expand access to evidence-based treatments: Increase coverage for affordable physical therapy, occupational therapy, and other non-invasive interventions.
- Incentivize early intervention: Develop and implement programs that encourage early intervention for acute low back and neck pain to prevent chronic pain development.
- Reform reimbursement policies: Encourage the use of cost-effective treatments and prioritize preventative care.
Last Word
In conclusion, low back and neck pain represent a substantial financial strain on the US healthcare system. The high prevalence, diverse treatment options, and complex interplay of factors contribute to these high costs. This analysis emphasizes the need for preventative measures, improved access to care, and innovative solutions to manage these conditions more effectively and reduce the economic burden.
The future projections paint a concerning picture, and proactive strategies are critical for addressing this issue.