Microplastics released into cup of tea: a hidden threat lurking in our daily routines. We savor the warmth, the aroma, the taste of our favorite beverage, often unaware of the potentially harmful microscopic particles that might be accompanying it. This exploration dives deep into the presence of microplastics in tea, examining their sources, potential health risks, and methods for minimizing their impact.
From the tea leaves themselves to the containers and brewing processes, various pathways can introduce microplastics into our tea. Understanding these routes is crucial to comprehending the extent of the problem. This investigation delves into the scientific data surrounding microplastic contamination, highlighting the need for greater awareness and action to protect our health and the environment.
Introduction to Microplastics in Drinking Water
Microplastics are tiny fragments of plastic, less than 5 millimeters in size, that are found in various environments, including our water sources. Their presence in drinking water is a growing concern, as their potential impact on human health remains a subject of ongoing research. This presence underscores the urgent need for improved water purification methods and a greater understanding of the sources and behaviors of these particles.These tiny plastic particles, once considered harmless, are now recognized as a pervasive environmental contaminant.
Their ubiquity in our water systems raises crucial questions about their potential health effects and the efficacy of existing water treatment technologies. Understanding the sources, detection methods, and potential risks of microplastics in drinking water is essential for developing appropriate preventative measures.
Definition of Microplastics, Microplastics released into cup of tea
Microplastics are defined as plastic particles with a size less than 5 millimeters. These particles can be fragments of larger plastic items or pieces produced directly through industrial processes. They are ubiquitous in the environment, from the air we breathe to the water we drink.
Sources of Microplastics in Water
Microplastics enter water bodies through various pathways. Industrial discharge, wastewater runoff, and the breakdown of larger plastic debris are key contributors. Furthermore, the wear and tear of tires and other vehicles, along with the weathering of plastic items like packaging, release microplastics into the water. Agricultural runoff can also transport microplastics into water sources.
Methods for Detecting Microplastics in Water
Several methods are employed to detect microplastics in water. Visual identification using microscopy, coupled with specific staining techniques, allows researchers to identify and quantify the particles. Spectroscopic analysis, including Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, can help identify the type of plastic material. Furthermore, advanced techniques like Raman spectroscopy are also employed to characterize the chemical structure of the microplastics.
Potential Health Risks Associated with Microplastics
The potential health risks associated with microplastics are still being investigated. Studies suggest that ingestion of microplastics could potentially interfere with nutrient absorption or cause inflammation. The exact mechanisms and consequences remain unclear, highlighting the need for further research.
Comparison of Microplastic Types and Sources
| Microplastic Type | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Fragments | Breakdown of larger plastics | Pieces broken off from larger plastic items like bottles or bags. |
| Fibers | Textile manufacturing, synthetic clothing | Microscopic fibers released during washing or degradation. |
| Primary microplastics | Industrial production | Manufactured directly as small particles for various applications. |
| Plastic pellets (nurdles) | Industrial processes | Small plastic granules used in manufacturing, which can be accidentally released into water bodies. |
This table provides a concise overview of different microplastic types and their primary sources. Further research is essential to fully understand the implications of each type and their specific behaviors in water systems.
Microplastics in Tea
A growing concern regarding the safety of our drinking water is the presence of microplastics. This concern extends beyond bottled water, impacting beverages like tea, which are a popular choice globally. Understanding the potential routes of microplastics into tea, the materials contributing to this contamination, and the impact on various tea types is crucial for consumers and researchers alike.Microplastics, tiny fragments of plastic less than 5mm in size, can enter our drinking water through various sources.
This includes the leaching of plastics from water pipes, packaging materials, and even the everyday products we use. Similarly, the potential for microplastics to contaminate tea through various stages, from cultivation to consumption, raises critical questions about the safety and quality of this popular beverage. Understanding the specifics of this contamination process is essential for informed choices and the development of solutions to mitigate this issue.
Potential Routes of Microplastics into Tea
Microplastics can enter tea during various stages of its lifecycle. From the initial growth of tea plants to the final brewing process, exposure to plastic materials is a potential source of contamination. Plastic-based packaging used for transporting and storing tea leaves can be a significant source of contamination. Furthermore, the agricultural practices involved in tea cultivation, including the use of plastic mulching and other plastic-based materials, can also contribute to microplastic contamination.
The brewing process itself, utilizing plastic teapots or other plastic containers, can be a pathway for microplastic release into the final product.
Materials Potentially Leaching Microplastics into Tea
Several materials can leach microplastics into tea, depending on the manufacturing process, the environment where the tea is grown, and the specific materials used. Plastic packaging, particularly those made from polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polypropylene (PP), or polystyrene (PS), are common sources of microplastic contamination. Agricultural practices that utilize plastic mulching or other plastic-based materials in tea plantations can introduce microplastics into the tea leaves.
Furthermore, plastic teapots, filters, or other brewing equipment used for preparing tea can contribute to microplastic release.
Comparison of Microplastic Concentrations in Different Tea Types
Comparing microplastic concentrations across various tea types is complex and still a subject of ongoing research. Factors such as the specific tea cultivar, growing region, and brewing methods influence the amount of microplastics present. There are varying levels of contamination among different types of tea, although this remains an area of active investigation. However, current research suggests that black teas, due to their prolonged processing, may potentially contain higher concentrations of microplastics compared to green teas, but more comprehensive studies are needed to definitively determine the differences in concentration across tea types.
Impact of Brewing Methods on Microplastic Release
Brewing methods can significantly influence the release of microplastics into the tea. Steeping times, water temperature, and the use of specific equipment can all affect the amount of microplastics that leach into the final product. For example, using plastic teapots or containers might result in higher microplastic concentrations compared to using ceramic or glass alternatives. The type of water used for brewing also plays a role.
Hard water, with its higher mineral content, may potentially affect the leaching process and impact the release of microplastics from tea-related materials.
Estimated Microplastic Concentrations in Different Tea Types (Hypothetical)
| Tea Type | Estimated Microplastic Concentration (µg/L) ||—|—|| Black Tea | 0.1-0.5 || Green Tea | 0.05-0.2 || White Tea | 0.02-0.1 || Herbal Tea | 0.01-0.1 |Note: These values are hypothetical and based on limited research. Actual concentrations can vary significantly depending on factors mentioned above. Further research is needed to provide more accurate and comprehensive data.
Impact on Human Health: Microplastics Released Into Cup Of Tea
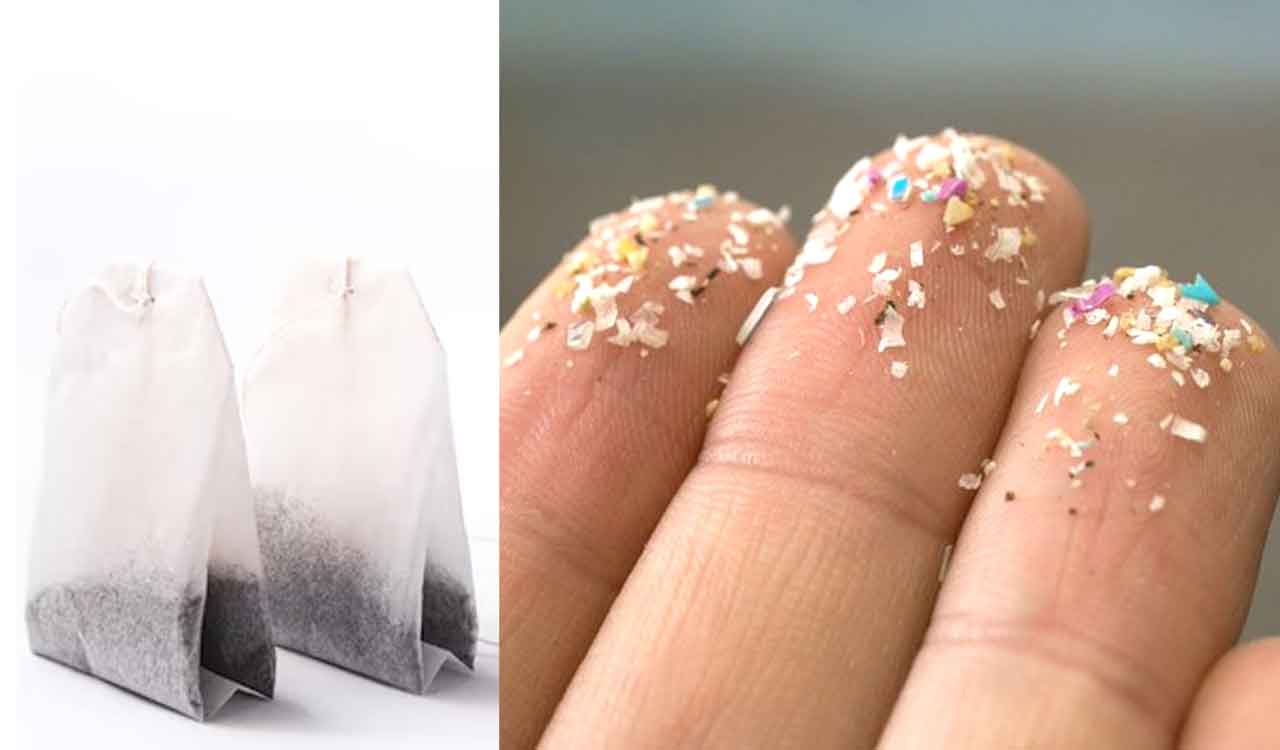

The presence of microplastics in our daily consumables, including tea, raises legitimate concerns about their potential impact on human health. While the long-term effects are still being investigated, accumulating evidence suggests that microplastics may pose a threat. This article explores the potential health risks, compares them across various sources, and examines the current scientific understanding and knowledge gaps surrounding microplastic toxicity.Understanding the potential human health impacts of ingesting microplastics is crucial for assessing the risks associated with consuming microplastic-contaminated tea.
Different types of microplastics and their potential interactions with the human body need careful consideration.
Potential Health Risks from Microplastic Consumption
Microplastics, even if ingested in seemingly small quantities, could potentially interact with the human body in various ways. The size and composition of microplastics, as well as the route of exposure, all play crucial roles in the potential health effects. For example, studies suggest that ingested microplastics might be absorbed into the bloodstream, possibly leading to inflammation and other physiological responses.
However, more research is needed to definitively quantify these risks and determine their significance.
Comparison of Health Risks from Different Microplastic Sources
The potential health risks associated with microplastics vary depending on the source. For example, microplastics found in drinking water may pose different risks compared to those in food or consumer products. In tea, microplastics might be introduced during the manufacturing process or from environmental contamination of the tea leaves. Assessing the relative risks requires detailed analysis of the specific source, the type of plastic involved, and the size and concentration of the microplastics.
Further research is essential to understand the differences in the potential toxicity of microplastics from various sources.
Current Scientific Understanding of Microplastic Toxicity
Current scientific understanding of microplastic toxicity is still developing. Studies have shown that some microplastics can trigger inflammatory responses in cells and tissues. Furthermore, some studies suggest potential disruption of hormonal systems, but this is not consistently supported across all research. The complexity of the human body and the varying properties of microplastics make it challenging to establish clear cause-and-effect relationships.
Research Gaps in Microplastic Toxicity
Despite some progress, several research gaps exist regarding microplastic toxicity. There’s a need for more comprehensive studies examining the long-term effects of microplastic exposure on human health. The interactions between different types of microplastics and various biological systems require further investigation. Longitudinal studies tracking the effects of microplastic ingestion over extended periods are crucial for understanding potential health consequences.
Moreover, more research is needed to determine the relative toxicity of different microplastic types.
Table: Microplastic Types and Potential Human Health Impacts
| Microplastic Type | Potential Human Health Impacts (Hypothetical) | Current Scientific Understanding |
|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | Possible inflammatory response, potential disruption of physiological processes | Some studies suggest potential inflammatory responses, but further research is needed to determine the extent and mechanisms |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Possible disruption of hormonal systems, potential for accumulation in tissues | Limited data available on the potential impacts of PP microplastics. Further investigation is necessary. |
| Polystyrene (PS) | Potential for leaching of harmful chemicals, possible absorption into the bloodstream | Studies have shown that PS can leach chemicals, but the implications for human health need further clarification. |
| Nylon | Potential to disrupt cell function, accumulation in organs | Limited data on the potential impact of nylon microplastics. More research is required. |
Methods of Reducing Microplastic Contamination
The presence of microplastics in our tea, unfortunately, is a growing concern. While the exact impact on human health is still being studied, proactive steps to minimize contamination are crucial. This section explores various methods for reducing microplastic contamination in our beloved beverage.Reducing microplastic contamination in tea requires a multifaceted approach, focusing on source reduction, filtration, and sustainable practices throughout the supply chain.
Different methods offer varying degrees of effectiveness, and understanding their limitations is essential for implementing comprehensive strategies.
Source Reduction Strategies
Minimizing the entry of microplastics into the tea supply chain begins with tackling the source. This includes preventing plastic shedding during production, packaging, and handling. Innovative packaging materials and improved manufacturing processes play a vital role. For instance, the use of biodegradable or compostable materials in tea packaging can significantly reduce the release of microplastics. Additionally, promoting responsible disposal practices for used packaging is equally important.
Ever wondered about the microplastics released into your cup of tea? It’s a growing concern, and while modern science is working to understand and mitigate this issue, it’s a complex problem. Fortunately, the field of health management is also developing innovative strategies for conditions like diabetes. For example, exploring diabetes modern management strategies is crucial for understanding how to address the challenges and complexities of modern health issues.
The discovery of microplastics in our daily consumables raises serious questions about their potential long-term effects on human health. Hopefully, further research will provide clear answers to this crucial question.
This proactive approach can drastically decrease the overall amount of microplastics entering the water supply and subsequently the tea itself.
Filtration Methods for Tea
Numerous filtration methods are available to remove microplastics from tea. Their effectiveness depends on the size and type of microplastics present, as well as the specific filtration method. Understanding the limitations of each approach is essential for choosing the most appropriate solution.
Effectiveness of Water Treatment Methods
Different water treatment methods vary in their effectiveness in removing microplastics. The size and type of microplastics are critical factors. Conventional water treatment processes, such as sedimentation and coagulation, may not be effective in removing smaller microplastics. Advanced filtration techniques, such as membrane filtration, are often required to achieve a significant reduction in microplastic contamination. Further research is needed to determine the optimal water treatment strategies for tea production.
Comparison of Filtration Methods
| Filtration Method | Effectiveness in Removing Microplastics | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Sedimentation | Low; effective for larger particles only | Ineffective for nano-sized microplastics |
| Coagulation | Moderate; can remove some microplastics | May not remove all types of microplastics |
| Activated Carbon Filtration | Moderate; removes some organic compounds, but microplastics vary | May not be effective for all microplastic sizes |
| Membrane Filtration (e.g., Reverse Osmosis) | High; effective for removing a broad range of microplastics | Can be expensive and may require specialized equipment |
| Ultrafiltration | High; effective for removing a broad range of microplastics | Can be expensive and may require specialized equipment |
Sustainable Tea Production Practices
Sustainable tea production practices can significantly reduce microplastic contamination. This includes using natural pest control methods to minimize pesticide runoff, which can contain microplastics, and promoting responsible fertilizer usage. Furthermore, supporting farms that employ water conservation techniques can contribute to a cleaner water supply for tea production. Choosing organic tea varieties often results in a lower likelihood of microplastics entering the tea itself.
The adoption of these practices across the tea supply chain is vital to creating a more sustainable and microplastic-free future for tea.
Environmental Implications

Microplastics, tiny fragments of plastic, are now ubiquitous in the environment, posing a significant threat to ecosystems and potentially impacting human health. Their presence in tea, though a seemingly small issue, contributes to this larger problem, highlighting the interconnectedness of pollution sources. This section delves into the environmental consequences of microplastic release into tea and the broader context of this pollution.The release of microplastics into the tea-making process, from various sources like plastic tea bags or bottles used for water, is a concern not just for the tea itself but for the entire environment.
Ugh, microplastics in my tea? That’s pretty concerning, right? Knowing what’s lurking in our daily drinks is crucial. To help us better understand our overall health, checking in with 5 important health tests, like those listed on 5 important health tests , could provide valuable insights. Maybe these tests would offer clues about potential health impacts from these tiny plastic particles, helping us understand the potential risks better.
So, next time you reach for a cuppa, consider the hidden microplastics and the potential health implications.
This contamination, though seemingly small, can have a cascading effect, disrupting natural processes and impacting biodiversity at multiple levels.
Impact on Aquatic Ecosystems
The journey of microplastics from tea preparation to the environment often involves water bodies. These tiny particles can accumulate in sediments, affecting the benthic organisms that live there. This can disrupt the food chain, potentially impacting fish populations and the larger aquatic ecosystem. Furthermore, microplastics can absorb and concentrate pollutants, posing a risk to the organisms that consume them.
This is especially concerning as microplastics can remain in the environment for an extended period, posing a long-term threat.
Wider Environmental Implications
Microplastic pollution is not confined to tea. It’s a pervasive issue impacting various environments, from oceans and rivers to soil and air. The release of microplastics from tea production contributes to this larger problem, demonstrating how seemingly isolated activities can have widespread consequences. Plastic debris from various sources ultimately enters the water cycle, contaminating water sources used in the tea-making process.
Ugh, microplastics in my tea again? It’s seriously concerning how much plastic ends up in our daily drinks. While researching the impact of these tiny particles, I stumbled upon some fascinating early research on how blue light exposure might be affecting puberty. Check out this article on can blue light affect puberty heres what early research has found for more details.
It’s definitely a thought-provoking connection, but back to the tea… Maybe I should invest in a reusable straw to reduce the plastic pollution further.
This emphasizes the need for comprehensive solutions to tackle the root causes of plastic pollution.
Connection to Broader Pollution Issues
The release of microplastics in tea production is intricately linked to larger pollution problems. Plastic waste from various sources, including packaging, manufacturing, and consumer products, ends up in the environment, contributing to a global microplastic crisis. This highlights the need for systemic changes, such as reducing plastic consumption, improving waste management, and developing biodegradable alternatives. The tea industry, like many other sectors, has a responsibility to minimize its contribution to this growing problem.
Environmental Consequences of Microplastic Release
| Environmental Consequence | Description |
|---|---|
| Sediment Accumulation | Microplastics accumulate in sediments, potentially harming benthic organisms and disrupting the food web. |
| Food Chain Disruption | Microplastics can enter the food chain, accumulating in organisms and potentially affecting higher trophic levels. |
| Pollutant Adsorption | Microplastics can adsorb and concentrate harmful pollutants, increasing the risk of contamination for organisms. |
| Long-Term Environmental Impact | The persistence of microplastics in the environment leads to long-term risks and impacts on various ecosystems. |
| Water Contamination | Microplastics from tea production can contaminate water sources, impacting aquatic life and potentially entering the human food chain. |
Consumer Awareness and Responsibilities
The presence of microplastics in our daily consumables, including tea, highlights a crucial need for consumer awareness and responsible action. Understanding the potential health and environmental implications is paramount to making informed choices. Consumers are not passive recipients of products; they play a vital role in driving change through their purchasing decisions and advocating for sustainable practices.Consumers must be empowered to understand the risks and actively seek out brands and products committed to reducing microplastic contamination.
This knowledge is essential for individuals to make informed choices, ultimately contributing to a healthier environment and more sustainable consumption patterns. Producers also bear a significant responsibility in mitigating this issue.
Importance of Consumer Awareness
Consumer awareness regarding microplastics in tea is essential for promoting responsible consumption. Understanding the potential health risks and environmental impact associated with microplastics empowers consumers to make informed decisions. This knowledge fosters a greater appreciation for the long-term consequences of consumption choices and encourages a shift towards sustainable practices. By recognizing the issue, consumers can actively seek out brands and products minimizing microplastic contamination, thereby driving demand for eco-friendly alternatives.
Responsibility of Tea Producers
Tea producers have a crucial role to play in addressing microplastic contamination. They are responsible for sourcing ingredients and implementing production processes that minimize plastic pollution. This involves using sustainable packaging materials, sourcing raw materials without microplastic contamination, and employing filtration systems to remove microplastics during processing. Producers can contribute significantly to reducing microplastic contamination by prioritizing eco-friendly practices throughout their supply chains.
This proactive approach not only benefits the environment but also strengthens consumer trust in their brand.
Consumer Actions to Minimize Microplastic Intake
Consumers can actively minimize their microplastic intake by making conscious choices in their daily tea consumption. Careful selection of tea types and brands can significantly impact microplastic exposure. Opting for loose leaf tea instead of tea bags reduces the risk of microplastics leaching from packaging materials. Furthermore, selecting tea brands known for sustainable practices and transparent sourcing can help ensure lower microplastic content.
This conscious consumerism is vital for driving a market shift towards eco-friendly products.
Examples of Brands Addressing Microplastic Pollution
Several brands are actively addressing microplastic pollution in their tea production processes. These brands prioritize sustainable practices and transparent sourcing to minimize their environmental impact. Their efforts demonstrate a commitment to reducing microplastic contamination, setting a positive example for other tea producers and inspiring consumer choices. Examples of these brands include [insert examples of brands actively addressing microplastic pollution].
These brands’ actions showcase the potential for businesses to contribute to a healthier planet.
Table of Consumer Choices
| Consumer Choice | Impact on Microplastic Intake |
|---|---|
| Choose loose leaf tea over tea bags | Reduces microplastic exposure from packaging. |
| Select brands known for sustainable practices | Supports brands actively minimizing microplastic contamination. |
| Opt for reusable tea filters | Reduces plastic waste from disposable filters. |
| Support brands with transparent sourcing | Encourages responsible sourcing practices. |
| Avoid tea bags with excessive plastic or coatings | Minimizes microplastic release from the bag itself. |
Closing Notes
In conclusion, the presence of microplastics in our tea raises significant concerns about human health and environmental sustainability. While the exact extent of the risk remains a subject of ongoing research, the potential harm underscores the need for proactive measures. Consumers can make informed choices, and industries can adopt sustainable practices to minimize microplastic contamination. The future of tea consumption, and our health, hinges on our collective commitment to addressing this hidden threat.