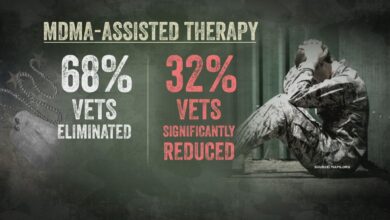
No proof yet that marijuana helps with PTSD symptoms. While the allure of using cannabis for treating PTSD is strong, the current research is far from conclusive. This exploration dives deep into the existing studies, examining their methodologies, findings, and limitations. We’ll also look at alternative treatments and the complexities of public perception and policy implications surrounding this controversial topic.
The research, summarized in tables, highlights the challenges in establishing a direct link between marijuana use and PTSD symptom relief. Potential mechanisms of action are discussed, but conclusive evidence remains elusive. Ultimately, this comprehensive look underscores the need for further rigorous research before any definitive conclusions can be drawn.
Potential Mechanisms of Action

Marijuana, with its diverse cannabinoid components, has shown potential in alleviating certain symptoms, prompting investigation into its possible mechanisms of action in relation to PTSD. While more research is needed, the interaction of cannabinoids with the brain’s neurochemical pathways suggests avenues for exploring its potential therapeutic role. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing targeted treatments and predicting potential benefits or drawbacks.The brain’s complex network of neurotransmitters, including serotonin, dopamine, and glutamate, plays a vital role in regulating mood, anxiety, and memory.
PTSD often involves dysregulation of these neurochemicals, leading to symptoms like anxiety, flashbacks, and avoidance behaviors. Marijuana’s cannabinoids, notably tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), can potentially influence these neurotransmitter systems, potentially affecting the brain’s response to stress and trauma. This influence is not fully understood, and further investigation is needed.
Cannabinoid Receptors and Neurotransmitter Interactions
The brain possesses cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) that interact with various neurotransmitters. These receptors are widely distributed throughout the brain, including regions associated with emotional processing and memory formation. When cannabinoids bind to these receptors, they can modulate the activity of other neurotransmitters, potentially affecting the intensity of stress responses and the associated symptoms of PTSD. The specific impact of cannabinoids on neurotransmitter systems is complex and not yet fully understood, however.
While there’s still no definitive proof that marijuana helps with PTSD symptoms, it’s important to note the ongoing research. Meanwhile, the CDC recently reported that monkeypox isn’t likely airborne, with 45 cases in the US, as reported here. This highlights the diverse health concerns we face, and the need for more conclusive studies on marijuana’s potential therapeutic uses for PTSD.
Understanding these complex interactions is critical to evaluating the potential therapeutic effects of marijuana for PTSD.
Effects of Different Cannabinoids
Different cannabinoids exhibit varied effects on brain function. THC, the primary psychoactive component, can influence mood and perception, potentially affecting emotional regulation. CBD, the non-psychoactive component, has demonstrated potential in reducing anxiety and inflammation, which might contribute to alleviating PTSD symptoms. The combined effects of THC and CBD, in varying ratios, are also being investigated for their potential therapeutic benefits.
The precise mechanisms through which these cannabinoids interact with the brain and their influence on PTSD symptoms are still being researched.
Comparison with Other PTSD Treatments
Existing PTSD treatments, including psychotherapy and medication, often target specific neurotransmitter systems or behavioral patterns. Pharmacological treatments, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), primarily focus on serotonin regulation. Psychotherapy approaches, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), aim to modify maladaptive thought patterns and behaviors associated with PTSD. Marijuana’s potential mechanisms, if proven effective, would offer a potentially complementary approach, targeting various neurotransmitter systems and potentially reducing symptom severity in conjunction with existing treatments.
Potential Effects of Different Marijuana Compounds on PTSD Symptoms (Table)
| Cannabinoid | Potential Effect on PTSD Symptoms | Mechanism of Action (Summary) |
|---|---|---|
| THC | Potential mood alteration, possible anxiety reduction (depending on dosage and individual response). | Interacts with cannabinoid receptors, potentially influencing neurotransmitter systems associated with emotional processing. |
| CBD | Potential anxiety reduction, potential anti-inflammatory effects, possible reduction in stress response. | Interacts with cannabinoid receptors, potentially modulating neurotransmitter activity, and possibly reducing inflammation. |
| THC:CBD Ratio | Potential synergistic effects, varying impact depending on ratio, further research needed. | The combined impact of THC and CBD on cannabinoid receptors and neurotransmitters is complex and not yet fully understood. |
Limitations and Challenges in Research
Unraveling the intricate relationship between marijuana and PTSD is fraught with complexities. Existing research, while suggestive, often struggles to definitively establish a clear causal link. The challenges stem from the inherent difficulties in studying a multifaceted condition like PTSD, combined with the inherent sensitivities surrounding cannabis use. These complexities make drawing firm conclusions about the efficacy of marijuana in treating PTSD symptoms challenging.Methodological limitations, potential biases, and the inherent difficulty in establishing causality all contribute to the uncertainty surrounding this area of research.
Understanding these obstacles is crucial for interpreting existing findings and guiding future investigations, ultimately aiming for more reliable and conclusive results.
Key Limitations of Existing Research
The existing research on marijuana and PTSD suffers from several critical limitations. Sample sizes are often small, making it difficult to generalize findings to broader populations. Furthermore, the heterogeneity of PTSD symptoms and varying levels of marijuana use among participants can obscure the specific effects of cannabis. The lack of standardized assessment tools for PTSD and marijuana use further complicates the analysis and comparison of studies.
These factors contribute to the variability and inconsistency in reported outcomes.
While there’s no definitive proof yet that marijuana helps with PTSD symptoms, it’s a fascinating area of research. Interestingly, the question of whether brain aneurysms are hereditary are brain aneurysms hereditary is also complex and has significant implications for medical science, which, in turn, adds layers to the puzzle of how we understand and treat mental health conditions like PTSD.
Ultimately, more research is needed to determine the true impact of various factors on PTSD, including potential treatments like marijuana.
Methodological Challenges in Studying the Complex Relationship
Studying the complex interplay between marijuana and PTSD presents considerable methodological challenges. The inherent subjective nature of PTSD symptoms, including flashbacks and nightmares, makes objective measurement difficult. Furthermore, the potential for confounding factors, such as pre-existing mental health conditions, co-occurring substance use disorders, and environmental stressors, can obscure the direct effects of marijuana use. The need for rigorous control groups and careful consideration of these confounding variables is essential.
Potential for Bias in Research Design and Data Interpretation
Bias can infiltrate research in numerous ways. For instance, researcher bias, where preconceived notions influence data collection or interpretation, can skew results. Participant bias, where individuals report symptoms or use patterns in ways that align with their expectations or desires, is also a significant concern. Publication bias, where studies with positive results are more likely to be published than those with negative or inconclusive findings, further distorts the overall picture.
Addressing these potential biases requires meticulous research design, transparent reporting, and independent review processes.
While there’s still no definitive proof that marijuana eases PTSD symptoms, it’s crucial to remember that health concerns like this often require thorough research and careful consideration. Consider the devastating news surrounding this strain of bird flu, where this strain of bird flu kills one third of patients , highlighting the serious impact certain illnesses can have.
The lack of conclusive evidence for marijuana’s PTSD benefits underscores the need for cautious approaches to new treatments.
Difficulty in Establishing Causality
Establishing a direct causal link between marijuana use and PTSD symptoms is a significant hurdle. Correlation does not equate to causation, and existing studies often struggle to definitively prove that marijuana usecauses* improvements or exacerbations of PTSD symptoms. Other factors, such as the individual’s overall health, coping mechanisms, and support systems, can play significant roles in influencing the relationship.
This necessitates longitudinal studies that track participants over extended periods to observe the interplay of various factors.
Ethical Considerations in Research on Marijuana and PTSD, No proof yet that marijuana helps with ptsd symptoms
| Ethical Consideration | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Informed Consent | Participants must fully understand the study’s purpose, procedures, potential risks and benefits, and their right to withdraw at any time. |
| Confidentiality | Protecting the privacy and anonymity of participants is paramount, ensuring their personal information is handled securely. |
| Minimizing Harm | Researchers must take steps to minimize potential harm to participants, including careful consideration of the potential for adverse effects associated with marijuana use, particularly in vulnerable populations. |
| Vulnerable Populations | Special consideration must be given to vulnerable populations, such as minors or individuals with pre-existing conditions, to ensure their safety and well-being. |
| Transparency and Objectivity | Researchers must maintain transparency in their methodology, data analysis, and reporting, ensuring objectivity and avoiding potential conflicts of interest. |
Alternative Treatment Approaches for PTSD
Navigating the complexities of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) requires a multifaceted approach that considers various treatment modalities. While the potential benefits of marijuana for PTSD are still under investigation, established and emerging treatments offer proven efficacy in managing symptoms and improving quality of life. This exploration delves into these alternative approaches, highlighting their potential benefits and risks, and emphasizes the crucial role of personalized treatment plans.Effective PTSD treatment often involves a combination of therapies and strategies tailored to individual needs.
This necessitates careful consideration of each approach’s strengths, weaknesses, and potential side effects. Understanding the diverse landscape of available options empowers both patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions.
Established Treatment Approaches for PTSD
Numerous evidence-based treatments are available for PTSD, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. These established methods have demonstrated efficacy in reducing symptoms and improving overall well-being. A significant portion of PTSD treatment focuses on psychotherapeutic interventions, alongside medication management when necessary.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT aims to identify and modify negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with PTSD. This approach equips individuals with coping mechanisms to manage triggers and reduce emotional distress. Examples include cognitive restructuring, exposure therapy, and relaxation techniques. CBT’s strength lies in its structured, problem-solving focus, which helps patients develop long-term strategies for managing PTSD symptoms.
Limitations may include the time commitment required for therapy sessions and the need for patient engagement and motivation.
- Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT): This specialized form of CBT is specifically designed for individuals who have experienced trauma. It integrates principles of CBT with trauma-informed approaches. TF-CBT emphasizes the understanding of the trauma’s impact on the individual and provides strategies for processing the traumatic experience. This approach is particularly effective for individuals struggling with intrusive thoughts, flashbacks, and nightmares. Potential drawbacks include the intensive nature of the therapy and the need for trained therapists specializing in TF-CBT.
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): EMDR utilizes bilateral stimulation, such as eye movements, to help process traumatic memories and reduce their emotional impact. It’s a relatively short-term therapy that has shown promise in reducing PTSD symptoms. However, its mechanism of action isn’t fully understood, and its efficacy may vary across individuals. EMDR’s strength lies in its focus on processing traumatic memories, which can significantly impact the patient’s well-being.
Emerging Treatment Approaches
While established approaches remain cornerstones of PTSD treatment, new therapies and strategies continue to emerge. Research into these innovative techniques is ongoing, and their efficacy and safety are often still being evaluated.
- Mindfulness-Based Therapies: Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and yoga, are increasingly recognized for their potential to manage stress and anxiety. These practices can help individuals develop a greater awareness of their thoughts and emotions, promoting emotional regulation and reducing the impact of trauma-related symptoms. The strength of mindfulness lies in its accessibility and integration with daily life.
Limitations might include the need for consistent practice and a degree of personal commitment.
- Neurofeedback: This technique involves monitoring brain activity and providing real-time feedback to individuals. The aim is to help them regulate their brainwaves and potentially reduce symptoms associated with PTSD. Neurofeedback shows promise, but more research is necessary to establish its long-term efficacy and safety profile. A strength is the potential for individualized treatment tailored to specific brainwave patterns.
Comparison of Treatments
| Treatment | Efficacy | Safety | Accessibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | High | Generally safe | Moderate |
| Trauma-Focused CBT (TF-CBT) | High | Generally safe | Moderate |
| Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) | Potentially high | Generally safe | Moderate |
| Mindfulness-Based Therapies | Potentially moderate | Generally safe | High |
| Neurofeedback | Potentially moderate | Generally safe | Low |
| Marijuana | Varied and inconclusive | Potential for side effects | Varied depending on location |
This table highlights the relative efficacy, safety, and accessibility of various PTSD treatments, including marijuana. Factors such as individual needs, preferences, and insurance coverage should be considered when selecting a treatment option.
Public Perception and Policy Implications: No Proof Yet That Marijuana Helps With Ptsd Symptoms
Public perception of marijuana use, particularly for treating conditions like PTSD, is a complex and often polarized issue. While some view it as a potential avenue for relief, others harbor concerns about its potential risks and the need for careful regulation. This divergence in opinion directly impacts policy decisions surrounding marijuana use for medical purposes. Understanding these public perceptions and the associated policy implications is crucial for fostering responsible and effective healthcare approaches.Public opinion on medical marijuana often intertwines with broader societal attitudes toward cannabis use.
Preconceived notions, misinformation, and differing cultural contexts contribute to varying levels of acceptance and skepticism. This makes creating evidence-based policies that address both public health concerns and individual needs a challenging but essential task. The policy landscape surrounding marijuana is dynamic, with ongoing debates and evolving regulations shaping the future of its medical applications.
Public Perceptions of Marijuana for PTSD Treatment
Public perception of marijuana’s potential role in PTSD treatment is influenced by a multitude of factors. These include existing attitudes toward cannabis use in general, levels of trust in scientific evidence, and concerns about potential side effects. Some individuals may be more open to considering marijuana as a treatment option due to anecdotal evidence or personal experiences, while others may be wary due to concerns about potential dependence or other negative consequences.
Education and awareness campaigns play a vital role in fostering informed public discourse and addressing misconceptions.
Policy Implications of Marijuana Use for PTSD Relief
Policies surrounding marijuana use for PTSD relief must consider several key aspects. These include potential benefits for patients, potential risks, and the need for rigorous research to evaluate efficacy and safety. Policymakers need to strike a balance between allowing access to potentially beneficial treatments while safeguarding public health and safety. Regulations should address issues like appropriate dosage, potential interactions with other medications, and the need for strict controls on illicit markets.
Existing Regulations and Legal Frameworks Surrounding Marijuana Use
Different jurisdictions have adopted varying approaches to regulating marijuana use. Some countries have legalized recreational use, while others have focused on strict controls. In countries where marijuana is legal for medical use, regulations often specify conditions for use, dosage limits, and restrictions on sales. These regulations aim to ensure responsible use and limit potential harm. For instance, in some states of the US, regulations dictate the specific conditions under which medical marijuana can be prescribed, the types of products that are allowed, and the procedures for obtaining a license to cultivate or distribute the plant.
These regulations are in constant flux, with ongoing adjustments based on research findings and public feedback.
Importance of Considering Public Health and Safety in Policy Decisions
Ensuring public health and safety is paramount in any policy decision regarding marijuana use for PTSD treatment. Policies should prioritize the well-being of patients while minimizing potential risks associated with misuse or inappropriate use. Comprehensive research on the long-term effects of marijuana use is crucial. Regulatory frameworks should incorporate safety measures such as age restrictions, limitations on driving under the influence, and public awareness campaigns on responsible use.
Summary Table of Countries’ Legal Frameworks Regarding Marijuana
| Country | Legal Status for Medical Use | Specific Regulations |
|---|---|---|
| United States (Selected States) | Legal in some states | Varying regulations on cultivation, sale, and prescription |
| Canada | Legal | Strict regulations on cultivation, sale, and prescription |
| Netherlands | Legal | Strict regulations on cultivation, sale, and prescription |
| Israel | Legal | Regulations exist for medical use |
| Australia (Selected States) | Legal in some states | Varying regulations on cultivation, sale, and prescription |
Future Directions for Research

The exploration of marijuana’s potential therapeutic role in PTSD is a complex and evolving field. While current research offers intriguing insights, significant gaps remain in our understanding of its mechanisms of action and efficacy. Future research must address these shortcomings to provide a more robust evidence base and inform the development of effective treatment strategies. A crucial component of this involves a commitment to rigorous methodologies and a nuanced approach that considers the diverse needs and experiences of individuals with PTSD.
Potential Areas for Future Research
Further investigation into the specific cannabinoids and their interactions within the brain is crucial. Research should explore the interplay between different cannabinoids, such as THC and CBD, and their effects on the neurobiological pathways implicated in PTSD. This could involve investigating the dose-response relationships for these compounds and examining their potential synergistic or antagonistic effects. Exploring the role of specific receptors and their associated signaling cascades is equally important.
Studies should examine how cannabinoids interact with these pathways and how they may impact symptoms like anxiety, hyperarousal, and intrusive memories.
Innovative Methodologies for Research
The use of advanced neuroimaging techniques, such as fMRI and PET scans, can provide valuable insights into the brain activity patterns associated with PTSD and the effects of marijuana. These techniques can help identify specific brain regions and networks that are affected by PTSD and how cannabinoids might modulate their activity. Combining these neuroimaging studies with behavioral assessments and self-report measures will provide a more comprehensive understanding of the complex interplay between brain activity, behavior, and subjective experience.
Moreover, longitudinal studies tracking individuals over extended periods will allow researchers to observe the long-term effects of marijuana use on PTSD symptoms.
Large-Scale Clinical Trials
The need for large-scale, well-designed clinical trials cannot be overstated. These trials should incorporate rigorous control groups and standardized assessment tools to accurately measure the efficacy and safety of marijuana-based interventions. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are essential for establishing cause-and-effect relationships and determining the optimal dosage and administration methods. Such trials will be crucial for establishing the efficacy of marijuana for PTSD and provide robust data for regulatory bodies to consider.
Pilot studies can help identify promising avenues for further investigation and refine trial protocols, thereby reducing the risk of wasting resources on ineffective approaches.
Considering Diverse Populations
Research on marijuana and PTSD should actively recruit and include diverse populations. This includes individuals from various ethnic and racial backgrounds, socioeconomic statuses, and genders. Cultural factors and potential disparities in access to treatment and resources must be considered. Studies should also consider the potential impact of pre-existing conditions and co-occurring disorders on the effectiveness and safety of marijuana-based interventions.
Furthermore, research should involve individuals with varying levels of PTSD severity and duration of symptoms to ascertain whether marijuana is effective across the spectrum of the condition.
Research Questions
- What are the specific neurobiological mechanisms through which marijuana affects PTSD symptoms?
- How do different types of marijuana preparations (e.g., smoked, edibles, topical) impact PTSD symptoms?
- What is the optimal dosage and administration method for marijuana-based interventions for PTSD?
- How does the frequency and duration of marijuana use impact the long-term effectiveness and safety of these interventions?
- What are the potential risks and side effects of using marijuana for PTSD treatment, and how can these be mitigated?
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, while some studies suggest potential benefits, the current body of research lacks strong evidence to support the use of marijuana for treating PTSD. The complexities of the condition, combined with methodological limitations in the studies reviewed, make drawing firm conclusions difficult. Alternative treatments and a cautious approach are crucial. Future research, focusing on large-scale clinical trials, is vital to fully understand the potential effects of marijuana on PTSD symptoms.