Hay fever can look like behavior or learning issues, a hidden culprit often overlooked in children. This fascinating exploration delves into the surprising ways hay fever symptoms can manifest as behavioral or learning challenges. We’ll uncover the similarities between typical allergy symptoms and those commonly mistaken for behavioral issues, providing insights into how fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and irritability might be mistaken for underlying behavioral problems.
Understanding the overlap between hay fever symptoms and behavioral issues is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management. This post will guide you through recognizing the symptoms, understanding their impact on learning and behavior, and exploring effective management strategies.
Symptoms of Hay Fever
Hay fever, also known as allergic rhinitis, is a common seasonal condition triggered by allergens like pollen. While often associated with sneezing and runny noses, the symptoms can be more pervasive and potentially mistaken for other issues, particularly in children. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
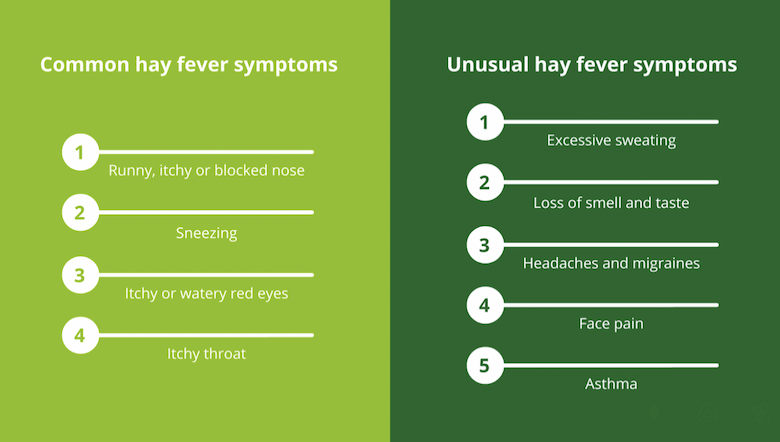
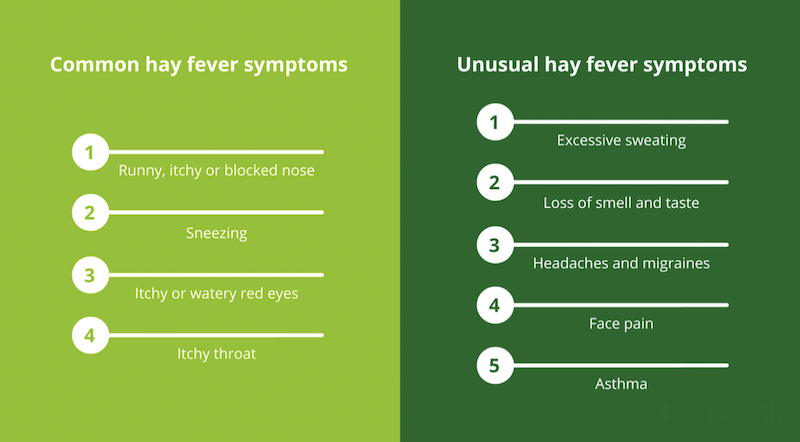
Common Hay Fever Symptoms
Hay fever symptoms typically manifest in the respiratory system, but they can also impact other areas of the body. Common symptoms include sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, itchy eyes, nose, or throat, and postnasal drip. These symptoms can vary in severity depending on the individual and the pollen count. Other common symptoms include fatigue, headaches, and difficulty concentrating.
Hay Fever Symptoms Mimicking Behavioral Challenges
Hay fever symptoms can sometimes be misinterpreted as behavioral or learning challenges, especially in children. The physical discomfort and fatigue associated with hay fever can significantly impact a child’s ability to focus, leading to difficulties in school and social settings.
Physical Symptoms Mistaken for Behavioral Issues
Fatigue is a prominent symptom of hay fever, often leading to decreased energy levels and difficulty concentrating. This can manifest as inattentiveness, restlessness, or disengagement during activities. Irritability, stemming from the discomfort of nasal congestion or itchy eyes, can be mistaken for defiance or mood swings. A child experiencing hay fever might exhibit difficulty sleeping due to nasal congestion, further exacerbating daytime fatigue and impacting their behavior.
Headaches can also occur, leading to discomfort and potential irritability.
Sometimes, hay fever can manifest in ways that mimic behavioral or learning issues in kids. It’s easy to overlook, especially when considering the many other possible factors. Similarly, heart disease is the top cause of death in women but few know warning signs, highlighting the importance of awareness and early detection. This underscores the need for thorough evaluations when unusual symptoms appear, as hay fever can present in surprising ways.
It’s crucial to remember that if a child’s behavior or learning difficulties seem unusual, consulting a doctor is always best practice. heart disease is the top cause of death in women but few know warning signs Ultimately, a comprehensive approach to understanding these issues is essential.
Comparison of Hay Fever and Behavioral Issues in Children
Hay fever symptoms often overlap with typical behavioral or learning challenges in children. Both can present with difficulty focusing, tiredness, and mood changes. However, the underlying cause differs significantly. While behavioral issues are typically rooted in emotional or developmental factors, hay fever is an allergic response to environmental triggers. Careful observation and a thorough evaluation are essential to differentiate between these conditions.
Table: Overlap of Hay Fever and Behavioral Symptoms
| Hay Fever Symptoms | Possible Behavioral Interpretations |
|---|---|
| Difficulty concentrating | Lack of attention, disinterest, or defiance |
| Tiredness | Laziness, unwillingness to participate, or a general lack of motivation |
| Mood changes (irritability, frustration) | Emotional outbursts, temper tantrums, or oppositional behavior |
| Runny nose, sneezing, itchy eyes | Excessive nose-picking, rubbing of eyes, or avoidance of social interaction (secondary to discomfort) |
| Headaches | Complaints of head pain, possible avoidance of physical activity |
Table: Symptoms and Possible Behavioral Interpretations
| Symptom | Possible Behavioral Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Fatigue | Lack of motivation, laziness, or unwillingness to participate in activities |
| Difficulty concentrating | Distractibility, inattentiveness, or poor academic performance |
| Irritability | Defiance, temper tantrums, or mood swings |
| Nasal congestion | Refusal to participate in activities, avoidance of social situations, or complaints about discomfort |
| Itchy eyes | Excessive rubbing, eye irritation, or avoidance of light |
Impact on Learning and Behavior

Hay fever, while seemingly a minor ailment, can significantly impact a child’s ability to learn and behave in the classroom. The persistent symptoms often disrupt concentration, leading to frustration and impacting overall school performance. Understanding these effects is crucial for educators and parents to effectively support children experiencing hay fever.The constant sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and congestion associated with hay fever create significant physical discomfort.
This discomfort can make it challenging for children to focus on their studies, leading to missed learning opportunities and potential behavioral issues. The impact on sleep, a critical component of learning, further exacerbates the problem.
Hay fever can sometimes manifest in ways that mimic behavioral or learning challenges in kids. It’s a tricky thing, because the symptoms can be easily misinterpreted. For example, a child experiencing the fatigue and brain fog associated with hay fever might struggle in school, which could be mistakenly attributed to a learning issue. And while a high fat keto diet might seem like a great solution for various health concerns, high fat keto diet a health concern can actually be detrimental in some cases.
Ultimately, it’s crucial to rule out allergies and other medical factors when a child isn’t performing up to their potential at school or displaying unusual behaviors.
Sleep Disturbances and Physical Discomfort
Hay fever symptoms often disrupt a child’s sleep. The constant itching, sneezing, and congestion can make it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep. This sleep deprivation contributes to daytime fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating, hindering their academic performance. The physical discomfort associated with hay fever can also lead to restlessness and difficulty participating in classroom activities.
For instance, a child constantly battling a runny nose might feel self-conscious, leading to decreased social interaction and further hindering their ability to engage in the learning process.
Difficulty Concentrating and Irritability
Hay fever can impair a child’s ability to concentrate on classroom tasks. The constant need to clear their nose, wipe their eyes, or control sneezing can be a significant distraction. This difficulty concentrating leads to decreased academic performance and potential behavioral problems, such as inattentiveness, restlessness, and reduced participation in class discussions. Furthermore, the physical discomfort and fatigue associated with hay fever can heighten irritability and frustration levels, making children more prone to emotional outbursts or negative behaviors.
For example, a child struggling to concentrate due to itchy eyes might exhibit signs of fidgeting or inattention, which could be misinterpreted as defiance or a lack of interest in the subject matter.
Misinterpretations of Behavior
Educators and parents may misinterpret a child’s behavior stemming from hay fever as other issues, such as defiance, poor motivation, or attention deficit disorder. It is essential to understand that the physical and emotional discomfort of hay fever can manifest as behavioral issues, masking the underlying cause. For instance, a child who is often restless or inattentive in class might be struggling with hay fever symptoms rather than a learning disability.
Link to Anxiety and Emotional Responses
The chronic discomfort and unpredictability of hay fever symptoms can contribute to increased anxiety and emotional responses in children. The constant struggle to manage symptoms can lead to feelings of frustration, stress, and even fear. These emotional responses can be misinterpreted as behavioral problems or emotional disorders. This can lead to misdiagnosis or inappropriate interventions if the underlying cause of the child’s emotional distress is not identified.
Classroom Scenarios
There are various classroom scenarios where hay fever symptoms might be misinterpreted as behavioral issues. For example, a child who frequently fidgets or has difficulty following instructions might be exhibiting symptoms of hay fever rather than exhibiting oppositional behavior. Similarly, a child who appears withdrawn or unmotivated during class time might be experiencing physical discomfort or difficulty concentrating due to hay fever.
A child who suddenly displays increased irritability or emotional outbursts could be reacting to the discomfort of hay fever.
Diagnosis and Misdiagnosis
Accurately diagnosing hay fever in children can be challenging, especially when symptoms overlap with those of behavioral or learning issues. Misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate interventions and hinder proper treatment. A precise diagnosis is crucial for effective management of the condition and preventing long-term complications.Identifying hay fever requires a careful differentiation from other medical conditions, particularly those presenting with similar symptoms.
This process necessitates a comprehensive evaluation, incorporating medical history, physical examination, and potentially allergy testing.
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Precise diagnosis of hay fever is paramount to avoid misinterpreting symptoms as behavioral or learning problems. Early and accurate identification allows for timely intervention, minimizing the impact of symptoms on a child’s well-being and development. A proper diagnosis guides appropriate treatment, alleviating suffering and maximizing learning potential.
Methods to Differentiate Hay Fever from Other Conditions
Several methods are employed to distinguish hay fever from other medical conditions. Medical history plays a vital role, providing insight into the timing and pattern of symptoms. For instance, seasonal patterns strongly suggest an allergic etiology. A thorough physical examination helps rule out other potential causes. Furthermore, allergy testing can pinpoint specific allergens, confirming the allergic nature of the symptoms.
Role of Medical History and Physical Examination
A detailed medical history is essential in identifying hay fever. Parents or caregivers should be questioned about the presence of seasonal symptoms, such as sneezing, runny nose, or itchy eyes, and whether these symptoms coincide with exposure to specific allergens. A thorough physical examination is also critical. The absence of physical findings suggestive of other conditions further supports the possibility of hay fever.
For example, absence of skin lesions or fever in the context of respiratory symptoms leans toward allergic causes.
Comprehensive Evaluation Including Allergy Testing
Allergy testing plays a critical role in confirming the presence of hay fever. Skin prick tests or blood tests can identify specific allergens triggering the allergic reaction. These tests are vital in distinguishing hay fever from other conditions presenting with similar symptoms. Positive allergy test results for common allergens like pollen, dust mites, or pet dander strongly support the diagnosis of hay fever.
Questions to Determine Hay Fever as a Contributing Factor
Parents and teachers can ask specific questions to ascertain if hay fever might be a contributing factor to behavioral or learning issues. These include inquiries about seasonal variations in symptoms, triggers such as pollen exposure, and the impact of symptoms on sleep and concentration. Specific questions about symptoms like itching, sneezing, and congestion, and their correlation with school performance, are crucial.
For example, “Does your child’s behavior change noticeably during pollen season?”
Comparison of Symptoms
| Symptom | Hay Fever | Behavioral/Learning Issues | Other Possible Conditions (e.g., Upper Respiratory Infection) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sneezing | Frequent, often in bursts, typically seasonal | May occur, but not typically in seasonal patterns | Can occur, but often with other symptoms like fever or cough |
| Runny Nose | Watery, clear discharge, often seasonal | May be present, but not always associated with allergies | Can occur, but often with other symptoms like fever or cough |
| Itchy Eyes | Common, often with watery eyes | Possible, but not a defining characteristic | Possible, but not always associated with other symptoms |
| Fatigue | Possible, due to sleep disruption and congestion | Possible, due to various underlying factors | Possible, due to infection or other illness |
| Difficulty Concentrating | Possible, due to discomfort and sleep disruption | Common characteristic | Possible, due to infection or illness |
Management Strategies: Hay Fever Can Look Like Behavior Or Learning Issues
Hay fever, while often perceived as a mild inconvenience, can significantly impact a child’s ability to learn and behave. Effective management strategies are crucial for minimizing these effects and ensuring a positive learning environment. By understanding the triggers, employing appropriate medications, and adopting a supportive lifestyle, parents and educators can help children thrive despite their allergy.Managing hay fever effectively requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing allergy avoidance, medication use, lifestyle adjustments, and strong communication between all parties involved.
The goal is to create an environment where symptoms are minimized, allowing children to focus on their education and participate fully in their daily lives.
Allergy Avoidance Strategies
Minimizing exposure to allergens is a fundamental aspect of hay fever management. Identifying and avoiding triggers can dramatically reduce symptoms. This involves a proactive approach, rather than simply reacting to symptoms.
- Identifying Triggers: Thorough allergy testing, often conducted by an allergist, is crucial to pinpoint specific allergens like pollen, mold, or dust mites. This personalized information enables targeted avoidance strategies.
- Controlling Indoor Allergens: Regularly cleaning and dusting, using air purifiers with HEPA filters, and keeping humidity levels within a recommended range can significantly reduce exposure to indoor allergens. Using allergen-proof bedding and covers for pillows and mattresses can also help.
- Outdoor Avoidance: Avoiding outdoor activities during peak pollen seasons or selecting locations with lower pollen counts can be effective. Wearing a mask when necessary, especially during high-pollen days, can further reduce exposure.
Medication Use
Medications play a vital role in managing hay fever symptoms. These treatments help alleviate the body’s allergic response.
Hay fever can sometimes manifest in ways that mimic behavioral or learning challenges in kids. It’s a sneaky little condition, and sometimes we overlook the possibility of allergies when we’re seeing struggles in the classroom or at home. Just like with Zika, where we’re now seeing how devastating the virus can be for infants remember zika we now know how bad the virus was for infants , it’s crucial to consider all potential factors, including allergies, when diagnosing and supporting children.
So, the next time you’re seeing puzzling behaviors, don’t rule out hay fever as a possible cause.
- Antihistamines: Oral antihistamines, both over-the-counter and prescription, can help block the effects of histamine, a chemical released during an allergic reaction. These medications can effectively reduce symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, and itching.
- Decongestants: Decongestants can help relieve nasal congestion, allowing for easier breathing. However, they should be used cautiously, and for short periods, as overuse can lead to rebound congestion. Consult with a healthcare professional before using.
- Nasal Corticosteroids: These medications, often delivered as nasal sprays, are highly effective in reducing inflammation in the nasal passages. They are generally considered a safe and long-term solution for managing hay fever.
Lifestyle Factors
A healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the severity of hay fever symptoms. Consistent routines and healthy choices are crucial for optimal health and well-being.
- Consistent Sleep Schedule: Adequate sleep is essential for the body’s natural healing processes. A regular sleep schedule helps regulate the immune system, making it better equipped to manage allergy symptoms. A lack of sleep can worsen symptoms.
- Balanced Diet: A nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides the body with the necessary nutrients to support a healthy immune system. Avoiding processed foods and sugary drinks can contribute to improved overall well-being and allergy management.
Communication and Education
Open communication between parents, teachers, and healthcare professionals is essential for effective hay fever management. Educating school staff about the condition can foster a supportive learning environment.
- Communication Channels: Regular communication between parents and teachers about the child’s symptoms, triggers, and medication needs is crucial for tailoring classroom accommodations.
- Teacher Education: Educating teachers and school staff about hay fever symptoms, triggers, and appropriate management strategies is beneficial. This knowledge can facilitate a more understanding and supportive environment for the child.
Management Strategies Summary
| Management Strategy | Potential Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Allergy Avoidance | High; significantly reduces exposure to triggers |
| Medication Use (Antihistamines, Decongestants, Nasal Corticosteroids) | Variable; effectiveness depends on the individual and medication type |
| Consistent Sleep Schedule | Moderate; supports overall health and immune function |
| Balanced Diet | Moderate; provides nutrients for a healthy immune system |
| Communication and Education | High; creates a supportive and understanding environment |
Case Studies (Illustrative Examples)
Understanding how hay fever manifests in children is crucial. Often, the symptoms are mistaken for other conditions, particularly behavioral or learning challenges. These case studies illustrate how misdiagnosis can impact a child’s well-being and highlight the importance of a thorough evaluation to identify the true cause of the difficulties.
Misdiagnosis as Behavioral Issue
A young student, Emily, presented with persistent inattentiveness and disruptive classroom behavior. Teachers and parents initially attributed these issues to a lack of focus and poor discipline. However, Emily’s symptoms worsened during pollen seasons, coinciding with a pattern of sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes. A detailed allergy assessment revealed a severe hay fever allergy to ragweed.
Once treated with appropriate allergy medication, Emily’s disruptive behaviors significantly reduced, demonstrating how untreated hay fever can mask itself as behavioral issues.
Improved Learning and Behavior through Diagnosis and Management, Hay fever can look like behavior or learning issues
Ethan, a bright but easily frustrated student, struggled with reading comprehension and exhibited frequent outbursts in class. He often missed assignments and struggled to complete tasks. Extensive testing revealed a strong allergy to dust mites, which was causing constant nasal congestion and eye irritation. By addressing the allergies with immunotherapy, Ethan’s symptoms were significantly mitigated. The improvement in his physical comfort translated directly to a marked improvement in his focus and behavior in the classroom.
Ethan’s grades and overall participation in class improved dramatically.
Interplay with Anxiety and Stress
Sophia, a highly anxious child, exhibited symptoms like difficulty concentrating, emotional outbursts, and sleep disturbances. While anxiety was identified as a contributing factor, hay fever was also playing a crucial role. The seasonal allergy symptoms aggravated her existing anxiety, creating a vicious cycle. Identifying and managing the hay fever with medication and environmental controls allowed Sophia to better cope with her anxiety.
This case emphasizes how co-occurring conditions can significantly impact a child’s well-being and that a comprehensive evaluation is necessary to disentangle these factors.
Improvement after Allergy Treatment
Liam, a child with persistent headaches and fatigue, struggled to keep up in school. He experienced frequent nosebleeds and nasal congestion. His symptoms were linked to a variety of allergens, including pollen, pet dander, and dust mites. Following allergy testing and immunotherapy, Liam’s symptoms drastically improved. The alleviation of physical discomfort from the allergy symptoms translated to a notable increase in energy levels, improved focus, and reduced fatigue.
He was able to participate more actively in class and his academic performance improved noticeably.
Case Study Table
| Symptoms | Diagnosis | Treatment | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inattentiveness, disruptive behavior, worsening during pollen season, sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes | Misdiagnosed as behavioral issue, later identified as hay fever (ragweed allergy) | Allergy medication | Significant reduction in disruptive behaviors, improved focus |
| Difficulty with reading comprehension, frequent outbursts, missed assignments, struggling with tasks, nasal congestion, eye irritation | Hay fever (dust mite allergy) | Immunotherapy | Marked improvement in focus, behavior, grades, and class participation |
| Difficulty concentrating, emotional outbursts, sleep disturbances, seasonal exacerbation of symptoms | Hay fever, co-occurring anxiety | Allergy medication, anxiety management techniques | Improved coping mechanisms for anxiety, reduced symptoms, and better academic performance |
| Persistent headaches, fatigue, nosebleeds, nasal congestion, frequent allergy triggers | Hay fever (multiple allergens) | Allergy testing, immunotherapy | Significant improvement in energy levels, focus, reduced fatigue, and improved academic performance |
Closing Summary
In conclusion, recognizing the potential for hay fever to masquerade as behavioral or learning issues is paramount. By understanding the symptoms, their impact, and effective management strategies, we can ensure that children receive the appropriate support and treatment, ultimately fostering a more positive learning environment and a better quality of life. The key takeaway here is the importance of a comprehensive evaluation and open communication between parents, teachers, and healthcare professionals.
