Alcohol addiction alternative treatments offer a compelling pathway to recovery, moving beyond conventional methods. This exploration delves into various approaches, from mindfulness practices to holistic strategies, examining their potential benefits and drawbacks. We’ll explore the growing interest in these alternative therapies, examining their efficacy alongside conventional treatments.
Understanding the limitations of traditional alcohol addiction treatments has spurred a search for more comprehensive and individualized approaches. This search for alternative therapies encompasses a wide range of methods, including support groups, holistic practices, and evidence-based techniques. This overview will present a comparative analysis of conventional and alternative methods.
Introduction to Alternative Treatments: Alcohol Addiction Alternative Treatments
Alcohol addiction is a significant global health concern, affecting millions of individuals and families worldwide. Its devastating consequences extend beyond the individual, impacting social structures and healthcare systems. The chronic nature of the disease often necessitates long-term treatment, and while conventional approaches offer valuable tools, their limitations have spurred exploration into alternative recovery methods. This exploration is driven by the desire for more comprehensive and holistic approaches to address the root causes of addiction and promote lasting recovery.Conventional treatments often focus on symptom management and abstinence, but may not always address the underlying psychological and emotional factors contributing to the addiction.
This has led to a growing interest in alternative therapies that aim to achieve a more profound and lasting recovery by integrating various healing modalities. These methods are diverse, and often incorporate approaches that emphasize self-discovery, emotional well-being, and a broader understanding of the individual’s experience with addiction.
Overview of Alternative Treatments
A wide range of alternative treatments are gaining traction in the field of alcohol addiction recovery. These treatments often complement conventional methods, or provide unique pathways for individuals seeking different approaches. Some of the most commonly encountered methods include:
- Mindfulness-based therapies, like meditation and yoga, promote self-awareness and stress reduction, which can be helpful in managing cravings and emotional triggers.
- Nutritional therapy and dietary interventions, recognizing the impact of diet on overall well-being and potentially reducing cravings, may be considered.
- Hypnotherapy can be employed to address underlying psychological factors contributing to the addiction, using a trance-like state to help individuals reframe their relationship with alcohol.
- Acupuncture and other traditional Eastern medicine practices aim to restore balance in the body, which proponents believe can help manage cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
- Support groups and peer-led recovery programs offer a supportive community, allowing individuals to share experiences and learn from others who have overcome similar challenges.
Comparison of Conventional and Alternative Treatments
The following table provides a comparative overview of conventional and alternative approaches to alcohol addiction treatment, highlighting their different approaches, potential benefits, and limitations.
| Treatment Type | Approach | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional (e.g., Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, Medications) | Focuses on symptom management, cognitive restructuring, and pharmacological interventions. | Proven efficacy in managing withdrawal symptoms, reducing cravings, and promoting abstinence. Often readily available and well-researched. | May not address the underlying emotional or psychological factors contributing to the addiction. Can have side effects from medication. May require significant time commitment. |
| Alternative (e.g., Mindfulness-based therapies, Nutritional therapy) | Emphasizes holistic well-being, self-awareness, and lifestyle changes. | Potential to address underlying emotional issues, promote long-term recovery, and improve overall well-being. May be more tailored to individual needs. | May lack robust scientific evidence for effectiveness. Accessibility may be limited, and cost can vary considerably. Not a substitute for conventional treatment in acute situations. |
Types of Alternative Treatments
Beyond the traditional approaches, a diverse range of alternative therapies offers promising avenues for addressing alcohol addiction. These methods often focus on holistic well-being, acknowledging the interconnectedness of mind, body, and spirit in recovery. These approaches often complement conventional treatments, providing additional support and personalized strategies for managing cravings and promoting long-term sobriety.
Mindfulness-Based Therapies
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and mindful awareness exercises, are increasingly recognized for their potential in managing cravings and promoting emotional regulation. These techniques help individuals develop a non-judgmental awareness of their thoughts, feelings, and bodily sensations, enabling them to observe cravings without succumbing to them. By cultivating present-moment awareness, individuals can develop healthier coping mechanisms for stress and emotional distress, reducing the likelihood of relapse.
Mindfulness-based therapies, like Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR), can be incorporated into a broader treatment plan, complementing other strategies for long-term recovery.
Holistic Approaches
Holistic therapies recognize the interconnectedness of physical, emotional, and spiritual well-being. They emphasize the importance of addressing underlying causes of addiction, such as stress, trauma, and emotional imbalances. These approaches often incorporate a range of modalities, including nutritional counseling, herbal remedies, and energy work. For example, nutritional counseling can help identify and address potential nutritional deficiencies that may contribute to cravings.
Herbal remedies, when used appropriately, can assist in reducing withdrawal symptoms and promoting overall well-being. These therapies should always be integrated with the advice of medical professionals to ensure safety and efficacy.
Support Groups and Peer Support
Support groups provide a safe and supportive environment for individuals struggling with alcohol addiction. These groups offer a sense of community and shared experience, allowing individuals to connect with others who understand their struggles. The shared experiences and support from peers can be incredibly valuable in fostering a sense of belonging and reducing feelings of isolation. Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) is a well-known example of a support group, offering a structured program of peer support and guidance.
Other support groups, such as those focusing on specific demographics or needs, can also offer personalized support tailored to individual experiences.
Integrative Therapies
Combining various alternative therapies with conventional treatments creates a personalized and comprehensive approach. This approach, often termed “integrative therapy,” blends the strengths of multiple techniques, offering a tailored strategy for each individual. For instance, a therapist might integrate mindfulness exercises with nutritional counseling and support group participation to create a holistic recovery plan. This integration aims to address the unique needs of each individual, fostering a deeper understanding of their addiction and empowering them to develop sustainable coping mechanisms.
| Treatment Type | Core Principles | Target Areas | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mindfulness-Based Therapies | Cultivating present-moment awareness, non-judgmental observation of thoughts and feelings, stress reduction | Emotional regulation, craving management, relapse prevention | Improved coping mechanisms, reduced stress, increased self-awareness |
| Holistic Approaches | Addressing underlying causes, promoting physical, emotional, and spiritual well-being | Nutritional imbalances, stress, trauma, emotional distress | Improved physical health, reduced cravings, enhanced emotional well-being |
| Support Groups & Peer Support | Shared experience, community support, encouragement | Social isolation, feelings of loneliness, lack of understanding | Increased sense of belonging, reduced feelings of isolation, enhanced motivation |
| Integrative Therapies | Combining various therapies for personalized treatment | Addresses individual needs and preferences, creates a holistic approach | Tailored strategies, comprehensive support, improved treatment outcomes |
Evidence-Based Practices
Exploring alternative treatments for alcohol addiction requires a critical evaluation of the available evidence. While many alternative therapies show promise, rigorous scientific research is crucial to determine their efficacy and safety. This section delves into the existing studies and research findings surrounding these therapies, highlighting both the positive results and the limitations of the current knowledge base. A comparative analysis with conventional treatments will also be presented, providing a comprehensive overview of the field.
Evaluating the Efficacy of Alternative Treatments
A significant challenge in assessing alternative treatments lies in the variability of methodologies across studies. Different studies employ diverse sampling techniques, measurement tools, and follow-up protocols. This heterogeneity makes direct comparisons challenging and often necessitates careful consideration of the study design when evaluating the findings. A critical analysis of the methodology is essential for determining the reliability and validity of the results.
Specific Studies and Research Findings
Acupuncture, for example, has shown some promise in reducing cravings and withdrawal symptoms in some studies. A meta-analysis of several randomized controlled trials found that acupuncture may be associated with a statistically significant reduction in alcohol consumption compared to a control group. However, the magnitude of this effect varies across studies, and the mechanisms by which acupuncture exerts its influence remain unclear.
Comparison with Conventional Treatments
Comparing the effectiveness of alternative treatments with established conventional treatments, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and medications, requires a nuanced approach. While some studies suggest positive outcomes for alternative therapies, rigorous clinical trials and meta-analyses consistently demonstrate the efficacy of CBT and medications in managing alcohol dependence. These conventional approaches often have well-defined mechanisms of action and are supported by a substantial body of evidence.
Exploring alternative treatments for alcohol addiction is a journey of discovery, and understanding the body’s complex reactions is key. For example, some research suggests that nutritional deficiencies might play a role in cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Learning about conditions like primary hyperoxaluria, a rare genetic disorder impacting oxalate metabolism, what to know about primary hyperoxaluria , could offer insights into how metabolic imbalances might contribute to alcohol addiction.
Ultimately, understanding these intricate connections is crucial to developing effective and personalized alternative treatment plans.
Limitations and Gaps in Current Research
A key limitation in current research on alternative treatments is the lack of large-scale, well-controlled studies. Many studies have small sample sizes, making it difficult to generalize findings to a wider population. Furthermore, the lack of standardized treatment protocols across studies hinders direct comparisons and limits the ability to draw conclusive statements about the efficacy of specific therapies.
Summary Table of Key Findings
| Treatment Type | Study Findings | Sample Size | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acupuncture | Some studies suggest reduced alcohol consumption and cravings. | Varied, often small | Heterogeneity in study design, unclear mechanisms, lack of large-scale trials. |
| Hypnotherapy | Some studies show potential for reducing alcohol cravings and improving motivation for change. | Varied, often small | Limited standardization of techniques, potential for placebo effects, difficulty in measuring sustained change. |
| Mindfulness-Based Interventions | Preliminary evidence suggests a potential role in managing cravings and improving emotional regulation. | Varied, often small | Need for more robust longitudinal studies, potential for variability in implementation. |
| Herbal Remedies | Limited evidence of efficacy, often anecdotal and not rigorously tested. | Small, often uncontrolled | Lack of standardization, potential for interactions with medications, lack of safety data. |
Holistic Approaches
Embarking on a journey to overcome alcohol addiction often requires more than just abstinence. A holistic approach recognizes the interconnectedness of mind, body, and spirit, acknowledging that healing extends beyond the physical withdrawal process. It emphasizes the importance of nurturing all aspects of one’s well-being to achieve lasting recovery. This multifaceted approach aims to address the root causes of the addiction, fostering a healthier lifestyle and promoting resilience.
Understanding Holistic Recovery
Holistic recovery from alcohol addiction views the individual as a complete being, not merely a collection of symptoms. This perspective integrates physical, mental, and spiritual well-being into the recovery process. It acknowledges that past traumas, emotional imbalances, and spiritual disconnection can contribute to the development and maintenance of alcohol addiction. By addressing these underlying factors, holistic approaches create a more profound and lasting healing process.
Integrating Physical Well-being
Physical health plays a crucial role in managing cravings and withdrawal symptoms. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can significantly improve energy levels and overall well-being. Regular exercise, such as walking, yoga, or swimming, can help reduce stress, improve mood, and regulate the body’s natural endorphins. This promotes a sense of physical well-being, empowering individuals to cope with challenges more effectively.
Addressing Mental Well-being
Mental well-being is equally vital in the recovery process. Techniques like mindfulness, meditation, and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals identify and manage negative thought patterns and emotions. These practices promote emotional regulation and reduce stress, thereby minimizing the likelihood of relapse. Support groups and counseling sessions further foster a supportive environment for emotional processing and growth.
Nurturing Spiritual Well-being
Spiritual well-being, often neglected in traditional recovery programs, is critical to a holistic approach. This can involve exploring personal values, beliefs, and purpose. Connecting with a higher power, engaging in spiritual practices like prayer or meditation, or finding meaning in life’s experiences can provide a sense of direction and purpose, promoting resilience and inner peace. This aspect encourages a deeper connection with oneself and the world around them.
Strategies for Integrating Holistic Elements
| Element | Strategies | Expected Outcomes | Potential Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrition | Following a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins; limiting processed foods and sugary drinks; consulting with a registered dietitian. | Improved energy levels, reduced cravings, enhanced overall health, and improved mood regulation. | Difficulty adjusting to dietary changes; lack of access to healthy foods; potential for food sensitivities. |
| Exercise | Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, yoga, or team sports; gradually increasing intensity and duration; focusing on activities that promote enjoyment. | Reduced stress, improved mood, increased energy levels, and enhanced self-esteem. | Lack of time; physical limitations; motivation to stick with an exercise routine; finding suitable exercise locations. |
| Stress Management | Practicing mindfulness and meditation techniques; engaging in relaxation exercises like deep breathing; utilizing stress-reduction apps; seeking support from friends, family, or support groups. | Reduced stress levels, improved coping mechanisms, and enhanced emotional regulation. | Difficulties in maintaining consistent practice; lack of awareness of stress management techniques; resistance to implementing changes. |
| Spiritual Well-being | Engaging in activities that foster a sense of purpose and meaning, such as journaling, attending religious services, or exploring nature; seeking guidance from a spiritual advisor or counselor. | Increased self-awareness, improved resilience, enhanced sense of purpose, and a stronger sense of connection. | Lack of faith or religious beliefs; difficulty identifying personal values and beliefs; challenges in finding appropriate spiritual guidance. |
Mindfulness-Based Therapies
Mindfulness-based therapies offer a powerful approach to addiction recovery, focusing on present-moment awareness and emotional regulation. These techniques can help individuals develop a deeper understanding of their thoughts, feelings, and bodily sensations, ultimately reducing the power of cravings and emotional distress associated with addiction. By cultivating a non-judgmental awareness of the present, individuals can navigate challenging situations with greater equanimity and resilience.Mindfulness-based therapies work by interrupting the automatic, often negative, thought patterns and emotional responses that can trigger cravings and relapse.
Instead of reacting impulsively to cravings or difficult emotions, individuals learn to observe these experiences without judgment, allowing them to pass without succumbing to them. This skill-building approach fosters greater self-awareness and emotional regulation, which are crucial for long-term recovery.
Principles of Mindfulness
Mindfulness practices are rooted in the principles of non-judgmental awareness, acceptance, and present-moment focus. These principles cultivate a non-reactive stance toward thoughts, feelings, and bodily sensations, fostering emotional regulation and reducing reactivity to cravings. Practicing mindfulness allows individuals to observe their inner world without getting caught up in it, promoting a sense of detachment from addictive behaviors.
Mindfulness Techniques for Addiction Recovery
Mindfulness techniques offer various strategies for managing cravings and emotional distress. These techniques aim to cultivate present-moment awareness and acceptance, allowing individuals to navigate challenging emotions and cravings with greater resilience.
Step-by-Step Guide to Incorporating Mindfulness into Daily Life
This structured approach provides a framework for integrating mindfulness practices into daily routines.
- Start with brief, regular practice. Begin with short mindfulness sessions, such as 5-10 minutes, and gradually increase the duration as you become more comfortable. Consistency is key.
- Find a quiet and comfortable space. Choose a location where you can sit or lie down without distractions, promoting a sense of calm and focus.
- Focus on your breath. Bring your attention to the sensation of your breath entering and leaving your body. Notice the rise and fall of your chest or abdomen. Acknowledge the physical sensations of breathing without trying to control them.
- Acknowledge and accept thoughts and feelings. As thoughts and feelings arise, observe them without judgment. Recognize that they are passing experiences, not permanent realities. Acknowledge the presence of thoughts and feelings without engaging with them.
- Expand your awareness. Gradually extend your awareness to other sensations in your body, such as sounds, smells, and bodily sensations.
- Practice regularly. Make mindfulness a consistent part of your daily routine to cultivate its benefits.
- Be patient with yourself. Developing mindfulness takes time and practice. Don’t get discouraged by setbacks; acknowledge them and gently return to your practice.
Mindfulness Exercises
These examples offer structured ways to incorporate mindfulness into daily life.
Mindful Breathing Exercise: Close your eyes and gently bring your attention to your breath. Notice the sensation of the air entering and leaving your nostrils, or the rise and fall of your chest or abdomen. Continue to follow your breath for a few minutes, acknowledging any thoughts or sensations that arise without judgment.
Mindful Walking Exercise: Pay attention to the sensation of your feet making contact with the ground as you walk. Notice the movement of your body, the feeling of your muscles working, and the sensations in your feet. Observe the sights, sounds, and smells around you as you walk.
Mindful Eating Exercise: Choose a simple food item, such as an apple. As you eat, pay attention to the colors, textures, and aromas of the food. Notice the taste and the sensation of chewing and swallowing. Savor each bite, and be present with the entire experience of eating.
Support Systems and Community

A crucial component of any effective alcohol addiction treatment program is the development of a robust support system. Isolation often exacerbates the challenges of recovery, making the presence of understanding and encouraging individuals and groups invaluable. This support network provides a sense of belonging, accountability, and encouragement that can significantly enhance the chances of long-term sobriety. It fosters a safe space for sharing experiences, coping with cravings, and navigating the emotional rollercoaster of recovery.Strong support systems play a critical role in preventing relapse and promoting lasting behavioral changes.
They provide a safety net during difficult moments and offer a foundation of encouragement when setbacks occur. A supportive community nurtures self-esteem and helps individuals feel empowered to make positive choices.
The Importance of Support Groups
Support groups, such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or similar programs, offer a unique environment for individuals to connect with others facing similar struggles. These groups provide a sense of community and shared understanding, reducing feelings of isolation and fostering a sense of belonging. The anonymity and shared experience within these groups allow members to open up, share vulnerabilities, and receive support from peers who have been through similar experiences.
The accountability and encouragement fostered within these settings can significantly impact recovery outcomes.
The Role of Family and Friends
Family and friends play a vital role in supporting someone recovering from alcohol addiction. Their understanding, patience, and encouragement can be instrumental in the recovery process. Family members can provide practical support, such as helping with childcare, household tasks, or transportation. Friends can offer emotional support, companionship, and a listening ear. Open communication and willingness to adapt to the needs of the recovering individual are crucial.
They can also provide a sense of accountability and encourage positive choices.
Strategies for Building a Supportive Community
Creating a supportive community involves proactive steps to foster connection and mutual understanding. Encouraging open communication within families and between friends and the recovering individual is essential. Learning about the challenges of addiction and developing empathy can improve the support system. Seeking professional guidance for family members and friends can equip them with the tools and knowledge to provide effective support.
Support groups, both formal and informal, offer valuable avenues for building community and connection. This can include joining online forums or creating a dedicated support network among individuals in recovery.
Building a Supportive Community: A Table of Examples
| Support System | Role | Impact | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) | Provides a peer-support network, sharing experiences and strategies for coping with cravings and triggers. | Offers a sense of community, accountability, and encouragement. Fosters a safe space for vulnerability and support. | Maintaining anonymity, overcoming stigma associated with the group, and ensuring ongoing participation. |
| Family Members | Offer practical assistance (e.g., childcare, transportation), emotional support, and encouragement. | Provide a sense of belonging and security. Can offer valuable resources and connections. | Dealing with conflicting emotions, managing expectations, and potentially experiencing guilt or frustration. |
| Friends | Provide emotional support, companionship, and a listening ear. | Offer a sense of normalcy and encouragement during difficult times. | Maintaining healthy boundaries, understanding the limitations of their support, and avoiding enabling behaviors. |
| Support Groups (Online and In-Person) | Connect individuals with others experiencing similar challenges. | Provides shared experiences, coping strategies, and a sense of community, potentially reducing feelings of isolation. | Finding trustworthy and reliable groups, overcoming the digital divide, and ensuring effective communication in online forums. |
Integration with Conventional Treatments
Alcohol addiction is a complex issue requiring a multifaceted approach. While alternative treatments offer valuable support, they are often most effective when integrated with conventional medical and therapeutic strategies. This integration can lead to a more comprehensive and potentially more successful recovery journey.Conventional treatments, such as detoxification, medication-assisted treatment (MAT), and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), provide the foundation for addressing the physical and psychological aspects of addiction.
Alternative treatments, on the other hand, can complement these efforts by fostering holistic well-being, enhancing coping mechanisms, and promoting long-term recovery.
Exploring alternative treatments for alcohol addiction can be a really helpful journey. While battling a tough condition like Ewing sarcoma stage 4 here can bring immense challenges, finding support and diverse approaches to recovery is crucial. Ultimately, various alternative therapies, like acupuncture or mindfulness, can offer valuable support alongside conventional treatments for alcohol addiction.
Strategies for Combining Approaches, Alcohol addiction alternative treatments
Integrating alternative and conventional treatments necessitates careful planning and collaboration between healthcare professionals. A collaborative approach, where alternative practitioners and conventional therapists work together, is crucial. Clear communication channels and shared understanding of treatment goals are essential for effective integration. This collaborative effort allows for a comprehensive assessment of the individual’s needs and tailoring the treatment plan accordingly.
Exploring alternative treatments for alcohol addiction is crucial, and it’s fascinating how advancements in various fields intersect. For example, recent developments, like the FDA’s decision to make medical abortions easier to get here , highlight the growing acceptance of alternative approaches to healthcare. Ultimately, these advancements in various medical sectors can potentially inspire new avenues for addressing alcohol addiction, fostering hope for recovery and better outcomes.
Examples of Successful Integration Strategies
One successful integration strategy involves combining acupuncture with motivational interviewing (MI). Acupuncture can help manage withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings, while MI can motivate the individual to make positive changes in their life. Similarly, yoga and mindfulness practices can be integrated with CBT to enhance self-awareness, emotional regulation, and stress management. These combined approaches can provide a more holistic and supportive environment for recovery.
Illustrative Table of Combined Treatments
| Alternative Treatment | Conventional Treatment | Combined Approach | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acupuncture | Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT) | Acupuncture sessions alongside MAT to manage withdrawal symptoms and cravings, potentially reducing the need for high doses of medication. | Reduced withdrawal symptoms, potentially lower medication needs, improved adherence to MAT. |
| Yoga and Mindfulness | Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | Yoga and mindfulness practices incorporated into CBT sessions to enhance self-awareness, stress management, and emotional regulation. | Improved coping mechanisms, reduced stress, increased self-awareness, potentially leading to more effective CBT outcomes. |
| Nutritional Counseling | Detoxification | Nutritional counseling integrated with detoxification protocols to support healthy eating habits and nutrient replenishment during withdrawal. | Improved nutritional status, potentially smoother detoxification process, reduced nutrient deficiencies, and improved overall health. |
| Herbal Remedies (with medical supervision) | Group Therapy | Herbal remedies used under medical supervision alongside group therapy to support emotional processing and provide a supportive community. | Potential for symptom relief, improved emotional well-being, and fostering a sense of community. Crucially, medical supervision is paramount to ensure safety. |
Addressing Specific Challenges
Navigating the path to recovery from alcohol addiction is often fraught with obstacles. Alternative recovery programs, while offering a diverse range of approaches, don’t magically erase the challenges. Understanding and proactively addressing these difficulties is crucial for successful outcomes. This section delves into common hurdles faced by individuals in alternative recovery and provides strategies to overcome them, illustrating how these treatments can be tailored to specific issues.Alternative treatments, by their very nature, emphasize individual needs and tailor interventions to address the root causes of addiction.
This personalized approach is vital in tackling the unique challenges encountered by each recovering individual.
Common Challenges in Alternative Recovery
Alternative recovery programs, though diverse, share common hurdles for those seeking sobriety. These include issues with social stigma, potential for relapse, difficulty in coping with triggers, and emotional distress. Overcoming these obstacles requires a multifaceted approach.
Relapse Prevention Strategies
Relapse, a significant concern in addiction recovery, is often linked to unmet emotional needs, stress, or triggers. Alternative treatments often incorporate relapse prevention strategies into their programs. These strategies are tailored to each individual’s specific vulnerabilities. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), for example, equips individuals with coping mechanisms to recognize and manage high-risk situations, while mindfulness practices help individuals develop awareness of cravings and triggers.
Coping with Triggers
Triggers, whether environmental, social, or emotional, can significantly impact an individual’s ability to maintain sobriety. Alternative therapies address these triggers by teaching coping mechanisms. For example, guided imagery or relaxation techniques help individuals manage stress responses and emotional distress, diminishing the power of triggers to derail their progress. Support groups, a cornerstone of many alternative programs, offer a safe space to share experiences and learn from others facing similar challenges.
Addressing Emotional Distress
Emotional distress is a significant factor in alcohol addiction. Alternative therapies often incorporate emotional processing and healing techniques, such as expressive arts therapy or somatic experiencing. These methods allow individuals to explore and process underlying emotions that contribute to the addiction, providing a path to healing and long-term well-being. This holistic approach addresses the emotional needs often neglected in conventional treatment methods.
Table: Challenges and Strategies in Alternative Recovery
| Challenge | Description | Strategies | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Relapse | Returning to alcohol use after a period of sobriety. | Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) to identify triggers, develop coping mechanisms, and modify maladaptive thoughts; Mindfulness practices to enhance awareness of cravings; Support groups for peer support and encouragement; Relapse prevention planning and relapse scenarios | Increased self-awareness of triggers and cravings; Improved coping mechanisms; Reduced likelihood of relapse; Enhanced ability to navigate high-risk situations. |
| Coping with Triggers | Environmental, social, or emotional cues that increase the likelihood of using alcohol. | Mindfulness exercises to enhance awareness of triggers; Relaxation techniques like deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation; Guided imagery to manage stress responses; Support systems to provide emotional support during challenging times; Identifying and challenging negative thought patterns. | Enhanced awareness of triggers; Development of healthy coping mechanisms; Reduced emotional reactivity to triggers; Improved ability to manage stress and emotions; Stronger support network. |
| Emotional Distress | Underlying emotional issues that contribute to the addiction. | Expressive arts therapy to process emotions through creative outlets; Somatic experiencing to address trauma and physical sensations associated with past experiences; Mindfulness-based stress reduction to manage stress and promote emotional regulation; Individual therapy to explore personal history and develop coping mechanisms. | Reduced emotional distress; Enhanced emotional processing and regulation skills; Improved self-awareness and self-acceptance; Greater ability to manage emotional responses; Reduced vulnerability to relapse. |
| Social Stigma | Negative perceptions and judgments from others about addiction. | Support groups and peer networks to build community and foster understanding; Educational workshops to address misconceptions about addiction; Building confidence and self-esteem through personal development; Advocacy and awareness campaigns to destigmatize addiction. | Increased social support; Reduced feelings of isolation and shame; Enhanced self-esteem and self-acceptance; Greater ability to interact with others without judgment; Increased social integration. |
Illustrative Examples

Exploring alternative treatments for alcohol addiction requires understanding how these approaches can support individuals on their recovery journey. Real-life examples demonstrate the potential of these methods, often used in conjunction with conventional therapies, to help people overcome their dependence. These examples highlight the importance of tailored interventions and the significance of holistic support systems.
A Case Study of Success
A 45-year-old male, diagnosed with alcohol dependence, participated in a comprehensive alternative treatment program. The program integrated a variety of techniques including mindfulness meditation, yoga, and nutritional counseling. The individual initially struggled with cravings and withdrawal symptoms, but consistent engagement with the program, coupled with support from a dedicated therapist, helped him manage these challenges. He actively participated in support groups, which provided a safe space to share experiences and receive encouragement from peers.
The combination of these approaches led to a significant reduction in cravings and a marked improvement in his overall well-being. Within six months, he achieved sobriety and maintained it for over a year, demonstrating the potential of holistic recovery strategies.
Holistic Approach to Recovery: Image Description
Imagine a vibrant image depicting a serene natural setting. A person, dressed comfortably, sits amidst lush greenery, surrounded by calming elements like flowing water and blooming flowers. Sunlight gently filters through the trees, casting a warm glow on the scene. In the foreground, a small, handcrafted wooden box containing essential oils and herbs is placed next to a journal and pen.
The image subtly suggests the integration of nature, aromatherapy, and journaling into the recovery process. The person’s expression reflects a sense of peace and well-being, emphasizing the holistic nature of the treatment. A gentle breeze seems to caress the scene, further symbolizing the calming influence of the environment on the individual’s journey.
Recovery Process: Infographic
This infographic presents a visual representation of the steps in the alcohol addiction recovery process. The process begins with a strong foundation of understanding the individual’s unique needs. The next stage focuses on creating a tailored treatment plan, which may include a range of therapies, like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), support groups, and mindfulness techniques. Crucially, the infographic emphasizes the continuous monitoring and adaptation of the treatment plan throughout the recovery journey, ensuring that the individual remains engaged and supported.
This ongoing adaptation ensures that the plan remains relevant to the individual’s changing needs. The final stage highlights the importance of long-term support and relapse prevention strategies to sustain sobriety. This holistic approach underscores the need for a multi-faceted approach to recovery.
- Understanding the Individual’s Needs: A comprehensive assessment of the individual’s physical, emotional, and social needs is vital to develop a personalized recovery plan. This stage ensures that the treatment addresses the root causes of the addiction and the individual’s specific vulnerabilities. Factors such as past trauma, co-occurring mental health conditions, and social support systems are considered to create a comprehensive plan.
- Tailored Treatment Plan: The treatment plan is designed to address the individual’s unique needs. It may include a combination of alternative therapies, such as mindfulness, yoga, and nutrition counseling, along with conventional therapies like CBT. The specific interventions are carefully selected to promote a holistic approach to recovery.
- Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation: The recovery process is dynamic. The treatment plan needs ongoing monitoring and adjustments to ensure it remains relevant and effective. This allows for flexibility in response to the individual’s changing needs and challenges. Regular check-ins and feedback mechanisms are essential for maintaining progress.
- Long-Term Support and Relapse Prevention: The focus shifts to building sustainable habits and coping mechanisms for long-term sobriety. This involves strategies for relapse prevention, ongoing support groups, and access to resources that help maintain a healthy lifestyle. A strong support system is critical to sustained recovery.
Outcome Summary
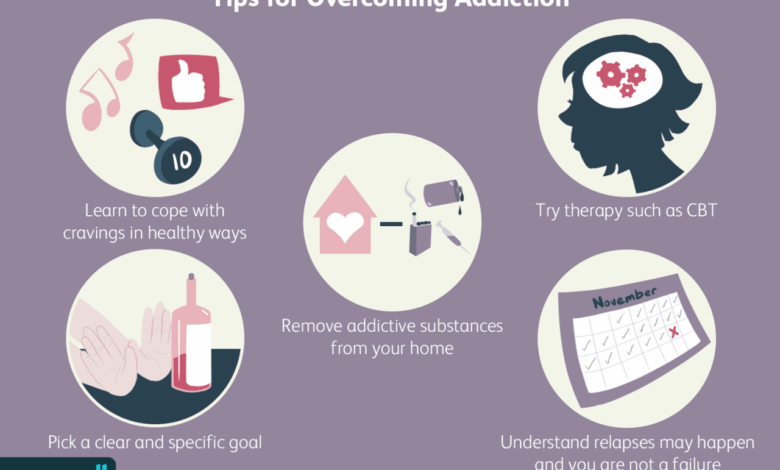
In conclusion, alternative treatments for alcohol addiction provide a diverse range of options for those seeking recovery. While conventional treatments remain crucial, the potential of alternative methods, including mindfulness and holistic approaches, should not be underestimated. This exploration underscores the importance of personalized treatment plans that incorporate a variety of strategies to address the unique needs of each individual struggling with alcohol addiction.
Further research and ongoing support systems are key to continued success in this field.
