Alcohol related deaths double in two decades – Alcohol-related deaths double in two decades sets the stage for this in-depth look at a significant public health crisis. We’ll explore historical trends in alcohol consumption, examining the various factors contributing to this alarming rise. From policy changes to societal shifts, we’ll investigate the root causes of these tragic fatalities, highlighting the impact on individuals, families, and healthcare systems.
This critical examination will also look at potential solutions and interventions to address this concerning issue.
The data reveals stark regional disparities in alcohol-related death rates. Comparing alcohol policies across countries and regions provides valuable insight into how effective strategies can be implemented. This analysis delves into the leading causes of these deaths, encompassing accidents, liver disease, and alcohol poisoning. Furthermore, the physiological effects of alcohol abuse and the societal factors influencing these tragedies are meticulously examined, including cultural norms and peer pressure.
Background on Alcohol Consumption Trends
Alcohol-related deaths have unfortunately doubled in the past two decades, necessitating a thorough examination of consumption patterns and associated factors. This involves scrutinizing historical trends, policy shifts, data collection methods, and the variations in consumption across different demographics. Understanding these aspects is crucial for developing effective prevention strategies and targeted interventions.A significant increase in alcohol-related deaths across many regions over the past two decades highlights the urgency to analyze the contributing factors.
This detailed exploration will encompass various aspects, including historical consumption rates, policy changes, data collection methodologies, and demographic variations in alcohol use.
Historical Alcohol Consumption Rates
Alcohol consumption rates have fluctuated across different regions over the past two decades. Variations exist in the average consumption levels, and the patterns of increase or decrease vary substantially. Access to reliable data on consumption is essential to understanding these trends.
- Data from the World Health Organization (WHO) shows considerable differences in average alcohol consumption across regions, with some nations experiencing increases, others decreases, and some maintaining relatively stable levels.
- Analyzing trends in specific countries or regions over time requires careful consideration of data collection methodologies, as these can vary significantly. Some countries might have robust data collection systems, while others may not.
Policy Changes Related to Alcohol Consumption
Numerous policy changes impacting alcohol consumption have been implemented over the past two decades. These changes often reflect societal shifts in attitudes towards alcohol and aim to address related health issues. These measures can include minimum legal drinking ages, taxation policies, advertising restrictions, and licensing regulations.
- Many countries have implemented stricter regulations on alcohol advertising, particularly targeting youth, and restricting marketing campaigns that could promote excessive consumption.
- Increased taxes on alcoholic beverages aim to curb consumption by making it less affordable. The effectiveness of these measures varies depending on the cultural context and the availability of alternative beverages.
Methods Used to Collect Data on Alcohol Consumption and Related Deaths
Different methods are employed to collect data on alcohol consumption and associated deaths. The accuracy and reliability of these methods significantly influence the analysis and interpretation of trends. Common approaches include surveys, sales data from the alcohol industry, and mortality records.
- Surveys, often conducted through household interviews or online questionnaires, provide insights into individual drinking habits. However, self-reported data can be subject to bias and underreporting, impacting the accuracy of the data.
- Alcohol sales data offer a measure of consumption volume. However, this data often does not capture the full picture of consumption patterns, including illicit or unreported alcohol.
- Mortality records are crucial in tracking alcohol-related deaths. Careful analysis of these records is vital in identifying patterns and associating deaths with alcohol consumption. However, accurate record-keeping practices and consistent definitions of alcohol-related deaths vary across different regions.
Alcohol Consumption Patterns in Different Demographics
Alcohol consumption patterns vary across different demographic groups, including age, gender, and socioeconomic status. Understanding these variations is essential for tailoring interventions and prevention strategies.
| Demographic | Consumption Pattern | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Consumption often peaks in young adulthood, declines in middle age, and then may increase again in older age, sometimes due to health or lifestyle changes. | Young adults may be more susceptible to peer pressure or social norms. |
| Gender | Men often consume more alcohol than women, although this gap is narrowing in some regions. | Societal expectations and cultural norms can play a role in gender differences in alcohol consumption. |
| Socioeconomic Status | Higher socioeconomic status is sometimes associated with greater alcohol consumption, but this pattern is not uniform across all regions and cultures. | Access to resources and social networks can influence consumption patterns. |
Causes of Alcohol-Related Deaths
The tragic rise in alcohol-related deaths over the past two decades underscores the urgent need to understand the multifaceted causes behind this alarming trend. While societal factors play a significant role, the physiological effects of alcohol abuse are undeniable and contribute substantially to fatalities. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing effective prevention strategies and support systems.Alcohol abuse can lead to a cascade of health problems, ultimately resulting in death.
The mechanisms by which alcohol impacts the body are complex and involve various organs and systems. The severity of these effects depends on factors like frequency, amount, and duration of consumption, as well as pre-existing health conditions. Addressing these issues requires a holistic approach that considers both individual behaviors and environmental influences.
Leading Causes of Alcohol-Related Deaths
Alcohol-related fatalities stem from a variety of factors, each with its own physiological consequences. Accidents, often involving impaired judgment and coordination, are a prominent cause. Examples include car crashes, falls, and drownings. Liver disease, a direct result of chronic alcohol abuse, is another major contributor. Alcohol poisoning, a severe and potentially fatal condition, represents a significant concern.
Physiological Effects of Alcohol Abuse
Alcohol’s effects on the body are multifaceted and detrimental. It impairs the central nervous system, affecting coordination, reaction time, and judgment. This impairment significantly increases the risk of accidents and injuries. Chronic alcohol abuse can lead to severe liver damage, including cirrhosis, which can be fatal. Furthermore, alcohol can suppress the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
Alcohol’s impact on the cardiovascular system can lead to high blood pressure and heart problems.
Role of Access and Affordability
Alcohol’s accessibility and affordability play a significant role in the number of deaths. Easy access, particularly through readily available sales, can contribute to increased consumption. Low prices can make alcohol more attractive, especially for vulnerable populations. This increased availability can lead to a higher incidence of alcohol-related issues. For example, the presence of numerous liquor stores in a densely populated area can increase the risk of excessive consumption.
Societal Factors Influencing Alcohol-Related Deaths
Cultural norms and peer pressure can influence alcohol consumption patterns. Societal acceptance of excessive drinking can normalize unhealthy habits. Peer pressure, especially among young people, can encourage experimentation and excessive consumption. These societal factors can create a climate where alcohol-related deaths are more likely to occur. For example, certain cultural events may emphasize heavy drinking, contributing to the problem.
Geographic Variations in Trends

Global alcohol-related deaths are a significant public health concern, and understanding regional disparities is crucial for effective intervention strategies. Different societal factors, cultural norms, and regulatory environments contribute to varying levels of alcohol consumption and subsequent mortality rates. Examining these differences allows for a more targeted approach to prevention and treatment.The disparity in alcohol-related death rates across various regions highlights the need for tailored interventions.
Specific approaches to address alcohol misuse should be informed by the unique circumstances and cultural contexts of each region, ensuring interventions are effective and culturally sensitive.
Regional Disparities in Alcohol-Related Deaths
Alcohol-related deaths exhibit notable variations across countries and regions. These variations reflect differences in alcohol consumption patterns, socioeconomic factors, and public health policies. Analyzing these regional differences provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of existing strategies and identifies areas requiring improvement.
Comparative Data on Alcohol-Related Death Rates
This table presents the estimated rates of alcohol-related deaths per 100,000 population in various regions over the past two decades. Note that data may vary slightly depending on the specific source and methodology.
| Region | 2000-2002 | 2010-2012 | 2020-2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | 15.2 | 17.8 | 19.5 |
| Western Europe | 12.5 | 11.8 | 13.2 |
| Eastern Europe | 18.9 | 25.3 | 27.9 |
| Latin America | 9.8 | 11.5 | 12.9 |
| Sub-Saharan Africa | 3.5 | 4.2 | 5.1 |
| Asia | 7.1 | 8.8 | 9.9 |
Alcohol Policies and Their Impact
Different alcohol policies, including taxation, advertising restrictions, and access limitations, have varying effects on alcohol-related death rates. A comprehensive analysis of these policies is necessary to understand their effectiveness and potential for improvement.
| Alcohol Policy | Description | Potential Impact on Alcohol-Related Death Rates | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum Unit Pricing (MUP) | Sets a minimum price for alcoholic beverages. | Generally associated with decreased consumption and reduced alcohol-related harm. | Ireland, Scotland, and others |
| Advertising Restrictions | Limits the promotion of alcoholic beverages. | Can potentially reduce alcohol consumption, particularly among young people. | Many countries with advertising bans on TV and in specific contexts. |
| Stricter Licensing Regulations | Increases the difficulty and cost of obtaining alcohol licenses for establishments. | May reduce the availability of alcohol in high-risk areas. | Regulations regarding the sale of alcohol in certain areas, like those near schools. |
| Graduated Licensing Systems | Gradually allows individuals to consume alcohol based on age and experience. | Could help prevent underage drinking and reduce risky behaviors. | Specific laws and licensing requirements for different age groups. |
Impact on Healthcare Systems
The escalating toll of alcohol-related deaths places a significant strain on healthcare systems worldwide. These deaths aren’t isolated incidents; they represent a complex web of interconnected challenges that demand substantial resources for treatment, rehabilitation, and prevention. The financial burden and emotional toll on healthcare providers and the broader community are substantial and growing.The healthcare system faces a multifaceted challenge in responding to the increasing number of alcohol-related deaths.
From emergency room visits for alcohol poisoning to long-term care for those with alcohol-related liver disease, the costs associated with treating these conditions are substantial. Furthermore, the prevention and early intervention strategies are equally critical in mitigating the long-term effects and reducing the overall burden on the healthcare system.
Strain on Healthcare Resources
The increasing number of alcohol-related deaths places a considerable strain on hospital resources. Emergency departments frequently see patients suffering from alcohol-related issues, from intoxication to withdrawal symptoms. This influx necessitates additional staff, equipment, and resources to provide adequate care. Hospitals must also allocate resources to long-term care for individuals with alcohol-related conditions like cirrhosis, pancreatitis, and heart disease.
These conditions often require specialized care and extended stays, leading to further strain on hospital beds and staff.
Allocation of Resources for Treatment, Alcohol related deaths double in two decades
The financial commitment to treating alcohol-related illnesses is substantial. Funding for specialized alcohol treatment centers, inpatient rehabilitation programs, and community-based support groups is critical. Public health initiatives focusing on early intervention and prevention are equally important. Data from various countries demonstrate a correlation between the amount of funding allocated to alcohol-related treatment and the rates of alcohol-related mortality.
For instance, countries with robust funding for prevention and treatment programs often show lower rates of alcohol-related deaths compared to those with limited resources.
Healthcare Provider Responses
Healthcare providers are employing a range of strategies to address the growing issue of alcohol-related deaths. This includes the development and implementation of specialized treatment protocols, training programs for healthcare professionals on alcohol use disorders, and collaborations with community organizations to provide comprehensive support services. For example, many hospitals now have dedicated alcohol detoxification units and support networks for patients and their families.
Moreover, a growing emphasis is placed on early intervention and prevention programs targeting at-risk populations.
It’s truly shocking that alcohol-related deaths have doubled in just two decades. This alarming statistic highlights the pervasive issue of substance abuse, and the need for increased awareness and support. The hesitancy to disclose health conditions, like with people with HIV, for example, people with HIV reluctant to tell others , often creates a barrier to accessing vital resources and support networks.
Ultimately, tackling the root causes of these issues and fostering open communication is crucial in reducing the devastating toll of alcohol-related deaths.
Cost Implications
The economic burden of alcohol-related deaths on the healthcare system is significant. Costs include direct expenses for hospitalizations, medical procedures, and medications. Indirect costs, such as lost productivity due to illness or premature death, are often substantial and difficult to quantify. These costs place a burden not only on healthcare systems but also on society as a whole.
Studies have shown a strong correlation between increased alcohol consumption and higher healthcare costs. For example, a study in the United States estimated that the annual cost of alcohol-related healthcare was over \$200 billion.
Public Health Interventions: Alcohol Related Deaths Double In Two Decades
Addressing the rising tide of alcohol-related deaths demands a multifaceted approach. Public health interventions are crucial in mitigating the risks associated with excessive alcohol consumption. Effective strategies must be tailored to specific populations and contexts, encompassing prevention, treatment, and support systems. A proactive approach that promotes responsible alcohol use and reduces the availability of alcohol to vulnerable populations is essential.
It’s alarming that alcohol-related deaths have doubled in the past two decades. While this is a serious public health concern, there’s also hope on the horizon. Research into fields like regenerative medicine has a bright future regenerative medicine has bright future , potentially offering new avenues for treating and preventing alcohol-related illnesses. Ultimately, though, tackling this growing issue requires multifaceted solutions that go beyond medical advancements.
Strategies for Reducing Alcohol-Related Deaths
Public health interventions aim to reduce the demand and supply of alcohol, while also supporting individuals struggling with alcohol misuse. This requires a comprehensive strategy, encompassing various approaches. These include creating awareness, restricting access, promoting responsible consumption, and providing support for those seeking help. Interventions are typically evaluated based on their ability to reduce alcohol-related harms, such as deaths, hospitalizations, and injuries.
Types of Public Health Campaigns
Different campaigns address specific aspects of alcohol-related harm. These campaigns employ various strategies, from media awareness to community-based programs. Their effectiveness depends on factors like target audience, message clarity, and sustained implementation.
| Campaign Type | Focus | Example Strategies | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Awareness Campaigns | Raising awareness about the dangers of excessive alcohol consumption | Educational materials, public service announcements (PSAs), social media campaigns, community events | Increased knowledge and understanding of alcohol-related risks |
| Restricting Access to Alcohol | Controlling the availability of alcohol to vulnerable populations | Raising the legal drinking age, implementing stricter regulations on alcohol sales, restricting advertising | Reduced access to alcohol for those at higher risk |
| Promoting Responsible Consumption | Encouraging moderation in alcohol consumption | Alcohol awareness programs in schools, educational resources for adults, promoting non-alcoholic options | Shifting attitudes towards responsible drinking |
| Support for Individuals with Alcohol Use Disorders | Providing treatment and support services for those struggling with alcohol misuse | Counseling, therapy, support groups, detoxification services | Improved health outcomes and reduced likelihood of relapse |
Effectiveness of Prevention Strategies
The effectiveness of public health interventions in reducing alcohol-related deaths varies depending on the specific strategy and the context in which it is implemented. Comprehensive strategies that combine several approaches, including awareness campaigns, access restrictions, and support services, are generally more effective than single-pronged interventions. For instance, a community-based program that combines educational workshops, access restrictions, and peer support networks has shown promising results in reducing alcohol-related hospitalizations in some areas.
The success of these programs often hinges on community engagement and long-term commitment. Strong community partnerships and sustained funding are essential for program sustainability. Evidence-based approaches are crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of interventions. Evaluation metrics should encompass various factors, including changes in drinking patterns, hospitalizations, and mortality rates.
Examples of Successful Interventions
Numerous communities and countries have implemented successful public health interventions to reduce alcohol-related deaths. One example is the introduction of mandatory alcohol awareness programs in high schools in several states in the US, which has been associated with a decrease in underage drinking and related problems. Another example is the implementation of stricter regulations on alcohol advertising in some European countries, which has been linked to a decline in alcohol consumption among young people.
These examples highlight the importance of targeted interventions, community involvement, and long-term commitment in achieving positive outcomes.
Public Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness about the dangers of excessive alcohol consumption is crucial in curbing alcohol-related deaths. Effective campaigns can shift societal attitudes, prompting individuals to make healthier choices and ultimately reducing the devastating impact of alcohol misuse. This requires a multifaceted approach that combines targeted messaging with educational initiatives to empower individuals with the knowledge and tools to manage their alcohol intake responsibly.Public awareness campaigns play a vital role in changing attitudes towards alcohol.
By emphasizing the long-term health consequences and the potential for dependence, campaigns can motivate individuals to reconsider their drinking habits. Furthermore, educational initiatives complement these campaigns by providing concrete knowledge about alcohol’s effects on the body and mind, offering practical strategies for responsible consumption, and encouraging help-seeking behaviors. This combined effort is essential to create a society that values moderation and promotes well-being.
Importance of Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns are critical for reducing alcohol-related deaths by promoting understanding of the dangers of excessive alcohol consumption. They create a shared understanding of the issue within communities, motivating individuals to make informed choices. Effective campaigns can also challenge social norms that encourage excessive drinking.
Examples of Effective Public Awareness Campaigns
Several successful campaigns have utilized various approaches to raise awareness. One prominent example involves partnering with media outlets to showcase the stories of individuals affected by alcohol misuse. This humanizes the issue, making it relatable and fostering empathy among the audience. Another effective strategy is to create interactive online platforms and social media campaigns that provide easily digestible information about alcohol’s health consequences and responsible consumption.
It’s shocking that alcohol-related deaths have doubled in just two decades. While the reasons are complex, a healthy lifestyle, like focusing on plant-based nutrition fueling workouts, might offer a more sustainable path to well-being. Plant based nutrition fueling workouts can contribute to overall health, which could indirectly help mitigate some of the risk factors associated with excessive alcohol consumption, ultimately reducing these tragic statistics.
Furthermore, campaigns often feature celebrity endorsements or collaborations with prominent figures in public health to enhance their impact and credibility.
Educational Initiatives to Prevent Alcohol Abuse
Educational initiatives play a vital role in empowering individuals to make informed decisions about alcohol consumption. These programs are often integrated into school curricula, aiming to educate adolescents about the risks of alcohol abuse and promote healthy habits early in life. They can also involve workshops for young adults and adults, focusing on strategies for responsible drinking and recognizing the signs of alcohol dependence.
These educational programs not only equip individuals with knowledge but also empower them with the skills to make healthy choices. Additionally, they can provide resources for seeking help and support if needed.
Improving Public Awareness about Dangers of Excessive Consumption
To enhance public awareness about the dangers of excessive alcohol consumption, a multi-pronged strategy is essential. This includes creating easily accessible educational materials, employing diverse communication channels, and ensuring that information is presented in a clear, concise, and engaging manner. Community-based initiatives can also play a crucial role, organizing events and workshops that promote discussions about responsible alcohol consumption and the potential consequences of excessive drinking.
Utilizing visuals, such as impactful statistics or personal stories, can help capture attention and reinforce the message. Moreover, campaigns must be sustained over time to ensure their impact on changing societal norms.
Long-Term Consequences of Alcohol Abuse
Alcohol abuse, unfortunately, doesn’t just end with a hangover. The long-term effects can be devastating, impacting every aspect of a person’s life, from their physical health to their financial stability and social relationships. Understanding these consequences is crucial for prevention and intervention efforts.The damage caused by chronic alcohol abuse is multifaceted and insidious. It often manifests gradually, making it difficult to recognize the severity of the problem until it’s deeply entrenched.
This insidious nature underscores the importance of early intervention and support systems.
Physical Health Consequences
Alcohol’s corrosive effect on the body is well-documented. Regular heavy drinking can lead to a range of serious health problems, impacting virtually every organ system. These problems are not isolated incidents; they often develop gradually, becoming increasingly difficult to manage over time.
- Liver Disease: Cirrhosis, alcoholic hepatitis, and liver cancer are severe consequences of chronic alcohol abuse. These conditions can lead to significant health complications and even death. For example, a person who consistently drinks excessively over many years could develop cirrhosis, eventually requiring a liver transplant.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Alcohol abuse can increase the risk of high blood pressure, heart failure, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases. A person with a history of heavy drinking may experience irregular heartbeats or hypertension, impacting their quality of life and requiring ongoing medical attention.
- Gastrointestinal Problems: Alcohol can irritate the digestive system, leading to ulcers, gastritis, and pancreatitis. For instance, a person with a drinking problem could experience chronic abdominal pain and discomfort, impacting their daily routines.
- Neurological Damage: Brain damage, including Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, can result from alcohol abuse due to deficiencies in essential nutrients. This can lead to memory loss, confusion, and difficulty with coordination. A person struggling with chronic alcoholism might experience significant memory loss, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks or maintain relationships.
- Weakened Immune System: Alcohol weakens the body’s natural defenses, increasing susceptibility to infections. This is often seen in those with prolonged alcohol abuse who have a higher risk of developing various infections.
Financial Burden
The financial burden of alcohol-related illnesses extends far beyond medical costs. Lost productivity, increased healthcare expenses, and caregiving responsibilities all contribute to a significant financial strain on individuals and families. This financial burden can lead to significant hardship for affected individuals and their loved ones.
- Medical Expenses: Treatment for alcohol-related illnesses, such as liver transplants, can be extraordinarily expensive, placing a heavy financial strain on individuals and their families. The costs associated with hospitalizations, medications, and long-term care can be crippling.
- Lost Wages: Absenteeism and reduced productivity due to alcohol-related health problems and treatment can significantly impact an individual’s income. This loss of income can severely impact their ability to support themselves and their families.
- Caregiver Costs: Families often shoulder the burden of caregiving for loved ones struggling with alcohol-related illnesses. This can involve lost wages for family members, and the emotional toll can be immense.
Impact on Relationships and Social Life
Alcohol abuse often disrupts relationships and isolates individuals from their social networks. Trust is eroded, communication breaks down, and personal connections suffer. This isolation can exacerbate the problem, creating a cycle of loneliness and addiction.
- Strained Family Relationships: Conflicts, arguments, and emotional distance are common consequences of alcohol abuse within families. This can result in significant distress for all members.
- Damage to Social Connections: Alcohol abuse can lead to strained friendships, social isolation, and a decline in overall social well-being. The individual may lose touch with loved ones, contributing to a sense of isolation and despair.
- Erosion of Trust: Alcohol abuse frequently erodes trust within relationships, creating a sense of betrayal and insecurity. This can be especially difficult to repair.
Correlation Table
| Alcohol Abuse | Associated Health Problems |
|---|---|
| Heavy, chronic alcohol consumption | Liver cirrhosis, alcoholic hepatitis, liver cancer, high blood pressure, heart failure, stroke, ulcers, gastritis, pancreatitis, Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, weakened immune system |
Illustrative Data Visualization
Understanding the scope and nature of alcohol-related deaths requires a visual representation of the trends. Visualizations allow for a quick grasp of patterns, highlighting key areas of concern and facilitating comparisons across time and geography. This section presents illustrative data visualizations to aid in comprehending the complexities of this public health issue.
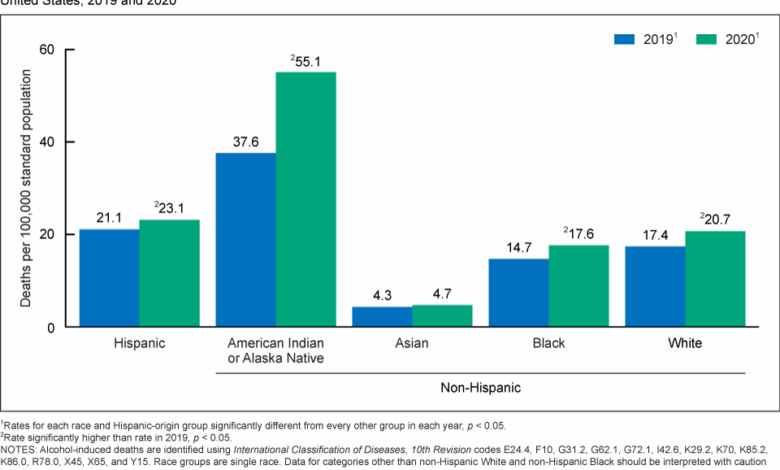
Alcohol-Related Death Trends Over Time
This visual displays the increase in alcohol-related fatalities over a specific period. A bar chart, for instance, can clearly show the rising number of deaths each year. Each bar represents a year, with the height corresponding to the number of alcohol-related deaths. This format allows for a simple yet powerful comparison of mortality rates across the years, revealing the severity and persistence of this issue.
For example, the bar chart might illustrate a steady increase from 2000 to 2020, with a marked jump in 2015, perhaps correlating with a change in alcohol consumption patterns or public health campaigns.
Causes of Alcohol-Related Deaths
A breakdown of the different causes contributing to alcohol-related deaths is crucial. A pie chart effectively represents this data. Each slice of the pie represents a specific cause, such as alcohol poisoning, accidents involving alcohol, liver disease, or other related conditions. The size of each slice directly corresponds to the proportion of deaths attributable to that cause. For instance, the chart might show that accidents account for the largest portion, followed by liver disease and alcohol poisoning, allowing for a quick assessment of the relative importance of each contributing factor.
Geographical Distribution of Alcohol-Related Deaths
A map, employing different shades or colors to represent the density of alcohol-related deaths in various regions, can effectively demonstrate geographical variations. Darker shades might indicate higher mortality rates. This visual tool offers insights into the regions most affected by this issue, enabling targeted public health interventions and resource allocation. For example, the map might highlight a cluster of high-mortality areas in specific states or countries, suggesting potential localized risk factors or societal vulnerabilities.
Trends in Visual Representations
The visual representations—a bar chart, pie chart, and map—display a clear trend of increasing alcohol-related deaths over time. The pie chart illustrates the diverse factors contributing to these deaths, highlighting the significant impact of accidents, liver disease, and other alcohol-related conditions. The map demonstrates the uneven geographical distribution of these deaths, suggesting potential disparities in risk factors, access to healthcare, or public health awareness programs.
Understanding these patterns is crucial for developing effective prevention strategies and resource allocation plans to combat this public health concern.
Last Word

In conclusion, the doubling of alcohol-related deaths over two decades underscores a profound public health challenge requiring urgent attention. The multifaceted nature of this crisis demands a comprehensive approach that considers individual behaviors, societal influences, and regional variations. This analysis emphasizes the crucial role of public awareness campaigns, educational initiatives, and effective public health interventions in mitigating the tragic consequences of alcohol abuse.
Ultimately, a concerted effort involving policymakers, healthcare providers, and communities is essential to reversing this disturbing trend.