All about insulin infusion sets for diabetes, a comprehensive guide to understanding these crucial devices for managing diabetes. This in-depth exploration covers everything from the fundamental purpose of infusion sets to the practical aspects of user experience, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
Insulin infusion sets are a vital part of diabetes management, enabling precise and controlled insulin delivery. This article will walk you through the different types of sets, their mechanisms of action, safety considerations, and practical applications. Understanding these sets is key to effective blood glucose control and overall well-being for individuals with diabetes.
Introduction to Insulin Infusion Sets: All About Insulin Infusion Sets For Diabetes
Insulin infusion sets are a crucial part of diabetes management for individuals requiring continuous insulin delivery. They provide a precise and controlled way to administer insulin, allowing for flexibility in managing blood glucose levels throughout the day. This method is particularly important for those with type 1 diabetes or those with type 2 diabetes who require intensive insulin therapy.Insulin infusion sets are devices that deliver insulin subcutaneously (just beneath the skin) at a steady rate.
They are designed to provide a continuous flow of insulin, eliminating the need for frequent injections and enabling more accurate blood glucose control. These devices are an advancement in diabetes care, significantly improving quality of life for those managing this chronic condition.
Common Types of Insulin Infusion Sets
Insulin infusion sets come in various forms, each with unique features and benefits. Understanding these differences can help individuals select the best option for their needs. The most common types are:
- Pump-based systems: These sets are integrated with insulin pumps, providing a programmable delivery of insulin. Pump-based systems offer the most precise control over insulin delivery and are popular for their ability to accommodate different insulin needs throughout the day.
- Pen-based systems: These sets are usually attached to a pen-like device. While offering convenience, they typically provide less precise control compared to pump-based systems.
Fundamental Purpose of Insulin Infusion Sets
The fundamental purpose of insulin infusion sets is to provide a consistent and controlled delivery of insulin, mirroring the natural release of insulin in healthy individuals. This continuous infusion helps maintain stable blood glucose levels, preventing both high and low blood sugar fluctuations. This regulated delivery is vital for preventing acute complications and long-term health risks associated with uncontrolled diabetes.
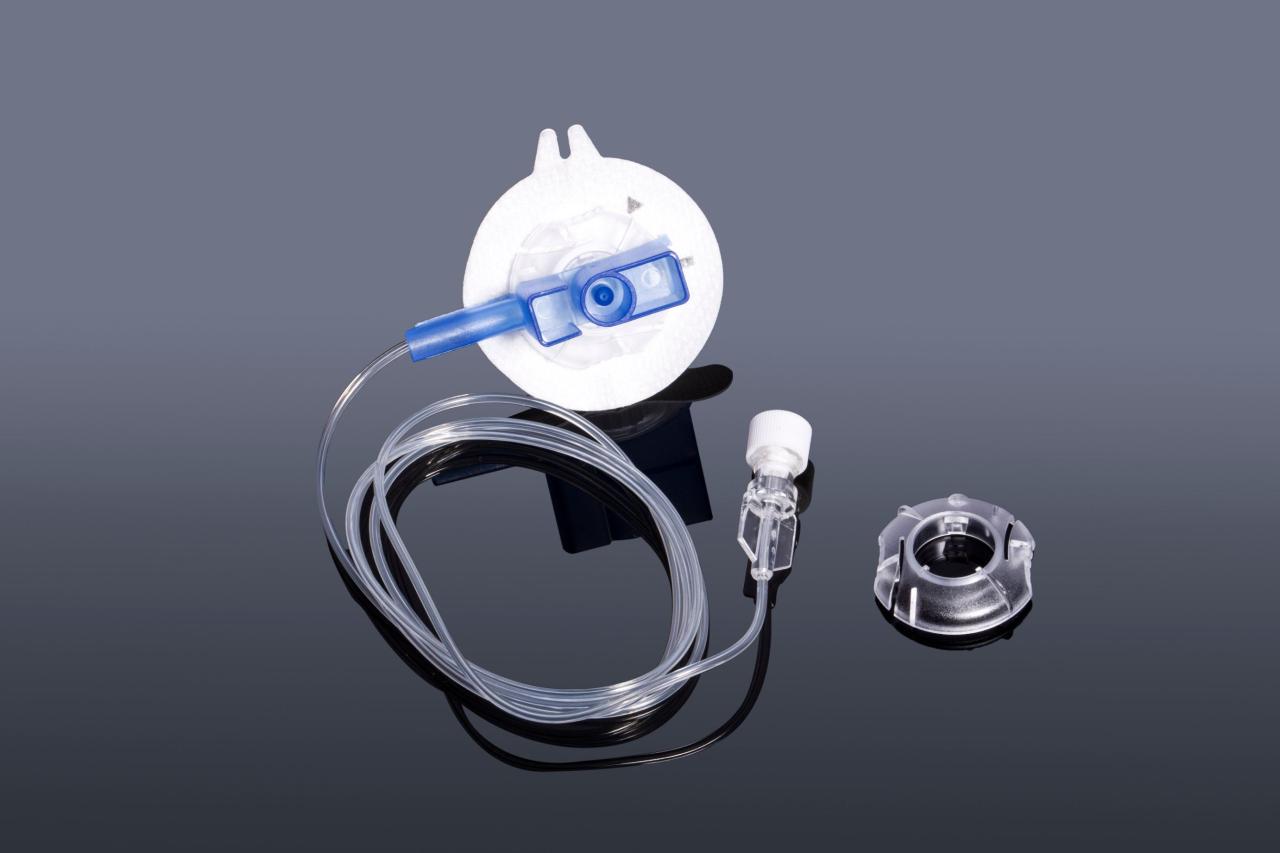
Components of a Typical Insulin Infusion Set
A typical insulin infusion set comprises several essential components. These include:
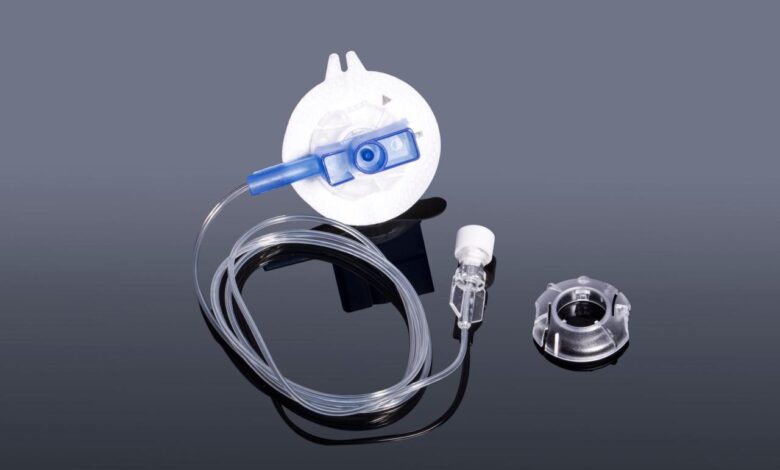
- The infusion set: This part connects to the insulin pump or pen, allowing for the flow of insulin to the insertion site.
- The cannula: This is a small, thin tube that is inserted just under the skin. It is responsible for delivering the insulin.
- The insertion site: This is the area where the cannula is placed, typically the abdomen, arms, thighs, or buttocks.
- The insulin reservoir: This is the area where the insulin is stored in the pump, ensuring continuous availability.
Importance of Proper Insulin Infusion Set Selection
Proper selection of an insulin infusion set is crucial for optimal diabetes management. Factors to consider include the individual’s lifestyle, insulin needs, and preferences. Individuals should consult with their healthcare providers to determine the best type of set for their specific requirements.
Key Features and Benefits of Various Infusion Sets
The following table Artikels the key features and benefits of different types of insulin infusion sets:
| Type | Delivery Method | Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pump-based | Programmable, continuous | Adjustable basal rates, bolus doses, customizable profiles | Precise control over insulin delivery, flexibility in managing varying needs, potential for better glucose control |
| Pen-based | Manual, intermittent | Portable, convenient for on-the-go administration | Ease of use, relatively straightforward operation, potentially lower cost |
Mechanism of Action
Insulin infusion sets are a crucial part of diabetes management, allowing for continuous insulin delivery. These sets, combined with insulin pumps, provide a more flexible and precise method of controlling blood glucose levels compared to traditional injection methods. This precise delivery system helps individuals with diabetes achieve better metabolic control and improve their overall quality of life.The process of insulin delivery through infusion sets relies on a combination of factors, including the insulin pump, the infusion set itself, and the individual’s specific needs.
The pump acts as a sophisticated delivery system, dispensing precise amounts of insulin into the bloodstream over time. This constant, controlled release is key to maintaining stable blood glucose levels throughout the day and night.
Insulin Delivery Process
The insulin pump, a small, portable device, houses a reservoir of insulin. It delivers insulin continuously at a basal rate, similar to the body’s natural insulin production. The infusion set, a thin plastic catheter, is connected to the pump and inserted under the skin. The catheter’s tip sits in the subcutaneous tissue, allowing for the continuous flow of insulin into the bloodstream.
The pump precisely regulates the flow rate, ensuring accurate delivery of insulin.
Role of the Infusion Pump
The insulin pump is the heart of the delivery system. It’s a programmable device that allows for precise control over insulin delivery. The pump stores the insulin solution and delivers it according to the programmed instructions. The basal rate, bolus doses, and any adjustments are all managed by the pump’s software. Advanced pumps offer features like continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) integration, enabling real-time adjustments to insulin delivery based on blood glucose readings.
Programming the Insulin Pump
Programming an insulin pump involves setting the basal rate and bolus doses. The basal rate is the continuous insulin delivery rate. It’s programmed to mimic the body’s natural insulin release throughout the day and night. Bolus doses are additional insulin amounts given in response to meals or to correct high blood sugar levels. The programming process usually involves inputting carbohydrate counts, meal times, and anticipated blood glucose changes.
It requires careful calibration and adjustments based on individual needs.
Types of Infusion Sites
Infusion sites are crucial for the success of insulin therapy. The most common sites are the abdomen, upper arms, thighs, and buttocks. The abdomen is frequently preferred due to its accessibility and subcutaneous fat distribution. Other sites can be used depending on the individual’s needs and preferences. It’s essential to rotate infusion sites to prevent skin irritation and lipohypertrophy (a buildup of fat tissue).
Regulating Blood Glucose Levels
Insulin infusion sets help regulate blood glucose levels by delivering insulin continuously and precisely. The basal rate, adjusted based on individual needs, mimics the body’s natural insulin release, maintaining a stable baseline glucose level. Bolus doses, administered in response to meals or blood glucose fluctuations, provide targeted insulin delivery to control spikes in blood glucose. This continuous, controlled delivery system helps keep blood glucose within a healthy range, reducing the risk of complications associated with uncontrolled diabetes.
Setting Up an Insulin Infusion Set
Setting up an insulin infusion set involves several critical steps.
- Gather necessary supplies, including the insulin pump, infusion set, alcohol pads, and gauze.
- Clean the chosen infusion site with an alcohol pad and allow it to dry.
- Attach the infusion set to the insulin pump according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Insert the catheter into the subcutaneous tissue at the selected site, ensuring it’s correctly placed.
- Secure the infusion set with a bandage or dressing.
- Program the insulin pump according to the individual’s diabetes management plan.
- Monitor blood glucose levels frequently to adjust the pump settings as needed.
Types and Features
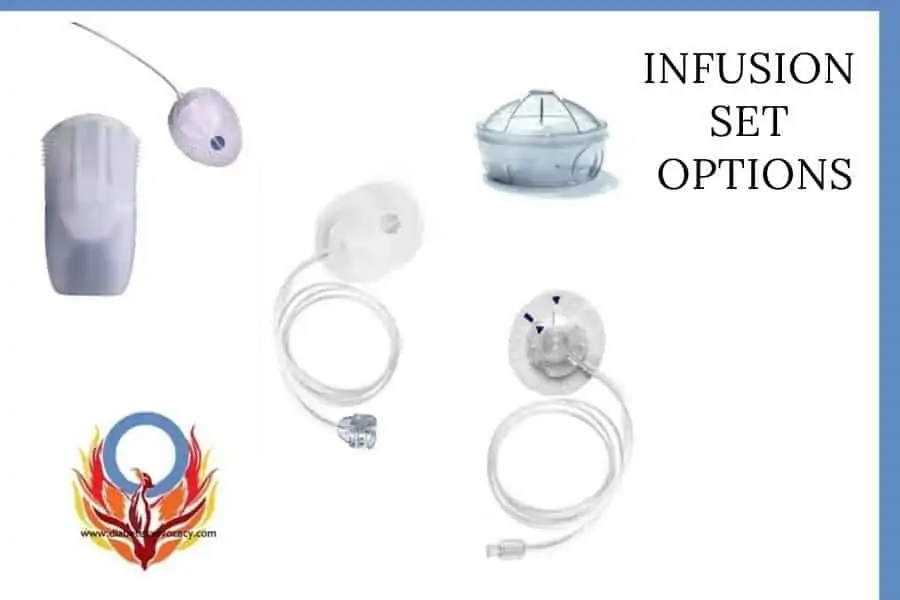
Insulin infusion sets are crucial tools for managing diabetes. Understanding the various types available, their features, and appropriate usage is vital for optimal blood glucose control. Different types cater to specific needs and preferences, allowing individuals to tailor their insulin delivery to their lifestyles.Various factors influence the choice of an insulin infusion set, including the individual’s activity level, lifestyle preferences, and the type of diabetes they have.
The design, materials, and features of each set directly impact comfort, safety, and ease of use.
Subcutaneous Infusion Sets
Subcutaneous insulin infusion sets are the most common type. They deliver insulin beneath the skin, usually into the abdomen. This method allows for flexible positioning and regular blood glucose monitoring. The convenience and relative ease of subcutaneous administration are significant advantages.
- Advantages: Subcutaneous infusion sets offer greater flexibility in terms of placement, enabling users to change infusion sites, potentially reducing the risk of lipohypertrophy and improving comfort. The ability to easily switch between sites and the generally lower risk of infection compared to intravenous options make them a popular choice.
- Disadvantages: Subcutaneous insulin absorption can vary based on factors like body temperature and subcutaneous fat thickness. This variability in absorption requires meticulous calibration and adjustment of insulin delivery rates to achieve optimal blood glucose control.
- Materials: Common materials used in subcutaneous infusion sets include plastic for the cannula and tubing, and various types of adhesives for securing the device to the skin. The quality of these materials, along with the design of the infusion set, significantly affects the user experience.
- Design: Subcutaneous infusion set designs vary regarding cannula length, catheter size, and adhesive strength. The set’s design also plays a crucial role in minimizing discomfort and maximizing patient adherence. Features like a smooth catheter and a secure locking mechanism are often incorporated to ensure a comfortable and reliable experience.
Intravenous Infusion Sets
Intravenous infusion sets are generally used for short-term, intensive insulin therapy, such as in the hospital setting or for managing severe hyperglycemia. This method offers rapid insulin delivery, allowing for precise control of blood glucose levels in critical situations.
- Advantages: Intravenous infusion sets offer rapid insulin delivery, allowing for a quicker response to fluctuating blood glucose levels. They are often the preferred method in critical care settings due to their speed and precision.
- Disadvantages: Intravenous infusion sets typically require close monitoring by healthcare professionals. The risk of infection is higher with intravenous administration, and the limited mobility can be a significant drawback for some users.
- Materials: Intravenous infusion sets often use specialized materials designed for compatibility with the bloodstream. These materials are rigorously tested to ensure safety and prevent complications.
- Design: Intravenous infusion sets are designed for sterile use and often feature a built-in filter to prevent particulate matter from entering the bloodstream. The infusion set design is crucial for preventing complications and maintaining patient safety.
Comparison Table
| Type | Features | User Profile |
|---|---|---|
| Subcutaneous | Flexible placement, relatively low infection risk, user-friendly | Individuals requiring long-term insulin therapy, active lifestyles |
| Intravenous | Rapid insulin delivery, precise control, used in critical care | Patients requiring intensive insulin therapy in hospital settings or for managing severe hyperglycemia |
Safety and Maintenance
Insulin infusion sets are crucial for managing diabetes, but their safe use and proper maintenance are paramount. Neglecting these aspects can lead to serious complications, from infections to inaccurate insulin delivery. Understanding the potential risks and implementing meticulous maintenance procedures are vital for a safe and effective diabetes management routine.Proper maintenance of insulin infusion sets is critical to prevent infections, ensure accurate insulin delivery, and minimize the risk of complications.
This involves meticulous cleaning, regular replacement, and safe handling practices. This section delves into the safety and maintenance protocols surrounding insulin infusion sets.
Potential Complications and Risks
Incorrect handling or inadequate maintenance of insulin infusion sets can lead to several complications. These include localized infections at the insertion site, such as cellulitis or abscesses, if hygiene standards are not met. Furthermore, improper maintenance can result in inaccurate insulin delivery due to clogging or malfunction of the set, potentially leading to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Rarely, but potentially, air bubbles in the tubing or infusion line can also cause issues with insulin delivery.
Learning about insulin infusion sets for diabetes can be tricky, but mastering them is crucial. Beyond the technicalities, it’s important to find healthy and satisfying ways to manage your blood sugar levels, like exploring various bean dishes. Check out some easy ways to use beans for delicious and protein-packed options to incorporate into your diet.
Ultimately, understanding insulin infusion sets is key to effective diabetes management.
Importance of Proper Set Maintenance and Hygiene
Maintaining meticulous hygiene and regularly replacing insulin infusion sets are crucial for preventing infections and ensuring precise insulin delivery. Maintaining proper hygiene protocols reduces the risk of bacterial or fungal infections at the insertion site, which can potentially spread to other parts of the body. Regular replacements, as per manufacturer guidelines, are vital to avoid the buildup of contaminants, ensuring accurate insulin flow and minimizing the risk of complications.
Understanding insulin infusion sets for diabetes is crucial, but what about minimizing errors during medical procedures? Careful labeling and meticulous verification procedures, like those discussed in what can we do to make no mix ups during surgery , are equally vital. Ultimately, precise handling and clear communication are key to ensuring the right insulin infusion sets are used for the right patients, especially in the context of diabetes management.
Cleaning and Replacing Infusion Sets
Following the manufacturer’s instructions is essential for cleaning and replacing infusion sets. This includes thoroughly cleaning the insertion site with antiseptic solutions, as per the doctor’s instructions. Replacing the entire set according to the prescribed intervals is crucial for preventing contamination and ensuring the accurate delivery of insulin.
- Cleaning Procedure: Always follow the specific instructions provided by the manufacturer. This usually involves gently cleaning the insertion site with a mild antiseptic solution, ensuring thorough rinsing and patting dry. Avoid harsh scrubbing, which can damage the delicate tubing or the insertion site.
- Replacement Schedule: Adhere to the prescribed replacement schedule for your specific insulin infusion set. This is crucial for preventing infection and maintaining accurate insulin delivery. Failure to replace the set on time can result in a buildup of contaminants that could potentially cause issues.
Handling and Storing Insulin Infusion Sets
Proper handling and storage practices are crucial for maintaining the integrity and efficacy of insulin infusion sets. Always handle the infusion set with clean hands, and avoid touching the insertion site or the infusion tubing directly. Store the infusion set in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Troubleshooting minor issues with insulin infusion sets can be done at home. For example, if the insulin delivery is erratic, first check the tubing for kinks or blockages. If the problem persists, consult your healthcare provider.
Learning about insulin infusion sets for diabetes is crucial for managing blood sugar levels. The recent tragedy at Las Vegas hospitals, las vegas hospitals mass shooting , highlights the importance of healthcare systems’ resilience and the need for effective care in moments of crisis. Ultimately, understanding insulin infusion sets remains a critical component of diabetes management, ensuring patients receive the precise insulin doses they need.
- Erratic Delivery: If the insulin delivery is inconsistent, check the tubing for kinks, blockages, or air bubbles. If the problem persists, consult your doctor.
- Leakage: Leakage from the insertion site can indicate a loose connection or a damaged infusion set. Consult your healthcare provider.
- Pain or Discomfort: If the insertion site becomes painful or inflamed, discontinue use immediately and consult your healthcare provider.
Comparison of Maintenance Procedures
| Type | Cleaning Steps | Precautions |
|---|---|---|
| Basal-bolus Infusion Sets | Follow manufacturer instructions, clean insertion site with antiseptic solution, and replace tubing as needed. | Ensure all connections are secure and tubing is free of kinks. |
| Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion (CSII) Sets | Clean insertion site thoroughly with antiseptic solution, replace the entire set as per manufacturer guidelines. | Avoid touching the infusion site or tubing. |
| Pre-filled Insulin Syringes | Follow manufacturer’s instructions for cleaning and storage. | Dispose of used syringes properly and do not reuse. |
User Experience and Practical Applications
Insulin infusion sets are more than just medical devices; they’re a critical part of daily life for many people with diabetes. Understanding how to use them effectively and comfortably is key to managing blood sugar levels and maintaining overall well-being. This section dives into the practical aspects of setting up, using, and maximizing the benefits of these systems.
Setting Up a Standard Insulin Infusion Set
Proper setup is paramount for safe and effective insulin delivery. Follow these steps carefully:
- Prepare the site: Clean the insertion site thoroughly with an alcohol swab, ensuring it’s dry before insertion. This step prevents infection and ensures proper adhesion of the infusion set.
- Select the appropriate infusion set: Choose a set appropriate for the patient’s needs and the type of insulin being administered. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Insert the cannula: Insert the cannula (the thin tube) into the subcutaneous tissue at the chosen site, ensuring it’s properly inserted and not too deep or shallow.
- Secure the set: Secure the infusion set with the provided adhesive dressing. Properly securing the set prevents dislodgement and leakage. Adjust the dressing to ensure a snug fit without causing discomfort.
- Connect to the pump: Connect the infusion set tubing to the infusion pump, confirming a secure connection. Always double-check for leaks or obstructions in the tubing.
Infusion Pump User Interface Features
Modern infusion pumps are designed with user-friendliness in mind. Key features often include:
- Display screen: Displays critical information like the current insulin dose, infusion rate, and remaining insulin. Clear and intuitive displays are essential for easy monitoring.
- Programming functions: Allows users to adjust basal rates (background insulin delivery), bolus doses (meal-time insulin), and other settings. User-friendly programming prevents errors and ensures accurate insulin delivery.
- Alarm systems: Alerts users to potential problems like low battery, occlusion (blockage), or infusion rate deviations. These alerts are vital for prompt intervention and maintaining safe insulin delivery.
- Battery life indicators: Provides an indication of the battery’s remaining charge. This feature is crucial for preventing unexpected pump shutdowns.
Maximizing Efficiency and Effectiveness
Effective insulin management relies on a few key strategies:
- Regular site rotation: Change the infusion site location frequently to avoid skin irritation and lipohypertrophy (a build-up of fat tissue at the infusion site).
- Proper pump maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for pump cleaning and maintenance to ensure optimal functionality.
- Monitoring: Continuously monitor blood glucose levels and adjust insulin delivery as needed. Consistent monitoring is crucial for accurate dose adjustments and optimal blood sugar control.
Patient Education
Patient education is critical for successful insulin infusion set usage.
- Comprehensive instruction: Detailed instruction manuals, videos, and hands-on training should be provided to equip patients with the knowledge and skills necessary for safe and effective insulin delivery.
- Addressing concerns: Addressing any patient concerns or questions about the device is crucial. Clear communication and support are essential for building trust and confidence.
- Ongoing support: Provide ongoing support and resources to ensure patients feel comfortable asking questions and seeking assistance when needed.
Common Questions and Answers
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| How often should I change the infusion set? | Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for recommended change intervals. Factors like site characteristics and the patient’s condition might influence the frequency. |
| What should I do if the pump malfunctions? | Contact the manufacturer or healthcare provider immediately. Following the emergency protocol provided will help ensure the safety and well-being of the patient. |
| Can I shower or bathe with the infusion set? | Consult the manufacturer’s instructions. Some infusion sets are waterproof or water-resistant. Check the specifications to avoid complications. |
Troubleshooting and Emergencies
Insulin infusion sets, while crucial for managing diabetes, can sometimes encounter complications. Understanding potential issues and knowing how to respond promptly is vital for maintaining stable blood glucose levels and preventing serious health risks. This section Artikels the common problems, symptoms, and emergency procedures associated with insulin infusion sets.
Signs and Symptoms of Potential Infusion Set Complications, All about insulin infusion sets for diabetes
Infusion set complications often manifest with noticeable signs. These can include:
- Pain or discomfort at the insertion site: This could indicate infection, irritation, or a problem with the cannula placement.
- Redness, swelling, or warmth around the insertion site: These are possible signs of inflammation or infection.
- Leakage of insulin from the insertion site: This indicates a loose connection or a malfunctioning set.
- Changes in blood glucose levels: Sudden fluctuations in blood glucose levels, either high or low, can be a symptom of infusion set problems. For example, a sudden drop in blood glucose might indicate an over-infusion or accidental disconnection from the pump. Conversely, a sudden increase could indicate an under-infusion or an occlusion.
- Occlusion: This means a blockage in the tubing. Symptoms might include a reduced or absent insulin flow and an inability to calibrate the insulin pump.
- Accidental disconnection: This is a serious concern and could lead to a sudden stop of insulin delivery. The individual might experience symptoms associated with hypoglycemia if the disconnect occurs while the infusion set is active.
- Visible air bubbles in the tubing: While not always a serious problem, air bubbles can interfere with insulin delivery and should be addressed.
- Signs of infection: This includes pus, drainage, fever, or a rapid increase in pain or swelling around the insertion site.
Common Infusion Set Problems
A range of problems can arise with insulin infusion sets. Understanding these common issues is crucial for proactive management:
- Occlusion: Blockages in the tubing, often caused by blood clots or fibrin, are frequent problems. This can disrupt insulin delivery.
- Accidental disconnections: Accidental disconnections from the pump are a potential danger. This can stop the insulin delivery abruptly.
- Loose connections: Loose connections between the cannula and tubing or between the tubing and pump can cause leakage or poor insulin delivery.
- Infusion set malfunction: The infusion set itself may malfunction, leading to incorrect or interrupted insulin delivery.
- Improper insertion technique: Incorrect insertion can cause discomfort, leakage, or infection. A professional should be consulted for proper insertion instructions.
Steps to Take if Complications Occur
Addressing complications promptly is essential. Following a clear procedure is vital for patient safety:
- Assess the situation: Identify the specific problem and determine the severity of the complication. For example, a small leak might be less critical than an accidental disconnection.
- Document the problem: Record the time, symptoms, and any relevant information about the event. This can help healthcare professionals to better understand the issue.
- Stop the infusion (if possible): If the issue is affecting insulin delivery, stop the infusion if it is safe to do so. But do not stop it without a clear understanding of the situation and the potential consequences. If you are unsure, consult with a healthcare professional.
- Follow your diabetes management plan: If possible, follow your diabetes management plan to address the situation. This may include taking supplemental insulin, testing blood glucose levels more frequently, or contacting your healthcare provider.
- Contact your healthcare provider or diabetes educator immediately: It’s crucial to seek guidance from a medical professional. A healthcare provider can advise on the appropriate actions based on the specific complication.
Emergency Procedures for Managing Infusion Set Issues
Addressing infusion set emergencies swiftly is essential. These steps Artikel the procedure for various scenarios:
- Accidental disconnection: If the infusion set disconnects, reconnect it as soon as possible. If reconnection is not possible, contact your healthcare provider immediately. If you’re unsure, it’s better to err on the side of caution and seek professional guidance.
- Occlusion: If the insulin pump displays a blockage, try to clear the occlusion by gently pressing or tapping the tubing. If this does not work, contact your healthcare provider.
- Severe hypoglycemia: If you experience severe hypoglycemia, follow your emergency plan and contact your healthcare provider immediately.
How to Contact Healthcare Providers for Immediate Assistance
Knowing how to reach your healthcare provider or diabetes educator quickly is crucial in an emergency. Have their contact information readily available, including phone numbers and emergency contact information.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, mastering insulin infusion sets is crucial for diabetes management. By understanding the various types, mechanisms, safety protocols, and practical applications, individuals can optimize their treatment and improve their quality of life. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview, empowering you to make informed decisions about your diabetes care.