Ask dmine new pump really old insulin – this is a crucial question for anyone navigating a diabetes management change. Switching to a new insulin pump while still using older insulin can be tricky, and understanding the potential challenges is key. This discussion delves into the complexities of this transition, considering potential issues, patient concerns, medical advice, and troubleshooting steps to ensure a smooth and safe process.
This in-depth exploration will guide you through the various aspects of using older insulin with a new insulin pump, offering valuable insights into compatibility, potential risks, and the importance of professional consultation.
Understanding the Context
The phrase “ask dmine new pump really old insulin” suggests a potential issue in managing diabetes. It highlights a concern about compatibility between a new insulin pump and older insulin preparations. This raises questions about the safety and effectiveness of using outdated insulin with a modern insulin delivery system. Understanding the intricacies of insulin types, pump functionalities, and potential complications is crucial for anyone dealing with this situation.The phrase implies a user is seeking advice on using older insulin with a newly acquired insulin pump.
I’ve been researching the compatibility of a new insulin pump with really old insulin. It’s fascinating how healthcare is one of the fastest growing industries, with constant innovation in devices and treatments. Healthcare among fastest growing industries is driving this need for compatibility, and it’s crucial to find reliable information about mixing old and new technologies like this for optimal results with my insulin regimen.
Hopefully, I’ll find a clear answer soon!
The concern is likely centered on whether the older insulin is compatible with the new pump’s features and whether the older insulin is still effective or might have degraded over time. It also touches on the importance of proper storage and handling of insulin, which can impact its efficacy.
Insulin Pump Types
Insulin pumps are designed to deliver insulin continuously or in bolus doses. Different types offer varying levels of features and flexibility in managing blood sugar. These pumps vary in complexity, from basic models with fixed basal rates to advanced models allowing for more personalized adjustments. Some pumps offer features like real-time glucose monitoring and automatic dose adjustments.
The choice of pump depends on individual needs, preferences, and the complexity of the diabetes management plan.
Insulin Types and Compatibility
Various types of insulin are available, each with distinct characteristics in terms of onset, peak, and duration of action. Rapid-acting insulins, such as lispro or aspart, are designed for rapid absorption and are typically used for mealtime boluses. Short-acting insulins, like regular insulin, have a slower onset but are still suitable for mealtime coverage. Intermediate-acting insulins, such as NPH, are used for basal coverage.
Long-acting insulins, like glargine or detemir, provide a steady release of insulin throughout the day. The compatibility of different insulin types with different pumps depends on the pump’s ability to handle various insulin types and delivery profiles. Manufacturers’ instructions and healthcare professional guidance are critical to ensuring compatibility.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of Using Older Insulin with a New Pump
| Aspect | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Efficacy | May still be effective if properly stored and within expiry date. | Potential for reduced effectiveness if the insulin has degraded. |
| Accuracy | May work with the pump’s algorithms, though potentially less precise than newer insulins. | Potential for inaccurate dosing if the pump’s software isn’t calibrated for the older insulin type. |
| Safety | May be safe if the insulin is within the expiry date and stored correctly. | Potential for hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia if not managed correctly. |
| Cost | Potentially less expensive than newer insulins. | May require more frequent monitoring and adjustments to maintain blood sugar control. |
| Storage | If stored properly, older insulins might still be usable. | Proper storage and handling are crucial to maintain efficacy and prevent degradation. |
Using older insulin with a new pump might work in some cases, but careful consideration of its potential benefits and drawbacks is essential. The efficacy and accuracy of the insulin delivery will be influenced by the insulin type and pump’s compatibility. Consulting a healthcare professional is paramount to assess the suitability of using older insulin with a new pump.
I’ve been asking myself, and DMing, about using a new insulin pump with really old insulin. It’s a bit of a worry, right? It’s crucial to explore the potential implications for kidney health. For example, researching “kidney health doctor questions” kidney health doctor questions might give you a better understanding of potential issues. Ultimately, consulting a medical professional about using a new insulin pump with old insulin is the best approach.
Potential Issues and Risks
Using older insulin with a new insulin pump can introduce a range of potential complications. Compatibility issues, dosage discrepancies, and adverse health effects are all possible outcomes if proper precautions are not taken. Understanding these risks is crucial for safe and effective diabetes management.Older insulins may not be fully compatible with the new pump’s delivery system. The pump’s software might not accurately calculate the dose or properly administer the insulin, leading to inaccurate blood sugar control.
This can result in unpredictable blood glucose levels, potentially triggering hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Therefore, consulting with a healthcare professional is critical to ensure a safe transition.
Compatibility Problems
Proper insulin compatibility is vital when switching from older insulin to a new insulin pump. Different insulin types have varying characteristics that can affect their interaction with the pump’s technology. Some older insulins may not mix well with the pump’s software algorithms, resulting in inaccurate dose calculations. This mismatch can lead to unexpected fluctuations in blood glucose levels.
Complications from Using Old Insulin with a New Pump
Using older insulin with a new pump can cause various complications. The pump’s calibration and software may not be designed to handle the specific characteristics of older insulin formulations. This can result in improper dose delivery, leading to inconsistent blood sugar control. For example, a pump designed for newer insulins might struggle to accurately measure the absorption rate of a specific older insulin, potentially causing either high or low blood sugar levels.
Importance of Consulting a Healthcare Professional
A healthcare professional is essential for navigating the transition from older insulin to a new insulin pump. They can assess the specific characteristics of both the insulin and the pump to determine if they are compatible. They can also provide guidance on appropriate dosage adjustments and monitor blood glucose levels closely to ensure safe and effective management. This personalized approach is crucial to prevent adverse effects.
Examples of Improper Insulin Usage
Improper insulin usage can have serious consequences. For instance, if the dosage is too high, it can lead to hypoglycemia, a potentially dangerous condition characterized by low blood sugar levels. Conversely, insufficient insulin can lead to hyperglycemia, a condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. Both situations can lead to significant health complications if not managed promptly.
Accurate Dosage Calculations
Accurate dosage calculations are critical when using a new insulin pump with older insulin. The pump’s software may not accurately calculate the dose for older insulin types, potentially leading to significant errors in insulin delivery. Healthcare professionals must precisely determine the correct insulin dosage to maintain optimal blood glucose control. A miscalculation can lead to significant health risks.
Potential Side Effects
| Potential Side Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Hypoglycemia | Low blood sugar, characterized by symptoms like shakiness, sweating, and confusion. |
| Hyperglycemia | High blood sugar, characterized by symptoms like increased thirst, frequent urination, and blurred vision. |
| Insulin Resistance | Reduced effectiveness of insulin, potentially requiring higher doses for adequate blood sugar control. |
| DKA (Diabetic Ketoacidosis) | Serious complication of high blood sugar, requiring immediate medical attention. |
| Hypokalemia | Low potassium levels, which can occur with some insulin regimens. |
Patient Concerns and Questions: Ask Dmine New Pump Really Old Insulin
Using pre-existing insulin with a new insulin pump raises legitimate concerns for patients. Understanding these anxieties and addressing them proactively is crucial for ensuring a smooth transition and positive treatment outcomes. This section delves into potential patient questions, concerns, and anxieties related to this practice, highlighting the importance of open communication between patients and healthcare providers.
Potential Patient Questions
Patients transitioning to a new insulin pump while continuing to use older insulin formulations may have a multitude of questions. These questions stem from a desire for clarity, safety, and efficacy in their treatment regimen. Concerns regarding dosage adjustments, compatibility issues, and potential complications are common.
- How will my current insulin dosage translate to the new pump’s delivery system?
- Are there any potential side effects or complications associated with using older insulin in a new pump?
- What specific instructions should I follow to ensure safe and effective insulin delivery with my new pump and existing insulin?
- What are the potential risks of not adjusting my insulin dosage appropriately when switching to a new pump?
- Will the new pump affect the absorption rate of my current insulin, requiring dosage modifications?
- How often should I monitor my blood glucose levels during the transition to the new pump?
Methods of Expressing Concerns
Patients may voice their concerns in various ways. Some might be direct and explicit, while others might express them subtly through hesitation or questions about specific aspects of the transition. Understanding the nuances of communication is essential for healthcare professionals to address these concerns effectively.
I’ve been researching my new insulin pump, and it’s surprisingly challenging to find information about compatibility with really old pumps. It got me thinking about how obesity can narrow airways, leading to asthma, and how that could affect managing my diabetes. Understanding the potential link between weight and respiratory issues is crucial when considering the long-term implications of my new insulin pump.
Hopefully, the information on obesity narrows airway leads to asthma will help me connect those dots and find a more suitable solution for my insulin pump needs.
- Direct questioning about dosage adjustments and potential risks.
- Hesitation or reluctance to fully embrace the change.
- Expressing anxieties about the unknown through indirect questions.
- Displaying uncertainty or fear during discussions about the procedure.
- Seeking reassurance and clarification about the process.
Anxieties Associated with the Combination
Patients often experience a range of anxieties when faced with the combination of older insulin and a new pump. These anxieties can stem from concerns about efficacy, safety, and the unknown. Addressing these anxieties through open communication and clear explanations can foster trust and confidence.
- Fear of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia due to dosage discrepancies.
- Uncertainty about the pump’s ability to accurately deliver the pre-existing insulin.
- Concern about potential complications arising from incompatibility of the insulin and the pump.
- Worry about the accuracy of blood glucose monitoring and adjustment in the transition phase.
Significance of Addressing Concerns
Addressing patient concerns proactively is vital for successful management of diabetes. Open communication between patients and healthcare professionals fosters a collaborative approach to treatment. This approach leads to improved patient outcomes and satisfaction.
- Improved patient adherence to the treatment plan.
- Reduced risk of complications related to improper insulin use.
- Increased patient confidence and trust in the healthcare team.
- Enhanced understanding of the new insulin pump system and its potential effects on the patient’s body.
Summary Table of Patient Questions
| Category of Question | Example Questions |
|---|---|
| Dosage Adjustments | How will my current insulin dosage translate to the new pump? |
| Potential Complications | Are there any potential side effects or complications associated with using older insulin in a new pump? |
| Safety and Efficacy | What specific instructions should I follow to ensure safe and effective insulin delivery? |
| Transition Concerns | Will the new pump affect the absorption rate of my current insulin, requiring dosage modifications? |
Medical Advice and Recommendations
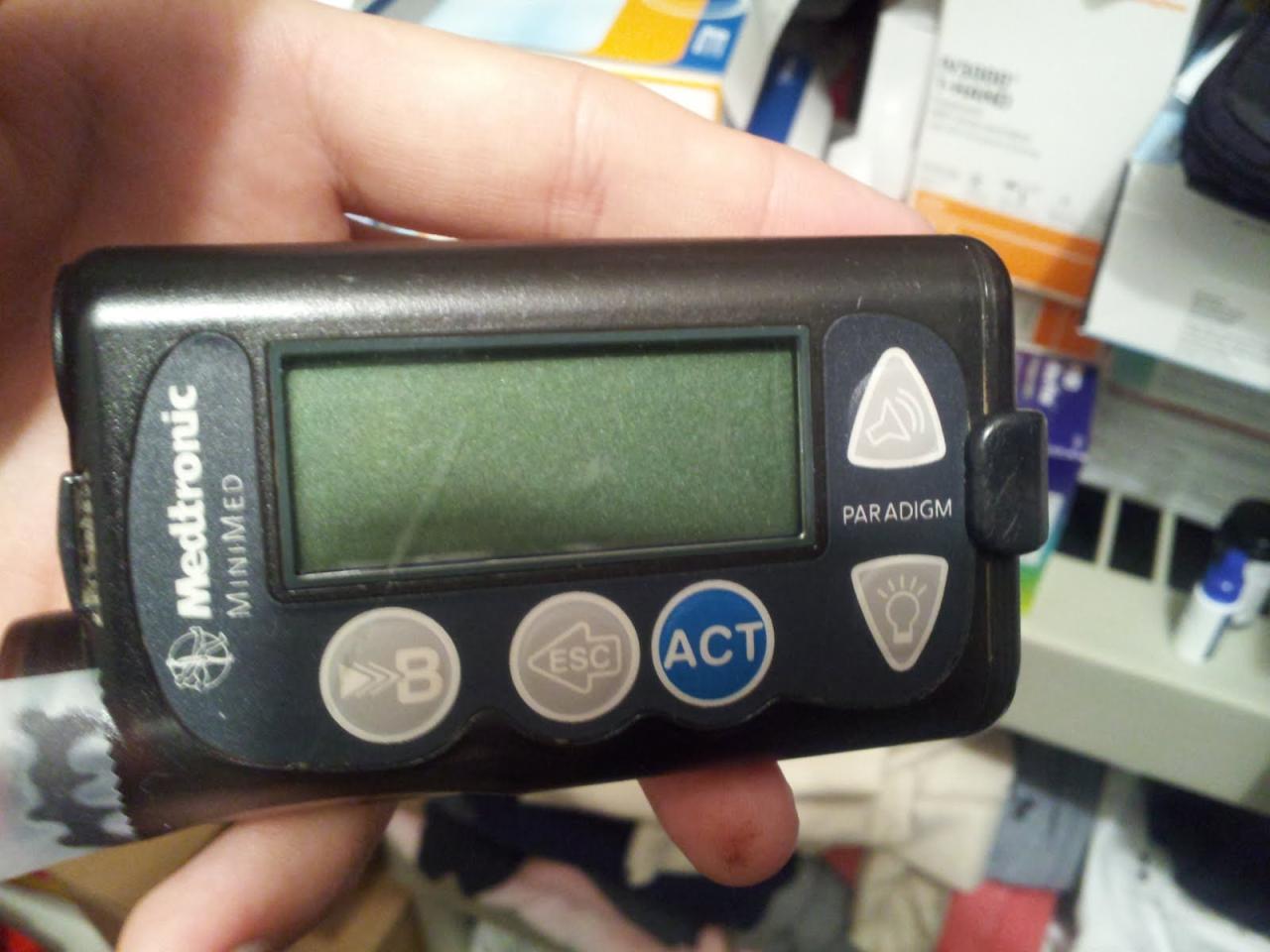
Navigating a change in insulin regimens, especially when switching to a new insulin pump with pre-existing insulin, requires careful planning and professional guidance. This crucial transition necessitates a proactive approach to ensure smooth management of your diabetes and prevent complications. A doctor or certified diabetes educator is indispensable throughout this process.
Importance of Professional Consultation
Changing insulin regimens, even seemingly minor adjustments, should always be overseen by a healthcare professional. A doctor or diabetes educator can assess your individual needs, evaluate the compatibility of the new pump with your existing insulin, and tailor a safe transition plan. They can also address any concerns you may have. Ignoring professional guidance can lead to significant health risks.
Safe Transition Steps
A safe transition involves a gradual adjustment of insulin doses. Sudden changes can cause unpredictable blood sugar fluctuations. This careful approach minimizes the risk of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
- Consult your doctor or diabetes educator for a personalized transition plan.
- Follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer of the new insulin pump meticulously.
- Maintain meticulous blood glucose monitoring records, documenting both basal and bolus insulin doses.
- Monitor for any unusual blood glucose fluctuations or symptoms during the transition period.
Adjusting Insulin Doses
Adjusting insulin doses during the transition period is a critical step. A healthcare professional can provide specific instructions.
- A doctor or diabetes educator can prescribe a specific schedule for reducing the dose of the previously used insulin while gradually increasing the dose of insulin used with the new pump.
- Careful monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential. A decrease in insulin dose might result in a need to increase the insulin dose with the new pump to maintain blood glucose levels within the target range.
- The dosage adjustments will be specific to the individual, based on their individual response to the new pump and the insulin it uses.
Blood Glucose Monitoring During Transition
Maintaining vigilant blood glucose monitoring is paramount during the transition to a new insulin pump. It provides real-time feedback on the effectiveness of the new regimen.
- Frequent blood glucose checks are vital to track how your body responds to the changes in insulin.
- Record your readings, noting the time of the measurement, your meal intake, and any physical activity.
- Pay close attention to trends in your blood glucose readings and any unusual fluctuations.
Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are crucial throughout the transition. This ensures that the transition is progressing smoothly and that any adjustments are necessary.
- Regular check-ups allow for evaluation of blood glucose control and any potential complications.
- They offer a platform to discuss any concerns or challenges you are facing during the transition.
- Regular monitoring helps in preventing long-term health issues.
Recommended Steps for a Safe Insulin Transition
This table Artikels a suggested approach for a safe insulin transition. Remember to always consult with your healthcare provider before making any changes.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Consult your doctor or diabetes educator for a personalized transition plan. |
| 2 | Follow manufacturer instructions for the new insulin pump. |
| 3 | Maintain meticulous blood glucose monitoring records. |
| 4 | Monitor for unusual blood glucose fluctuations. |
| 5 | Adjust insulin doses gradually under the guidance of your healthcare provider. |
| 6 | Attend regular check-ups with your doctor. |
Troubleshooting and Solutions
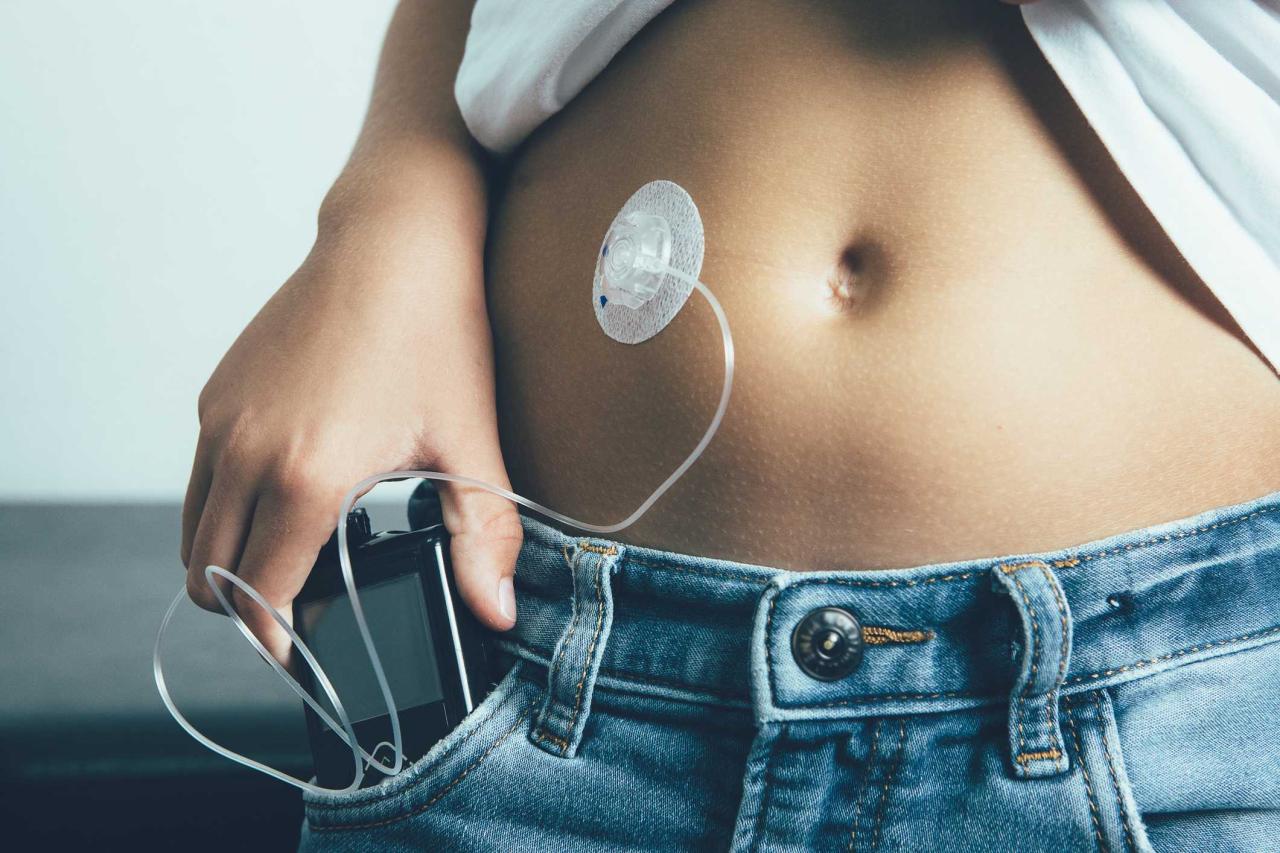
Transitioning to a new insulin pump, especially when using previously prepared insulin, can sometimes present unexpected challenges. Understanding potential issues and having a proactive approach to troubleshooting is crucial for maintaining optimal blood glucose control. This section Artikels common problems and provides practical solutions to ensure a smooth transition.Troubleshooting during this transition requires a methodical approach, focusing on identifying the root cause of any discrepancies in glucose levels.
By carefully analyzing pump settings, insulin delivery, and the interaction with older insulin, we can effectively resolve issues and maintain stable blood sugar control.
Common Insulin Pump Issues
A new insulin pump often requires adjustments to settings and routines. It’s important to carefully monitor your blood glucose levels during this adjustment period. This includes checking your blood sugar more frequently than usual.
Insulin Delivery Issues
Potential problems with insulin delivery include incorrect dosage calculations, malfunctioning pumps, or interactions between the new pump and older insulin. These issues can be resolved through a systematic approach to troubleshooting.
Potential Problems with Pump Settings
Improper pump settings can lead to inaccurate insulin delivery. This includes incorrect basal rates, bolus calculations, or issues with the pump’s calibration.
Examples of Issues with Older Insulin and New Pumps
One common example involves using older insulin vials that have been stored improperly. This can lead to variations in insulin potency and result in unexpected blood sugar fluctuations. Another scenario is when the older insulin has a different concentration than what the pump is calibrated for. This miscalibration can lead to inaccurate dosages.
Troubleshooting Table, Ask dmine new pump really old insulin
| Insulin Pump Issue | Potential Cause | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Inaccurate Dosage Delivery | Incorrect pump settings, insulin degradation, or pump malfunction | Verify pump settings, check insulin expiration date and storage conditions, perform a calibration check as per the pump manufacturer’s instructions. If the issue persists, contact the manufacturer or your healthcare provider. |
| Blood Glucose Fluctuations | Mismatched insulin and pump settings, incorrect bolus calculations, or underlying medical conditions | Adjust pump settings based on blood glucose readings. Check bolus calculations for accuracy. Monitor blood glucose levels more frequently. Consult with your healthcare provider if fluctuations persist. |
| Pump Malfunction | Technical problem with the pump, such as a software glitch or hardware failure. | Check the pump’s error codes. Consult the pump’s user manual or contact the manufacturer for troubleshooting. If the issue persists, replace the pump as directed by your healthcare provider. |
| Unstable Blood Sugar After Bolus | Incorrect bolus calculation, timing issue with bolus delivery, or poor carb counting | Review the bolus calculation. Adjust the timing of the bolus. Improve carb counting accuracy. Consult with your healthcare provider. |
Illustrative Scenarios
Navigating the transition to a new insulin pump while continuing to use older insulin can be tricky. This section presents various scenarios to illustrate the process, highlighting potential challenges and successful strategies. Understanding these situations can empower patients and healthcare providers to work together for a smooth and safe transition.The process of switching insulin delivery methods, especially when maintaining the use of older insulin types, requires careful planning and monitoring.
Success hinges on a patient’s ability to closely track blood glucose levels and adjust the insulin regimen accordingly, all under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional.
Patient Transitioning to a New Pump While Using Older Insulin
A patient, Sarah, is transitioning from multiple daily injections to an insulin pump. She continues using her existing vial of NPH insulin for basal coverage. Her healthcare provider carefully adjusts the basal rate on the pump to mimic the action of her NPH insulin. Regular blood glucose monitoring is crucial to identify any discrepancies and make necessary adjustments to both the pump settings and the NPH insulin dosage.
Successful Transition with Provider Support
Another patient, David, successfully transitioned to a new insulin pump while using a pre-mixed insulin. He worked closely with his endocrinologist, meticulously tracking his blood glucose levels and adjusting his insulin regimen based on the results. His healthcare provider offered valuable guidance on pump settings and insulin dose adjustments, ensuring a smooth transition. Regular check-ups were crucial for identifying and resolving any problems early on.
Scenario with Complications and Seeking Medical Advice
Emily, after transitioning to a new insulin pump, noticed an increasing trend in high blood sugar levels. She immediately contacted her endocrinologist. Her healthcare provider helped her adjust the pump settings and medication dosage. She also highlighted the importance of accurately measuring insulin dosages and maintaining proper injection techniques to minimize potential issues.
Healthcare Provider’s Role in Guiding Patients
A healthcare provider plays a critical role in guiding patients through the transition. This involves:
- Thorough assessment of the patient’s current insulin regimen, including dosage, type, and timing.
- Careful adjustment of pump settings to mimic the action of older insulin.
- Education on proper pump use, including troubleshooting common problems.
- Emphasizing the importance of consistent blood glucose monitoring and the significance of reporting any unusual readings.
- Regular follow-up appointments to monitor progress and address any emerging concerns.
Importance of Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
Maintaining consistent blood glucose monitoring is essential during this transition. Variations in blood glucose levels can be attributed to several factors, including changes in diet, exercise, stress, and underlying medical conditions. Frequent monitoring allows for timely adjustments in insulin doses, ensuring stable blood glucose levels and preventing complications.Regular monitoring helps identify patterns and trends in blood glucose levels.
This data is crucial for making adjustments to insulin regimens and preventing complications.
Conclusive Thoughts
Ultimately, transitioning to a new insulin pump while using older insulin requires careful consideration and professional guidance. This comprehensive guide offers a thorough understanding of the process, emphasizing the importance of consulting healthcare professionals and diligently monitoring blood glucose levels throughout the transition. Remember, your health is paramount, and proactive communication with your medical team is essential.