Boost your fertility give up fast food. It might seem counterintuitive, but ditching those greasy burgers and sugary fries could be a game-changer for your reproductive health. A diet packed with processed foods and empty calories can wreak havoc on your body’s delicate hormonal balance, making it harder to conceive. This article delves into the surprising link between fast food and fertility, exploring the nutritional needs for optimal reproductive health, and offering practical strategies to swap those unhealthy habits for nourishing alternatives.
We’ll explore the impact of fast food on fertility, examining the specific ways processed ingredients, high sugar, and unhealthy fats can affect your body’s ability to conceive. We’ll also offer a sample meal plan to help you transition to a fertility-boosting diet, complete with delicious, healthy recipes to replace your favorite fast food options.
Understanding the Link Between Diet and Fertility: Boost Your Fertility Give Up Fast Food
A healthy diet is fundamental to overall well-being, and its importance extends significantly to reproductive health. Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in supporting optimal hormone function, ensuring the development of healthy eggs and sperm, and fostering a supportive environment for conception and pregnancy. This understanding is crucial for both men and women striving to conceive. This article delves into the intricate connection between diet and fertility, exploring how specific nutrients, inflammation, and balanced nutrition contribute to reproductive success.The relationship between diet and fertility is multifaceted.
A well-balanced diet, rich in essential nutrients, provides the building blocks for healthy reproductive tissues and processes. Conversely, nutritional deficiencies or imbalances can negatively impact fertility by disrupting hormone production, reducing egg and sperm quality, and increasing inflammation in the reproductive system. Understanding these interactions is key to optimizing reproductive health.
Impact of Diet on Fertility in Men and Women
Diet profoundly impacts both male and female fertility. In women, adequate nutrition supports the development and release of healthy eggs, ensuring proper hormonal function throughout the menstrual cycle. In men, a healthy diet supports sperm production, motility, and morphology. Nutritional deficiencies can severely impair these processes, hindering conception.
Nutritional Deficiencies Affecting Reproductive Health
Nutritional deficiencies can negatively impact reproductive health in various ways. Deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals can lead to hormonal imbalances, impacting ovulation in women and sperm production in men. For example, iron deficiency can lead to anemia, affecting energy levels and potentially impacting both egg and sperm development. Similarly, deficiencies in vitamin D, zinc, and other key nutrients can disrupt hormonal balance and reduce the quality of reproductive cells.
These deficiencies can manifest in decreased fertility rates or difficulties conceiving.
Cutting back on fast food is a great way to boost your fertility, and it’s a healthy change overall. Speaking of healthy habits, did you check out some of the best videos of the year? best videos of the year really showcased some inspiring documentaries on holistic health, and that, in turn, got me thinking about how crucial a balanced diet is to overall well-being and fertility.
So, let’s ditch the greasy burgers and embrace a healthier lifestyle for a better chance at parenthood!
Nutrients Crucial for Fertility
Several nutrients are particularly vital for fertility. These include folic acid, crucial for preventing neural tube defects in developing fetuses and also promoting cell division. Vitamin D is essential for hormone regulation and immune function, both critical for reproductive health. Iron is vital for carrying oxygen throughout the body, including to the reproductive organs, and thus critical for the development of healthy eggs and sperm.
Zinc is essential for the development of healthy sperm and is also critical for immune function, which can affect the success of the reproductive process.
Inflammation and Fertility
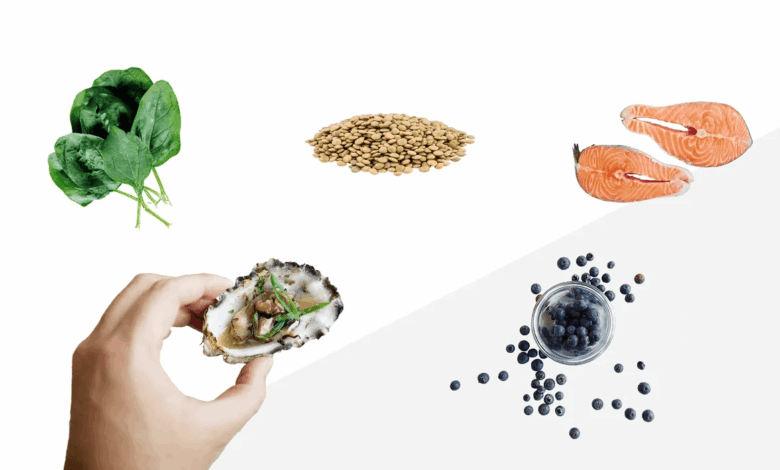
Chronic inflammation can significantly reduce fertility in both men and women. A diet rich in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can contribute to inflammation. Conversely, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can help reduce inflammation. Anti-inflammatory foods, such as berries, leafy greens, and fatty fish, are essential in managing inflammation and optimizing fertility.
Nutritional Needs of Men and Women
While both men and women require a balanced diet for optimal fertility, some nutritional needs differ. Women require sufficient iron for maintaining healthy blood levels and supporting egg development. Men require adequate zinc for sperm production. However, both genders need a comprehensive intake of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants to support overall reproductive health. Both genders need to be mindful of their dietary choices to maintain overall health and reproductive success.
Importance of a Balanced Diet for Overall Reproductive Health
A balanced diet that includes a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is essential for overall reproductive health. This approach ensures adequate intake of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants crucial for supporting healthy reproductive functions in both men and women. Furthermore, a balanced diet contributes to overall health, which is also a significant factor in achieving and maintaining reproductive success.
The Impact of Fast Food on Fertility
Fast food, while convenient, often comes at a cost, particularly when it comes to reproductive health. The processed nature and high calorie content of many fast food options can negatively affect fertility in various ways. Understanding these impacts can empower individuals to make healthier choices that support optimal reproductive function.Excessive consumption of fast food can negatively impact fertility due to the combination of unhealthy fats, high sugar content, and lack of essential nutrients.
This imbalance can disrupt hormonal regulation, contribute to weight gain, and ultimately affect the body’s ability to conceive. Choosing healthier alternatives and mindful portion control are crucial for maintaining reproductive well-being.
Harmful Components in Fast Food Affecting Fertility
Fast food often contains high levels of unhealthy fats, including saturated and trans fats. These fats can contribute to inflammation in the body, which may interfere with hormonal balance and overall reproductive health. The high sugar content in many fast food items can also disrupt insulin regulation, impacting ovulation and other aspects of fertility.
The Role of Processed Foods, High Sugar, and Trans Fats
Processed foods, a staple in many fast food restaurants, often contain refined carbohydrates and high fructose corn syrup. These ingredients can lead to blood sugar spikes and crashes, further disrupting hormonal balance. The presence of trans fats in some fast food items contributes to inflammation and interferes with the body’s ability to utilize essential nutrients, potentially impacting fertility.
A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and trans fats can increase the risk of insulin resistance and obesity, both known factors in reduced fertility.
Hormonal Imbalances Linked to Fast Food Consumption
The high fat, sugar, and processed food content of fast food can lead to hormonal imbalances. These imbalances can disrupt the delicate hormonal cycles necessary for ovulation and conception. High levels of insulin, caused by a diet rich in processed foods and sugars, can lead to the development of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a condition often associated with fertility issues.
Alternative Healthy Food Choices
Instead of relying on fast food, individuals can opt for a variety of nutritious and healthy alternatives. Fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains provide essential nutrients that support reproductive health. Examples include incorporating more fresh produce, lean meats, and whole-grain options into meals. These choices can help balance blood sugar levels, promote hormonal regulation, and provide essential vitamins and minerals.
Prioritizing a diet rich in antioxidants can also aid in combating inflammation.
Obesity and its Connection to Fertility Issues
Fast food consumption often leads to excess calorie intake and weight gain, increasing the risk of obesity. Obesity significantly impacts fertility. It disrupts hormonal balance, making it harder for the body to regulate ovulation and maintain a healthy reproductive environment. Studies have shown a strong correlation between obesity and reduced fertility rates. For instance, women with a body mass index (BMI) exceeding 30 may experience irregular periods and reduced chances of conception.
Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is essential for optimal reproductive health.
Strategies for Improving Fertility Through Dietary Changes

Nourishing your body with the right foods is crucial for overall health, and fertility is no exception. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can significantly impact reproductive health. This involves making conscious choices about what you eat and understanding how different foods affect your body’s ability to conceive. By replacing fast food with nutrient-rich alternatives and adopting mindful eating habits, you can support your fertility journey.A healthy diet plays a vital role in optimizing reproductive health.
Giving up fast food can seriously boost your fertility, just like the incredible journey of Randy Travis’s long road back to success demonstrates the power of perseverance. A healthy diet plays a crucial role in overall well-being, impacting everything from energy levels to reproductive health. Prioritizing nutritious foods and cutting out processed junk will significantly improve your chances of conceiving.
It’s a marathon, not a sprint, but the rewards are well worth the effort.
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats provides the necessary vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants to support hormonal balance and egg and sperm development. Reducing processed foods, including fast food, is equally important as these often contain high levels of unhealthy fats, sodium, and added sugars that can negatively impact fertility.
Sample Meal Plan for Fertility
This sample meal plan provides a framework for incorporating fertility-boosting foods into your daily routine. It emphasizes whole foods and nutrient density while minimizing processed ingredients. Adjust portion sizes to fit your individual needs and activity level.
- Breakfast (Example): Oatmeal with berries, nuts, and a sprinkle of chia seeds. This provides complex carbohydrates, antioxidants, and healthy fats, supporting energy levels and overall well-being.
- Lunch (Example): A large salad with grilled chicken or fish, mixed greens, and a light vinaigrette dressing. Include a variety of colorful vegetables to ensure a wide range of nutrients.
- Dinner (Example): Baked salmon with roasted vegetables (broccoli, carrots, sweet potatoes) and quinoa. This provides lean protein, essential vitamins, and minerals crucial for reproductive health.
- Snacks (Examples): Fruits like apples, bananas, or oranges; a handful of almonds or walnuts; Greek yogurt with a drizzle of honey. These offer quick energy boosts and essential nutrients.
Healthy Recipes Replacing Fast Food
Replacing fast food with homemade, healthy alternatives is essential for optimizing your diet for fertility. These recipes prioritize fresh ingredients and minimize processed foods.
- Instead of burgers, try grilled chicken or fish burgers on whole-wheat buns with plenty of fresh vegetables.
- Instead of fries, bake or air-fry sweet potato fries, or enjoy roasted vegetables like broccoli, carrots, or bell peppers.
- Instead of pizza, make homemade whole-wheat pizza with vegetables and lean protein.
- Instead of fried chicken, bake or air-fry chicken with herbs and spices.
Nutritional Comparison of Fast Food and Healthy Alternatives
This table compares the nutritional content of common fast food items with their healthier counterparts, highlighting the significant differences in calories, fat, sodium, and other essential nutrients.
| Fast Food Item | Healthy Alternative | Key Nutritional Differences |
|---|---|---|
| Burger with fries | Grilled chicken or fish burger with baked sweet potato fries | Lower fat, calories, and sodium; higher fiber and vitamins. |
| Pizza | Homemade whole-wheat pizza with vegetables | Reduced saturated fat and sodium; increased fiber and nutrients from vegetables. |
| Fried chicken | Baked or air-fried chicken with herbs and spices | Lower fat and calories; increased nutrients from fresh ingredients. |
| French fries | Roasted or baked vegetables | Lower fat and calories; higher fiber and vitamins. |
Importance of Portion Control and Mindful Eating
Portion control is essential for maintaining a healthy weight and managing calorie intake. Mindful eating involves paying attention to your body’s hunger and fullness cues, eating slowly, and savoring each bite. These practices can help prevent overeating and promote a healthier relationship with food.
Significance of Hydration and its Impact on Fertility
Adequate hydration is crucial for overall health and fertility. Water is essential for transporting nutrients, regulating body temperature, and supporting cellular function. Staying properly hydrated can improve blood flow and support the reproductive system.
Overcoming Fast Food Cravings
Developing healthy alternatives to fast food cravings is key to long-term dietary changes. Identify the triggers for your cravings and find healthy alternatives that satisfy those cravings. For example, if you crave the salty taste of fast food, try a homemade trail mix or a snack of roasted chickpeas.
Potential Benefits of Reducing Fast Food Intake

Giving up fast food isn’t just about losing weight; it’s about unlocking a cascade of positive changes for your overall well-being. By swapping sugary sodas and greasy burgers for nutritious meals, you’re paving the way for improved energy levels, a brighter mood, and a healthier relationship with your body. This shift can significantly impact your fertility journey, as a healthy body is better equipped to support a healthy pregnancy.
Positive Effects on Overall Health
Reducing fast food consumption can lead to a multitude of positive changes in your physical and mental health. Fast food often lacks essential nutrients, promoting deficiencies that can impact your overall well-being. A balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, provides the necessary vitamins, minerals, and fiber to support your body’s functions.
- Improved Nutrient Intake: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides a wider array of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, supporting overall health. For example, leafy greens are excellent sources of vitamins A, C, and K, while berries are packed with antioxidants. This contrasts sharply with fast food, which is often low in these crucial nutrients.
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: A diet rich in processed foods and fast food increases the risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers. By reducing intake of these foods, you lessen these risks and promote long-term health.
- Enhanced Digestive Health: Fast food often contains high levels of unhealthy fats and processed ingredients that can disrupt digestion. Switching to a diet rich in fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can improve digestion and prevent constipation.
Relationship Between Diet and Energy Levels/Mood
The foods we consume directly impact our energy levels and mood. A diet rich in processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats can lead to energy crashes and mood swings. Conversely, a balanced diet provides sustained energy and promotes emotional stability. A diet rich in complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats provides a steady release of energy, avoiding the highs and lows associated with simple sugars.
- Sustained Energy Levels: A diet rich in complex carbohydrates provides sustained energy throughout the day, reducing energy crashes and fatigue. This is in contrast to fast food, which often leads to spikes in blood sugar followed by dips.
- Improved Mood: Nutrients like vitamin D, magnesium, and omega-3 fatty acids play a vital role in maintaining a positive mood. A diet rich in these nutrients can contribute to a more stable and positive emotional state, whereas fast food can negatively impact mood regulation.
Weight Management and its Impact on Fertility
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for fertility. Obesity can negatively impact hormonal balance and ovulation, while being underweight can also disrupt these processes. A diet rich in nutrient-dense foods can help with weight management, while fast food often contributes to weight gain due to its high calorie and low nutrient content.
- Improved Hormonal Balance: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for hormone regulation. Excess weight can disrupt the delicate balance of hormones, including those involved in ovulation and menstruation. A balanced diet promotes healthy weight management, contributing to a better hormonal environment.
- Enhanced Ovarian Function: A healthy weight contributes to optimal ovarian function, which is essential for regular ovulation and fertility. Excess weight can negatively impact ovarian reserve and overall reproductive health.
Reduced Inflammation and Reproductive Health
Inflammation plays a significant role in reproductive health. A diet high in processed foods and fast food can contribute to chronic inflammation, which can negatively impact fertility. By reducing fast food consumption, you can help reduce inflammation and create a more favorable environment for conception.
- Lowering Inflammation Markers: A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation markers in the body. This is a significant contrast to fast food, which often contributes to inflammation.
- Improved Ovarian Health: Reducing inflammation can improve ovarian health and the overall health of the reproductive system. This can lead to better egg quality and a more favorable environment for fertilization.
Hormone Regulation and Fertility
Hormonal balance is crucial for fertility. A diet rich in processed foods and fast food can disrupt hormonal balance, affecting ovulation and menstrual cycles. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can support healthy hormone production and regulation.
- Supporting Healthy Hormone Production: Essential nutrients like zinc, vitamin D, and iron play a vital role in hormone production. A diet rich in these nutrients can support healthy hormone production, whereas fast food lacks these vital nutrients.
- Regulating Menstrual Cycles: A healthy diet supports regular menstrual cycles, which are essential for fertility. Fast food consumption can disrupt menstrual cycles, making it more challenging to conceive.
Short-Term and Long-Term Effects of a Fast-Food-Reduced Diet
The effects of reducing fast food intake are noticeable both in the short and long term. Short-term benefits include improved energy levels, better digestion, and a more positive mood. Long-term benefits include reduced risk of chronic diseases, better weight management, and improved reproductive health.
- Short-Term Effects: Immediate improvements include better energy levels, improved digestion, and a more positive mood. These effects are often noticeable within a few days or weeks of reducing fast food intake.
- Long-Term Effects: Over time, a fast-food-reduced diet contributes to better weight management, reduced risk of chronic diseases, and improved reproductive health. These benefits accumulate over months and years.
Addressing Specific Dietary Concerns for Fertility
Nourishing your body with the right nutrients is crucial for optimal reproductive health. A balanced diet rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and other compounds plays a vital role in supporting healthy egg and sperm production, as well as the overall health of the reproductive system. Understanding the specific dietary needs for fertility empowers individuals to make informed choices that contribute to their reproductive well-being.
Cutting back on fast food can seriously boost your fertility, and that’s something worth exploring. While unrelated health conditions like Epstein-Barr virus and its potential link to multiple sclerosis symptoms ( epstein barr multiple sclerosis symptoms ) can complicate things, a healthy diet is still crucial for overall well-being, and that includes optimizing fertility. So, ditch the greasy burgers and pizza for a healthier, more fertile you!
The Role of Protein in Reproductive Health
Protein is an essential building block for tissues, including those in the reproductive system. Adequate protein intake is vital for the development and maintenance of healthy eggs and sperm. It also plays a role in hormone production, which is critical for regulating the menstrual cycle and ovulation in women, and for maintaining healthy testosterone levels in men. A deficiency in protein can negatively impact fertility by hindering the development and function of reproductive organs.
Include lean sources of protein in your diet, such as fish, poultry, beans, lentils, and tofu.
The Importance of Fiber for Digestive Health and Fertility
Fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy digestion. A healthy digestive system is important for overall well-being, and it is strongly linked to fertility. Fiber promotes regular bowel movements, which can contribute to a healthy weight, and it also helps regulate blood sugar levels. Irregular bowel movements and digestive issues can sometimes be associated with fertility problems, so ensuring sufficient fiber intake can contribute to better overall reproductive health.
Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet to increase your fiber intake.
The Benefits of Antioxidants and Their Role in Protecting Reproductive Cells
Antioxidants are compounds that help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage reproductive cells, potentially impacting fertility. Consuming a diet rich in antioxidants can help combat this damage and support healthy reproductive function. Fruits and vegetables, especially those with vibrant colors, are excellent sources of antioxidants. Examples include berries, leafy greens, and citrus fruits.
Healthy Fats and Fertility
Healthy fats are essential for hormone production, cell growth, and overall reproductive health. These fats are crucial for the development and function of reproductive organs and for the production of hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle and sperm production. Examples of healthy fats include avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
Avoiding Excessive Caffeine and Alcohol Intake, Boost your fertility give up fast food
Excessive caffeine and alcohol intake can negatively impact fertility. Caffeine can interfere with hormone regulation, while alcohol can damage reproductive cells. Limiting or avoiding these substances can significantly improve your chances of conception.
Strategies for Addressing Potential Dietary Deficiencies
Identifying and addressing potential dietary deficiencies is crucial for optimal fertility. A balanced diet rich in a variety of nutrient-dense foods is generally sufficient to meet the majority of dietary needs. However, certain individuals may benefit from supplementation under the guidance of a healthcare professional. If you suspect a deficiency, consult a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to discuss appropriate dietary changes or supplementation.
They can help you create a personalized plan to address any specific needs. A blood test can reveal specific nutrient deficiencies that may be impacting fertility.
Practical Advice and Tips
Taking control of your diet is a powerful step towards optimizing your fertility. This involves not just avoiding fast food but also understanding how to incorporate nutritious alternatives into your daily routine. Making gradual, sustainable changes is key to long-term success and preventing feelings of deprivation. Remember, consistency is crucial for achieving positive results.
Key Takeaways from Diet and Fertility Discussion
Understanding the connection between diet and fertility involves recognizing the impact of various food choices on reproductive health. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is crucial for optimal reproductive function. Limiting processed foods, including fast food, and focusing on whole, unprocessed options is essential.
| Category | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Fast Food Impact | High in unhealthy fats, sodium, and processed ingredients, fast food can negatively affect fertility. |
| Nutrient-Rich Foods | Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats for optimal reproductive health. |
| Portion Control | Maintaining a healthy weight through mindful portion control is beneficial for fertility. |
| Hydration | Sufficient water intake supports overall health and contributes to better fertility outcomes. |
Practical Steps for Implementing Dietary Changes
Making sustainable changes to your diet requires a thoughtful approach. Start by gradually reducing your fast food intake, replacing those meals with healthier options.
- Gradual Reduction of Fast Food: Instead of completely eliminating fast food overnight, aim to reduce your consumption by one meal per week, then two, and so on. For example, one week, skip lunch; the next week, skip lunch and dinner. This approach is much more sustainable than a drastic change, and it allows your body to adjust to healthier alternatives.
- Incorporating Healthy Alternatives: Explore recipes using fresh ingredients and whole foods. Prepare meals at home to have better control over the ingredients. For example, instead of ordering a burger, try a grilled chicken salad with plenty of vegetables.
- Mindful Meal Planning: Plan your meals and snacks in advance. This helps you make conscious choices and avoid impulsive fast food purchases.
Examples of Gradually Reducing Fast Food Consumption
Transitioning away from fast food requires a gradual approach to ensure success.
- Replace one fast food meal per week with a home-cooked meal. For example, if you usually eat fast food for lunch on Wednesdays, switch to a homemade salad or soup that week. Then, gradually increase the frequency of home-cooked meals.
- Introduce healthy snacks as alternatives. If you crave a salty snack, choose air-popped popcorn, nuts, or a piece of fruit instead of a fast food snack.
- Choose healthier fast food options when possible. For example, opting for a grilled chicken sandwich instead of a burger, or a salad instead of fries. However, remember that even “healthier” fast food options are still not as nutritious as home-cooked meals.
Incorporating Healthy Alternatives into Daily Meals
Substituting fast food with nutritious alternatives is crucial for fertility.
- Breakfast Alternatives: Swap sugary cereals for oatmeal with fruit and nuts. Replace sugary pastries with whole-grain toast topped with avocado or eggs.
- Lunch Alternatives: Swap fried foods for salads, sandwiches with lean protein and vegetables, or lentil soup.
- Dinner Alternatives: Choose lean proteins like grilled fish or chicken with plenty of steamed or roasted vegetables. Replace fried rice with brown rice stir-fries.
Resources for Further Learning
Numerous resources provide valuable information on nutrition and fertility. Consult credible sources for accurate and up-to-date information.
- Registered Dietitians: Consult with a registered dietitian specializing in women’s health or fertility for personalized dietary advice.
- Reputable Nutrition Websites: Look for websites from reputable organizations like the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics or the Mayo Clinic.
- Books on Nutrition and Fertility: Explore books written by experts in the field for comprehensive insights into the relationship between diet and fertility.
Reliable Sources for Accurate Information
To ensure accurate information, verify the credentials of the author or organization.
- Medical Professionals: Seek guidance from medical doctors or certified nutritionists for personalized recommendations.
- Peer-Reviewed Studies: Look for research articles published in peer-reviewed scientific journals to understand the evidence base.
- Government Health Agencies: Refer to information from reputable government health organizations for comprehensive and verified information.
Summary
Ultimately, boosting your fertility involves a conscious shift towards a healthier lifestyle. By understanding the crucial role of nutrition and making informed choices about your diet, you can significantly improve your chances of conceiving. Giving up fast food is just one step in a journey toward optimal reproductive health, but a crucial one. So, ditch the drive-thru and embrace a diet that supports your body’s natural ability to conceive.
Remember, consistency is key, and you’ve got this!