Can ecstasy help with PTSD sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into the potential benefits and risks of MDMA-assisted therapy for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. This exploration delves into the science behind the treatment, examining potential mechanisms of action, research findings, ethical considerations, and comparisons with other established PTSD therapies. We’ll also hear from individuals who’ve experienced this treatment, and consider the future of this controversial approach to mental health.
The potential of MDMA (ecstasy) to treat PTSD is a complex issue, sparking both excitement and apprehension. While promising research suggests a possible path toward effective treatment, potential risks and ethical considerations must be carefully weighed. This comprehensive look at the subject will provide a nuanced understanding of the complexities involved.
Potential Benefits of Ecstasy for PTSD
The potential of MDMA (ecstasy) as a therapeutic agent for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) has sparked significant interest in the mental health community. While still in the research phase, preliminary findings suggest a unique pathway toward alleviating the debilitating symptoms of PTSD. This exploration delves into the purported benefits, highlighting the potential mechanisms and comparing them to existing treatments.The purported benefits of MDMA in treating PTSD stem from its unique effects on the brain, which may facilitate emotional processing and memory restructuring.
While not a cure-all, it holds promise for those struggling with PTSD who have not found relief through traditional methods. Important ethical considerations, including careful safety protocols and rigorous research, are paramount in the development of any new treatment.
Potential Benefits in Treating PTSD
Early research indicates that MDMA may facilitate a sense of safety and trust within the therapeutic setting, allowing individuals to confront traumatic memories in a controlled environment. This heightened emotional connection and openness can lead to a more profound processing of distressing memories.
Psychological Mechanisms of MDMA in PTSD Treatment
MDMA’s impact on the brain may involve multiple interconnected mechanisms. One potential mechanism involves modulating the release of neurochemicals, such as oxytocin and serotonin. These neurochemicals are known to be involved in social bonding, emotional regulation, and memory consolidation. This alteration in neurochemistry may contribute to a reduction in fear and anxiety associated with PTSD. The enhanced emotional processing during MDMA-assisted therapy could allow for the integration of traumatic memories, reducing their impact on daily life.
Impact on Memory Processing
MDMA may impact memory processing in ways that could be beneficial for PTSD. The drug may facilitate the creation of new, less emotionally charged memories alongside the retrieval of existing traumatic memories. This dual impact may aid in the re-evaluation and re-integration of traumatic experiences into a broader context. By reducing the emotional intensity surrounding traumatic memories, MDMA might allow individuals to develop new, healthier narratives around these experiences.
Impact on Emotional Regulation
MDMA’s potential effect on emotional regulation is another promising area of investigation. It might facilitate a shift towards more adaptive coping mechanisms and emotional responses, enabling individuals to manage difficult emotions more effectively. This could lead to improved emotional resilience and a reduction in the avoidance behaviors often associated with PTSD.
Comparison with Other PTSD Treatments
| Treatment | Potential Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| MDMA-Assisted Therapy | Potentially facilitates emotional processing, enhances trust, and may lead to reduced avoidance and emotional reactivity. | Requires careful monitoring, potential side effects, and further research to establish long-term efficacy and safety. |
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | Effective in modifying negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with PTSD. | May not be as effective in addressing the intense emotional components of trauma. |
| Exposure Therapy | Helps individuals confront and process traumatic memories. | Can be highly distressing and may not be suitable for all individuals. |
| Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) | May help reduce the emotional distress associated with traumatic memories. | Effectiveness varies among individuals, and the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood. |
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Ecstasy Use
While MDMA, or ecstasy, might offer some potential benefits for individuals with PTSD, it’s crucial to acknowledge the significant risks associated with its use. These risks are particularly pronounced for those grappling with PTSD, as the drug’s effects can interact with existing vulnerabilities and potentially exacerbate mental health issues. Understanding these risks is essential for informed decision-making and responsible exploration of potential treatment options.Ecstasy’s impact on the body and mind can be complex and unpredictable, leading to both immediate and long-term consequences.
This includes potential physical harm, psychological instability, and a heightened risk of relapse for those struggling with PTSD. It’s important to be aware of the spectrum of potential issues to avoid any misunderstandings about the drug’s therapeutic use.
Physical Risks Associated with Ecstasy Use
Ecstasy use can lead to a range of physical complications, particularly when combined with the stress and physiological alterations already present in PTSD. These include dehydration, overheating, and an increased risk of cardiovascular issues, including irregular heartbeat and dangerously high blood pressure. The body’s natural regulatory systems can be severely disrupted, and the individual may not be able to adequately regulate temperature or fluid balance.
Furthermore, prolonged ecstasy use can damage the body’s ability to regulate neurochemicals, leading to chronic health issues.
Psychological Risks of MDMA Use in PTSD
The psychological risks of MDMA use, particularly for individuals with PTSD, are significant and multifaceted. A heightened vulnerability to relapse is a critical concern. The drug can temporarily mask or alleviate PTSD symptoms, leading to a false sense of recovery, and subsequently creating a cycle of relapse when the drug’s effects wear off. This can trigger a cascade of negative emotions, re-traumatization, and an intensification of negative thoughts and memories.
The potential for exacerbation of existing PTSD symptoms, such as flashbacks, nightmares, and intrusive thoughts, is also a concern. MDMA’s influence on emotional regulation and self-awareness can disrupt coping mechanisms, further complicating recovery.
Long-Term Effects of Ecstasy Use on Mental Health (PTSD Focus)
Prolonged ecstasy use can have lasting negative impacts on mental health, potentially compounding existing PTSD symptoms. Damage to the brain’s neurochemical pathways, responsible for mood regulation and memory processing, is a concern. This disruption can lead to long-term difficulties with emotional regulation, cognitive function, and social interaction. Individuals with PTSD might experience a heightened sensitivity to stress and emotional triggers, further jeopardizing their recovery.
Furthermore, the drug’s impact on serotonin levels can significantly impact mood, potentially contributing to depressive episodes or anxiety disorders. In severe cases, chronic use can lead to severe mental health issues.
Potential Side Effects of Ecstasy Use (Table)
| Side Effect Category | Short-Term Effects | Long-Term Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Physical | Dehydration, overheating, increased heart rate, high blood pressure, teeth grinding, nausea, jaw clenching, muscle cramps, blurred vision, confusion | Cardiovascular damage, kidney damage, liver damage, long-term mood disturbances, cognitive impairment, and permanent neurological damage |
| Psychological | Anxiety, paranoia, depression, flashbacks, nightmares, confusion, distorted perceptions, and hallucinations | Increased risk of developing mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, and psychosis. Difficulty with emotional regulation, memory, and decision-making. Increased risk of substance use disorders. |
Ethical Considerations and Regulatory Issues: Can Ecstasy Help With Ptsd
The potential of MDMA-assisted therapy for PTSD presents exciting possibilities, but it also raises complex ethical and regulatory questions. Balancing the potential benefits with the inherent risks requires careful consideration of informed consent, potential biases, and the necessary safeguards to protect vulnerable populations. The regulatory framework surrounding MDMA-assisted therapy is still evolving, demanding careful navigation of existing laws and the development of new guidelines to ensure responsible and ethical implementation.The ethical implications of using a psychoactive substance like MDMA for therapeutic purposes demand meticulous attention to patient well-being and autonomy.
A crucial aspect of any MDMA-assisted therapy program is the provision of comprehensive information to potential participants. This information must include not only the potential benefits but also the risks and potential side effects. A thorough understanding of the procedure, its limitations, and alternative treatment options is paramount to ensuring truly informed consent.
Informed Consent and Potential Biases
Ensuring truly informed consent requires a robust process that goes beyond simply presenting the risks and benefits. Clinicians must meticulously assess the patient’s understanding of the treatment, considering their individual circumstances and potential vulnerabilities. This includes addressing any pre-existing mental health conditions and the potential for substance use disorders. The potential for implicit bias in patient selection must also be acknowledged.
For instance, biases based on socioeconomic status or cultural background could inadvertently influence treatment access.
Current Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape surrounding MDMA-assisted therapy is currently in a state of flux. While some jurisdictions are exploring clinical trials and pilot programs, the overall regulatory framework remains fragmented. There’s a clear need for standardized protocols and guidelines that can be adopted across different regions to ensure consistency and quality control.
Regulatory Hurdles and Precautions
Implementing MDMA-assisted therapy in clinical settings requires careful consideration of regulatory hurdles. The rigorous standards for clinical trials, the need for strict adherence to safety protocols, and the development of trained personnel all present challenges. Furthermore, maintaining the integrity of the research process and ensuring that data is collected and analyzed ethically are crucial considerations. A crucial aspect of the process is the development of rigorous safety protocols, incorporating regular monitoring of participants throughout the treatment process, and the availability of appropriate support systems to address potential adverse reactions.
Existing and Potential Regulations and Guidelines
The development of specific guidelines and regulations for MDMA-assisted therapy is ongoing. While the FDA has granted Breakthrough Therapy designation for MDMA-assisted therapy for PTSD, specific protocols and regulatory frameworks for clinical practice remain in development. Further research and careful consideration of the potential risks and benefits are critical in developing effective and ethical regulatory frameworks. These guidelines should address crucial elements like dosage, administration protocols, and the ongoing monitoring of participants.
Comparison with Other Treatments for PTSD
MDMA-assisted therapy is a relatively new approach to treating PTSD, and its effectiveness needs to be carefully considered alongside existing evidence-based treatments. Understanding the strengths and limitations of various PTSD therapies allows for a more informed discussion about MDMA’s potential role in the treatment landscape. This comparison considers the efficacy, safety, and accessibility of different approaches.Various evidence-based treatments are available for PTSD, each with its own mechanisms of action and potential benefits and drawbacks.
These treatments aim to address the symptoms, reduce the emotional distress, and promote healing associated with the trauma.
Different PTSD Treatments
Various therapeutic approaches are used to address PTSD. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) focuses on identifying and modifying negative thought patterns and behaviors related to the trauma. Exposure therapy gradually exposes individuals to trauma-related stimuli, helping them process and adapt to these experiences. Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) uses rhythmic eye movements or other bilateral stimulation to facilitate the processing of traumatic memories.
Medication, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and other antidepressants, plays a role in managing the symptoms of PTSD by regulating neurochemical imbalances. Group therapy provides a supportive environment for individuals to connect with others experiencing similar challenges. These different approaches target different aspects of PTSD, often requiring a combination of methods for optimal outcomes.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a cornerstone of PTSD treatment. It helps patients identify and challenge negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to their PTSD symptoms. A strength of CBT is its focus on empowering patients to develop coping mechanisms and problem-solving skills. Limitations include its potential to be less effective for individuals with severe trauma or co-occurring disorders.
The effectiveness of CBT depends on the patient’s engagement and motivation.
Exposure Therapy
Exposure therapy gradually exposes individuals to trauma-related stimuli, either in imagination or in real-life situations. This approach helps desensitize the patient to these triggers and reduce the intensity of their emotional responses. A significant strength is its focus on confronting the trauma directly, allowing patients to process and integrate these experiences. Potential limitations include the intensity of the exposure and the potential for triggering overwhelming emotional responses.
Successful implementation requires careful monitoring and support.
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR)
EMDR uses rhythmic eye movements or other bilateral stimulation to facilitate the processing of traumatic memories. A strength of EMDR is its ability to potentially address trauma-related memories and reduce their impact. Potential limitations include the need for specific training and the potential for triggering intense emotions during the process. EMDR may not be suitable for everyone.
While some people explore using ecstasy to potentially manage PTSD symptoms, the research on its effectiveness is still pretty limited. Finding ways to improve adherence to diabetes devices is a real challenge, and innovative solutions like leading skin wipes to make diabetes devices stick are crucial for better patient outcomes. Ultimately, though, ecstasy’s role in treating PTSD remains a complex and largely unproven area of study.
Medication
Medication plays a crucial role in managing PTSD symptoms. Antidepressants, such as SSRIs, are commonly prescribed to regulate neurochemical imbalances that contribute to the symptoms. A strength is the potential to reduce the severity of symptoms and improve overall functioning. Potential limitations include the possibility of side effects and the need for ongoing monitoring. The effectiveness of medication varies among individuals.
While some explore the potential of ecstasy for PTSD treatment, it’s crucial to be cautious. The potential for harm is significant, and research is still needed. Interestingly, a recent study highlights the alarming trend of e-cigarette use among teens, with mint being the most popular flavor, as reported in this article. Ultimately, responsible choices and careful consideration are essential when exploring any potential treatment options for PTSD.
Group Therapy
Group therapy provides a supportive environment for individuals to connect with others who have experienced similar challenges. A strength is the opportunity to gain insight from others and develop a sense of community. Limitations include the potential for triggering discussions or the need for a supportive environment. Group therapy is most effective when facilitated by experienced professionals.
Comparison Table
| Treatment | Efficacy | Safety | Accessibility | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDMA-assisted therapy | Potentially high, but ongoing research needed | Requires careful monitoring; potential side effects | Limited availability due to regulatory hurdles | Potentially rapid and profound impact on trauma processing | Limited research; potential for side effects; ethical concerns |
| CBT | Proven effective for many | Generally safe with appropriate guidance | Widely available | Focuses on cognitive and behavioral changes | May not be sufficient for severe trauma |
| Exposure Therapy | Demonstrated effectiveness | Generally safe with appropriate guidance | Widely available | Direct confrontation of trauma triggers | Potential for triggering intense emotions |
| EMDR | Demonstrated effectiveness | Generally safe with appropriate guidance | Requires trained professionals | Potentially efficient for memory processing | May not be suitable for everyone |
| Medication | Effective for symptom reduction | Potential for side effects | Widely available | Quick symptom relief | May not address the root causes of trauma |
| Group Therapy | Supportive and potentially beneficial | Generally safe in a controlled setting | Varied availability | Community and peer support | May not be suitable for everyone |
Research and Clinical Trials on MDMA and PTSD

The exploration of MDMA-assisted therapy for PTSD is a rapidly evolving field, driven by promising early results and rigorous clinical trials. Understanding the methodologies and current stages of these trials is crucial to evaluating the potential of this treatment approach.
Summary of Existing Research
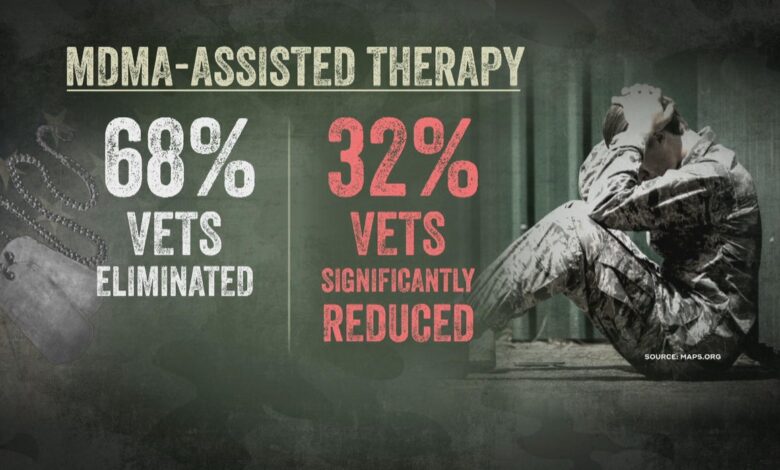
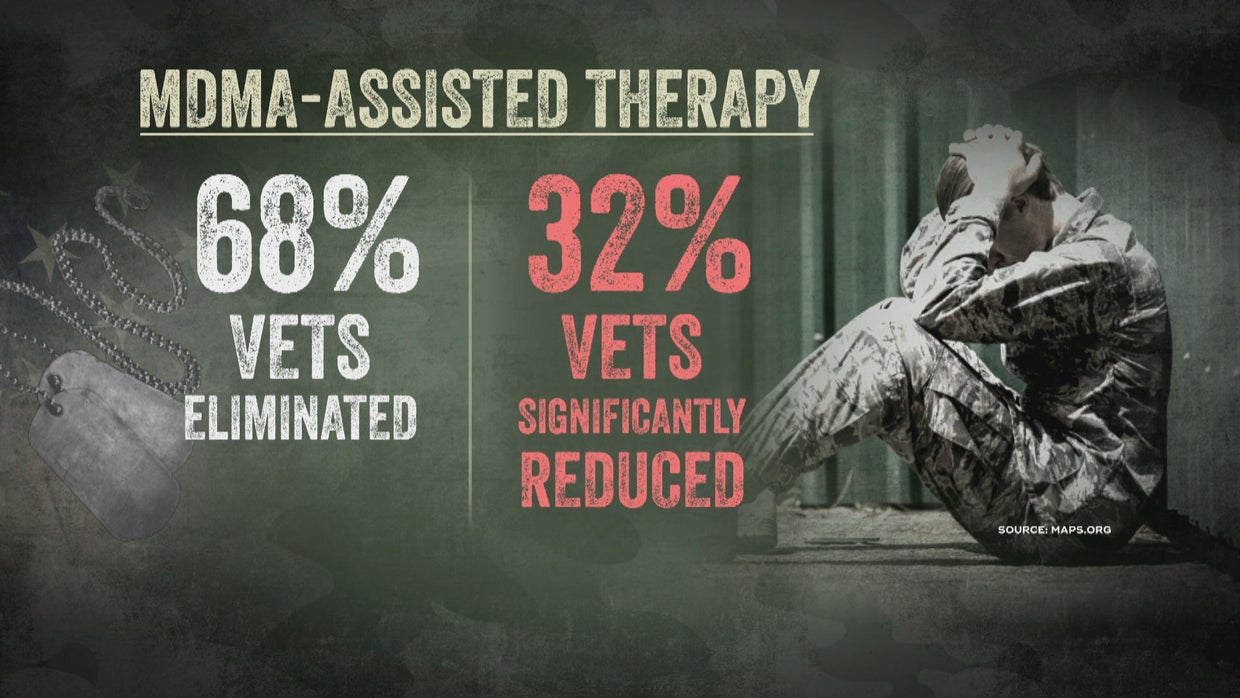
Existing research on MDMA-assisted therapy for PTSD primarily focuses on controlled clinical trials. These studies aim to evaluate the safety and efficacy of MDMA in conjunction with psychotherapy to reduce PTSD symptoms. Key findings often highlight significant symptom reductions in participants compared to control groups receiving standard PTSD treatments.
Methodologies Used in Clinical Trials
Clinical trials investigating MDMA-assisted therapy typically employ a double-blind, placebo-controlled design. This ensures that neither the participants nor the researchers know who is receiving MDMA and who is receiving a placebo. The trials also involve a detailed assessment of PTSD symptoms before, during, and after treatment, using standardized questionnaires. Therapists are rigorously trained in providing specific types of psychotherapy that are tailored to MDMA-assisted therapy protocols.
The inclusion and exclusion criteria for participants are also meticulously defined to ensure a consistent group of individuals who meet the necessary conditions for the study. This rigorous methodology aims to minimize bias and accurately assess the treatment’s effectiveness.
Current Stages of Clinical Trials and Results
Phase 3 clinical trials are currently underway, testing the effectiveness of MDMA-assisted therapy in larger patient populations. These trials aim to confirm the positive results seen in earlier phase trials and to establish the treatment’s efficacy and safety in a broader context. Preliminary results from these trials indicate that MDMA-assisted therapy shows significant promise in reducing PTSD symptoms, with reported improvements in areas such as intrusive memories, avoidance behaviors, and negative emotions.
It is important to note that the specific metrics and measures used in these trials can vary, leading to some differences in reported results. However, the general trend suggests a positive impact on PTSD symptoms.
Ongoing Research Efforts
Ongoing research efforts are exploring the mechanisms by which MDMA exerts its therapeutic effects on PTSD. Researchers are also investigating the optimal combination of MDMA and psychotherapy techniques to maximize treatment outcomes. Further research is focusing on developing personalized treatment plans that consider individual patient characteristics to further enhance the efficacy and safety of MDMA-assisted therapy. For instance, studies are looking into whether specific types of psychotherapy used alongside MDMA might be more effective for particular types of PTSD.
Potential Mechanisms of Action
MDMA’s potential to alleviate PTSD symptoms hinges on its intricate interactions with the brain’s neurochemical systems. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing effective and targeted treatments. This exploration delves into the neurobiological pathways that might underpin MDMA’s therapeutic effects, highlighting its impact on emotional processing and memory, and the associated neurochemical shifts.
Neurobiological Effects on Emotional Processing
MDMA is believed to influence the brain’s emotional processing centers by affecting neurotransmitter systems. These neurotransmitters play critical roles in regulating mood, fear responses, and emotional memories. The specific mechanisms are still under investigation, but research suggests that MDMA may modulate the release and reuptake of key neurochemicals, including serotonin, norepinephrine, and oxytocin.
Neurobiological Effects on Memory
Memory consolidation and retrieval are deeply intertwined with emotional processing. MDMA’s potential impact on memory, particularly emotional memory, is a significant aspect of its potential therapeutic value in PTSD. Studies suggest that MDMA might facilitate the reconsolidation of traumatic memories, potentially leading to a shift in the emotional valence associated with these memories. This could allow for a re-evaluation of the experience, leading to a reduction in the distress associated with the memory.
Neurochemical Changes Associated with MDMA’s Impact on PTSD
MDMA’s effects are multifaceted, affecting various neurotransmitter systems. Increased levels of serotonin, norepinephrine, and oxytocin are observed during MDMA use, and these changes are believed to contribute to the therapeutic effects. For example, increased oxytocin levels might promote feelings of bonding and trust, potentially mitigating social withdrawal often associated with PTSD. The release of these neurotransmitters may also play a role in modulating the activity of the amygdala and hippocampus, brain regions crucial for emotional processing and memory.
Summary Table of Neurobiological Processes
| Neurobiological Process | Potential Mechanism | Impact on PTSD Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Serotonin Release and Reuptake Modulation | Increased serotonin levels may improve mood regulation and reduce anxiety. | Potentially reduces anxiety and depressive symptoms. |
| Norepinephrine Release and Reuptake Modulation | Norepinephrine modulation may reduce arousal and hypervigilance. | Potentially reduces hyperarousal and associated symptoms. |
| Oxytocin Release | Increased oxytocin levels may enhance social bonding and trust. | Potentially improves social functioning and reduces isolation. |
| Amygdala and Hippocampal Modulation | Altered activity in these regions may influence emotional processing and memory reconsolidation. | Potentially facilitates a re-evaluation of traumatic memories and reduces emotional distress. |
Individual Experiences and Patient Perspectives
Understanding the lived experiences of individuals who have undergone MDMA-assisted therapy for PTSD is crucial to evaluating its potential. Patient testimonials and case studies offer valuable insights into the positive and negative aspects of this treatment, providing a more nuanced understanding beyond clinical trials. These accounts help us grasp the subjective impact of the therapy and identify potential challenges and benefits, enriching the overall picture of MDMA-assisted therapy for PTSD.
Patient Testimonials and Case Studies
Many individuals report significant improvements in their PTSD symptoms after undergoing MDMA-assisted therapy. These improvements often involve a deeper processing of traumatic memories, leading to reduced emotional distress and a greater sense of safety and control. However, the experience is not uniform, and some patients report challenges like feelings of vulnerability or heightened emotional responses during the therapy sessions.
A critical aspect is the careful monitoring and support provided during and after the therapy, aiming to mitigate potential negative experiences.
Common Experiences and Outcomes
While experiences vary, several common themes emerge from patient accounts. These commonalities, along with their associated outcomes, provide a clearer understanding of the therapeutic journey.
While some explore the potential of ecstasy for PTSD treatment, it’s crucial to remember that accessing quality mental healthcare is paramount. Unfortunately, the Texas healthcare system, one of the worst in the country, as many articles report , often makes this access challenging. This highlights the need for comprehensive solutions beyond just individual treatments like ecstasy.
| Common Experience | Potential Outcomes |
|---|---|
| Increased emotional processing and understanding of trauma | Reduced emotional distress, improved coping mechanisms, and enhanced self-awareness |
| Improved relationships and social connections | Enhanced trust, greater intimacy, and improved communication |
| Increased sense of safety and control | Reduced fear and anxiety, leading to a more stable and fulfilling life |
| Difficulties with emotional regulation or intense emotional responses | The need for additional support and therapy, or potential for worsening symptoms if not managed properly |
| Experiences of heightened vulnerability or discomfort during sessions | Careful selection of therapists and preparation are essential to manage potential negative reactions and improve the patient experience |
Challenges and Benefits Reported
Patients report a range of challenges and benefits during and after MDMA-assisted therapy. Challenges might include feelings of vulnerability, difficulty regulating emotions, or intense emotional responses. However, significant benefits include a deeper understanding of trauma, improved coping mechanisms, and stronger relationships. The successful outcomes are contingent on the comprehensive support structure surrounding the treatment.
Future Directions and Implications
The burgeoning field of MDMA-assisted therapy for PTSD presents a multitude of exciting opportunities and critical considerations for the future. While early research is promising, significant questions remain about optimizing treatment protocols, ensuring accessibility, and integrating this novel approach into mainstream mental health care. This exploration delves into potential future research avenues, broader implications for mental health treatment, and strategies for broader implementation.
Potential Future Research Avenues, Can ecstasy help with ptsd
Further research is crucial to refine MDMA-assisted therapy protocols. Investigating different dosages, administration schedules, and combined therapies (e.g., cognitive behavioral therapy) can optimize treatment effectiveness. This includes exploring variations in patient responses, tailored to individual needs and characteristics. Determining long-term effects and identifying specific biomarkers that predict treatment success are essential steps. This will lead to more precise and personalized treatment strategies.
Potential Implications for Mental Health Treatment in General
The success of MDMA-assisted therapy for PTSD could have profound implications for mental health treatment in general. If proven safe and effective, this approach might lead to the development of similar psychedelic-assisted therapies for other mental health conditions, such as depression, anxiety disorders, and substance use disorders. The potential to access and process deeply ingrained emotional trauma could revolutionize how we approach these complex issues.
It is important to acknowledge the ethical and regulatory considerations inherent in such a development.
Improving Accessibility and Affordability
Making MDMA-assisted therapy accessible and affordable is crucial for widespread implementation. This requires a multi-pronged approach, including cost-effective treatment models, strategic partnerships between research institutions and healthcare providers, and potential government funding for research and training programs. Insurance coverage will be vital to ensure equal access for all those who might benefit from this therapy. Public awareness campaigns can play a key role in addressing stigma and promoting understanding.
Impacts on Healthcare Policy and Practices
The integration of MDMA-assisted therapy into healthcare policy and practice necessitates careful consideration of regulatory frameworks, training standards, and ethical guidelines. This will involve creating specialized treatment centers, training therapists to administer and supervise the therapy, and establishing robust safety protocols. A collaborative effort between policymakers, healthcare professionals, and researchers is needed to ensure responsible and effective implementation.
This will set precedents for how we address complex mental health challenges in the future.
Ethical Considerations and Regulatory Issues
Addressing ethical considerations is paramount in the advancement of MDMA-assisted therapy. This includes ensuring patient safety, informed consent, and protecting vulnerable populations. Robust regulatory frameworks are essential to guarantee safety and efficacy. This involves careful monitoring and evaluation to prevent misuse and unintended consequences. Strict guidelines for the use of MDMA-assisted therapy, including training and oversight procedures, are needed to mitigate potential risks.
The development of clear and consistent ethical guidelines will pave the way for the safe and responsible use of this novel approach to treatment.
Last Recap
In conclusion, the use of MDMA in treating PTSD presents a compelling yet challenging area of research. While promising results emerge from clinical trials, potential risks and ethical concerns must be carefully addressed. Ultimately, the future of MDMA-assisted therapy for PTSD hinges on ongoing research, ethical considerations, and careful regulation. Individual experiences and perspectives play a crucial role in shaping the understanding of this evolving field.





