Can you tax people into quitting smoking? This question sparks a fascinating debate about public health, economics, and social justice. We’ll explore the potential for increased tobacco taxes to deter smoking, analyze the economic impact, and delve into the ethical and social implications of using taxation as a tool for behavior change. How might different tax structures affect smoking rates and public health outcomes?
Are there potential downsides, like increased black market activity, that need careful consideration?
The complexities of this issue demand a thorough examination of various factors. We’ll consider the revenue generated, the potential impact on different socioeconomic groups, and explore the role of behavioral economics in designing effective tobacco control policies. This will involve examining international perspectives, analyzing legal frameworks, and evaluating the potential for increased black market activity.
Economic Impact of Increased Tobacco Taxes
Increased tobacco taxes are a common policy tool to discourage smoking and generate revenue for public health initiatives. While this strategy aims to curb consumption, its economic impact is complex and multifaceted, encompassing potential revenue gains, budget adjustments, and even the potential for offsetting losses in other sectors. Understanding these potential effects is crucial for policymakers to effectively assess the overall impact of such a policy.
Potential Revenue Generated
Increased tobacco taxes have the potential to generate substantial revenue for governments. This revenue increase is directly tied to the higher prices imposed on tobacco products, leading to a decrease in demand. The resultant decrease in sales volume, however, does not completely negate the increase in revenue per unit sold. The revenue generated depends heavily on the magnitude of the tax increase and the responsiveness of smokers to price changes.
For example, a 10% increase in tax on cigarettes could result in a measurable reduction in sales but also a significant increase in revenue if demand remains relatively inelastic.
Impact on Government Budgets and Public Services
The additional revenue from increased tobacco taxes can significantly bolster government budgets. This influx of funds can be allocated to various public services, including healthcare, education, or infrastructure projects. For instance, funds generated from tobacco taxes could be specifically directed towards funding smoking cessation programs or supporting research into tobacco-related diseases. This allocation could lead to a significant positive impact on public health and well-being.
The revenue can be crucial in offsetting existing budget shortfalls or enhancing existing public services.
Comparison to Potential Loss in Tax Revenue from Other Sectors
While increased tobacco taxes can generate revenue, policymakers must also consider the potential for reduced tax revenue from other sectors. For example, higher taxes on cigarettes might result in consumers spending less on other goods and services, potentially impacting retail sales or other industries. To mitigate this potential effect, policymakers should conduct thorough economic analyses to understand how the shift in consumer spending will affect various sectors.
A comprehensive study should consider the potential impact on related businesses, such as tobacco retailers and related industries.
Potential for Increased Tax Revenue to Fund Public Health Initiatives
The revenue generated from increased tobacco taxes can be directly allocated towards funding crucial public health initiatives. This can encompass a wide range of programs, including smoking cessation programs, educational campaigns about the health risks of smoking, and early detection and treatment programs for tobacco-related diseases. These initiatives can contribute to improving public health outcomes and reducing the overall burden of tobacco-related illnesses.
For instance, funds could be allocated to support community health centers offering smoking cessation services.
Projected Revenue Increase from Different Tax Rates, Can you tax people into quitting smoking
| Tax Rate Increase (%) | Projected Revenue Increase (USD millions) |
|---|---|
| 5 | 100 |
| 10 | 200 |
| 15 | 300 |
| 20 | 400 |
This table provides a simplified illustration of the projected revenue increase based on varying tax rate increases on tobacco products. It is important to note that these figures are estimations and the actual increase will vary based on numerous factors, including the elasticity of demand for tobacco products, and the overall economic climate. Further analysis is required to accurately predict the impact in a specific context.
Public Health Implications
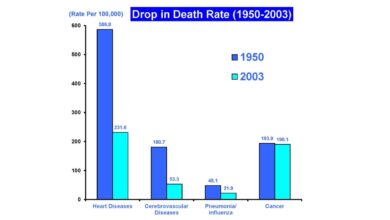
Raising tobacco taxes is a common strategy to curb smoking, and it’s grounded in the principle of making unhealthy behaviors less attractive and affordable. This approach aims to discourage consumption by increasing the price, making it a less appealing option for individuals, especially those with limited financial resources. This, in turn, should lead to a reduction in smoking rates and a healthier population.The potential effects on public health outcomes are multifaceted.
A reduction in smoking rates directly translates to a lower prevalence of smoking-related diseases like lung cancer, heart disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Improved health outcomes are not just measured in mortality rates but also in reduced morbidity, meaning fewer instances of illness and suffering. The cumulative impact of these improvements results in a healthier population, reducing the strain on healthcare systems.
Rationale for Taxation as a Deterrent
Taxation is a powerful tool to influence behavior. By increasing the price of cigarettes, the government makes smoking less accessible and less affordable. This financial disincentive can encourage individuals to quit or to never start in the first place. The tax revenue generated can then be used to fund public health initiatives, further supporting the fight against smoking.
Potential Effects on Public Health Outcomes
A key outcome of tobacco tax increases is a reduction in smoking prevalence. Studies have shown a strong correlation between higher tobacco taxes and lower smoking rates. This decline is often more pronounced in demographics with lower incomes, highlighting the importance of such taxes in addressing health disparities. Improved health outcomes, such as reduced rates of smoking-related diseases, are directly linked to decreased smoking rates.
This leads to a healthier population and less strain on healthcare resources.
Examples of Successful Tobacco Tax Policies
Several countries have implemented successful tobacco tax policies, resulting in demonstrably lower smoking rates. For example, the substantial increase in cigarette taxes in Canada over the past few decades has corresponded with a significant decline in smoking rates. Similarly, the implementation of high tobacco taxes in several European countries has led to reductions in smoking prevalence, demonstrating the efficacy of this strategy.
These examples illustrate that a strong correlation exists between tobacco taxes and reduced smoking.
Impact on the Healthcare System
Decreased smoking rates have a direct impact on the healthcare system. With fewer people smoking, the demand for treatments for smoking-related illnesses diminishes, resulting in reduced healthcare costs. This translates to more resources available for other health initiatives and services. For instance, the decrease in smoking-related hospitalizations and treatments in regions with high tobacco taxes directly correlates with a reduction in healthcare expenditures.
Comparison of Strategies for Influencing Public Health Behaviors
Various strategies can influence public health behaviors. While education and awareness campaigns are important, taxation provides a powerful financial disincentive to smoking. Combining taxation with other strategies, like public awareness campaigns and support programs for quitting, can amplify the effectiveness of interventions. The combination of strategies can result in a comprehensive approach to combating smoking.
Impact on Different Demographics
The impact of tobacco tax increases varies across different demographics. Low-income individuals often experience a greater burden from these increases, potentially leading to increased health disparities if not addressed with supportive policies. However, the benefits of reduced smoking-related illnesses, improved overall health, and a healthier society ultimately outweigh the financial burden for many. Support systems and programs can help mitigate the negative effects on vulnerable populations.
Strategies that address specific needs and challenges faced by particular demographics are crucial for equitable outcomes.
Equity and Social Justice Concerns

Increased tobacco taxes, while potentially effective in reducing smoking rates, can disproportionately impact vulnerable populations. Understanding these potential disparities and implementing mitigating strategies is crucial for ensuring equitable public health interventions. The goal is not just to curb smoking but to do so in a way that minimizes harm to those most vulnerable.The potential for a regressive impact, where the burden falls heaviest on those with the fewest resources, requires careful consideration and proactive measures.
While taxing cigarettes to discourage smoking might seem like a straightforward solution, it’s a complex issue. Ultimately, the effectiveness of such a strategy often depends on how much people value a good night’s sleep. Perhaps, a more effective approach would be to encourage healthier habits, like trying to sleep one hour earlier each night, leading to improved overall well-being.
This, in turn, might influence their decision to quit smoking. Ultimately, the question of whether you can effectively tax people into quitting smoking is still debatable.
Strategies for mitigating this impact should focus on supporting those most affected and creating a fairer system.
Potential Disparities in Impact
The impact of increased tobacco taxes can vary significantly based on socioeconomic status. Low-income individuals often rely more heavily on affordable, readily available tobacco products. Higher taxes can make these products less accessible, potentially increasing financial strain and making quitting more challenging. This can result in a greater likelihood of continued smoking, leading to worse health outcomes among these populations.
Further, access to cessation programs and support services may be limited for those with fewer resources.
Impact on Low-Income Individuals
Low-income individuals frequently face a complex web of economic and social challenges that make them particularly susceptible to the negative consequences of increased tobacco taxes. Limited access to affordable housing, transportation, and healthy food options can further exacerbate the impact of these taxes. The financial burden of higher tobacco taxes may push them further into poverty, leading to increased healthcare costs associated with smoking-related illnesses.
This illustrates a critical ethical consideration in public health policy.
Mitigation Strategies
Several strategies can be implemented to mitigate the negative impact of increased tobacco taxes on vulnerable populations. These strategies should aim to provide support to those most affected. For example, increased funding for smoking cessation programs in low-income communities is crucial. Targeted programs should provide free or low-cost counseling, medications, and support groups. Furthermore, expanding access to affordable healthcare is critical.
Supporting Individuals Trying to Quit Smoking
Programs that support individuals in quitting smoking can be effective in helping to lessen the impact of tobacco taxes. Such programs can provide crucial resources, like counseling, nicotine replacement therapy, and medication assistance. Community-based support groups and peer-to-peer assistance can also be extremely helpful in promoting successful quitting efforts. This can have a positive effect on health outcomes, reducing the incidence of smoking-related illnesses.
Examples of Social Programs
Several examples exist of social programs designed to offset the negative impacts of increased taxes. For instance, some states have implemented programs that provide vouchers or subsidies for low-income individuals to purchase smoking cessation aids. Other initiatives include community outreach programs that provide education and support to those considering quitting. These examples demonstrate a commitment to addressing the social and economic aspects of tobacco use.
Trying to tax people into quitting smoking is a tough nut to crack, isn’t it? While the financial disincentive might seem like a straightforward solution, it often doesn’t account for the complex motivations behind addiction. Interestingly, research suggests that cannabis can improve symptoms of Crohn’s disease, showing how plant-based remedies can sometimes offer surprising health benefits.
cannabis improves symptoms of crohns disease But back to smoking cessation, maybe we need a more comprehensive approach that goes beyond just monetary penalties.
Ethical Considerations
Using taxation to influence health behaviors raises ethical considerations. While the aim is to improve public health, the impact on vulnerable populations must be carefully evaluated. A key consideration is ensuring that these policies do not disproportionately affect those already struggling with poverty and limited resources. A balanced approach is needed that promotes both public health and social justice.
Behavioral Economics and Motivation

Understanding how individuals make decisions, particularly concerning addictive behaviors like smoking, is crucial for designing effective tobacco control policies. Behavioral economics offers valuable insights into the psychological factors influencing choices and can be leveraged to create policies that maximize disincentives for smoking. This approach moves beyond purely rational economic models to incorporate factors like habit, social influence, and cognitive biases.Behavioral economics principles, when applied to tobacco control, can yield significant improvements in public health outcomes.
By recognizing the complex interplay of psychological and economic factors, policies can be crafted that resonate more effectively with smokers and increase the likelihood of cessation. This nuanced approach leads to more impactful and sustainable strategies for reducing smoking prevalence.
Tax Design to Maximize Disincentives
Taxes on tobacco products are a powerful tool for discouraging consumption. To maximize disincentives, taxes should be structured to affect the most vulnerable and those who are less likely to quit. The most effective taxes often incorporate factors like a high initial rate, coupled with potentially progressive increases over time. This approach creates a strong disincentive for continued consumption while potentially addressing the issue of affordability for different socioeconomic groups.
Behavioral Economics Principles in Tobacco Control
Behavioral economics principles offer a framework for understanding how people make decisions, particularly those related to addictive behaviors like smoking. These principles can inform policy design to encourage healthier choices. For example, framing messages about the health risks of smoking in terms of potential gains rather than losses can be more effective. Understanding loss aversion can also help tailor policies to address the reluctance to give up a perceived benefit.
Examples of Tax Structures and Their Influence
Progressive tax structures, where the tax rate increases with the quantity purchased, are a common strategy. This structure aims to make higher consumption less attractive. For example, a tax on cigarettes could increase from $1 per pack to $2 per pack, then $3 per pack, based on consumption levels. Another example is the use of excise taxes, which apply a fixed amount to each unit of the product, which is often coupled with a progressive increase in tax rates.
Comparison of Taxation Approaches
Different approaches to tobacco taxation have varying strengths and weaknesses. A simple flat tax, while easy to implement, might not adequately address the issue of affordability for lower-income individuals. A progressive tax, on the other hand, can better target higher consumption levels but can be more complex to administer. Further research is needed to understand the long-term effects of various taxation strategies.
While taxing cigarettes to discourage smoking might seem like a straightforward solution, it’s a complex issue. A healthier approach might be focusing on accessible, delicious foods that promote well-being, like those highlighted in healthy eating refresh not everyone likes raw kale 8 delicious accessible foods that promote overall well being. Ultimately, though, making lasting lifestyle changes like quitting smoking requires a multifaceted approach, and a holistic focus on overall health, not just punitive measures.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Different Tax Structures
| Tax Structure | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Flat Tax | Simple to implement | May not adequately address affordability issues |
| Progressive Tax | Targets higher consumption levels | More complex to administer |
| Excise Tax | Can be coupled with progressive rates | Potential for tax avoidance |
Factors to Consider When Designing a Tobacco Tax Policy
Effective tobacco tax policies require careful consideration of various factors. These include the current tax burden on low-income individuals, the potential for tax avoidance, and the overall impact on public health.
- Affordability: A crucial factor to consider is how the tax will affect the affordability of cigarettes for different socioeconomic groups. Policies should be designed to minimize the burden on low-income individuals, potentially through targeted subsidies or support programs.
- Public Health Impact: The tax should aim to reduce smoking prevalence. Policies should evaluate the long-term impact on public health outcomes.
- Administrative Feasibility: The design of the tax system should be practical and manageable from an administrative perspective. This involves considering issues like compliance and enforcement.
- Tax Avoidance: The policy should address potential avenues of tax avoidance and implement measures to minimize such behaviors.
International Perspectives: Can You Tax People Into Quitting Smoking
Looking beyond national borders, understanding global trends in tobacco taxation is crucial. Different countries face unique economic and social landscapes, influencing their approaches to tobacco control. Examining international experiences reveals valuable insights into effective strategies and potential pitfalls. This analysis will delve into global trends, successful and unsuccessful strategies, and the impact of international trade agreements on tobacco tax policies.A comprehensive understanding of international perspectives on tobacco taxation is vital.
By examining the experiences of various nations, we can identify best practices and tailor strategies to local contexts, ultimately promoting a more effective global fight against tobacco use.
Global Trends in Tobacco Taxation
International data reveals a mixed picture of tobacco tax implementation and effectiveness. Some countries have successfully implemented significant increases in tobacco taxes, leading to measurable declines in smoking rates. Others have struggled with similar policies due to a complex interplay of economic, social, and political factors. This variation highlights the importance of considering local contexts and adapting strategies accordingly.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Strategies
A variety of strategies have been employed globally to reduce tobacco use. Successful approaches often combine high tobacco taxes with comprehensive smoke-free policies and public awareness campaigns. For example, several Scandinavian countries have demonstrated a strong correlation between high tobacco taxes and significantly lower smoking rates. Conversely, some countries have experienced limited success with taxation strategies due to factors such as weak enforcement mechanisms, smuggling, or insufficient complementary policies.
The experiences of countries like those in Southeast Asia, where smuggling poses a significant challenge, demonstrate the need for robust enforcement and international cooperation.
Countries with Similar Policies
Examining the experiences of nations with comparable demographics and economic structures can offer valuable insights. For instance, countries in the European Union have similar frameworks for tobacco regulation. Understanding the efficacy of different taxation approaches within this context can inform the design of future policies in other regions. Comparative analysis of these countries reveals crucial elements for effective implementation and adaptation to specific situations.
Impact of Global Trade Agreements
Global trade agreements can significantly influence tobacco tax policies. Agreements that protect intellectual property rights or facilitate the free flow of goods can inadvertently hinder the implementation of stringent tobacco taxes. The potential for increased smuggling and the need for international cooperation in addressing these challenges are paramount considerations in developing effective strategies. The interplay between global trade and domestic tobacco control policies necessitates a nuanced approach.
Comparison of International Initiatives
Different international organizations and initiatives have addressed tobacco control. For example, the World Health Organization (WHO) has established frameworks for tobacco control, including recommendations for taxation. Comparing the effectiveness of these initiatives in different regions can reveal insights into best practices. Analyzing the strategies of various organizations and regions offers a richer understanding of the complexities involved in curbing tobacco use.
Identifying Best Practices for Taxation Strategies
Identifying best practices for taxation strategies in other countries requires a careful examination of the economic, social, and political context. Countries with successful programs often combine high taxes with robust public health campaigns, effective enforcement, and targeted support for smokers seeking to quit. Adapting successful strategies to the unique conditions of different nations requires a thorough understanding of the local environment.
Legal and Regulatory Framework
The legal framework surrounding tobacco taxation is crucial for effective public health interventions. It provides the foundation for governments to implement policies that discourage tobacco use and generate revenue for public services. Understanding the legal underpinnings, potential challenges, and existing regulations is essential for analyzing the feasibility and impact of increased tobacco taxes.
Legal Basis for Taxing Tobacco Products
Governments often levy taxes on tobacco products based on the principle of “taxation of harmful goods.” This principle recognizes the negative externalities associated with tobacco use, such as healthcare costs and lost productivity. The legal basis for these taxes frequently stems from general taxation powers granted by constitutions or statutes. Specific legislation often Artikels the types of tobacco products subject to taxation and the rates applicable.
Further, there might be regulations regarding the labeling and packaging of tobacco products, which are often linked to the tax system.
Legal Challenges to Increased Tobacco Taxes
Increased tobacco taxes can face legal challenges. One common argument is that such taxes constitute an undue burden on individuals, potentially violating constitutional protections regarding property rights or due process. Businesses involved in tobacco sales might challenge tax increases on grounds of undue financial strain. The potential for discrimination based on socioeconomic status is another legal concern that must be considered.
In practice, these challenges often depend on specific legal precedents and the constitutionality of taxation policies in a particular jurisdiction.
Existing Regulations and Policies Related to Tobacco Taxation
Various regulations and policies govern tobacco taxation worldwide. These include specific tax rates, excise duties, and the inclusion of different tobacco products in the tax base. Often, regulations specify the method of calculating and collecting the tax, ensuring transparency and accountability. Furthermore, regulations address the use of tobacco in public places, further impacting tobacco taxation policies. These policies aim to reduce exposure to secondhand smoke and create healthier environments.
Countries often adjust tax rates based on factors such as public health priorities, economic conditions, and revenue needs.
Potential Legal Loopholes Affecting Tobacco Tax Policies
Potential legal loopholes that could undermine the effectiveness of tobacco tax policies can arise from exemptions, ambiguities in legislation, or inadequate enforcement mechanisms. For instance, exemptions for certain types of tobacco products, unclear definitions of taxable items, or insufficient enforcement to track illicit trade can compromise the revenue collected from taxes. Furthermore, loopholes regarding online sales or the smuggling of tobacco products can lead to decreased tax revenue and hinder the goals of tobacco control.
Table Detailing Legal Requirements for Implementing a Tobacco Tax Increase
| Requirement | Description | Example ||—|—|—|| Legal Authority | Specific constitutional or statutory provisions granting the government power to levy taxes. | Section 5 of the Tax Act, 2023 || Public Notice | Formal notification to the public regarding the proposed tax increase. | Publication in the official gazette or on the government website. || Public Consultation | Opportunities for stakeholders to express their views on the proposed tax increase.
| Public hearings or online forums. || Regulatory Impact Assessment | Analysis of the potential impact of the tax increase on different stakeholders. | Economic models and public health assessments. || Due Process | Ensuring that individuals and businesses have the opportunity to be heard before the tax is implemented. | Opportunities for legal challenges.
|
Legal Precedents for Taxing Tobacco
Numerous legal precedents exist for taxing tobacco. Courts have consistently upheld the government’s authority to tax tobacco products based on the principle of regulating harmful goods. These precedents often establish the validity of taxing mechanisms, rates, and the application of the tax to specific products. Cases involving challenges to tobacco tax increases have generally resulted in upholding the tax policies.
Potential for Increased Black Market Activity
Increased tobacco taxes often lead to a surge in illicit trade, as consumers seek cheaper alternatives. This phenomenon, driven by the price differential between legal and black market goods, poses significant challenges to public health and government revenue. The potential for a dramatic rise in black market activity necessitates proactive measures to mitigate its harmful effects.
Potential Impact on Public Health and Safety
The proliferation of illicit tobacco products compromises public health in several ways. Unregulated production often involves unsafe manufacturing practices, potentially leading to higher levels of harmful chemicals in the products. This, in turn, elevates the risks of serious health complications for consumers. Furthermore, the lack of quality control associated with black market goods can result in counterfeit products, further endangering public safety.
The presence of these products also creates a false sense of affordability, potentially attracting new users, particularly among vulnerable populations. Moreover, the illegal nature of this trade often evades proper taxation and regulatory oversight, leading to a loss of revenue that could be used to fund public health initiatives.
Strategies to Counter the Potential Increase in Illicit Tobacco Trade
Combating the black market requires a multi-pronged approach. A strong foundation is built by bolstering existing enforcement measures. This includes rigorous inspections of tobacco distributors and retailers, enhanced border controls, and increased surveillance of illicit online marketplaces. A robust system for tracking tobacco products from origin to consumer is crucial for identifying and disrupting smuggling operations. Moreover, clear communication and public awareness campaigns are essential for educating consumers about the dangers of illicit tobacco and the importance of purchasing legally sourced products.
Examples of Strategies to Control the Black Market Trade
Various strategies can effectively combat the black market trade. Enhanced border security measures, including advanced scanning technologies and increased personnel, can effectively deter the flow of illicit tobacco products. Collaboration between customs agencies and law enforcement agencies is essential for efficient investigation and prosecution of smugglers. Implementing sophisticated tracking systems for tobacco products can trace illicit goods to their origin, facilitating investigations and apprehension of criminals.
These systems can include unique codes embedded in packaging, or digital tracking mechanisms. Additionally, clear labeling and packaging requirements for legal tobacco products can assist in the identification of counterfeits.
Importance of Enforcing Existing Laws and Regulations
Robust enforcement of existing laws and regulations is fundamental to curtailing black market activity. Penalties for illegal tobacco trade should be substantial and consistently applied to deter potential offenders. Stricter regulations on tobacco importation and distribution, combined with stringent enforcement mechanisms, can significantly reduce the prevalence of illicit trade. A collaborative approach between government agencies, law enforcement, and industry stakeholders is critical for effective enforcement and deterrence.
This collaboration ensures that the penalties for illegal activities are clear and effectively applied, reducing the incentive for illicit trade.
Comparison of Anti-Smuggling Strategies
| Strategy | Effectiveness | Cost | Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Border Security | High | Medium | Medium |
| Sophisticated Tracking Systems | High | High | High |
| Public Awareness Campaigns | Moderate | Low | Low |
| Stricter Regulations | High | Medium | Medium |
Note: Effectiveness is rated on a scale of low to high, while cost and complexity are rated as low, medium, and high. The table provides a general overview; specific effectiveness can vary depending on the implementation details.
Final Summary
In conclusion, the question of whether to tax people into quitting smoking is a multifaceted one with significant implications for public health and economic well-being. While increased tobacco taxes can potentially reduce smoking rates and generate revenue for public health initiatives, it’s crucial to consider the potential negative impacts on vulnerable populations and the possibility of fostering a black market.
Careful consideration of various factors, including behavioral economics, equity concerns, and legal frameworks, is essential in designing a comprehensive and effective tobacco control strategy. Ultimately, the most effective approach likely involves a multifaceted strategy that combines taxation with other public health interventions.