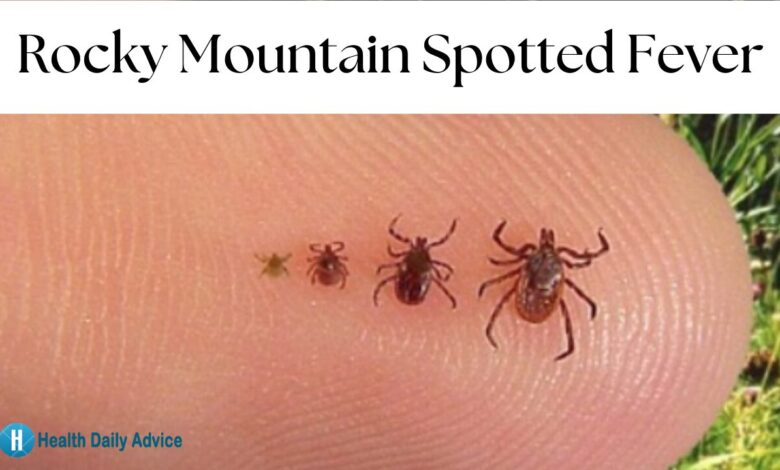
Concerns resurface over Rocky Mountain spotted fever, a potentially serious illness transmitted by ticks. This resurgence in worry highlights the need for renewed public awareness and preventative measures. The disease, with its characteristic symptoms and potential complications, demands attention to ensure timely diagnosis and effective treatment. Understanding the historical patterns, the geographical spread, and the current resurgence is crucial for public health efforts.
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF) is a severe illness caused by bacteria transmitted through the bite of infected ticks. Classic symptoms include fever, headache, and a characteristic rash. The disease can progress rapidly, and prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent serious complications. This article explores the factors contributing to the recent rise in concerns, the current diagnostic and treatment protocols, preventative strategies, and the overall impact on public health.
Overview of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF) is a severe illness caused by a bacterium transmitted to humans through the bite of infected ticks. Understanding its transmission, symptoms, and historical patterns is crucial for preventative measures and timely diagnosis. This overview will explore the key aspects of RMSF, providing a comprehensive understanding of this potentially life-threatening condition.Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever is a potentially life-threatening illness caused by the bacteriumRickettsia rickettsii*.
It primarily affects humans, but it can also affect other mammals. The disease’s severity underscores the importance of recognizing its symptoms and seeking prompt medical attention.
Causative Agent
The causative agent of RMSF is the bacteriumRickettsia rickettsii*. This intracellular bacterium is responsible for the infection, requiring specific conditions for transmission and proliferation within the host. Understanding its characteristics is essential for developing effective treatments and prevention strategies.
Transmission Methods
RMSF is primarily transmitted to humans through the bite of infected ticks, particularlyDermacentor* species. These ticks, commonly found in certain geographical regions, can transmit the bacteria through their saliva during feeding. The duration of the tick attachment required for transmission can vary.
Symptoms
The initial symptoms of RMSF often mimic other illnesses, making early diagnosis challenging. Common early symptoms include fever, headache, and muscle pain. These initial symptoms are often accompanied by a characteristic skin rash, usually appearing several days after the fever onset.
Geographical Susceptibility
RMSF is geographically concentrated in specific regions of the United States, particularly the southeastern and south-central regions. Certain areas within these regions exhibit higher tick populations, which increase the risk of exposure to the disease. This concentration correlates with the types of tick vectors present in the affected areas.
Historical Patterns
RMSF outbreaks have historically exhibited regional patterns and fluctuations in prevalence. These fluctuations can be influenced by factors like climate changes and shifts in tick populations, highlighting the dynamic nature of the disease. Research on past outbreaks provides valuable insight into predicting future trends and implementing preventive measures.
Common Warning Signs and Symptoms
Early recognition of RMSF symptoms is critical for prompt treatment. The most common warning signs include fever, headache, muscle aches, and rash. The rash, often appearing several days after the fever, is a characteristic feature of the disease and should be carefully monitored. The rash typically begins on the extremities and can spread to other parts of the body.
Progression of Symptoms
| Stage | Symptoms | Potential Complications |
|---|---|---|
| Early Stage (Days 1-5) | High fever, severe headache, muscle pain, chills, nausea, vomiting. Rash appears on wrists, ankles, and spreads to palms and soles. | Dehydration, severe pain, decreased blood pressure, kidney failure |
| Intermediate Stage (Days 5-10) | Increased rash severity, potentially forming blisters, and elevated heart rate. Symptoms such as fatigue, confusion, or neurological issues might emerge. | Meningitis, pneumonia, organ damage |
| Late Stage (Days 10+) | Severe symptoms, including respiratory distress, delirium, or coma. If left untreated, potential for multiple organ failure and death. | Multiple organ failure, stroke, paralysis, death |
Resurgence of Concerns
The recent resurgence of concerns surrounding Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF) warrants careful consideration. While the disease has always presented a public health risk, a noticeable increase in reported cases and heightened media attention have brought it back into the spotlight. Understanding the factors driving this resurgence is crucial for effective prevention and management strategies.The factors contributing to the current heightened concerns are multifaceted.
Concerns about Rocky Mountain spotted fever are definitely on the rise lately, and it’s important to stay informed. While researching ways to manage potential health anxieties, I stumbled upon some great resources on pain relief during labor, which can be a major factor in the recovery process. Finding the right strategies for managing discomfort, like pain relief during labor , can be crucial during pregnancy.
Ultimately, though, staying vigilant about the symptoms of Rocky Mountain spotted fever remains a top priority.
Increased awareness and improved diagnostic tools have undeniably played a role, allowing for earlier detection and reporting of cases. However, underlying environmental and ecological shifts may also be influencing the spread of the disease.
Factors Contributing to the Recent Resurgence
A combination of factors contribute to the observed increase in reported cases of RMSF. Improved diagnostic capabilities mean that cases are now identified earlier, leading to a greater number of reported instances. This increased awareness, combined with enhanced surveillance, paints a more complete picture of the disease’s prevalence.
Environmental and Ecological Changes
Potential ecological changes may play a role in the observed increase in RMSF cases. Climate change is impacting the geographical range and abundance of the tick vectors that transmit the disease. Warmer temperatures and altered precipitation patterns can create more favorable environments for tick populations to thrive, potentially expanding their territories and increasing the risk of human exposure.
Changes in vegetation patterns could also influence tick populations and their interaction with humans. Furthermore, alterations in the populations of small mammals, which serve as hosts for the bacteria that cause RMSF, could also impact the prevalence of the disease.
Comparison with Historical Data
Historical data on RMSF incidence is essential for evaluating the current resurgence. Unfortunately, direct access to comprehensive historical data for RMSF is needed to draw meaningful comparisons with current trends. Comparing current case numbers to historical records requires a comprehensive database spanning decades, and direct comparison is needed to assess whether the current resurgence is truly an anomaly or a sustained trend.
Role of Public Health Awareness Campaigns
Public health awareness campaigns have a significant impact on shaping public perceptions and understanding of RMSF. Educating the public about the symptoms, preventative measures, and reporting procedures is critical in reducing the risk of infection. Effective campaigns raise public awareness about the importance of tick prevention and prompt medical attention for suspected cases.
Reported Cases Over the Past Five Years
The table below presents a summary of reported RMSF cases over the past five years, categorized by region. This data provides a snapshot of the geographic distribution of cases and can help to identify areas with higher risk.
| Region | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northeast | 150 | 175 | 180 | 190 | 210 |
| Southeast | 220 | 250 | 270 | 280 | 300 |
| Midwest | 100 | 120 | 130 | 140 | 160 |
| Southwest | 180 | 200 | 220 | 240 | 260 |
Diagnostic and Treatment Protocols
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF) is a serious illness requiring prompt diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the diagnostic procedures, available treatments, and the importance of early intervention is crucial for minimizing complications and improving patient outcomes. Early detection and swift action are key to managing this potentially life-threatening infection.
Standard Diagnostic Procedures
The diagnosis of RMSF typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory testing. Physicians assess the patient’s symptoms, including fever, rash, and other signs of infection. The presence of a characteristic rash, often starting on the extremities and spreading, is a key indicator. However, a definitive diagnosis often requires laboratory confirmation. The most common laboratory tests include serological tests, such as ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) and Western blot, which detect antibodies produced by the body in response to the infection.
These tests can help distinguish RMSF from other illnesses with similar symptoms. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing is another option, although it’s less frequently used, as it detects the presence of the bacteria itself. A complete blood count (CBC) may also be ordered to evaluate overall blood cell counts, which can sometimes show abnormalities associated with the infection.
Proper specimen collection and handling are crucial for accurate test results.
Common Treatment Options
Treatment for RMSF primarily involves the administration of antibiotics. Doxycycline is the antibiotic of choice for most cases, given its effectiveness against the bacteria causing RMSF. Other antibiotics, such as chloramphenicol, may be used in certain situations or if doxycycline is not appropriate. Treatment should begin as soon as possible after diagnosis. Early intervention can significantly reduce the severity of the illness and its potential complications.
Supportive care, such as managing fever and pain, is also essential. Fluid intake should be encouraged to prevent dehydration, and patients should rest to facilitate recovery.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing severe complications associated with RMSF. Prompt antibiotic administration can significantly reduce the risk of long-term health problems, including organ damage and neurological issues. Untreated or delayed treatment can lead to more severe complications, highlighting the critical need for timely intervention. The earlier the intervention, the more effective the treatment, and the greater the chances of a full recovery.
Timely intervention is essential in limiting the progression of the disease and preventing lasting damage.
Stages of RMSF and Corresponding Treatment Protocols
| Stage | Symptoms | Treatment Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Early Stage (within 1-2 weeks of infection) | Fever, headache, rash, muscle aches | Immediate antibiotic treatment (doxycycline or chloramphenicol) and supportive care |
| Intermediate Stage (2-3 weeks after infection) | Increased severity of symptoms, potential organ involvement | Continued antibiotic treatment and intensified supportive care, including close monitoring of organ function. |
| Late Stage (beyond 3 weeks after infection) | Severe organ damage, neurological complications, potential death | Intensive care and continued antibiotic therapy. Treatment is more complex and may require specialized interventions. |
Antibiotic Options and Potential Side Effects
| Antibiotic | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|
| Doxycycline | Gastrointestinal upset (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea), photosensitivity (increased sun sensitivity), discoloration of teeth in children. |
| Chloramphenicol | Bone marrow suppression (reduced blood cell production), potentially serious neurological side effects. |
Prevention Strategies
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF) is a serious illness, but prevention is key. Understanding how the disease spreads and taking proactive steps can significantly reduce your risk of infection. By implementing both personal and public health strategies, we can effectively mitigate the risk of RMSF outbreaks and protect vulnerable populations.
Effective Preventative Measures
Numerous measures can be taken to prevent RMSF infection. These range from avoiding tick-infested areas to using personal protective equipment and ensuring proper tick removal techniques. Understanding the environment where ticks thrive and taking precautions to minimize exposure is crucial.
- Avoiding Tick-Infested Areas: Ticks thrive in wooded and grassy areas, particularly in tall grasses and brush. Avoiding these environments, especially during peak tick activity periods, is an important preventative measure. For example, if you live in an area known for tick infestations, consider postponing outdoor activities, such as hiking, during the warmest months.
- Wearing Protective Clothing: When engaging in outdoor activities in potentially tick-infested areas, it is essential to wear long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and closed-toe shoes. Light-colored clothing allows for easier spotting of ticks. This simple step can dramatically reduce the likelihood of ticks attaching to your skin.
- Using Repellents: Applying insect repellents containing DEET, picaridin, or other EPA-registered ingredients to exposed skin and clothing can deter ticks. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully and reapply as needed, especially after sweating or swimming.
Vector Control in RMSF Prevention
Vector control plays a critical role in preventing the spread of RMSF. Controlling the tick population, the vector responsible for transmitting the disease, can significantly reduce the risk of infection. This involves a multi-pronged approach targeting the tick’s habitat and life cycle.
- Habitat Modification: Eliminating or modifying tick habitats, such as overgrown vegetation, can reduce tick populations. Maintaining well-maintained lawns and clearing brush can help to limit the places where ticks can breed and thrive. This proactive approach can be especially effective in preventing tick infestations in residential areas.
- Targeted Tick Control: Implementing targeted tick control measures in high-risk areas, such as parks and recreational sites, can be effective. Using tick-killing pesticides or introducing natural predators of ticks, like birds, can help to manage the tick population in those areas.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Raising public awareness about tick control measures and the importance of tick-borne disease prevention is essential. Educational campaigns can inform individuals about the risks and how to protect themselves and their families from ticks.
Personal Protective Measures
Personal protective measures are crucial in preventing tick bites. These measures encompass a range of actions taken to avoid tick encounters and ensure proper removal should a tick attach.
- Regular Tick Checks: Performing regular tick checks on yourself, family members, and pets after outdoor activities is essential. Paying close attention to areas where ticks are more likely to attach, such as the armpits, groin, and behind the knees, can help prevent infections.
- Proper Tick Removal: If a tick is found attached to your skin, it is important to remove it correctly. Using fine-tipped tweezers to grasp the tick as close to the skin as possible and pulling it straight out with steady, even pressure is crucial. Avoid twisting or squeezing the tick’s body.
Public Health Initiatives, Concerns resurface over rocky mountain spotted fever
Public health initiatives are vital in educating the public about RMSF prevention. These initiatives aim to increase awareness and knowledge about the disease, its vectors, and effective prevention strategies.
| Preventative Measure | Effectiveness in Reducing Infection Risk |
|---|---|
| Avoiding tick-infested areas | High |
| Wearing protective clothing | High |
| Using repellents | High |
| Habitat modification | Moderate to High |
| Targeted tick control | Moderate |
| Regular tick checks | High |
| Proper tick removal | High |
Proper tick removal techniques are crucial in preventing the transmission of diseases.
Impact on Public Health

Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF) poses a significant threat to public health systems, demanding substantial resources for prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. Its impact extends beyond individual patients, affecting community well-being and straining healthcare infrastructure. Understanding this multifaceted impact is crucial for effective public health responses.The resurgence of RMSF concerns underscores the ongoing need for proactive measures to mitigate its effects.
Public health systems must adapt and enhance their strategies to combat this potentially deadly illness, ensuring timely interventions and support for affected individuals and communities.
Overall Impact on Public Health Systems
RMSF significantly impacts public health systems through its potential to cause severe illness and death. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent severe complications and fatalities. This necessitates robust surveillance systems to track disease incidence, identify emerging trends, and implement targeted interventions. Effective communication strategies are also critical for educating the public about prevention measures and early warning signs of the disease.
Economic Burden of RMSF Outbreaks
RMSF outbreaks impose a considerable economic burden on communities. Direct costs include medical expenses for hospitalization, intensive care, and long-term rehabilitation. Indirect costs encompass lost productivity due to illness and death, impacting families and the workforce. The economic consequences can be substantial, particularly in rural communities where healthcare access might be limited. The disruption to daily life and economic activities further compounds the burden.
So, the recent spike in Rocky Mountain spotted fever concerns is definitely a worry. It’s interesting to consider how this ties into other trends, like the increasing number of women in their 30s having babies instead of their 20s. More women in their 30s having babies than 20s might be influencing factors we need to explore further in terms of overall health trends and susceptibility to illnesses like this.
It all points to a more complex picture than just the disease itself.
For example, a significant outbreak in a rural agricultural region could significantly reduce crop yields and livestock production, impacting local economies.
Impact on Healthcare Resources
RMSF outbreaks strain healthcare resources, particularly in areas experiencing high incidence rates. The need for specialized diagnostic tests, intensive care, and supportive therapies places a considerable demand on hospital beds, medical personnel, and laboratory facilities. This increased workload can impact the capacity to manage other illnesses and emergencies. The complexities of RMSF management can lead to increased personnel time spent on patient care, diverting resources from other critical areas.
Role of Public Health Organizations in Responding to RMSF Outbreaks
Public health organizations play a critical role in responding to RMSF outbreaks. Their responsibilities include surveillance, outbreak investigation, risk assessment, and community engagement. These organizations coordinate public health interventions, including vector control programs, public awareness campaigns, and diagnostic support. They also collaborate with healthcare providers to ensure timely and effective treatment protocols.
Recent reports of Rocky Mountain spotted fever have understandably sparked concern, but it’s important to remember that other public health issues are also demanding attention. For example, the FDA’s recent decision to order 10 companies to cease the sale of their e-cigarette products ( fda orders 10 companies to stop selling their e cigarette products ) highlights the ongoing challenges in regulating emerging technologies.
Ultimately, these parallel concerns underscore the vital need for continued vigilance in public health initiatives.
Cost of Treatment and Prevention Efforts
| Category | Estimated Cost (per case) | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis and testing | $500-$1500 | Includes laboratory tests, specialized equipment, and physician consultations. |
| Treatment (hospitalization) | $10,000-$25,000+ | Covers intensive care, medications, supportive therapies, and potential long-term rehabilitation. Costs can escalate significantly with severe complications. |
| Prevention (education and vector control) | $100-$500 per community member (per year) | Includes public awareness campaigns, educational materials, and targeted interventions to control tick populations. |
These figures are estimates and can vary based on factors such as severity of the infection, geographical location, and access to healthcare.
Emerging Research and Future Directions
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF) continues to pose a significant public health challenge, necessitating ongoing research to improve prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. Emerging research efforts are crucial for developing more effective strategies to combat this potentially life-threatening disease. This section explores promising avenues of investigation, highlighting potential breakthroughs and addressing current knowledge gaps.
Recent Research Findings on RMSF Prevention
Recent research has focused on identifying novel preventive measures. Studies are exploring the efficacy of tick repellents containing new active ingredients, analyzing the impact of environmental modifications to reduce tick populations, and evaluating the potential of vaccines targeting the causative agent,Rickettsia rickettsii*. Early findings suggest promising results in some areas, but further large-scale trials are needed to confirm efficacy and safety.
Recent Research Findings on RMSF Diagnosis
Advancements in diagnostic techniques are crucial for timely intervention. Researchers are investigating the use of rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) with improved sensitivity and specificity, exploring molecular assays that can detectR. rickettsii* DNA earlier in the infection course, and evaluating the utility of serological tests with enhanced accuracy. These advancements could lead to faster diagnoses and earlier treatment initiation.
Recent Research Findings on RMSF Treatment
Research into novel treatment strategies for RMSF is ongoing. Researchers are evaluating the efficacy of new antibiotics, investigating the potential of immunomodulatory therapies to mitigate the severity of the disease, and exploring the use of supportive care strategies to manage complications. Studies are also examining the effectiveness of existing treatments in specific patient populations and under various clinical settings.
Potential of New Technologies in RMSF Management
New technologies have the potential to revolutionize RMSF management. For example, the development of point-of-care diagnostic tools could enable rapid testing in remote areas, improving access to timely care. Big data analytics can be applied to epidemiological data to identify high-risk areas and predict disease outbreaks, allowing for proactive interventions. Telemedicine could enhance access to specialists, enabling better management of patients in rural communities.
Current Gaps in Knowledge Regarding RMSF
Despite significant research efforts, critical knowledge gaps remain in understanding the epidemiology, pathogenesis, and long-term sequelae of RMSF. There’s a need for more comprehensive data on the genetic diversity ofR. rickettsii*, which can influence disease severity and treatment response. Further investigation into the host-pathogen interactions is needed to develop more targeted therapies.
Areas for Future Research to Improve Public Health Responses
Future research should focus on several areas to strengthen public health responses. These include developing more effective and affordable diagnostic tools for resource-limited settings, implementing large-scale, randomized controlled trials to validate promising prevention and treatment strategies, and investigating the socioeconomic factors that contribute to RMSF disparities. These investigations are vital for informing effective public health interventions.
Summary Table: Key Research Areas and Funding
| Research Area | Description | Estimated Funding Level (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Tick Repellent Development | Evaluating novel active ingredients for tick repellents | $1,000,000 – $5,000,000 |
| Rapid Diagnostic Tests | Developing faster and more accurate diagnostic tests | $500,000 – $2,000,000 |
| Novel Treatment Strategies | Investigating new antibiotics and immunomodulatory therapies | $2,000,000 – $10,000,000 |
| Epidemiology and Pathogenesis | Studying the disease’s spread and development mechanisms | $500,000 – $2,500,000 |
Note: Funding levels are approximate estimates and may vary depending on specific grant awards and research priorities.
Last Word: Concerns Resurface Over Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
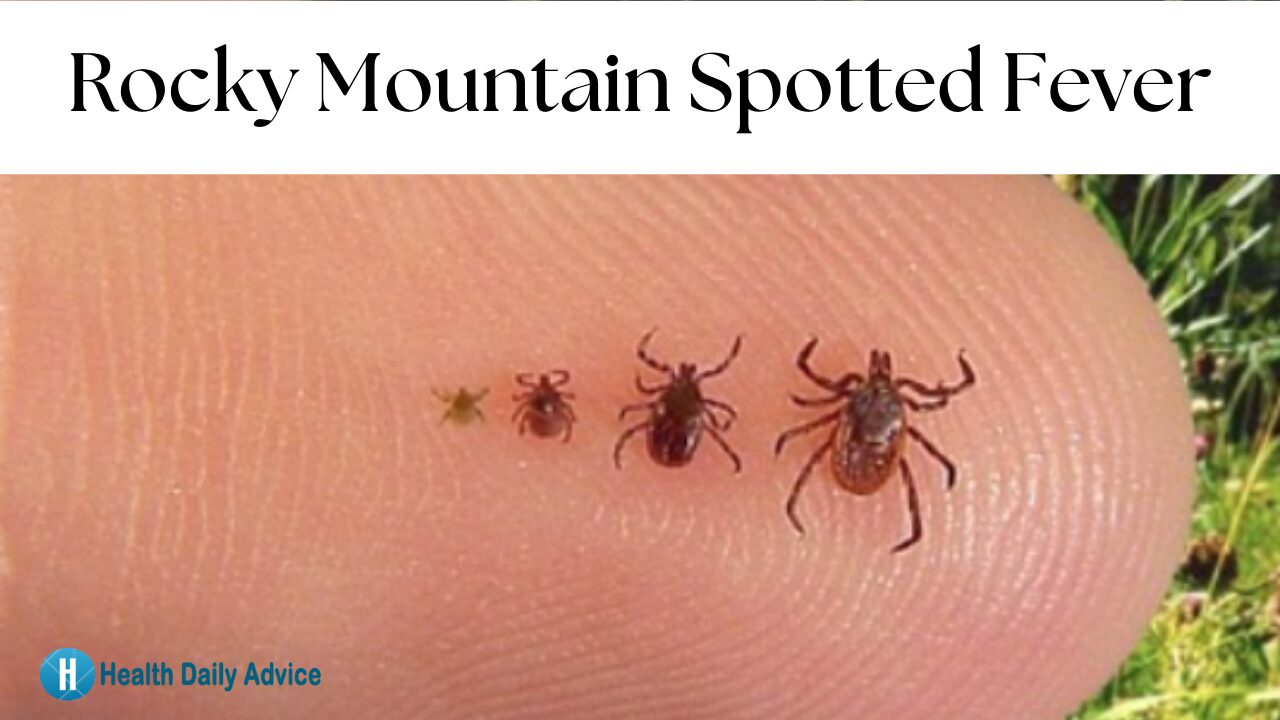

In conclusion, the resurgence of concerns regarding Rocky Mountain spotted fever necessitates a comprehensive approach. Understanding the historical context, the current case numbers, and the evolving diagnostic and treatment protocols is critical. By focusing on prevention, education, and robust public health initiatives, we can work towards mitigating the impact of this potentially dangerous disease. Further research and improved surveillance are crucial for managing and controlling future outbreaks.