Diet as major ms treatment – Diet as a major MS treatment is gaining increasing attention as a powerful tool for managing symptoms and improving overall well-being. This in-depth exploration delves into the multifaceted role of nutrition in MS, examining various dietary approaches, from the Mediterranean diet to the ketogenic diet, and considering their potential benefits and drawbacks. We’ll cover everything from practical meal planning strategies to potential risks and considerations, ensuring you have a comprehensive understanding of how diet can significantly impact your MS journey.
Understanding the complex relationship between diet and MS is crucial. This exploration will not only highlight the potential of different dietary strategies but also emphasize the importance of personalized approaches and consulting with healthcare professionals. By understanding the science behind dietary interventions, we aim to empower you with knowledge and resources to make informed decisions about your health and well-being.
Introduction to Diet in MS Management
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves. It disrupts the communication between these parts of the body, leading to a wide range of symptoms that vary significantly in severity and presentation among individuals. These symptoms can range from fatigue and numbness to vision problems, muscle weakness, balance issues, and cognitive difficulties, significantly impacting daily life, work, and relationships.Nutrition plays a crucial role in overall health and well-being.
A balanced diet provides the essential nutrients required for optimal bodily functions, including nerve function, immune system regulation, and cellular repair. The body’s ability to effectively utilize these nutrients can be affected by various factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and disease processes like MS.There’s growing interest in exploring potential links between dietary choices and MS symptom management. While there’s no cure for MS, some studies suggest that certain dietary patterns might help manage symptoms, potentially by reducing inflammation, improving immune response, and supporting nerve function.
However, it’s important to emphasize that more research is needed to fully understand the effectiveness and long-term impact of specific dietary interventions for MS. Current scientific understanding of dietary interventions for MS is still developing.
Dietary Patterns and MS
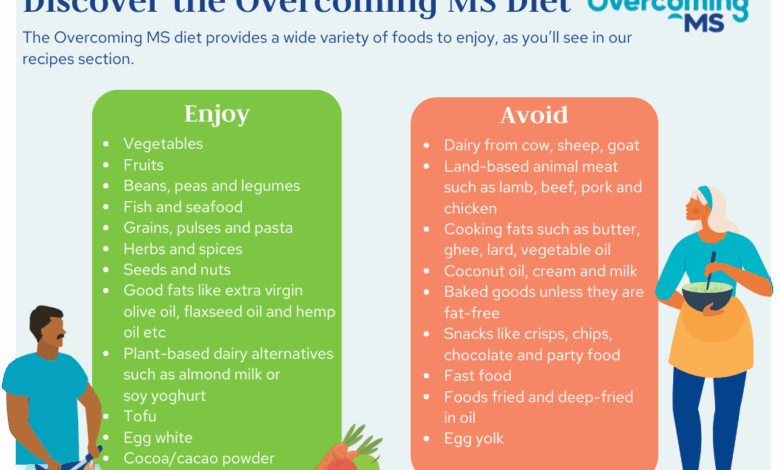
Different dietary approaches have been investigated for their potential impact on MS. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is generally recommended for overall health, and likely beneficial for managing MS symptoms.
| Dietary Pattern | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Mediterranean Diet | Rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, olive oil, and fish. May reduce inflammation and improve cardiovascular health, potentially benefiting MS. | May be challenging to maintain long-term due to cultural differences and cost considerations. Some individuals may experience digestive issues with high fiber intake. |
| Ketogenic Diet | Very high fat, moderate protein, and very low carbohydrate intake. Some studies suggest potential for reducing inflammation and improving certain symptoms. | Requires careful monitoring and may not be sustainable for long periods. Potential for nutrient deficiencies if not properly planned. May not be suitable for all individuals with MS. |
| Paleo Diet | Focuses on foods that were available during the Paleolithic era, emphasizing fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and fish. May reduce inflammation and improve gut health. | Limited variety and potentially restrictive. May be difficult to obtain all necessary nutrients without supplementation. May not be suitable for all individuals with MS. |
| Plant-Based Diet | Emphasizes plant-based foods, including fruits, vegetables, legumes, and grains. May reduce inflammation and improve overall health. | Potential for deficiencies in certain nutrients, such as vitamin B12 and iron, if not properly planned and supplemented. May require careful consideration of dietary needs and supplements. |
Current Scientific Understanding
Current research exploring the relationship between diet and MS focuses on identifying potential mechanisms through which dietary components may influence the disease process. These studies investigate how specific nutrients, such as antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins, might impact inflammation, nerve function, and immune response. However, the results of these studies are not always consistent, and more rigorous, long-term studies are needed to fully establish cause-and-effect relationships.
“The relationship between diet and MS is complex and requires further research to fully understand the potential benefits and risks of various dietary interventions.”
Specific Dietary Approaches for MS
Dietary strategies play a crucial role in managing MS symptoms. While a one-size-fits-all approach isn’t effective, various dietary patterns show promise in potentially mitigating inflammation and promoting overall well-being for people with MS. This exploration delves into specific dietary approaches, comparing and contrasting their potential benefits and drawbacks in managing MS.Different dietary patterns can influence inflammation and immune responses, which are key factors in MS.
By understanding the principles of each approach and their potential impact on MS symptoms, individuals can make informed choices about dietary modifications in consultation with healthcare professionals.
Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and healthy fats like olive oil. It’s rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds.
- Potential Benefits: The high fiber content promotes digestive health, and the abundance of fruits and vegetables provides essential vitamins and minerals. The focus on healthy fats can help improve cholesterol profiles. Preliminary research suggests a potential link between adherence to the Mediterranean diet and a reduced risk of MS progression.
- Potential Drawbacks: It can be challenging for those with specific dietary restrictions or preferences. The high intake of certain foods like nuts and olive oil can contribute to a higher fat intake, which might be a concern for individuals with certain health conditions.
- Scientific Evidence: Studies show that the Mediterranean diet is associated with reduced inflammation and improved cardiovascular health, which could be beneficial for MS management. However, more rigorous clinical trials are needed to definitively prove its impact on MS symptoms.
Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet drastically restricts carbohydrates, forcing the body to use fat for energy. This results in the production of ketones, which may have neuroprotective effects.
- Potential Benefits: Some individuals report improved energy levels and reduced fatigue on the ketogenic diet. Preliminary research suggests a potential role for ketones in reducing inflammation and promoting neuroprotection.
- Potential Drawbacks: The severe carbohydrate restriction can lead to nutrient deficiencies if not carefully planned. The high fat intake can also pose challenges for individuals with certain health concerns like gallbladder issues. Long-term adherence can be difficult, and some individuals may experience side effects like keto flu.
- Scientific Evidence: While some anecdotal evidence exists, the scientific evidence regarding the ketogenic diet’s effectiveness in managing MS symptoms is limited and not conclusive. More research is required to fully evaluate its potential benefits and risks.
Low-Inflammation Diet
The low-inflammation diet focuses on minimizing foods that trigger inflammation. This often involves limiting processed foods, refined sugars, red meat, and certain types of fats.
- Potential Benefits: By reducing pro-inflammatory foods, this diet may help mitigate symptoms associated with MS. The focus on whole foods and nutrient-dense options can promote overall health.
- Potential Drawbacks: Strict adherence can be difficult and may require careful planning to ensure adequate nutrient intake. Individual needs and tolerances can vary.
- Scientific Evidence: Studies on the effects of diets low in inflammatory foods show promise in reducing inflammation throughout the body. More research specific to MS is needed.
Macronutrient Breakdown
| Dietary Approach | Carbohydrates (%) | Protein (%) | Fat (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mediterranean Diet | 50-60 | 15-20 | 30-40 |
| Ketogenic Diet | 5-10 | 20-25 | 70-75 |
| Low-Inflammation Diet | Variable, but lower than Mediterranean | Variable, but adequate | Variable, but lower than ketogenic |
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing any of these dietary approaches requires careful planning and consideration. Individual tolerances, medical conditions, and medication interactions should be carefully assessed with a healthcare professional. Social support and ongoing monitoring are also important factors for long-term adherence. Nutritional counseling and support groups can aid in successful implementation.
Nutritional Considerations for MS Patients
Nourishing your body is crucial for managing multiple sclerosis (MS). A well-balanced diet, tailored to your individual needs, can play a significant role in alleviating symptoms and supporting overall well-being. This section delves into the specific nutritional considerations for MS patients, emphasizing the importance of hydration, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and mindful eating.A balanced diet for MS goes beyond simply avoiding certain foods.
It involves understanding how different nutrients interact with your body and how they might influence MS symptoms or medication efficacy. By carefully considering your dietary choices, you can better manage MS and maintain a healthier lifestyle.
Adequate Hydration
Maintaining adequate hydration is essential for everyone, but particularly crucial for MS patients. Dehydration can exacerbate MS symptoms, including fatigue and muscle weakness. Aim for at least eight glasses of water daily, and increase intake during periods of increased activity or heat exposure. Other hydrating beverages, such as herbal teas and diluted fruit juices, can also contribute to your daily fluid intake.
Be mindful of sugary drinks, as they can dehydrate you over time.
Fiber Intake
Dietary fiber is vital for digestive health and can positively impact MS symptoms. A high-fiber diet can help regulate bowel movements, which can be problematic for some individuals with MS. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in your meals. This will not only provide essential nutrients but also contribute to a healthier gut microbiome, which has been linked to improved immune function.
Gradually increasing fiber intake is recommended to avoid potential digestive discomfort.
While diet plays a significant role in managing MS symptoms, the complexities surrounding nutrition are vast. It’s a crucial aspect of MS treatment, but navigating the nuances of dietary interventions can be challenging. For example, the ethical debate around forcing food on individuals with anorexia nervosa is a deeply sensitive issue. The question of whether individuals with anorexia should be force-fed raises profound questions about autonomy and the balance between medical intervention and personal choice.
should people with anorexia be force fed is a crucial discussion to understand the many considerations. Ultimately, a balanced approach to diet, tailored to individual needs and circumstances, is vital for effectively managing MS.
Vitamin/Mineral Supplementation
Some vitamins and minerals may play a role in MS management. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine if any specific vitamin or mineral supplementation is necessary for you. A comprehensive blood test can help identify potential deficiencies. Remember, supplements should not replace a balanced diet, but rather complement it. Your healthcare provider can advise on appropriate dosages and potential interactions with medications.
Potential Interactions Between Nutrients and MS Medications
Certain nutrients can interact with MS medications, potentially reducing their effectiveness or causing adverse effects. For example, some medications may interfere with the absorption of specific vitamins or minerals. It’s crucial to discuss any dietary changes or supplements with your neurologist or other healthcare provider before making adjustments. They can assess potential interactions and advise on safe and effective dietary strategies.
Portion Control and Mindful Eating
Portion control and mindful eating can significantly impact MS symptom management. Mindful eating involves paying attention to your body’s hunger and fullness cues, eating slowly, and savoring your food. This approach can help prevent overeating and improve digestion, both of which can be beneficial for managing MS symptoms. Monitoring portion sizes and focusing on nutrient-dense foods can contribute to weight management, which is also important for overall health.
Recommended Daily Intakes of Key Nutrients for Individuals with MS
| Nutrient | Recommended Daily Intake (approximate) | Food Sources ||——————-|—————————————-|—————————————————|| Protein | 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight | Lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, tofu || Carbohydrates | 45-65% of total daily calories | Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes || Healthy Fats | 20-35% of total daily calories | Avocados, nuts, seeds, fatty fish || Fiber | 25-30 grams per day | Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes || Vitamin D | Consult healthcare provider | Fatty fish, egg yolks, fortified foods || Calcium | Consult healthcare provider | Dairy products, leafy greens, fortified foods || Iron | Consult healthcare provider | Red meat, beans, lentils, spinach || B Vitamins | Consult healthcare provider | Whole grains, legumes, meat, poultry, fish |
Incorporating Healthy Fats, Proteins, and Carbohydrates
A diet rich in healthy fats, proteins, and carbohydrates is crucial for MS patients. Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, and seeds, can support brain health and reduce inflammation. Lean proteins, from sources like fish, poultry, and beans, are essential for muscle repair and growth. Complex carbohydrates, found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, provide sustained energy and essential nutrients.
A balanced intake of these macronutrients is vital for overall well-being. A dietician specializing in MS can help you design a personalized meal plan.
Dietary Interventions and Symptom Management: Diet As Major Ms Treatment
Dietary choices play a crucial role in managing multiple sclerosis (MS) symptoms. While there’s no cure for MS, a well-planned diet can significantly impact fatigue, muscle weakness, pain, bowel and bladder function, and even cognitive function. This section explores how specific dietary interventions can help MS patients improve their quality of life.A balanced approach to nutrition is key.
Focusing on nutrient-rich foods, while minimizing processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats, can support the body’s natural healing processes and potentially mitigate MS-related symptoms.
Impact of Diet on Fatigue, Muscle Weakness, and Pain
Dietary choices can influence the energy levels and overall well-being of MS patients. A diet rich in complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats can provide sustained energy, reducing fatigue. Consuming sufficient iron and B vitamins, which are often deficient in MS patients, can help combat fatigue and muscle weakness. Furthermore, certain dietary approaches, like the Mediterranean diet, may have anti-inflammatory properties that can help manage pain associated with MS.
Chronic inflammation is a major contributor to many MS symptoms, and a diet rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce inflammation.
Role of Diet in Managing Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction
Dietary modifications can significantly impact bowel and bladder function in MS patients. Maintaining proper hydration is crucial, and a diet rich in fiber can promote regular bowel movements. Foods high in sodium and caffeine can worsen bladder symptoms. Individualized dietary plans, tailored to specific needs and symptoms, are often necessary to manage these issues effectively. For example, a patient experiencing frequent urge incontinence might need to reduce their intake of fluids before bedtime.
Link Between Diet and Cognitive Function in MS
Emerging research suggests a potential link between diet and cognitive function in MS. A diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and specific vitamins and minerals may support brain health and potentially slow cognitive decline. Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, which is influenced by dietary choices, is also crucial for overall brain health. For example, studies suggest that a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can help maintain cognitive function in individuals with MS.
Comparison of Dietary Effects on MS Symptoms
| Dietary Approach | Potential Impact on Fatigue | Potential Impact on Muscle Weakness | Potential Impact on Pain | Potential Impact on Bowel Dysfunction | Potential Impact on Bladder Dysfunction | Potential Impact on Cognitive Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mediterranean Diet | Potentially reduces fatigue | Potentially improves muscle strength | Potentially reduces pain | May improve regularity | May help manage frequency and urgency | Potentially supports cognitive function |
| Ketogenic Diet | May vary, depending on individual tolerance | May impact muscle strength (requires careful monitoring) | May reduce pain in some individuals | Potentially impact regularity (needs careful monitoring) | May impact bladder function (needs careful monitoring) | Limited research on long-term cognitive impact |
| Plant-Based Diet | May improve fatigue in some individuals | May improve muscle strength in some individuals | Potentially reduce pain in some individuals | May improve regularity | May help manage frequency and urgency | Potentially supports cognitive function |
Dietary Modifications for Specific MS-Related Issues
- Fatigue: Focus on nutrient-dense foods that provide sustained energy, such as whole grains, lean proteins, and fruits and vegetables. Adequate hydration is also crucial. Consider reducing processed foods and refined sugars, which can lead to energy crashes.
- Muscle Weakness: Prioritize protein-rich foods to support muscle repair and growth. Include foods rich in essential minerals, such as magnesium and potassium, which play a vital role in muscle function. Limit processed foods and focus on whole foods.
- Pain: A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and certain vitamins, may help reduce inflammation and pain. Consider incorporating foods with natural pain-relieving properties, such as ginger or turmeric.
- Bowel Dysfunction: Increase fiber intake gradually to avoid bloating or gas. Include foods high in soluble and insoluble fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Drink plenty of water to aid digestion.
- Bladder Dysfunction: Limit fluid intake before bedtime. Avoid caffeine and alcohol, as these can irritate the bladder. Monitor fluid intake and adjust based on individual response.
Practical Dietary Strategies for MS

Navigating MS can be challenging, but managing your diet effectively can significantly impact your well-being. This section delves into practical strategies for meal planning, ingredient awareness, and support systems, empowering you to take control of your dietary journey.Dietary management for MS is a personalized approach, and what works for one person might not be ideal for another. However, the core principles of a balanced diet rich in nutrients, and strategies to mitigate potential triggers remain essential.
Meal Planning and Preparation Strategies
Effective meal planning is crucial for managing MS. A structured approach can help ensure you’re consuming the necessary nutrients while minimizing fatigue and maximizing energy levels. Creating a weekly meal plan with a variety of nutritious foods is beneficial. Consider prepping ingredients or entire meals in advance to streamline weeknight routines.Meal prepping involves preparing ingredients or entire meals ahead of time, often on the weekend.
This reduces the stress of meal planning during the week, ensuring consistent nutritional intake. Portioning food and storing leftovers properly are essential components for meal prepping.
Food Labeling and Ingredient Awareness
Understanding food labels is essential for individuals with MS. Many processed foods contain hidden sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial ingredients, which can potentially exacerbate MS symptoms. Careful reading of nutrition labels, paying close attention to serving sizes, and understanding ingredient lists can empower you to make informed choices. Becoming familiar with potential dietary triggers, such as certain food additives, is equally important.
Diet plays a surprisingly significant role in managing MS, but recent research into alternative treatment approaches is also fascinating. For example, rethinking a cure for diabetes rethinking a cure for diabetes might offer some parallels. The potential for diet-based interventions to impact the underlying mechanisms of MS warrants further investigation, though.
Support Systems and Resources
Implementing dietary changes effectively requires support. Connecting with others facing similar challenges and accessing resources can significantly enhance the process. Support groups and healthcare professionals can offer guidance and encouragement.Finding a support system is crucial in making long-term dietary changes. Connecting with other individuals with MS who have experience with similar dietary approaches, can provide invaluable insights and motivation.
While diet isn’t a cure-all for multiple sclerosis (MS), a healthy eating plan can significantly impact symptoms. It’s crucial for managing the condition, just like it’s important for parents to navigate picky eating challenges. For those looking for practical strategies on how to deal with finicky eaters, check out this helpful guide on picky eating advice for parents picky eating advice on what parents should do.
Ultimately, a balanced and nutritious diet plays a key role in overall MS management and well-being.
Resources and Support Groups
| Organization | Description | Contact Information |
|---|---|---|
| National Multiple Sclerosis Society (NMSS) | Offers a wealth of information, support groups, and resources for people with MS and their families. | [Website and phone number] |
| The MS Navigator | Provides online resources and tools for navigating MS treatment and management, including dietary considerations. | [Website] |
| Local MS support groups | Connecting with others facing similar challenges can provide invaluable support and encouragement. | [Search online for local groups] |
Sample Weekly Mediterranean Meal Plan for an MS Patient
This sample meal plan focuses on the Mediterranean diet, known for its potential benefits for MS. Remember to adjust portion sizes and specific ingredients based on individual needs and preferences.
- Monday: Grilled Salmon with roasted vegetables (broccoli, peppers, zucchini), quinoa, and a lemon-herb dressing.
- Tuesday: Lentil soup with whole-wheat bread, a side salad with olive oil and lemon juice.
- Wednesday: Chicken breast with Mediterranean-style salad (tomatoes, cucumbers, olives), whole-wheat pita bread.
- Thursday: Baked chicken breast with roasted vegetables, couscous.
- Friday: Shrimp scampi with zucchini noodles and a side salad.
- Saturday: Leftovers and a simple vegetable and fruit plate.
- Sunday: Homemade pasta with marinara sauce and vegetables.
Potential Risks and Considerations
Following a specific diet for multiple sclerosis (MS) can be a powerful tool for symptom management. However, restrictive dietary approaches can carry potential risks if not carefully considered and implemented. It’s crucial to approach dietary changes for MS with caution, ensuring they align with individual needs and are overseen by healthcare professionals. This section will explore potential pitfalls, highlight the importance of balanced nutrition, and emphasize the necessity of personalized guidance.
Potential Risks of Restrictive Diets
Restrictive diets, while potentially beneficial in some cases, can lead to significant nutrient deficiencies if not carefully planned. Eliminating entire food groups without proper consultation can disrupt the body’s ability to absorb essential vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients necessary for overall health and well-being. This can lead to complications that may not be immediately apparent but can have long-term consequences.
For instance, an extreme low-carb diet might provide initial symptom relief but could also cause deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals obtained primarily from carbohydrates, potentially worsening MS symptoms in the long run.
Potential Nutrient Deficiencies
Proper nutrition is vital for maintaining overall health and supporting the body’s immune system, which can be compromised in individuals with MS. Dietary changes for MS should prioritize a balanced approach, ensuring adequate intake of all essential nutrients. A deficiency in any of these nutrients can have detrimental effects on physical and cognitive function, and may even exacerbate MS symptoms.
It’s crucial to understand the potential nutrient deficiencies that can arise from restrictive diets and how to address them.
Importance of Consulting Healthcare Professionals
Before making any significant dietary changes, consulting with a healthcare professional is absolutely essential. A registered dietitian or your neurologist can assess your individual nutritional needs, current health status, and potential risks associated with dietary restrictions. They can guide you in developing a personalized dietary plan that aligns with your MS management strategy, addressing specific needs and concerns while avoiding nutrient deficiencies.
This individualized approach is crucial for maximizing the benefits of dietary interventions while minimizing potential harm.
Common Nutrient Deficiencies and Potential Symptoms
The table below Artikels some common nutrient deficiencies and their potential symptoms. This is not an exhaustive list, and the specific symptoms may vary depending on the individual. It is imperative to consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and personalized recommendations.
| Nutrient Deficiency | Potential Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Vitamin B12 | Fatigue, weakness, neurological problems (e.g., numbness, tingling), anemia |
| Iron | Fatigue, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, dizziness |
| Calcium | Bone pain, osteoporosis, muscle cramps, tingling |
| Vitamin D | Muscle weakness, bone pain, fatigue, increased risk of infections |
| Magnesium | Muscle cramps, fatigue, weakness, irregular heartbeat |
| Fiber | Constipation, digestive issues, increased risk of cardiovascular problems |
Importance of Individualized Dietary Plans, Diet as major ms treatment
Developing an individualized dietary plan for MS is critical. A one-size-fits-all approach to diet is unlikely to be effective. Each individual’s MS presentation, symptoms, and overall health status are unique, necessitating tailored dietary recommendations. A personalized plan accounts for specific needs, preferences, and potential risks, maximizing the benefits of dietary interventions while minimizing the likelihood of nutrient deficiencies.
For example, an individual with a history of digestive issues may require a different approach to dietary fiber intake than someone without such concerns.
Concluding Remarks

In conclusion, diet plays a vital role in managing MS. While a personalized approach is essential, adopting a healthy, balanced diet rich in specific nutrients, coupled with proper hydration and mindful eating, can potentially alleviate MS symptoms and enhance overall quality of life. This comprehensive guide equips you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of dietary interventions for MS, enabling you to make informed choices about your health journey.
Remember to consult with your healthcare team for personalized advice and guidance.

