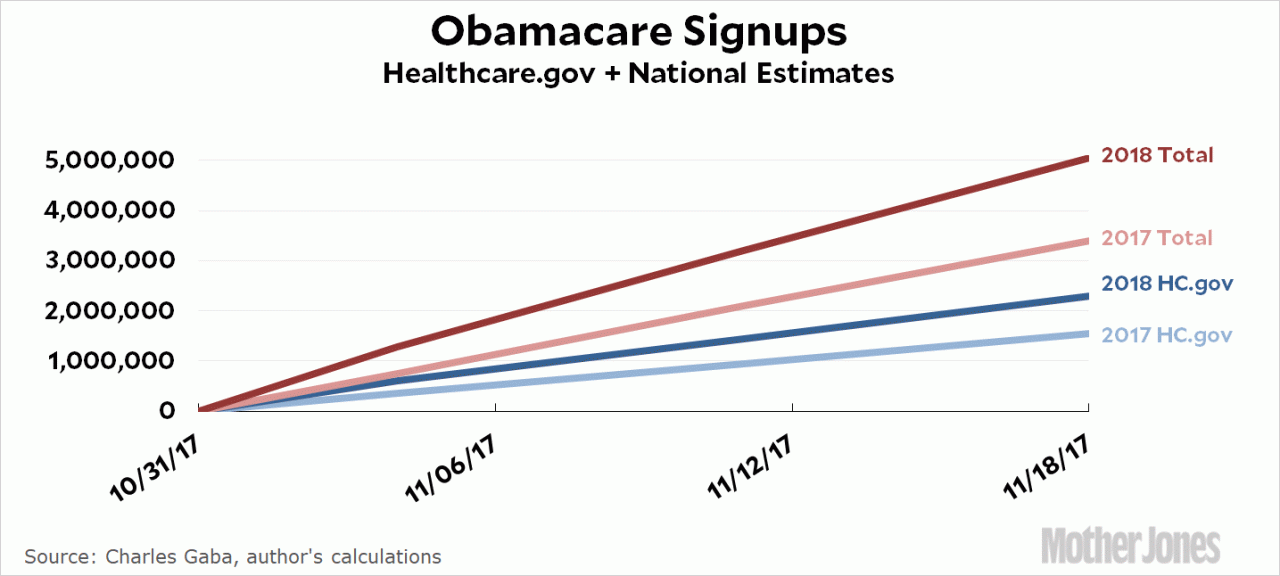
Do we need to create sanctuary hospitals? This complex question explores the potential for specialized healthcare facilities designed to address the unique needs of vulnerable populations. These facilities would differ from conventional hospitals, prioritizing compassion, accessibility, and culturally sensitive care. The discussion delves into potential benefits, challenges, existing models, resource allocation, public perception, and policy considerations.
The need for sanctuary hospitals stems from a growing recognition of healthcare disparities and the need for more holistic, patient-centered care. Examining various aspects, from funding to staffing, will shed light on the potential viability and impact of such facilities.
Defining Sanctuary Hospitals
Sanctuary hospitals represent a growing concept in healthcare, aiming to create a safe and supportive environment for patients, particularly those facing social or systemic challenges. They go beyond traditional medical care by addressing the broader needs of their patients, recognizing that health is intertwined with social determinants of well-being. This model acknowledges that access to care can be affected by factors like legal status, socioeconomic circumstances, or cultural background.Sanctuary hospitals are distinct from traditional hospitals in their core philosophy and approach to care.
They prioritize compassion and inclusivity, striving to create a welcoming and non-judgmental environment where patients feel safe and respected. This includes minimizing barriers to access, fostering trust, and empowering patients through education and support.
Key Characteristics of Sanctuary Hospitals
Sanctuary hospitals are characterized by several key principles. They are committed to providing comprehensive care, encompassing not only physical health but also mental health, social needs, and legal assistance when necessary. Crucially, these hospitals are designed to mitigate potential barriers to care, such as immigration status or financial instability. This approach aims to address the root causes of health disparities and improve overall health outcomes.
Types of Sanctuary Hospitals
While a standardized model doesn’t exist, sanctuary hospitals can be tailored to specific demographics or conditions. For example, a sanctuary hospital might specialize in serving undocumented immigrants, providing culturally sensitive care and legal support. Alternatively, a sanctuary hospital could focus on patients with mental health conditions, offering specialized therapeutic services in a safe, non-judgmental environment. Furthermore, hospitals might choose to focus on specific populations experiencing unique barriers, such as homeless individuals or victims of domestic violence.
The debate around sanctuary hospitals feels increasingly urgent. While we grapple with the complex issue of providing safe spaces for those struggling with addiction, innovative treatments like implantable drugs, as detailed in this fascinating article on implantable drugs changing addiction treatment , are rapidly changing the landscape. Ultimately, the question of sanctuary hospitals might need to be re-evaluated in light of these breakthroughs, considering the potential for more effective, less stigmatizing care.
Such targeted approaches are vital in meeting the specific needs of vulnerable populations.
Comparison of Sanctuary Hospitals and Traditional Hospitals
| Characteristic | Sanctuary Hospitals | Traditional Hospitals |
|---|---|---|
| Patient Care | Holistic, encompassing physical, mental, and social well-being; addresses social determinants of health; prioritizes patient safety and dignity. | Primarily focused on physical health; may address some social needs but not a central focus. |
| Staffing | Often includes social workers, legal advocates, and cultural liaisons to support patients’ complex needs. | Primarily staffed with medical professionals. |
| Funding | May rely on a combination of traditional hospital funding, grants, and philanthropic donations, as well as innovative funding models. | Primarily funded through patient charges, insurance reimbursements, and government funding. |
| Accessibility | Dedicated efforts to remove barriers to care for vulnerable populations. | May have some policies or procedures in place but may not actively address barriers to care. |
| Patient Experience | Creates a welcoming, non-judgmental, and inclusive environment to promote patient trust and comfort. | May vary depending on the hospital and the patient population. |
Potential Benefits of Sanctuary Hospitals

Sanctuary hospitals, designed with specific provisions for vulnerable populations, offer a unique opportunity to improve healthcare access and outcomes. By creating a safe and welcoming environment, these institutions can foster trust and encourage patients to seek necessary care, potentially leading to better health outcomes and a stronger public health system overall. They address the critical need for compassionate and culturally sensitive care for those who might otherwise face barriers to accessing essential medical services.These hospitals, beyond just offering physical care, strive to address the social determinants of health, recognizing that factors like poverty, discrimination, and lack of transportation can significantly impact a person’s ability to maintain their well-being.
By creating a supportive environment, sanctuary hospitals aim to create a system where all individuals, regardless of their background, can receive the care they need.
Advantages for Patients
Patients often face significant barriers to accessing healthcare, including financial constraints, language difficulties, and cultural differences. Sanctuary hospitals are designed to mitigate these barriers. A welcoming and understanding environment encourages patients to engage in their care and adhere to treatment plans, leading to improved health outcomes. This is especially important for patients with complex medical needs or those from marginalized communities, who may have faced prior negative experiences in the healthcare system.
The empathetic approach often leads to increased patient satisfaction and trust in the healthcare provider.
Thinking about sanctuary hospitals feels weighty, doesn’t it? But maybe we can find some small, comforting moments amidst the big questions. Consider the soothing aromas of holiday spices, like cinnamon and nutmeg, which can foster a sense of calm and well-being. Exploring these spices for festive self-care might just offer a helpful parallel to creating a space of healing, like a sanctuary hospital.
holiday spices for festive self care can be a surprisingly effective way to nurture ourselves, mirroring the healing potential we might find in a dedicated hospital space. Ultimately, the question of sanctuary hospitals remains, but maybe focusing on self-care can be a good stepping stone.
Improved Healthcare Access and Outcomes for Vulnerable Populations
Sanctuary hospitals actively address the unique needs of vulnerable populations, such as refugees, undocumented immigrants, and individuals experiencing homelessness. These hospitals provide culturally competent care, ensuring that language barriers and cultural sensitivities are addressed. This approach fosters a sense of trust and safety, encouraging participation in preventative screenings and follow-up care. Examples of improved outcomes include increased rates of vaccination, early detection of chronic diseases, and improved adherence to medication regimens.
Early intervention and preventative care are crucial for managing chronic diseases effectively.
Positive Impact on Public Health
Sanctuary hospitals can significantly contribute to public health by providing comprehensive care and preventive services to underserved communities. For example, by offering vaccination programs, they can help prevent the spread of infectious diseases. This preventative approach reduces the strain on the wider healthcare system and minimizes the potential for outbreaks. Furthermore, by addressing social determinants of health, sanctuary hospitals can contribute to a healthier community overall, fostering a cycle of wellness and community engagement.
Improved access to healthcare can lead to reduced healthcare disparities and a healthier community.
Potential Benefits Table
| Stakeholder | Potential Benefit |
|---|---|
| Patients | Increased access to care, improved health outcomes, culturally sensitive care, reduced fear and mistrust, and improved patient satisfaction. |
| Staff | Enhanced professional development through exposure to diverse patient populations, improved job satisfaction from a more meaningful work experience, increased cultural competency, and the ability to make a significant impact on the lives of others. |
| Community | Reduced healthcare disparities, improved public health outcomes, increased community well-being, and a more equitable and inclusive healthcare system. |
Challenges and Considerations

Establishing sanctuary hospitals, while a noble goal, faces significant hurdles. Navigating complex legal landscapes, securing sustainable funding, and addressing ethical dilemmas are crucial aspects to consider before implementing such a model. The potential benefits must be carefully weighed against the challenges to ensure the long-term viability and effectiveness of these institutions.The creation of a sanctuary hospital isn’t simply a matter of building a facility.
It requires careful planning, thorough legal review, and a comprehensive understanding of the ethical implications. Understanding these considerations is paramount for ensuring the successful implementation of such a crucial initiative.
Potential Obstacles in Establishing and Operating Sanctuary Hospitals
Implementing a sanctuary hospital model presents a multitude of obstacles. These obstacles range from securing sufficient funding to navigating complex legal and regulatory frameworks. The success of such an initiative depends heavily on addressing these potential roadblocks proactively.
- Securing adequate funding is a significant challenge. Sanctuary hospitals often require specialized equipment and staff, adding to the financial burden. Finding reliable and consistent funding sources is crucial for sustainability.
- Attracting and retaining qualified medical personnel is essential. Doctors and nurses specializing in the care of vulnerable populations are often in high demand, making recruitment and retention difficult.
- Navigating legal and regulatory frameworks can be complex. Hospitals must comply with existing regulations regarding patient care, data privacy, and emergency protocols. Potential legal challenges related to patient confidentiality and treatment protocols require careful consideration and proactive legal strategies.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are paramount in the establishment of a sanctuary hospital. Ensuring equitable access, protecting patient confidentiality, and maintaining a commitment to high-quality care are essential ethical principles. A thorough ethical framework is crucial for the hospital’s success.
- Defining the scope of services offered is critical. Sanctuary hospitals must carefully delineate the types of cases they will accept, considering the potential strain on resources and the ethical implications of turning away patients.
- Ensuring equitable access for all patients is paramount. The hospital must establish a system that prioritizes those most in need while maintaining fairness and avoiding discrimination.
- Protecting patient confidentiality is essential. Strict protocols must be implemented to safeguard patient information and maintain trust.
Potential Legal and Regulatory Hurdles
Legal and regulatory frameworks present significant challenges. Hospitals must comply with existing laws and regulations while navigating the complexities of international and domestic legal systems. Careful legal counsel is essential.
- Varying legal standards across jurisdictions can create difficulties in operating a sanctuary hospital. The hospital must be aware of and comply with the specific regulations of each jurisdiction where it provides services.
- Compliance with data privacy regulations is critical. Robust data security measures must be in place to protect patient information and adhere to applicable privacy laws.
- Navigating complex immigration laws and policies can pose considerable challenges. Understanding and complying with these laws is crucial for the smooth operation of a sanctuary hospital.
Funding Models and Their Potential Impact
Various funding models can be considered, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The chosen model significantly impacts the hospital’s sustainability and long-term success.
- Government funding, while potentially stable, may come with restrictions and regulations. The level of funding and the conditions attached can significantly influence the hospital’s operational freedom.
- Private philanthropy can provide a substantial source of funding but may be subject to fluctuations and specific conditions. Maintaining consistent philanthropic support is crucial for long-term sustainability.
- Partnerships with NGOs and international organizations can leverage diverse resources and expertise. However, such collaborations might introduce complexities in governance and decision-making.
Table of Potential Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
| Potential Challenges | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|
| Securing adequate funding | Explore diverse funding sources, develop strong fundraising strategies, and seek partnerships. |
| Attracting qualified personnel | Develop competitive compensation and benefits packages, offer specialized training, and promote the hospital as a desirable work environment. |
| Navigating legal and regulatory frameworks | Engage with legal experts to ensure compliance, establish clear protocols, and build strong relationships with relevant authorities. |
| Ensuring equitable access | Develop a transparent and fair patient intake system, implement clear criteria for prioritization, and ensure accessibility to information and resources. |
| Protecting patient confidentiality | Implement robust data security measures, train staff on confidentiality protocols, and adhere to strict privacy regulations. |
Existing Models and Examples
The concept of a sanctuary hospital isn’t entirely novel. Elements of compassionate care and specialized support exist within various healthcare models globally. Examining these existing models can offer valuable insights into designing and implementing sanctuary hospitals, highlighting successful approaches and potential pitfalls. Learning from past experiences and adapting existing structures can help streamline the process of creating a new model that prioritizes the well-being of individuals experiencing hardship and vulnerability.
Inspiration from Existing Healthcare Models
Several existing healthcare models offer valuable inspiration for creating sanctuary hospitals. These models demonstrate how compassion, specialized support, and tailored care can significantly improve patient outcomes. They often prioritize holistic well-being, addressing the physical, mental, and social needs of patients, rather than focusing solely on the medical condition.
Characteristics of Successful Initiatives
Successful initiatives in providing compassionate care share several key characteristics. These include a strong emphasis on patient-centered care, a commitment to cultural competency, and the integration of social support services. Furthermore, successful initiatives often foster strong interdisciplinary collaboration among healthcare professionals, social workers, and community partners. Effective communication and a collaborative approach are crucial for addressing the multifaceted needs of vulnerable individuals.
Examples of Existing Models
The following table Artikels several existing healthcare models, illustrating their key features and how they relate to the concept of sanctuary hospitals. Each model provides a unique perspective on incorporating compassionate care into the broader healthcare system.
The debate around sanctuary hospitals is intense. While many advocate for specialized care, considering conditions like Epstein-Barr virus and its potential link to multiple sclerosis symptoms is crucial. Epstein barr multiple sclerosis symptoms are complex and often misunderstood, making dedicated care for those affected essential. Ultimately, the question of whether we need sanctuary hospitals hinges on providing comprehensive and compassionate care for these challenging conditions.
| Model Name | Key Features | Relevance to Sanctuary Hospitals |
|---|---|---|
| Community Health Centers | Often located in underserved communities, offering comprehensive primary care, dental, and mental health services. Emphasize culturally sensitive care and access to resources. | Demonstrates accessibility and holistic care, crucial for a sanctuary hospital’s mission. Can provide a framework for integrating social services and addressing socioeconomic factors impacting health. |
| Refugee/Migrant Health Clinics | Specialized clinics catering to the unique healthcare needs of refugee and migrant populations. Often include language assistance, cultural sensitivity training, and trauma-informed care. | Highlight the importance of cultural sensitivity, language support, and trauma-informed care for sanctuary hospitals serving marginalized groups. |
| Free Clinics | Provide low-cost or free healthcare services to individuals who cannot afford traditional care. Often staffed by volunteer providers. | Demonstrate the feasibility of providing accessible care, even with limited resources. Highlight the role of volunteerism and community involvement in supporting sanctuary hospitals. |
| Patient Navigation Programs | Provide support and guidance to patients throughout their healthcare journey, particularly those with complex needs or limited resources. | Demonstrate the value of patient navigation in supporting patients’ access to resources and services essential for sanctuary hospitals. |
Addressing Challenges in Existing Models
While these models offer valuable lessons, each faces unique challenges. For example, resource constraints, staffing shortages, and a lack of coordination between healthcare providers and social service agencies can hinder their effectiveness. Furthermore, some models struggle to address the root causes of health disparities, focusing instead on immediate symptoms. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for creating a truly effective sanctuary hospital model.
Resource Allocation and Staffing
Sanctuary hospitals, by their very nature, require a unique approach to resource allocation and staffing. They must prioritize the needs of vulnerable populations while maintaining the high standards of care expected in any hospital setting. This necessitates careful planning and consideration of both financial resources and human capital. Effective resource management ensures the hospital can meet the complex needs of its patients without compromising quality or accessibility.
Effective Resource Allocation Strategies
Resource allocation in a sanctuary hospital requires a holistic approach that considers the specific needs of the patients. This involves careful budgeting and prioritization, ensuring that funds are allocated efficiently to essential services, such as mental health support, legal aid, and language interpretation. For instance, a portion of the budget could be earmarked for a dedicated social work team specializing in refugee resettlement and trauma care.
The hospital should also prioritize the purchase of equipment and supplies necessary to accommodate the diverse needs of patients.
Staffing Needs and Solutions
The staffing needs of a sanctuary hospital are multifaceted, demanding a diverse range of skills and expertise. This includes clinicians with experience in treating trauma, mental health professionals skilled in cultural competency, and legal aid professionals. To meet these needs, the hospital might consider employing a multidisciplinary team approach. This involves recruiting specialists with backgrounds in trauma care, mental health, and immigration law, alongside generalist medical staff.
Furthermore, establishing clear communication channels between different departments ensures seamless coordination of care. Interprofessional education and collaboration can also be implemented to enhance teamwork and address complex needs.
Volunteer and Community Partnerships
Volunteers play a vital role in supporting the operations of a sanctuary hospital. They can provide essential assistance with administrative tasks, translation services, and patient support. For example, trained volunteers can offer companionship to patients, assist with navigating the healthcare system, and provide emotional support. Community partnerships are equally crucial. Local organizations and NGOs can be valuable resources for providing specialized services and connecting patients with necessary resources.
Collaborating with community groups, like social service agencies, can significantly broaden the hospital’s support network.
Staff Roles and Responsibilities
| Staff Role | Primary Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Medical Director | Oversees the overall medical operations of the hospital, including policy development and resource allocation. |
| Trauma Specialist | Provides specialized care to patients experiencing trauma, integrating psychological support with physical treatment. |
| Mental Health Counselor | Provides counseling services, addressing mental health needs and providing support for patients experiencing trauma. |
| Legal Aid Advocate | Assists patients with legal matters, such as immigration processes and accessing legal resources. |
| Social Worker | Conducts assessments, provides case management, and links patients with community resources. |
| Language Interpreter | Facilitates communication between patients and healthcare providers, ensuring clear understanding of medical information and procedures. |
| Administrative Staff | Manages the daily operations of the hospital, including scheduling, record-keeping, and financial administration. |
Public Perception and Acceptance
The public’s perception of sanctuary hospitals will be crucial to their success. A positive reception can lead to increased patient volume and community support, while negative perceptions could hinder their establishment and utilization. Understanding the potential anxieties and concerns surrounding these facilities is essential for developing effective strategies to promote understanding and acceptance. Careful planning and community engagement are paramount in fostering trust and ensuring these hospitals become vital resources for vulnerable populations.Public perception hinges on trust and understanding.
Many potential anxieties exist, from questions about the quality of care to concerns about the financial burden on the community. Addressing these head-on, through transparent communication and community involvement, will be vital to building support. A well-structured communication strategy, emphasizing the unique benefits and the importance of the service, will be necessary to counter potential misgivings.
Potential Concerns and Anxieties
Public concerns surrounding sanctuary hospitals may stem from misconceptions about the nature of the services offered and the financial implications. Concerns about the quality of care, particularly for those with complex medical needs, are also likely. Fear of stigmatization for patients seeking care at these hospitals also needs careful consideration. Misunderstandings about the purpose and mission of these hospitals could also lead to public skepticism and resistance.
Understanding these anxieties is the first step towards mitigating them.
Strategies for Promoting Understanding and Acceptance
Building trust and support requires a multi-faceted approach. Transparent communication about the hospital’s mission, services, and patient care is essential. Highlighting the positive impact these hospitals can have on vulnerable communities is crucial. Community outreach programs, workshops, and educational campaigns can help address misinformation and promote understanding. Active involvement with local organizations and leaders will foster relationships and dispel fears.
Importance of Community Engagement and Outreach
Community engagement is paramount to gaining public trust and acceptance. Direct interaction with residents, community leaders, and healthcare professionals is essential. Open forums, town hall meetings, and presentations at local organizations can facilitate dialogue and answer questions. Utilizing social media and local media to share information and address concerns directly is also vital. By actively listening to and addressing community concerns, the hospital can build trust and foster a sense of shared responsibility for the well-being of the community.
Strategies for Building Public Trust and Support
| Strategy | Description | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Transparent Communication | Clearly articulate the hospital’s mission, services, and patient care protocols. | Increased understanding and reduced speculation. |
| Community Outreach Programs | Organize workshops, presentations, and forums to educate the community about sanctuary hospitals. | Enhanced public knowledge and dispel misconceptions. |
| Collaboration with Local Organizations | Partner with community groups, healthcare providers, and local leaders. | Enhanced credibility and support from trusted sources. |
| Active Listening and Response | Actively solicit and respond to community feedback and concerns. | Increased public trust and sense of ownership. |
| Media Engagement | Utilize local media channels to disseminate information, address concerns, and highlight success stories. | Wider public awareness and improved reputation. |
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks: Do We Need To Create Sanctuary Hospitals
Establishing sanctuary hospitals requires a supportive policy environment. This involves navigating existing regulations and crafting new ones that encourage and facilitate the creation of these specialized facilities. A well-defined policy framework will address critical aspects like funding, staffing, patient access, and ethical considerations. The goal is to create a system that fosters a compassionate and equitable healthcare system for all.
Necessary Policy Changes
Several policy changes are essential to support the creation of sanctuary hospitals. These changes must address the specific needs of these facilities, while respecting existing healthcare structures and protocols. Key areas for policy adjustments include funding mechanisms, regulatory approvals, and streamlined processes for patient access. Changes in these areas will help in ensuring that patients receive the best possible care, regardless of their ability to pay.
Examples of Successful Policy Implementations
Successful policy implementations in other healthcare sectors offer valuable lessons. The implementation of telemedicine programs, for example, has shown how policy changes can expand access to care, particularly in underserved areas. Similarly, initiatives to improve mental health access demonstrate the potential of targeted policy interventions. These examples highlight the positive impact of proactive policy adjustments on patient outcomes and healthcare accessibility.
Role of Government and Regulatory Bodies
Government and regulatory bodies play a crucial role in facilitating the establishment of sanctuary hospitals. Their involvement extends to providing funding, streamlining regulatory processes, and ensuring compliance with ethical standards. Clear guidelines and support from these bodies are vital for the successful operation of these facilities. The government’s role is essential in creating a conducive environment for innovation and equitable access to healthcare.
Impact of Policies on Patient Access
Policies significantly influence patient access to sanctuary hospitals. Policies that prioritize affordability and accessibility, such as subsidized care or simplified admission processes, will directly impact the number of patients who can utilize these services. Conversely, policies that create barriers, like complex bureaucratic procedures, will limit access and potentially exclude vulnerable populations. The policies in place will ultimately determine who can benefit from these specialized facilities.
Potential Policy Changes and Their Impact, Do we need to create sanctuary hospitals
| Potential Policy Change | Impact on Patients | Impact on Hospitals | Impact on Government/Regulators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subsidized care for qualifying patients | Increased access for low-income individuals | Potential for increased patient volume and potential strain on resources | Increased financial burden on government, but potential for long-term cost savings |
| Streamlined admission processes | Faster access to care, reducing wait times | Improved efficiency and potentially reduced administrative costs | Reduced administrative burden on regulatory bodies |
| Dedicated funding for sanctuary hospitals | Ensured provision of necessary resources and services | Enhanced ability to maintain high-quality care | Increased government investment in healthcare |
Financial Sustainability
Sanctuary hospitals, by their very nature, prioritize compassionate care over maximizing profit. This fundamental shift necessitates a unique approach to financial sustainability. Traditional healthcare models often rely on revenue from procedures and services, a model that may not fully support the holistic, long-term needs of a sanctuary hospital. Finding the right funding mechanisms is critical for ensuring the continued provision of these vital services.
Funding Models for Sanctuary Hospitals
Different funding models are suitable for various situations. A diversified approach, blending public and private sources, is often the most resilient. This allows the hospital to leverage the strengths of each funding stream. Public funding, often through government grants or subsidies, can provide crucial baseline support, while private donations, including individual contributions and philanthropic giving, can fill in gaps and offer flexibility.
Revenue generated from patient care, while not the primary source, can also play a vital role in sustaining operations.
Public Funding Considerations
Public funding for sanctuary hospitals needs careful consideration. Governments may be more inclined to support facilities that demonstrably meet specific public health needs, such as those catering to vulnerable populations or providing unique, specialized care. A clear articulation of the hospital’s mission, services, and projected impact on the community is essential when seeking public funding. Demonstrating a positive return on investment in terms of community health outcomes and reduced healthcare burdens can strengthen the case for public support.
Private Donations and Philanthropy
Private donations and philanthropic giving can play a critical role in supporting sanctuary hospitals. These donations can fund specific programs, equipment, or even the operating budget. Building strong relationships with philanthropic organizations and individuals is crucial. Effective fundraising strategies, including compelling narratives, community engagement, and showcasing the hospital’s impact, are key to securing private support. Examples of successful fundraising campaigns in other non-profit healthcare contexts can be instructive.
Examples of Successful Financial Models
Many non-profit hospitals, particularly those focused on underserved communities, have developed successful financial models. These models often incorporate a mix of public funding, private donations, and patient fees. For example, some hospitals have established partnerships with community organizations to leverage local resources and expertise. Other successful models have found innovative ways to raise funds, like establishing endowment funds to provide long-term financial security.
Potential Sources of Funding and Corresponding Amounts (Estimated)
| Source of Funding | Estimated Amount (USD) |
|---|---|
| Government Grants/Subsidies | $500,000 – $1,000,000 |
| Private Donations | $250,000 – $500,000 |
| Patient Care Revenue | $200,000 – $500,000 |
| Endowment Funds/Investments | $100,000 – $250,000 |
| Fundraising Campaigns | Variable |
Note: These figures are estimates and will vary significantly based on the specific location, size, and services of the sanctuary hospital.
Potential Impacts on Existing Healthcare System
The emergence of sanctuary hospitals presents a complex interplay with the existing healthcare infrastructure. These specialized facilities, designed to address specific needs and often lacking in traditional hospitals, could potentially reshape resource allocation, patient flow, and even healthcare policy. Understanding these potential impacts is crucial for a comprehensive evaluation of sanctuary hospitals.
Resource Allocation Effects
The establishment of sanctuary hospitals could lead to shifts in resource allocation within the overall healthcare system. Existing hospitals might see a decrease in patients requiring specialized care offered by sanctuary hospitals. This redistribution could impact the staffing levels, equipment utilization, and overall financial stability of traditional hospitals. Conversely, sanctuary hospitals will likely require dedicated resources, including specialized staff, equipment, and potentially new infrastructure, potentially affecting overall system capacity.
This shift in demand necessitates careful planning and forecasting to avoid exacerbating existing resource constraints or creating new imbalances.
Patient Flow Implications
Patient flow dynamics will be significantly altered by the introduction of sanctuary hospitals. Patients with specific needs, often underserved or facing systemic barriers in accessing care, will likely be directed to these facilities. This could lead to increased efficiency in addressing those specific needs. However, it also raises concerns about potential congestion or delays in accessing care at traditional hospitals, particularly if the referral process is not streamlined.
Effective communication and collaboration between sanctuary hospitals and existing healthcare providers are essential to ensure smooth patient flow and avoid unnecessary delays.
Potential Collaborations and Partnerships
To optimize the benefits and mitigate potential challenges, collaborations between existing hospitals and sanctuary hospitals are essential. Joint training programs for staff, shared protocols for patient referral and transfer, and coordinated research efforts can enhance the overall quality and effectiveness of the healthcare system. Partnerships can facilitate knowledge sharing and resource optimization. For instance, existing hospitals could offer training programs for sanctuary hospital staff in areas like general care, while sanctuary hospitals could offer expertise in specialized areas.
This shared learning can contribute to the overall enhancement of patient care across the system.
Influence on Healthcare Policy
The introduction of sanctuary hospitals could influence healthcare policy in several ways. The development of specific policies regarding patient referral pathways, funding mechanisms for sanctuary hospitals, and the integration of their services into the existing healthcare network will be essential. For instance, policies could be developed to address the ethical considerations regarding the allocation of resources and access to care.
Policymakers must consider the potential long-term impacts of these facilities on healthcare accessibility, equity, and sustainability.
Potential Impacts on the Existing Healthcare System
| Impact Area | Potential Positive Impact | Potential Negative Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Allocation | Potential for more efficient use of resources, especially specialized ones. | Possible strain on resources in traditional hospitals due to patient diversion. |
| Patient Flow | Streamlined care for specific needs, reduced wait times for specialized care. | Potential for increased congestion and delays in traditional hospitals if referral process is not well-managed. |
| Collaboration | Improved patient outcomes through shared knowledge and expertise. | Potential for bureaucratic hurdles and difficulties in establishing effective partnerships. |
| Policy | Development of targeted policies to address specific healthcare needs. | Potential for unintended consequences if policies are not carefully considered. |
Final Wrap-Up
Ultimately, the question of whether to create sanctuary hospitals is multifaceted, requiring careful consideration of potential benefits, challenges, and ethical implications. A thorough understanding of existing models and resource allocation strategies is crucial. Public perception and policy changes will play a significant role in the success of such facilities. While challenges remain, the potential for improving healthcare access and outcomes for vulnerable populations warrants further exploration.