Drugs that can cause erectile dysfunction are surprisingly common, affecting men’s sexual health. This comprehensive exploration dives into the various medications, their mechanisms, and how they impact erectile function. From cardiovascular drugs to antidepressants, we’ll uncover the surprising ways certain medications can lead to ED, examining the dosage, duration, and frequency of this side effect.
Understanding the link between specific medications and erectile dysfunction is crucial for informed decision-making. This article provides a detailed overview, exploring the underlying mechanisms and helping you understand how your choices might influence your sexual health.
Introduction to Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Erectile dysfunction (ED), often referred to as impotence, is a common sexual health concern affecting men of all ages. It’s characterized by the consistent inability to achieve or maintain an erection firm enough for satisfactory sexual intercourse. While ED can be a distressing condition, it’s important to understand that it’s treatable and often manageable with various options. Its prevalence increases with age, but it can affect men at any stage of life.Erectile dysfunction can stem from a complex interplay of physiological and psychological factors.
Physical causes include vascular diseases like atherosclerosis, neurological disorders such as multiple sclerosis, and hormonal imbalances like low testosterone levels. Psychological factors like stress, anxiety, depression, and relationship problems can also significantly contribute to ED. In many cases, a combination of these factors is at play.Common symptoms associated with ED include difficulty achieving an erection, maintaining an erection during intercourse, or a complete inability to achieve an erection.
These symptoms can vary in severity and frequency. It’s crucial to remember that occasional difficulties are normal, but consistent issues warrant a consultation with a healthcare professional.Treatment options for ED are diverse and often tailored to the individual’s underlying cause. Lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques, can play a crucial role.
Pharmaceutical treatments, such as oral medications, are often effective. Other options include vacuum erection devices, penile implants, and counseling.
Comparison of ED Treatments
Understanding the various treatment options available for erectile dysfunction requires a careful consideration of their effectiveness and potential side effects. The table below summarizes common treatments and their characteristics.
| Treatment | Effectiveness | Common Side Effects | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oral Medications (e.g., sildenafil, tadalafil) | Generally highly effective for many men. Studies show significant improvement in achieving and maintaining erections. | Headache, flushing, nasal congestion, visual disturbances (rare). May interact with certain medications. | Requires a prescription and may not be suitable for all individuals. Important to discuss potential interactions with other medications with a doctor. |
| Vacuum Erection Devices (VEDs) | Effective for many men, providing a mechanical method to achieve an erection. | Pain, bruising, discomfort at the base of the penis. Possible infection if not used properly. | Requires practice and understanding of proper use. May not be suitable for all individuals or all situations. |
| Penile Implants | Permanent solution for achieving erections, offering the most reliable results for some men. | Infection, mechanical failure, pain or discomfort in the penis, scarring. | Significant surgical procedure. Should only be considered after other treatment options have been explored. |
| Counseling/Therapy | Can be highly effective in addressing psychological factors contributing to ED. This approach focuses on identifying and managing underlying anxieties, stress, or relationship issues. | No significant physical side effects. May require time and effort. | Often a combination of treatments can be most effective, combining psychological support with other medical solutions. |
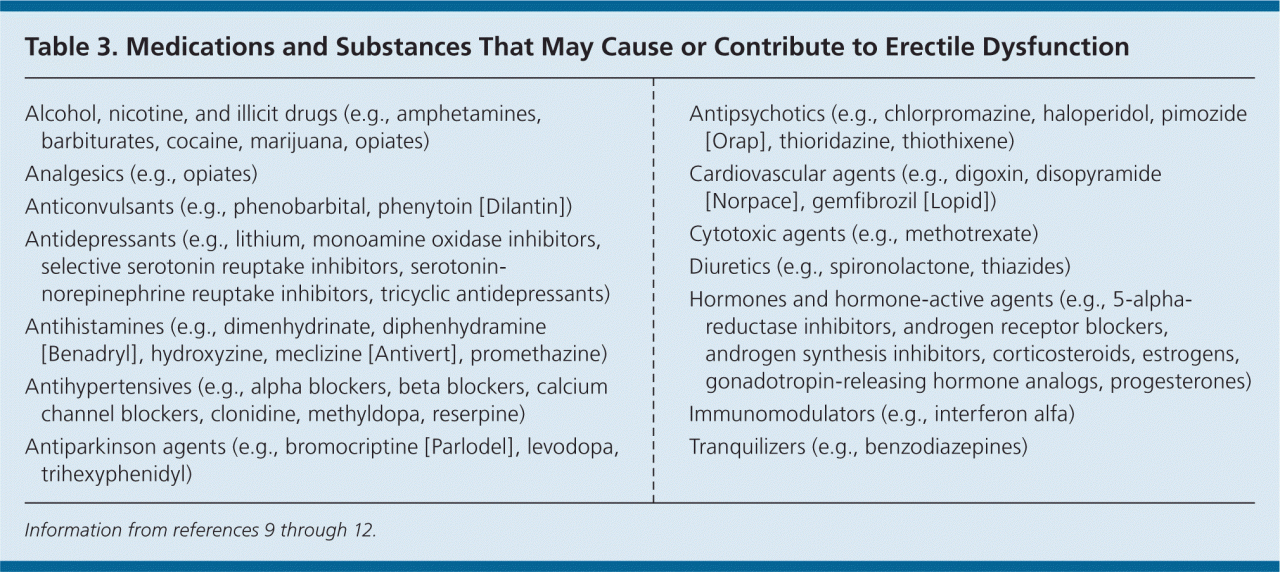
Medications Causing Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can unfortunately arise as a side effect of various medications. Understanding the connection between specific drugs and potential ED is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. This knowledge empowers informed decision-making regarding treatment options and potential alternatives.
Cardiovascular Medications
Many medications used to manage cardiovascular conditions, such as high blood pressure and cholesterol, can negatively impact erectile function. These drugs often affect the delicate balance of neurochemicals and blood flow essential for achieving and maintaining an erection. Beta-blockers, for example, can interfere with the nervous system’s signal transmission to the penis, thereby reducing blood flow. Certain diuretics can also deplete the body of essential fluids, which indirectly affects blood circulation.
- Beta-blockers, particularly non-selective ones, are frequently associated with ED. The frequency of reported ED varies significantly between different types of beta-blockers, and individual responses can differ.
- ACE inhibitors and ARBs, while not as commonly linked to ED as beta-blockers, can sometimes contribute to the problem. Reports of ED in patients using these drugs are generally less frequent than with beta-blockers.
- Diuretics, while often necessary for managing fluid retention, can sometimes have a negative impact on erectile function by reducing blood volume and potentially affecting hormonal levels.
Antidepressants
Certain antidepressants, particularly selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), are known to have ED as a potential side effect. The mechanism behind this is complex, involving disruptions in neurotransmitter balance, which can affect the nerve impulses required for proper erectile function.
- SSRIs are frequently associated with ED, often reported as a moderate to mild issue, although the specific frequency of occurrence varies greatly between different individuals.
- TCAs, due to their broader effect on neurotransmitter systems, may exhibit a higher frequency of ED reports compared to SSRIs, though individual responses remain highly variable.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines, while primarily used to treat allergies, can also contribute to ED in some cases. Some antihistamines, especially those with strong sedative properties, can interfere with the normal functioning of the nervous system, impacting nerve signals to the penis.
- First-generation antihistamines, which tend to have more pronounced sedative effects, may show a higher association with ED. The frequency of this side effect is generally lower than with the other classes mentioned.
Dosage and Duration
The dosage and duration of medication use can significantly influence the risk of ED. Higher doses and longer durations of treatment generally correlate with a greater likelihood of experiencing ED. For instance, a patient taking a high dose of a beta-blocker for an extended period might be more susceptible to ED compared to someone taking a lower dose for a shorter time.
Individual responses, however, can vary.
Certain medications, unfortunately, can impact sexual function, like those used in cancer treatment. My own two decade journey with cancer immunotherapy, my two decade journey with cancer immunotherapy , highlighted the often-unforeseen side effects of powerful drugs. These side effects can sometimes include erectile dysfunction, which is important to discuss with your doctor. It’s crucial to be aware of potential drug interactions and their impact on overall health.
Summary Table
| Medication | Class | Potential Side Effects (Including ED) | Frequency of Reports |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beta-blockers (e.g., Propranolol) | Cardiovascular | Fatigue, dizziness, depression, erectile dysfunction | Moderate to High |
| SSRIs (e.g., Sertraline) | Antidepressants | Nausea, insomnia, sexual dysfunction (including ED) | Moderate |
| TCAs (e.g., Amitriptyline) | Antidepressants | Dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision, sexual dysfunction (including ED) | High |
| First-generation antihistamines (e.g., Diphenhydramine) | Antihistamines | Drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, sexual dysfunction (including ED) | Low |
Underlying Health Conditions and ED
Erectile dysfunction (ED) isn’t always a standalone issue. Often, it’s a symptom of an underlying health condition. Understanding these connections can be crucial for diagnosis and effective treatment. This section explores the relationship between various medical conditions and ED, highlighting the potential impact on erectile function and available treatments.Certain medical conditions can significantly impair blood flow and nerve function, both essential for achieving and maintaining an erection.
This disruption can manifest as ED, ranging from occasional difficulty to persistent inability. Recognizing these underlying conditions is vital for prompt intervention and improving overall health.
Cardiovascular Diseases
Cardiovascular diseases, including high blood pressure, atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), and heart disease, frequently contribute to ED. These conditions often reduce blood flow to the penis, hindering the process of achieving an erection. The severity of ED often correlates with the severity of the cardiovascular disease. For example, a patient with mild hypertension might experience occasional ED, while a patient with severe coronary artery disease may have persistent ED.
Diabetes
Diabetes, both type 1 and type 2, can damage nerves and blood vessels throughout the body, including those supplying the penis. This damage can lead to ED as a complication. The longer a person has diabetes and the less controlled their blood sugar levels are, the higher the risk of developing ED. For instance, individuals with poorly managed diabetes for many years are more likely to experience severe ED than those who maintain tight control of their blood sugar.
Certain medications, unfortunately, can sometimes lead to erectile dysfunction. Knowing this can be frustrating, especially if you’re looking for solutions to maintain a healthy lifestyle. Finding the right support during challenging times is crucial, and that’s where options like how hospice can help people with dementia during their final days can make a difference in managing the various difficulties of aging.
It’s important to remember that exploring different treatment options, like adjusting medications or lifestyle changes, can help address erectile dysfunction effectively.
Neurological Conditions
Neurological conditions, such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and spinal cord injuries, can disrupt the nerve signals crucial for erections. These conditions can interfere with the brain’s communication with the penis, leading to difficulties in achieving or maintaining an erection. The impact on erectile function varies depending on the specific neurological condition and its progression. For instance, a person with a mild case of multiple sclerosis might experience intermittent ED, while a person with advanced Parkinson’s disease may experience persistent ED.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances, such as low testosterone levels, can significantly affect erectile function. Testosterone is essential for libido and the production of sperm, and its deficiency can lead to decreased sexual desire and ED. The impact of hormonal imbalances on ED can vary based on the severity of the imbalance and the individual’s response to treatment. For example, a person with mild hypogonadism (low testosterone) might experience reduced libido and mild ED, whereas a person with severe hypogonadism could experience a complete lack of libido and persistent ED.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors, such as smoking, obesity, and excessive alcohol consumption, can also contribute to ED. Smoking damages blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the penis. Obesity and excessive alcohol consumption can negatively affect hormonal balance and overall cardiovascular health, increasing the risk of ED.
Table of Underlying Health Conditions and ED
| Condition | Impact on Erectile Function | Potential Treatments | Severity Variation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Disease | Reduced blood flow to the penis, leading to difficulty achieving and maintaining an erection. | Lifestyle modifications (diet, exercise), medications to manage blood pressure and cholesterol, and in severe cases, surgery. | Severity of ED correlates with the severity of the cardiovascular disease. |
| Diabetes | Damage to nerves and blood vessels supplying the penis, leading to impaired erectile function. | Tight blood sugar control, lifestyle modifications, medications to manage diabetes, and potentially penile injections or other therapies. | Risk of ED increases with duration and poor control of blood sugar levels. |
| Neurological Conditions | Disruption of nerve signals crucial for erections, leading to difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection. | Management of the underlying neurological condition, medications, and potential therapies targeting nerve function. | Impact on erectile function varies depending on the specific condition and its progression. |
| Hormonal Imbalances | Reduced testosterone levels, affecting libido and erectile function. | Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), lifestyle modifications, and potentially other treatments. | Severity of ED correlates with the severity of the hormonal imbalance. |
| Lifestyle Factors (Smoking, Obesity, Alcohol) | Damages blood vessels, affects hormonal balance, and increases cardiovascular risk, contributing to ED. | Quitting smoking, weight management, moderation of alcohol consumption, and lifestyle modifications. | Risk of ED increases with the extent of these negative lifestyle choices. |
Lifestyle Factors and ED
Erectile dysfunction (ED) isn’t solely a medical issue; lifestyle choices play a significant role in its development and management. Understanding how diet, exercise, stress, and sleep impact erectile function is crucial for proactive health. By making conscious choices in these areas, men can significantly improve their overall well-being and potentially reduce their risk of ED.
Certain medications, like some used to treat high blood pressure, can unfortunately have side effects like erectile dysfunction. For instance, some hypertension treatments, such as those involving magnesium sulfate, might contribute to this issue. Learning more about the specific effects of different hypertension medications, like hypertension magnesium sulfate treatment , is crucial for understanding potential side effects and managing overall health.
Ultimately, it’s essential to discuss any concerns about potential drug-related erectile dysfunction with a healthcare professional.
The Role of Diet in Erectile Function
A healthy diet is fundamental to overall health and plays a crucial part in maintaining good erectile function. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients, while limiting processed foods, saturated fats, and excessive sugar consumption can contribute to a healthier vascular system. Improved blood flow is vital for optimal erectile function. For example, a diet high in antioxidants, found in berries and leafy greens, can help protect blood vessels from damage.
The Impact of Exercise on Erectile Function
Regular physical activity is not just beneficial for overall health; it positively impacts erectile function. Exercise improves blood flow, strengthens the cardiovascular system, and helps manage weight, all of which contribute to better erectile function. Aerobic exercise, such as running or cycling, and strength training are both effective in improving vascular health and potentially reducing ED risk. Maintaining a healthy weight is also crucial, as obesity is a known risk factor for ED.
Stress and Sleep’s Influence on Erectile Function
Chronic stress and inadequate sleep can significantly impair erectile function. Stress hormones, like cortisol, can negatively impact blood flow and overall sexual function. Adequate sleep allows the body to repair and rejuvenate, which is essential for optimal sexual performance. Stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, and prioritizing sufficient sleep can be beneficial in reducing ED risk.
How to Improve Lifestyle Choices for Erectile Function
Adopting healthier lifestyle choices is key to improving erectile function. This includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and prioritizing sleep. For example, incorporating regular walks into daily routines or opting for stairs instead of elevators can improve cardiovascular health and potentially reduce ED risk.
Comparison of Lifestyle Factors and ED Risk
Different lifestyle factors have varying degrees of impact on ED risk. Poor diet, especially one high in processed foods and saturated fats, can significantly contribute to vascular problems, increasing the likelihood of ED. Similarly, a sedentary lifestyle and lack of exercise negatively impact blood flow and contribute to weight gain, both of which are linked to ED. Stress and insufficient sleep can also hinder erectile function through their effect on hormones and blood flow.
Strategies for Improving Lifestyle Factors
Implementing strategies to improve lifestyle choices can significantly impact erectile function. These strategies encompass a holistic approach, encompassing dietary adjustments, exercise routines, stress management techniques, and prioritizing sufficient sleep.
| Lifestyle Factor | Potential Impact on Erectile Function | Strategies for Improvement | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diet | Poor diet can lead to vascular issues, affecting blood flow to the penis. | Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit processed foods, saturated fats, and excessive sugar. | Increase intake of fruits and vegetables; reduce consumption of fast food. |
| Exercise | Regular exercise improves blood flow and cardiovascular health, which benefits erectile function. | Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with strength training exercises. | Engage in daily walks, run regularly, and incorporate weightlifting exercises. |
| Stress | Chronic stress can negatively impact hormone levels and blood flow, potentially causing ED. | Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. | Engage in meditation sessions, participate in yoga classes, and practice deep breathing techniques. |
| Sleep | Insufficient sleep can impair the body’s ability to repair and rejuvenate, potentially affecting erectile function. | Prioritize 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Establish a regular sleep schedule. | Maintain a consistent sleep schedule, create a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensure a dark and quiet sleep environment. |
Diagnostic Considerations for ED
Understanding the root cause of erectile dysfunction (ED) is crucial for effective treatment. A thorough diagnostic process helps differentiate between various potential contributing factors, including underlying medical conditions, lifestyle choices, and even medication side effects. This process often involves a combination of physical examinations, medical history assessments, and specific diagnostic tests.The diagnostic approach to ED is multifaceted, aiming to identify the specific cause of the dysfunction rather than just treating the symptom.
This careful evaluation ensures that the chosen treatment strategy targets the underlying issue, leading to more effective and lasting results. A personalized approach is paramount, taking into account the individual patient’s unique circumstances.
Physical Examination and Medical History
A comprehensive medical history is essential in evaluating ED. This includes inquiries about the patient’s overall health, medications they are currently taking, and any past medical conditions. The history should also include details about the duration and severity of ED symptoms, including any associated factors such as stress, relationship issues, or lifestyle changes. A thorough physical examination, including a cardiovascular assessment, neurological evaluation, and examination of the genitalia, is also vital.
Physical findings may provide clues about underlying conditions potentially contributing to ED. For example, certain hormonal imbalances or vascular abnormalities might be detected during the examination.
Diagnostic Tools and Methods, Drugs that can cause erectile dysfunction
Various diagnostic tools are employed to assess erectile function. These methods aim to evaluate the patient’s ability to achieve and maintain an erection. One common method involves a physical exam that includes checking blood pressure, pulse, and other vital signs. Another key component is the review of the patient’s medical history, which might uncover relevant factors that could be influencing their erectile function.
Role of Distinguishing Medication-Induced ED
Identifying whether ED is a side effect of medication is critical. Carefully reviewing the patient’s current medications is crucial. This process involves discussing all prescribed and over-the-counter medications, supplements, and recreational drugs. Detailed documentation and communication with the patient are essential to pinpoint the connection between medication and the ED symptoms.
Diagnostic Tests: Purpose and Limitations
The table below Artikels various diagnostic tests used in evaluating ED, their purpose, and their potential limitations.
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose | Limitations | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nocturnal Penile Tumescence (NPT) | Evaluates nocturnal erections, reflecting penile vascular function. | May not accurately reflect daytime erectile function; can be affected by anxiety or sleep disorders. | Monitoring erections during sleep. |
| Blood Tests | Assess hormone levels (testosterone, prolactin), glucose levels, and other markers for underlying conditions. | Results can be influenced by recent meals, stress, or other factors. Doesn’t directly measure erectile function. | Checking blood sugar, testosterone levels. |
| Ultrasound | Assesses blood flow to the penis, identifying potential vascular issues. | Can be affected by anxiety, not always a definitive diagnostic tool for ED. | Doppler ultrasound to evaluate blood flow. |
| Penile Biothesiometry | Measures nerve sensitivity in the penis, assessing for neurological causes of ED. | Not always sensitive enough to detect subtle neurological problems. | Testing sensation in the penis. |
Preventing ED
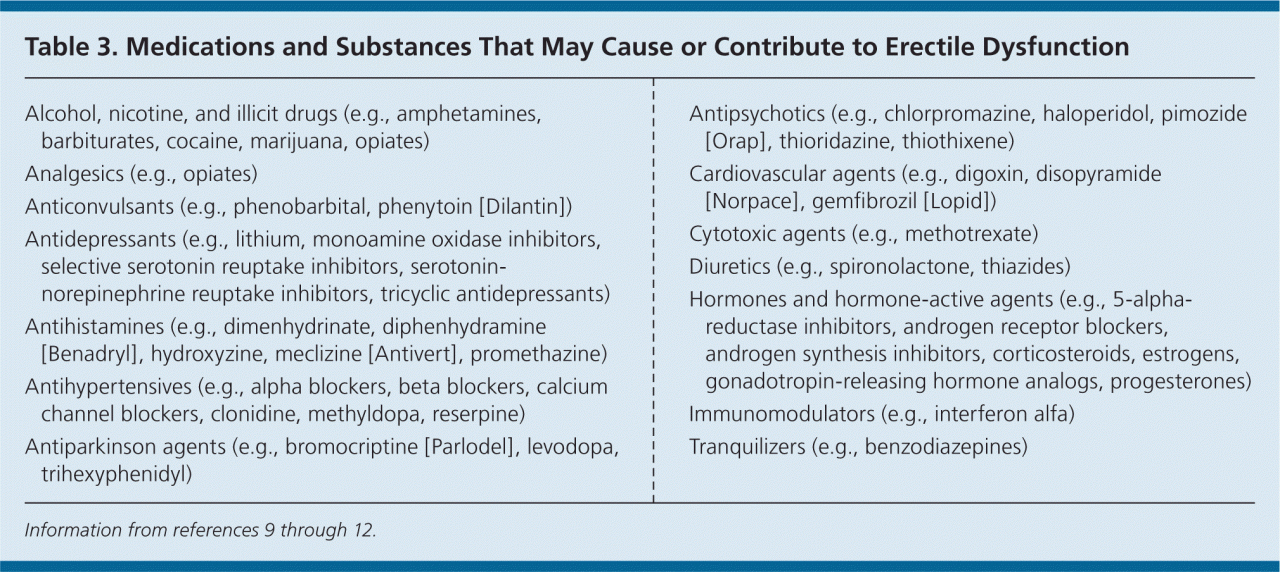
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a prevalent issue affecting millions worldwide, but it’s not an inevitable consequence of aging or a permanent condition. Many cases of ED are preventable or manageable through proactive lifestyle choices and diligent health management. Taking control of your health and adopting healthy habits can significantly reduce your risk of developing ED.
Lifestyle Modifications for ED Prevention
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial in preventing ED. This includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients, while regular physical activity helps improve cardiovascular health, a key factor in maintaining erectile function. Stress reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature can also play a significant role in improving overall well-being and reducing ED risk.
Proactive Health Management for ED Prevention
Early detection and management of underlying health conditions are paramount in preventing ED. Conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol significantly increase the risk of developing ED. Regular checkups with your doctor allow for early diagnosis and management of these conditions, potentially preventing or delaying the onset of ED. Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels is essential in preventing or managing ED.
Maintaining Good Overall Health
Maintaining good overall health through a combination of lifestyle choices and proactive medical management can significantly reduce the risk of ED. This includes not only focusing on physical health but also addressing mental and emotional well-being. Prioritizing sleep, managing stress, and maintaining a positive outlook on life contribute to overall health and well-being, indirectly reducing the risk of ED.
A balanced approach to health is essential, considering all aspects of well-being, not just the physical.
Minimizing Medication-Induced ED
Certain medications can contribute to ED as a side effect. If you’re taking any medications, discuss potential side effects with your doctor. If you suspect a medication is contributing to ED, consult your doctor about alternative options or adjustments to your dosage. Open communication with your doctor is key in managing any potential side effects and finding the best course of action.
Actionable Steps to Prevent ED
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is linked to various health problems, including ED. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can significantly reduce the risk of ED.
- Engage in regular physical activity: Regular exercise improves cardiovascular health, which is crucial for erectile function. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
- Adopt a balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients for overall health and can positively impact erectile function.
- Manage stress effectively: Chronic stress can negatively impact sexual health. Incorporate stress-reducing activities into your routine, such as meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature.
- Prioritize sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for overall health and well-being. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
- Manage underlying health conditions: Conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol significantly increase the risk of ED. Regular checkups and proactive management are crucial.
- Communicate openly with your doctor: Discuss any medications you’re taking with your doctor to identify potential side effects, including ED.
Understanding the Impact of ED: Drugs That Can Cause Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is more than just a physical issue; it significantly impacts a man’s overall well-being, affecting his self-esteem, relationships, and psychological state. Recognizing the multifaceted nature of ED is crucial for effective treatment and support. Addressing the emotional and social consequences alongside the physical symptoms is vital for a comprehensive approach to recovery.The impact of ED extends far beyond the inability to achieve or maintain an erection.
It can deeply affect a man’s self-perception, intimacy with partners, and social interactions. Understanding these broader implications is key to providing comprehensive support and care.
Impact on Overall Well-being
ED can have a profound effect on a man’s physical, emotional, and social well-being. Physical symptoms, such as fatigue and stress, can arise as a result of the condition itself and the emotional distress it causes. Emotional consequences can include feelings of inadequacy, shame, and anxiety, potentially leading to depression or other mental health issues. Social interactions can also be affected, as ED can impact a man’s confidence and ability to engage in social activities.
Impact on Self-Esteem
ED can significantly erode a man’s self-esteem. The inability to perform sexually can lead to feelings of inadequacy, worthlessness, and a diminished sense of masculinity. This can manifest in a variety of ways, from avoiding intimate situations to withdrawing from social interactions. The resulting emotional burden can further exacerbate the ED, creating a vicious cycle.
Impact on Relationships
ED can place a considerable strain on intimate relationships. Difficulties with sexual function can lead to misunderstandings, resentment, and conflict within the partnership. Communication and understanding are crucial to navigating these challenges effectively. Open and honest dialogue about concerns and seeking professional help can be vital steps toward restoring intimacy and strengthening the relationship.
Psychological Consequences of ED
ED can lead to a range of psychological consequences, including anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem. The pressure to perform sexually can be overwhelming, leading to heightened stress and anxiety. Furthermore, the fear of disappointing a partner or experiencing further failures can contribute to a cycle of negative emotions. Seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor can provide valuable support and strategies for managing these psychological challenges.
Social Implications of ED
The social implications of ED can be significant. A man experiencing ED might feel reluctant to participate in social activities involving intimacy or sexual situations. This can lead to social isolation and a reduced quality of life. Understanding the social implications of ED is crucial for creating supportive environments and encouraging open discussions about the condition.
“Erectile dysfunction is not merely a physical issue; it’s a multifaceted problem affecting a man’s self-esteem, relationships, and overall well-being. Addressing the emotional and social aspects of ED alongside the physical symptoms is crucial for effective treatment and support.”
Closing Notes
In conclusion, numerous medications can unfortunately contribute to erectile dysfunction. By understanding the potential side effects, the dosage implications, and the underlying mechanisms, men can make informed decisions about their health and well-being. This article provides a thorough overview, equipping readers with the knowledge to discuss these concerns with their healthcare providers and to make proactive choices about their health.
