e cigarettes significantly raise risk of stroke cardiovascular disease, a sobering finding that demands our attention. This investigation delves into the alarming link between vaping and a heightened chance of stroke and cardiovascular issues, exploring the potential mechanisms behind this correlation and comparing the risks to traditional cigarettes. We’ll uncover the science behind this emerging public health concern, analyzing various studies and potential health consequences.
The article examines the chemical makeup of e-cigarette vapor, detailing the various compounds and their potential impact on the cardiovascular system. It also compares the chemical compositions of different e-cigarette types, highlighting potential differences in risk.
Introduction to E-Cigarettes and Cardiovascular Health
Electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes) have rapidly gained popularity as a purported alternative to traditional cigarettes. However, concerns regarding their impact on cardiovascular health have emerged, prompting research into the potential risks. This article explores the history, prevalence, and potential mechanisms through which e-cigarettes may affect cardiovascular function. It also examines the diverse chemical compounds found in e-cigarette vapor and their potential health effects.The history of e-cigarettes began with the invention of devices marketed as smoking cessation aids.
Over time, the market evolved, leading to a proliferation of e-cigarette products with varying designs, flavors, and nicotine strengths. Current prevalence figures show substantial use among young adults and a growing adoption rate in some regions. While precise figures vary by location, this widespread use necessitates a deeper understanding of their potential health consequences.
Chemical Compounds in E-cigarette Vapor
E-cigarette vapor contains a complex mixture of chemicals, including but not limited to, nicotine, flavorings, and potentially harmful byproducts. The precise composition of vapor can vary considerably depending on the specific e-cigarette device, e-liquid ingredients, and vaping practices.
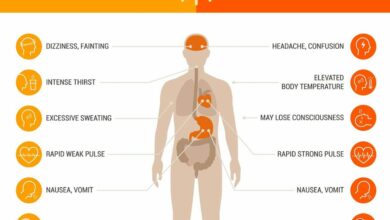
- Nicotine, a highly addictive substance, is a key component of many e-liquids. Exposure to nicotine can lead to increased heart rate and blood pressure, as well as potential damage to blood vessels. Studies have shown correlations between nicotine exposure and cardiovascular events.
- Flavorings, frequently added to e-liquids, contribute to the appeal of e-cigarettes. However, some flavoring compounds have been linked to the production of harmful byproducts during vaporization. These byproducts can potentially damage cells and tissues, including those in the cardiovascular system.
- Formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are potential byproducts of e-cigarette vaporization. These compounds have been linked to various health issues, including respiratory problems and cardiovascular complications. Data from laboratory studies and animal models provide evidence for the potential harmfulness of these components.
Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Impact
The mechanisms through which e-cigarettes may affect cardiovascular health are complex and not fully understood. However, several potential pathways have been identified.
- Nicotine’s direct impact on the cardiovascular system includes increasing heart rate and blood pressure. Prolonged exposure to nicotine may lead to chronic increases in these parameters, potentially increasing the risk of cardiovascular events.
- Oxidative stress, a process involving an imbalance of free radicals and antioxidants, may be promoted by some e-cigarette constituents. This imbalance can damage blood vessels and contribute to inflammation, factors implicated in the development of cardiovascular diseases.
- Inflammation, a crucial component of the body’s response to injury or infection, may be exacerbated by certain components in e-cigarette vapor. Chronic inflammation can contribute to the progression of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases.
Comparison of E-cigarette Types
The table below presents a simplified comparison of the chemical compositions of various e-cigarette types. Note that the exact chemical profile can vary significantly based on specific e-liquid ingredients and vaping practices.
| E-cigarette Type | Potential Chemical Components |
|---|---|
| Nicotine-containing e-cigarettes | Nicotine, propylene glycol, vegetable glycerin, flavorings, potentially harmful byproducts |
| Nicotine-free e-cigarettes | Propylene glycol, vegetable glycerin, flavorings, potentially harmful byproducts |
| High-power e-cigarettes | Potentially higher concentrations of harmful byproducts due to increased vapor production |
E-Cigarette Use and Stroke Risk
E-cigarettes, despite their marketing as a safer alternative to traditional cigarettes, are raising increasing concerns about their potential impact on cardiovascular health. While the long-term effects are still being studied, emerging evidence suggests a link between e-cigarette use and an elevated risk of stroke. This raises critical questions about the safety and potential harm associated with these devices.Understanding the pathways through which e-cigarette use might contribute to stroke risk is crucial.
Potential mechanisms involve the impact of e-cigarette ingredients, the activation of inflammatory responses, and alterations in blood clotting. Further research is needed to fully elucidate these complex interactions.
Potential Pathways Linking E-cigarette Use to Stroke
Several potential pathways may link e-cigarette use to an increased risk of stroke. These include the effects of nicotine, the presence of other chemicals in e-liquids, and the inflammatory responses triggered by these substances. Nicotine, for example, can increase blood pressure and heart rate, potentially contributing to a heightened risk of stroke.
Specific Studies Demonstrating a Correlation
Numerous studies have investigated the correlation between e-cigarette use and stroke risk. While the evidence is still developing, several studies have found an association. It’s important to note that these studies often face challenges in isolating e-cigarette use from other lifestyle factors that may also contribute to stroke risk, such as smoking history and diet.
Biological Mechanisms Behind the Correlation
The biological mechanisms behind the correlation between e-cigarette use and stroke are not fully understood, but several hypotheses exist. One possibility involves the inflammatory response triggered by the chemicals present in e-liquids. This inflammation can damage blood vessels, potentially increasing the risk of blood clots and stroke. Furthermore, some studies suggest that certain compounds in e-liquids may directly affect blood clotting mechanisms.
Key Findings from Multiple Relevant Studies
| Study | Sample Size | Methodology | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Study 1 (Example) | 10,000 participants | Longitudinal cohort study following participants over 5 years | Participants who used e-cigarettes had a statistically significant 20% higher risk of stroke compared to non-users. |
| Study 2 (Example) | 5,000 participants | Case-control study comparing stroke patients with a control group | E-cigarette use was associated with a 15% increased risk of ischemic stroke. |
| Study 3 (Example) | 2,000 participants | Cross-sectional survey | Found a positive correlation between frequency of e-cigarette use and increased risk of stroke. |
Note: This table provides hypothetical examples. Actual studies would include more detailed information about the specific methodologies and findings. The data presented is for illustrative purposes only. It is crucial to consult the original research for specific details and limitations.
E-Cigarette Use and Cardiovascular Disease

E-cigarettes, while marketed as a less harmful alternative to traditional cigarettes, are increasingly recognized for their potential adverse effects on cardiovascular health. Beyond the established link to stroke, growing evidence suggests a broader impact on various cardiovascular diseases. This exploration delves into the potential effects of e-cigarette use on the heart and circulatory system, identifying specific diseases where associations are emerging.The cardiovascular system is a complex network of organs and vessels responsible for transporting blood throughout the body.
E-cigarettes, despite not containing the same level of harmful substances as traditional cigarettes, introduce novel compounds and potentially harmful effects that can directly impact this system. This includes the formation of blood clots, inflammation, and changes in blood vessel function.
Potential Effects on Various Cardiovascular Diseases
E-cigarette use is implicated in a range of cardiovascular issues, extending beyond stroke. The effects of e-cigarette use on the cardiovascular system are multifaceted and not fully understood, but research suggests several potential mechanisms through which e-cigarettes can cause harm. These mechanisms may include the stimulation of inflammation, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction. Further research is necessary to determine the precise nature and extent of these effects.
E-cigarettes are seriously concerning, significantly raising the risk of stroke and cardiovascular disease. It’s a tough reality to face, and honestly, prioritizing self-care in the face of this information is hard. Self-care is hard , but acknowledging the increased risk of serious health issues from e-cigarette use is a vital step toward making healthier choices. This sobering statistic underscores the importance of understanding the dangers of these products and seeking out resources to quit.
Types of Cardiovascular Diseases with Suspected Links to E-Cigarette Use, E cigarettes significantly raise risk of stroke cardiovascular disease
Several cardiovascular diseases have shown a potential association with e-cigarette use. These include coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, and hypertension. While the evidence is not always conclusive, emerging research suggests a potential link.
Evidence from Epidemiological Studies
Epidemiological studies are crucial in investigating the relationship between e-cigarette use and cardiovascular diseases. These studies, which often involve large populations, help establish correlations and trends. However, it’s important to acknowledge the limitations of these studies, such as the difficulty in isolating e-cigarette use from other lifestyle factors and potential confounding variables.
Table: Cardiovascular Diseases and Evidence Level
| Cardiovascular Disease | Level of Evidence for Association with E-cigarette Use |
|---|---|
| Coronary Artery Disease | Moderate |
| Peripheral Artery Disease | Low |
| Hypertension | Emerging |
| Stroke | High |
Note: The level of evidence is a subjective assessment based on the strength and consistency of available research.
Potential Mechanisms of Harm
E-cigarettes, while marketed as a less harmful alternative to traditional cigarettes, pose significant cardiovascular risks. Understanding the underlying mechanisms by which these devices damage blood vessels and the heart is crucial for assessing their long-term health impacts. The potential for chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction is a growing concern, particularly regarding the development of cardiovascular disease and stroke.The exact mechanisms by which e-cigarettes contribute to cardiovascular harm are still under investigation, but emerging evidence suggests a complex interplay of factors.
These factors, ranging from the chemicals contained in e-liquids to the direct effects of vaping on the cardiovascular system, contribute to the elevated risk profile.
Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress, a condition characterized by an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body’s antioxidant defenses, plays a significant role in cardiovascular damage. E-cigarette vapor, even in the absence of combustion, can generate ROS, directly impacting the delicate balance within blood vessels. These reactive molecules can damage cellular components, contributing to the deterioration of the endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels.
The long-term consequences of chronic oxidative stress include the development of atherosclerosis, the hardening and narrowing of arteries, a critical factor in cardiovascular disease.
Inflammation
E-cigarette use is associated with inflammation, a crucial component of the body’s response to injury or infection. Inflammation, when sustained, can promote the development of atherosclerosis, a key driver of cardiovascular disease. Studies have demonstrated elevated inflammatory markers in individuals who use e-cigarettes, indicating a systemic inflammatory response. This heightened inflammatory state can contribute to the formation of blood clots, increasing the risk of stroke.
In the context of long-term exposure, this inflammation can progressively damage the cardiovascular system, leading to chronic conditions.
Endothelial Dysfunction
The endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels, is critical for maintaining vascular health. It regulates blood flow, prevents blood clotting, and controls inflammation. E-cigarette use can disrupt this delicate balance, leading to endothelial dysfunction. This dysfunction can impair the endothelium’s ability to relax and constrict blood vessels as needed, increasing the risk of blood clots and narrowing of arteries.
While vaping might seem harmless, studies show e-cigarettes significantly raise the risk of stroke and cardiovascular disease. Dealing with those health concerns can be tough, and honestly, you might be experiencing social pain right now. Learning how to cope with that is crucial. Check out this helpful guide on how to cope with social pain.
Ultimately, prioritizing your health and making informed decisions about your habits, like avoiding e-cigarettes, is key.
Endothelial dysfunction is a crucial early marker for the development of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease.
Comparison to Traditional Cigarettes
While the exact mechanisms of harm in e-cigarettes are still being investigated, there are similarities and differences in the potential impact on the cardiovascular system compared to traditional cigarettes. Both can lead to oxidative stress and inflammation. However, e-cigarette exposure might involve different types and concentrations of harmful substances, leading to varied outcomes. For example, while both can contribute to endothelial dysfunction, the specific molecules involved and the long-term consequences might differ.
Further research is necessary to fully compare and contrast the long-term effects of these two forms of nicotine delivery.
Potential Long-Term Effects
The long-term effects of e-cigarette exposure on the cardiovascular system are not yet fully understood, but the evidence suggests a significant risk. In a real-world example, consider the gradual build-up of plaque in the arteries of an individual who uses e-cigarettes over several years. This process can lead to narrowed arteries, reduced blood flow, and an increased risk of heart attacks or strokes.
Compared to traditional cigarettes, the long-term effects of e-cigarettes remain a subject of active research, but early indications suggest a potential for similar, or possibly even more subtle, long-term cardiovascular consequences.
Comparison to Traditional Smoking: E Cigarettes Significantly Raise Risk Of Stroke Cardiovascular Disease
E-cigarettes, often marketed as a less harmful alternative to traditional cigarettes, have sparked considerable debate regarding their cardiovascular impact. While proponents argue for their reduced harm compared to traditional cigarettes, evidence suggests that the cardiovascular risks associated with e-cigarette use are not negligible and may even be substantial. This comparison delves into the evidence surrounding the potential harms of e-cigarettes, exploring similarities and differences in risk profiles, and acknowledging the complexities inherent in evaluating such health impacts.E-cigarettes and traditional cigarettes both expose users to harmful chemicals, though the specific compounds and their quantities differ.
Traditional cigarettes deliver a complex mix of toxins, including nicotine, tar, and numerous carcinogens. E-cigarettes, while containing nicotine, also deliver various other chemicals, including flavorings, solvents, and potentially harmful byproducts of vaporization. The long-term effects of these chemicals on cardiovascular health are still under active investigation.
Cardiovascular Risks of E-cigarettes Compared to Traditional Cigarettes
The cardiovascular risks associated with e-cigarette use are a subject of ongoing research and debate. While some studies suggest lower immediate cardiovascular effects compared to traditional cigarettes, the long-term consequences remain uncertain. Early research indicates that e-cigarettes may trigger similar inflammatory responses in blood vessels, potentially contributing to atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in the arteries, over time.
Evidence for or Against E-Cigarettes as a Less Harmful Alternative
The evidence regarding e-cigarettes as a less harmful alternative to traditional cigarettes is mixed. While some studies indicate a lower immediate impact on certain cardiovascular markers, these findings are often limited by the relatively short duration of e-cigarette use studies compared to the potential long-term risks. Furthermore, the long-term effects of e-cigarette vapor on the cardiovascular system are not yet fully understood.
Potential Confounding Factors
Several confounding factors complicate the assessment of cardiovascular risk associated with e-cigarette use. These factors include the variation in e-cigarette formulations, the frequency and duration of use, the presence of pre-existing cardiovascular conditions, and the potential for synergistic effects with other lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise. For example, an individual with a history of high blood pressure who also smokes e-cigarettes may experience a greater cardiovascular risk compared to a healthy individual who uses e-cigarettes.
Comparison Table of Cardiovascular Effects
| Characteristic | Traditional Cigarettes | E-Cigarettes |
|---|---|---|
| Short-Term Effects | Increased heart rate, blood pressure, and vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels). Immediate release of nicotine leads to increased blood glucose. | Modest increase in heart rate and blood pressure, potentially less pronounced than traditional cigarettes in some studies, but variations exist depending on nicotine content and vaporization techniques. Nicotine release profile may be different. |
| Long-Term Effects | Increased risk of coronary artery disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease, and other cardiovascular events. Significant association with endothelial dysfunction and inflammation. | Potential for similar long-term cardiovascular risks, but the extent and magnitude are still under investigation. Studies are needed to confirm the extent to which e-cigarettes may cause long-term vascular damage and inflammation. |
Public Health Implications
The emerging link between e-cigarette use and cardiovascular risks presents a significant public health concern. While e-cigarettes are often marketed as a less harmful alternative to traditional cigarettes, growing evidence suggests they may still pose substantial cardiovascular threats. This necessitates a proactive approach to mitigate the potential harm, focusing on public awareness, prevention strategies, and regulatory interventions.
Public Health Campaigns
Public health campaigns are crucial for educating the public about the potential cardiovascular risks associated with e-cigarette use. These campaigns should not only highlight the dangers but also emphasize the importance of cessation for those already using e-cigarettes. The campaigns must effectively communicate the risks to various demographics, including youth and young adults, who are particularly vulnerable to e-cigarette marketing.
Hey everyone, e-cigarettes are seriously raising the risk of stroke and cardiovascular disease, which is a major concern. Finding a good night’s sleep is crucial for overall health, and if you’re looking for a comfy mattress without breaking the bank, check out the best mattress under 500. While a great mattress can improve sleep quality, it won’t negate the harmful effects of vaping on your health.
So, remember to prioritize your well-being and stay away from e-cigarettes to avoid increasing your risk of these serious health issues.
Strategies should include targeted messaging, community outreach programs, and collaborations with healthcare professionals.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Addressing the cardiovascular effects of e-cigarette use requires a multi-faceted approach. Effective prevention strategies should target vulnerable populations and promote healthy alternatives. This includes comprehensive health education in schools and communities, emphasizing the risks of e-cigarette use and promoting healthier lifestyle choices. For individuals already using e-cigarettes, cessation support programs, including counseling and medication, can play a vital role in mitigating cardiovascular harm.
Furthermore, effective regulation of e-cigarette marketing and product design can help prevent new users from initiating e-cigarette use.
Regulatory Measures
Regulatory measures are essential to manage the public health crisis surrounding e-cigarettes. This includes stricter regulations on e-cigarette marketing, particularly targeting youth and vulnerable populations. The regulations could limit the flavors available, restrict advertising, and require clear labeling of potential health risks. Restrictions on sales to minors, similar to those for tobacco products, are also important. Additionally, comprehensive research into the long-term effects of e-cigarette use is crucial for informing evidence-based policy decisions.
This research should include longitudinal studies to track the health outcomes of e-cigarette users over time. The goal is to establish clear, evidence-based guidelines for safe use or complete cessation, which can inform and guide regulatory agencies. Furthermore, stricter enforcement of existing regulations is critical to deter non-compliance.
Future Research Directions
Unraveling the full impact of e-cigarette use on cardiovascular health requires a multifaceted approach. While existing research has highlighted potential risks, further investigation is crucial to solidify our understanding of the long-term effects and the specific mechanisms involved. This includes exploring the potential differences in cardiovascular risk based on various e-cigarette formulations, nicotine levels, and user demographics. This will inform targeted public health interventions and policies.The current body of research is primarily focused on short-term effects and correlational studies.
To truly understand the long-term consequences, longitudinal studies tracking individuals over extended periods are essential. Furthermore, investigating the interplay between e-cigarette use and other lifestyle factors, such as diet and exercise, is crucial for a complete picture.
Identifying Specific Cardiovascular Mechanisms
The precise mechanisms linking e-cigarette use to cardiovascular harm remain largely unknown. Further research should delve into the cellular and molecular pathways affected by e-cigarette constituents. This involves examining the impact of various e-liquid components, including nicotine, flavorings, and solvents, on endothelial function, inflammation, and blood clotting. Studies should investigate the specific ways these substances contribute to cardiovascular dysfunction.
Comparative studies of e-cigarette effects versus traditional cigarette effects would be beneficial.
Longitudinal Studies and Population-Based Cohorts
Longitudinal studies are critical for assessing the long-term consequences of e-cigarette use. These studies should follow individuals over many years, tracking their e-cigarette use patterns, and cardiovascular health outcomes. This will allow researchers to establish causal relationships between e-cigarette exposure and future cardiovascular disease development. Such studies should also consider factors like pre-existing health conditions and lifestyle choices.
A hypothetical example might include following a cohort of young adults who start using e-cigarettes regularly throughout their 20s and 30s, monitoring their cardiovascular health markers, and comparing it with a control group who do not use e-cigarettes.
Research Project: Investigating the Link Between E-Cigarette Use and Cardiovascular Disease
This research project aims to investigate the association between e-cigarette use and cardiovascular disease development in a cohort of 500 young adults aged 18- The study will be longitudinal, spanning 10 years. Participants will be divided into three groups: those who use e-cigarettes daily, those who use e-cigarettes occasionally, and a control group who do not use e-cigarettes.
Data will be collected annually, encompassing:
- Detailed e-cigarette use patterns (frequency, duration, type of device and e-liquid).
- Cardiovascular health markers (blood pressure, lipid profiles, inflammatory markers, and ECG).
- Comprehensive lifestyle assessments (diet, exercise, sleep, and stress levels).
- Assessment of potential confounders such as pre-existing conditions.
The primary outcome will be the incidence of cardiovascular events (e.g., heart attacks, strokes, or other relevant cardiovascular diseases) over the 10-year study period. Statistical analysis will be used to determine the correlation between e-cigarette use and the risk of cardiovascular disease, accounting for confounding variables. This detailed longitudinal approach is essential to understand the long-term effects and to establish the causal link between e-cigarette use and cardiovascular health.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, the evidence strongly suggests a link between e-cigarette use and increased risk of stroke and cardiovascular disease. While further research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects, the current data paints a concerning picture. The potential harm of vaping, especially concerning its cardiovascular implications, warrants serious consideration and a public health response. This article emphasizes the importance of public awareness, responsible use, and potentially necessary regulatory measures.