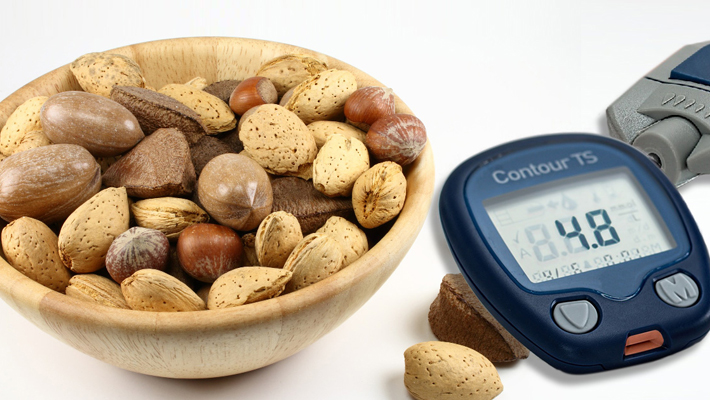
Eating nuts can improve heart health for people with type 2 diabetes, offering a delicious and potentially life-changing dietary approach. This exploration delves into the fascinating link between nuts, heart health, and managing type 2 diabetes. We’ll uncover the specific types of nuts that offer the most benefits, delve into the science behind their impact, and examine the potential downsides and practical considerations.
Finally, you’ll discover easy-to-follow recipes incorporating nuts for a healthy and delicious lifestyle.
Nuts, a diverse group of foods, are packed with nutrients that may help people with type 2 diabetes manage their condition and improve cardiovascular health. From almonds and walnuts to cashews and pecans, each type brings its own unique nutritional profile to the table. We’ll explore the key nutrients that are most beneficial and how these nutrients work together to support heart health and blood sugar control.
Understanding these nuances will empower you to make informed choices about incorporating nuts into your diet.
The Heart-Healthy Potential of Nuts for Type 2 Diabetes

Nuts, a delicious and nutritious food group, have been linked to improved cardiovascular health for years. This benefit is particularly relevant for individuals with type 2 diabetes, a condition often associated with increased risk of heart disease. This exploration delves into the connection between nut consumption and heart health in type 2 diabetes, examining the potential mechanisms through which nuts can mitigate cardiovascular risks.Type 2 diabetes significantly impacts heart health by increasing the risk of conditions like atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
These complications often lead to heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events. While medication and lifestyle changes are crucial for managing type 2 diabetes, incorporating nuts into a balanced diet may offer an additional layer of protection against these risks. Nuts, packed with healthy fats, fiber, and protein, can play a significant role in improving blood sugar control, reducing harmful cholesterol levels, and promoting overall cardiovascular well-being.
The Impact of Nuts on Cardiovascular Health
Nuts are a rich source of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which are beneficial for lowering LDL (“bad”) cholesterol. Studies consistently demonstrate that incorporating nuts into the diet can lead to a decrease in LDL cholesterol levels. This reduction in LDL cholesterol can contribute to improved blood vessel health and a decreased risk of atherosclerosis. Furthermore, the fiber content in nuts aids in blood sugar regulation, which is crucial for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
The presence of antioxidants and vitamin E further contributes to overall cardiovascular health.
Potential Mechanisms for Improved Heart Health
Nuts offer several potential mechanisms to improve heart health in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
- Improved Blood Sugar Control: The fiber and protein content in nuts slows down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream, leading to a more gradual rise in blood sugar levels after a meal. This sustained release can be beneficial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels, a key factor in managing type 2 diabetes and preventing cardiovascular complications.
- Reduced LDL Cholesterol: The healthy fats in nuts, particularly monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, can help reduce LDL cholesterol levels. This reduction is a crucial factor in mitigating the risk of atherosclerosis, a major contributor to cardiovascular diseases.
- Increased HDL Cholesterol: Some studies suggest that nut consumption may also increase HDL cholesterol (“good” cholesterol), which helps remove excess cholesterol from the arteries, further promoting cardiovascular health.
- Blood Pressure Management: Nuts contain compounds that may contribute to better blood pressure regulation. Maintaining healthy blood pressure is critical in preventing or managing hypertension, a significant risk factor for heart disease.
Dietary Recommendations for Type 2 Diabetes
For individuals with type 2 diabetes, incorporating nuts into their diet requires careful consideration of portion sizes. While nuts offer numerous health benefits, they are calorie-dense. A balanced approach is crucial to ensure that nut consumption aligns with overall dietary goals and doesn’t contribute to weight gain. Consulting a registered dietitian or a healthcare professional can provide personalized recommendations for incorporating nuts into a diabetes-friendly diet.
Specific Types of Nuts and Their Potential Benefits
Nuts offer a diverse range of nutritional benefits, making them a valuable addition to a healthy diet, particularly for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Their rich composition of healthy fats, protein, and fiber contributes to satiety and can help regulate blood sugar levels. Understanding the specific nutritional profiles of different nuts can help individuals tailor their intake to optimize their health outcomes.Different types of nuts offer unique nutritional profiles, impacting their potential benefits for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
The variations in fat content, protein, fiber, and micronutrients influence their effect on blood sugar management and overall health.
Nutritional Profiles of Different Nuts
Nuts vary significantly in their macronutrient and micronutrient content. These differences translate to varying effects on blood sugar control and overall health. Almonds, walnuts, and cashews are commonly consumed nuts, each with its unique nutritional composition.
Almonds, Eating nuts can improve heart health for people with type 2 diabetes
Almonds are a popular choice due to their high protein and fiber content. They also contain healthy fats, particularly monounsaturated fats. The combination of these nutrients contributes to satiety, which can help manage blood sugar levels. Almonds have been associated with improved blood lipid profiles.
Walnuts
Walnuts are a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health. They also contain antioxidants and other nutrients. The presence of omega-3s and antioxidants may have a positive effect on blood sugar control and overall health. Walnuts are also a good source of fiber and protein.
Cashews
Cashews are known for their mild flavor and creamy texture. They contain healthy fats, protein, and fiber. Cashews also provide essential minerals like magnesium and zinc. Their impact on blood sugar control, while not as extensively studied as almonds or walnuts, may be positive, owing to their fiber and nutrient content.
Comparison of Nutritional Value
The following table illustrates the approximate nutritional differences between almonds, walnuts, and cashews, highlighting the variation in calories, protein, fiber, and healthy fats.
| Nut | Calories (per 1 ounce) | Protein (grams per 1 ounce) | Fiber (grams per 1 ounce) | Healthy Fats (grams per 1 ounce) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Almonds | 160-165 | 6-7 | 3.5-4 | 13-14 |
| Walnuts | 180-190 | 4-5 | 2-3 | 15-16 |
| Cashews | 160-165 | 5-6 | 2-3 | 12-13 |
Note: Nutritional values may vary slightly depending on the specific brand and preparation method.
Scientific Evidence Supporting the Connection
Nuts, a delicious and versatile snack, have long been touted for their potential health benefits. For individuals with type 2 diabetes, the potential benefits of nuts for heart health are particularly intriguing. This section delves into the scientific research supporting the positive link between nut consumption and improved cardiovascular outcomes in this population.The evidence supporting the heart-healthy properties of nuts for people with type 2 diabetes is substantial and comes from a variety of well-designed studies.
These studies investigate the effects of nut intake on key cardiovascular risk factors, such as blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and inflammation. Understanding the methodology and results of these studies provides a strong foundation for the recommendation of nut consumption as part of a healthy diet for those with diabetes.
Meta-analyses and Reviews
Numerous meta-analyses and review articles have examined the collective findings of multiple studies on nut consumption and cardiovascular health in people with type 2 diabetes. These comprehensive overviews help to synthesize the evidence from diverse sources and identify overarching trends. Such analyses often consider the potential influence of different nut types, consumption amounts, and individual characteristics on the outcomes.
- A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) frequently shows a statistically significant reduction in LDL cholesterol (the “bad” cholesterol) and an improvement in blood pressure among participants consuming nuts compared to those on control diets. This reduction in LDL cholesterol is a key factor in mitigating cardiovascular risks. Meta-analyses typically examine the effect of nut intake across various study populations, helping to identify trends that may not be evident in single studies.
Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs)
Randomized controlled trials are considered the gold standard for evaluating cause-and-effect relationships. In these studies, participants are randomly assigned to either an intervention group (consuming nuts) or a control group (not consuming nuts). The rigorous design helps to isolate the impact of nut consumption on various health markers.
- One RCT, for example, might compare the effects of regular walnut consumption (a specific type of nut) on blood lipid profiles (cholesterol and triglycerides) and blood pressure in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Participants in the walnut group might show statistically significant improvements in these parameters compared to the control group, demonstrating a clear link between walnut intake and improved cardiovascular health markers.
Key Research Findings
Studies have consistently shown that regular consumption of nuts can positively impact various risk factors associated with heart disease in individuals with type 2 diabetes. The key findings frequently include:
- Improved Lipid Profiles: Nuts are generally rich in unsaturated fats and fiber, leading to a reduction in LDL cholesterol and an increase in HDL cholesterol (the “good” cholesterol). This positive impact on lipid profiles significantly reduces the risk of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular events.
- Blood Pressure Management: In many studies, nut consumption has been linked to lower blood pressure levels, a crucial factor in reducing the risk of hypertension-related complications.
- Reduced Inflammation: Some research indicates that nuts may help to reduce inflammation in the body, which is known to play a role in the development of cardiovascular disease.
Summary Table of Key Findings
| Study Type | Key Findings | Positive Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Meta-analyses | Significant reduction in LDL cholesterol and improvement in blood pressure | Lower risk of cardiovascular disease |
| RCTs | Improved lipid profiles (cholesterol and triglycerides), lower blood pressure | Reduced risk of atherosclerosis, hypertension |
Potential Considerations and Cautions
While nuts offer a wealth of heart-healthy benefits for people with type 2 diabetes, it’s crucial to approach their consumption with awareness of potential drawbacks. Understanding the nuances of nut consumption, including potential allergies, portion sizes, and interactions with medications, can help maximize the positive impact and minimize any negative effects.
Potential Allergic Reactions and Sensitivities
Nut allergies are a serious concern, affecting a significant portion of the population. Symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe life-threatening reactions. Individuals with known nut allergies should avoid all nuts, and those with a family history of allergies should exercise caution. Symptoms of a nut allergy can include hives, swelling, itching, difficulty breathing, and in severe cases, anaphylaxis.
It’s essential to be aware of cross-contamination, as traces of nuts can be present in processed foods. Individuals with nut allergies should always check labels carefully and be prepared for potential reactions.
Importance of Portion Control
Nuts are nutrient-dense, but their high calorie content necessitates careful portion control. A small handful (about 1 ounce or 28 grams) is generally recommended. Consuming larger portions can contribute to weight gain, which can negatively impact blood sugar control in people with type 2 diabetes. Overeating nuts can lead to an excess of calories, potentially negating some of the benefits and impacting overall health goals.
Potential Interactions with Medications or Other Health Conditions
Certain medications, such as blood thinners, can interact with the fats and minerals in nuts. Consult with a doctor or pharmacist before increasing nut consumption if taking any medications. Additionally, individuals with specific digestive conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), might experience discomfort or other issues with high nut intake. The interaction of nuts with other health conditions, such as kidney disease, should also be carefully considered, as nut consumption may impact certain dietary restrictions.
Table of Potential Cautions and Considerations for Nut Consumption
| Potential Consideration | Explanation | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Allergic Reactions | Nut allergies can range from mild discomfort to severe anaphylaxis. | Avoid nuts if allergic. Always check labels for cross-contamination. |
| Portion Control | High calorie density requires mindful portioning. | Stick to recommended serving sizes (1 ounce/28 grams). |
| Medication Interactions | Certain medications may interact with nut components. | Consult with doctor or pharmacist before increasing nut intake. |
| Digestive Issues | High nut intake may cause discomfort in individuals with digestive conditions like IBS. | Start with small portions and monitor for symptoms. |
| Other Health Conditions | Specific conditions (e.g., kidney disease) may require dietary adjustments. | Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance. |
Practical Recommendations and Lifestyle Implications: Eating Nuts Can Improve Heart Health For People With Type 2 Diabetes
Nuts, a delightful and nutritious addition to any diet, can significantly benefit people with type 2 diabetes. However, incorporating them effectively requires a mindful approach. This section will Artikel practical ways to include nuts in your daily life while maintaining a balanced diabetic-friendly eating plan.Effective nut consumption for individuals with type 2 diabetes hinges on understanding the portion sizes and the way they are integrated into overall dietary strategies.
The key is moderation and conscious planning.
Snacking on nuts can be a heart-healthy choice for those with type 2 diabetes, offering a wealth of nutrients. While the focus is often on individual dietary improvements, consider how policies like can bidens push for a public option lower your healthcare costs might impact overall access to healthcare, ultimately influencing the ability of people with diabetes to afford healthy choices like nuts.
Ultimately, eating nuts remains a key part of a holistic approach to managing heart health for those with type 2 diabetes.
Incorporating Nuts into a Healthy Diet
A balanced diet is crucial for managing type 2 diabetes, and nuts, in appropriate quantities, can be a valuable addition. Aim for a moderate intake of nuts, recognizing that even healthy foods can contribute to excess calorie consumption if not portion-controlled. Consult with a registered dietitian or diabetes educator for personalized recommendations.
Meal Planning Strategies
Strategic meal planning helps maintain blood sugar control and ensures nuts are part of a balanced meal. Include nuts as part of breakfast, lunch, or dinner, avoiding excessive consumption at any one time.
Different Ways to Consume Nuts
Nuts can be enjoyed in various ways. They can be a satisfying snack, adding healthy fats and protein to your day. Alternatively, incorporate them into recipes. For example, sprinkle them on salads, add them to yogurt or oatmeal, or use them as a crunchy topping for stir-fries or roasted vegetables. Including them in baked goods, like muffins or cookies, is also an option, but portion control is paramount.
Remember that certain recipes might require adjustments to maintain the appropriate carbohydrate balance.
Importance of a Balanced Diet and Overall Lifestyle
A balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein, is essential for managing type 2 diabetes. Nuts, while beneficial, should not be viewed as a replacement for a well-rounded diet. Regular physical activity, stress management techniques, and adherence to prescribed medications are also critical components of a comprehensive diabetes management strategy. The combination of a balanced diet and an active lifestyle significantly enhances the effectiveness of nut consumption in improving heart health.
Recipes Incorporating Nuts for Various Meals
- Breakfast: Overnight Oats with Almonds and Berries. Combine rolled oats, milk (dairy or non-dairy), chia seeds, almonds, and your favorite berries in a jar the night before. Enjoy a delicious and nutritious breakfast that provides sustained energy.
- Lunch: Mediterranean Quinoa Salad. Combine cooked quinoa with chopped cucumber, tomatoes, bell peppers, Kalamata olives, and a handful of walnuts. Dress with a lemon-herb vinaigrette for a light and satisfying lunch.
- Dinner: Nutty Chicken Stir-fry. Stir-fry chicken breast with mixed vegetables (broccoli, carrots, snap peas) and a sprinkle of cashews or almonds. Serve over brown rice for a complete and protein-rich meal.
- Snack: Apple slices with peanut butter and a sprinkle of pumpkin seeds. This combination provides fiber, protein, and healthy fats for a satisfying snack.
Illustrative Examples of Healthy Nut-Based Recipes
Nuts, particularly those rich in healthy fats, fiber, and protein, offer delicious and nutritious ways to enhance meals and snacks. Incorporating nuts into your diet can be a simple yet effective strategy to improve your overall well-being, especially for individuals with type 2 diabetes. These recipes are designed to be both flavorful and beneficial, highlighting the versatility of nuts in various culinary applications.These recipes illustrate how to seamlessly integrate nuts into your daily diet, providing a delightful and nutritious way to support your heart health and manage your blood sugar levels effectively.
They showcase the versatility of nuts, transforming them from simple snacks into satisfying components of complete meals.
Eating nuts can be a surprisingly healthy choice for those with type 2 diabetes, boosting heart health. While managing blood sugar is crucial, incorporating nuts into a balanced diet can help. For those considering advanced diabetes management options, exploring resources like medtronics implantable insulin pump what you might like to know could be beneficial. Ultimately, a multifaceted approach to managing type 2 diabetes, including a diet rich in healthy nuts, can significantly improve overall well-being.
Nutty Protein Power Breakfast Bowl
This breakfast bowl combines the protein and healthy fats of nuts with fiber-rich ingredients to create a satisfying and nutritious start to your day. It provides a balanced mix of nutrients, including protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates, promoting satiety and sustained energy.
- This recipe is a great source of protein, healthy fats, and fiber, all of which are crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels and promoting satiety.
- The combination of ingredients provides a good balance of nutrients, including protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates.
Ingredients: 1/2 cup rolled oats, 1 cup unsweetened almond milk, 1/4 cup chopped walnuts, 1/4 cup chopped almonds, 1/4 cup berries, 1 tablespoon chia seeds, a pinch of cinnamon.
Instructions: Cook rolled oats according to package directions. In a separate bowl, combine almond milk, walnuts, almonds, berries, chia seeds, and cinnamon. Pour the mixture over the cooked oats and enjoy immediately.
Nutritional Information (approximate): Calories: 450, Protein: 15g, Fat: 20g, Fiber: 10g.
Nut-Crusted Chicken Breast with Quinoa
This recipe demonstrates how nuts can be incorporated into a complete meal, enhancing the flavor and texture of the dish while providing additional nutrients.
- This recipe combines lean protein with healthy fats and fiber, promoting a balanced meal plan and sustained energy.
- The nut crust adds a delightful crunch and flavor, elevating the chicken breast into a more satisfying dish.
Ingredients: 2 boneless, skinless chicken breasts, 1/4 cup chopped pecans, 1/4 cup chopped walnuts, 1 tablespoon olive oil, 1 teaspoon paprika, salt and pepper to taste, 1 cup cooked quinoa.
Instructions: Preheat oven to 375°F (190°C). Combine pecans and walnuts in a shallow dish. Place chicken breasts in the nut mixture, ensuring they are fully coated. Season with paprika, salt, and pepper. Bake for 20-25 minutes, or until chicken is cooked through.
Studies show that eating nuts can be a surprisingly effective way to improve heart health for people with type 2 diabetes. It’s important to remember that while some health advice feels promising, like the kinds often promoted by certain wellness brands, it’s crucial to approach these claims with a critical eye. For example, a lot of the health advice coming from places like Goop has faced significant criticism for its lack of scientific backing criticism of paltrow goop health advice.
So, while incorporating nuts into a balanced diet can be beneficial, it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes, especially if you have type 2 diabetes.
Serve over cooked quinoa.
Nutritional Information (approximate): Calories: 500, Protein: 40g, Fat: 25g, Fiber: 8g.
Nut and Fruit Energy Bites
These energy bites offer a convenient and nutritious snack option, providing a good source of energy and essential nutrients.
- These energy bites are perfect for a quick and healthy snack on the go.
- The combination of nuts, dried fruits, and seeds creates a satisfying and nutritious snack.
Ingredients: 1/2 cup rolled oats, 1/4 cup chopped walnuts, 1/4 cup dried cranberries, 1/4 cup dried apricots, 2 tablespoons honey, 1 tablespoon peanut butter, 1 tablespoon flax seeds.
Instructions: Combine all ingredients in a bowl and mix well. Roll the mixture into small balls. Store in an airtight container in the refrigerator.
Nutritional Information (approximate): Calories: 150, Protein: 5g, Fat: 8g, Fiber: 5g.
| Recipe | Ingredients | Nutritional Information (approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| Nutty Protein Power Breakfast Bowl | Oats, Almond Milk, Walnuts, Almonds, Berries, Chia Seeds, Cinnamon | Calories: 450, Protein: 15g, Fat: 20g, Fiber: 10g |
| Nut-Crusted Chicken Breast with Quinoa | Chicken Breasts, Pecans, Walnuts, Olive Oil, Paprika, Salt & Pepper, Quinoa | Calories: 500, Protein: 40g, Fat: 25g, Fiber: 8g |
| Nut and Fruit Energy Bites | Oats, Walnuts, Cranberries, Apricots, Honey, Peanut Butter, Flax Seeds | Calories: 150, Protein: 5g, Fat: 8g, Fiber: 5g |
Visual Representation of Nut Nutritional Information
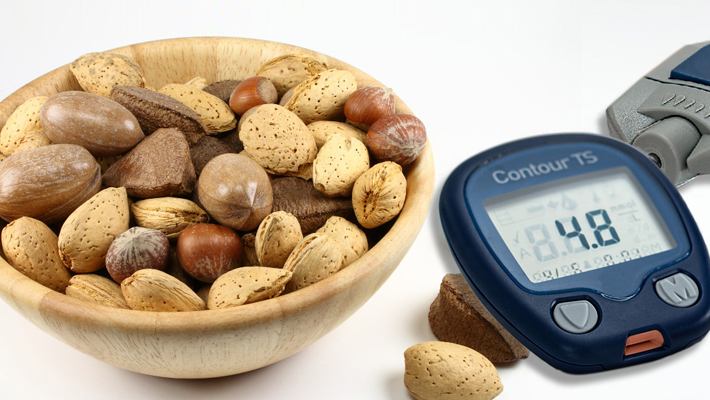

Nuts are a powerhouse of nutrients, offering a wide range of benefits for people with type 2 diabetes. Understanding their nutritional content is crucial for incorporating them safely and effectively into a healthy diet. Visual representations of this information can greatly enhance comprehension and make informed choices easier.
Key Nutrients in Nuts
Nuts are excellent sources of healthy fats, protein, fiber, and various vitamins and minerals. Visualizing these components is vital for appreciating their nutritional density. A well-designed infographic could display these nutrients in a visually appealing way. For example, a pie chart could show the percentage breakdown of fats, protein, and carbohydrates in different types of nuts, making it easy to compare their nutritional profiles.
Nutritional Value of Different Nut Types
Different nuts offer unique nutritional profiles. An infographic could present this information through bar charts or stacked column charts. For instance, a bar chart could illustrate the amount of protein, fiber, and healthy fats per 1-ounce serving of almonds, walnuts, cashews, and peanuts. This comparison enables users to identify which nuts best suit their dietary needs. Tables can also be included to present the specific amounts of nutrients.
Portion Sizes for Nut Consumption
Portion control is vital when incorporating nuts into your diet. A visual representation of appropriate portion sizes is essential. An infographic could include images or illustrations of common measuring tools (e.g., a ¼ cup) and corresponding visual representations of the nut quantities that make up the portion. This aids in accurate consumption and prevents overeating.
Impact of Nut Consumption on Health Markers
Nuts can positively impact various health markers. An infographic could use line graphs to display how nut consumption might influence blood sugar levels, cholesterol levels, and blood pressure. This visualization can help people understand the potential health benefits of incorporating nuts into their diets. For instance, a line graph could show how regular consumption of walnuts, over a period of time, might contribute to a reduction in LDL cholesterol.
Infographic Design Principles
An effective infographic should use clear and concise language, employ various visual elements (e.g., colors, icons), and adhere to a consistent design style. The infographic should be visually appealing and easy to understand. The design should prioritize clarity and accuracy. A simple, clean design with clear labels and easily readable text ensures the information is easily digestible.
For instance, using a color-coded system to differentiate different types of nuts or nutrients can enhance visual comprehension. The use of different fonts and sizes can emphasize key points.
Example Infographic – Nutritional Value of Almonds
| Nutrient | Amount per 1 ounce |
|---|---|
| Calories | 160 |
| Protein | 6 grams |
| Fiber | 3.5 grams |
| Healthy Fats | 14 grams |
| Vitamin E | 19% of daily value |
| Magnesium | 20% of daily value |
The table above illustrates a concise and easily understandable representation of the nutritional profile of almonds, focusing on key nutrients.
This straightforward presentation helps users quickly grasp the nutritional value of almonds in a single glance. A similar format could be used for other nuts, with specific values for each.
Summary
In conclusion, incorporating nuts into a balanced diet can be a powerful tool for people with type 2 diabetes looking to improve their heart health. While nuts offer significant benefits, portion control and awareness of potential allergies or interactions with medications are crucial. This comprehensive guide has provided the scientific evidence, practical recommendations, and delicious recipe ideas to support your journey toward a healthier lifestyle.
By understanding the specific types of nuts, their nutritional value, and the scientific backing for their benefits, you can confidently integrate them into your daily routine. Remember, a balanced approach, including regular exercise and a comprehensive dietary plan, is key to optimal health.