Ewing sarcoma stage 4 sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a challenging and often emotionally charged journey. This comprehensive guide delves into the specifics of this aggressive cancer, exploring its characteristics, diagnosis, treatment options, and the crucial support available to patients and families. We’ll examine the key distinctions between stage 4 and other stages, highlighting the unique symptoms and prognosis associated with this advanced form of Ewing sarcoma.
Understanding the complexities of Ewing sarcoma stage 4 is essential for navigating the emotional and practical challenges that come with this diagnosis. From the initial diagnostic procedures to the diverse treatment approaches and the crucial role of long-term care, we aim to provide a thorough and accessible overview. This includes examining the role of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery, while also considering the potential side effects of each treatment.
Furthermore, we will explore the emotional support systems available to those affected by this disease.
Overview of Ewing Sarcoma Stage 4
Ewing sarcoma, a rare but aggressive bone cancer, presents significant challenges for patients, especially when it reaches stage 4. Understanding the specific characteristics of stage 4 is crucial for effective management and treatment planning. This stage signifies a more advanced disease, requiring a multifaceted approach to address its spread and impact on the body.
Definition of Ewing Sarcoma Stage 4
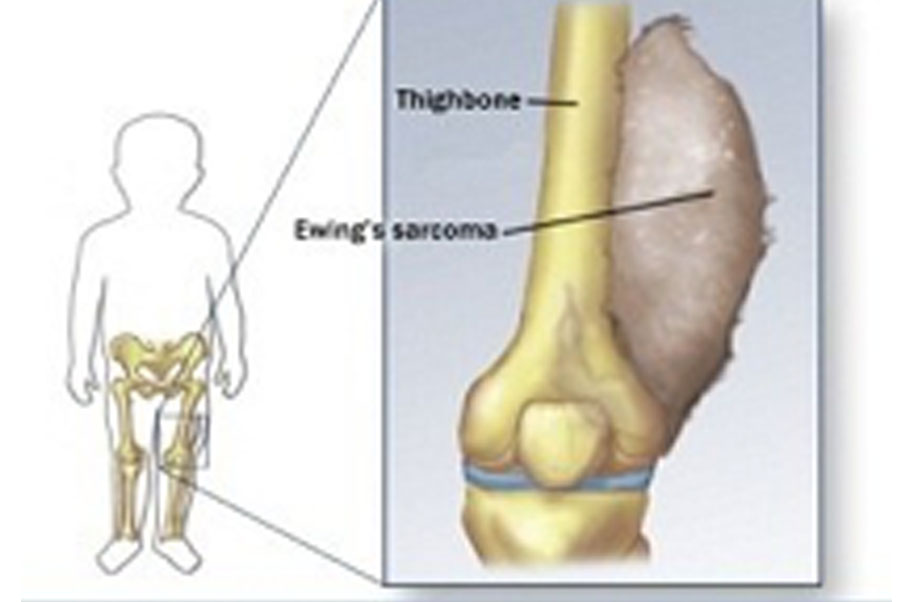
Stage 4 Ewing sarcoma is characterized by the presence of the tumor in multiple distant sites beyond the initial location. This signifies the disease’s advanced and disseminated nature, with the cancer cells having metastasized to other parts of the body. The primary tumor might still be present, but the presence of metastases in multiple organs or systems distinguishes it from earlier stages.
This advanced stage necessitates a more aggressive treatment approach.
Key Characteristics Distinguishing Stage 4
Stage 4 Ewing sarcoma stands apart from earlier stages due to the widespread nature of the disease. The key differentiator is the presence of metastasis, meaning the cancer has spread beyond the initial bone site to other organs. This signifies a significant shift in the disease’s trajectory, demanding more complex and often more intensive treatment strategies.
Typical Presentation at Stage 4
The presentation of Ewing sarcoma at stage 4 is highly variable, depending on the specific sites of metastasis. Common sites for metastasis include the lungs, bone marrow, liver, and other organs. Patients might experience symptoms related to the primary tumor site, but also symptoms stemming from the presence of the cancer in these secondary locations. Symptoms could include bone pain, persistent fatigue, unexplained weight loss, and organ-specific complications.
Common Symptoms Associated with Stage 4
A range of symptoms can manifest in stage 4 Ewing sarcoma, reflecting the diverse locations of metastasis. These can include:
- Bone pain: Pain in the affected bones, possibly increasing in intensity and frequency.
- Fatigue: A persistent and overwhelming feeling of tiredness, often unrelated to activity levels.
- Weight loss: Unexplained and progressive weight loss, often due to the metabolic demands of the disease and the impact on appetite.
- Fever: A persistent elevation in body temperature, potentially indicating an inflammatory response to the disease or an infection.
- Lungs: Symptoms like shortness of breath, coughing, or chest pain, if the lungs are involved.
- Other organs: Symptoms related to the specific organs affected by metastasis, such as liver dysfunction or neurological complications.
Comparison of Ewing Sarcoma Stages
| Stage | Symptoms | Prognosis | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1 | Localized tumor, minimal or no symptoms | Good, often curable with surgery | Surgery, radiation therapy |
| Stage 2 | Tumor extends to nearby tissues | Favorable, typically treatable | Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy |
| Stage 3 | Tumor involves multiple bones or bone marrow | Intermediate prognosis | Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy |
| Stage 4 | Metastasis to distant organs (lungs, liver, etc.) | Generally poor, with significant challenges | Aggressive chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, clinical trials |
Note: Prognosis and treatment options can vary based on individual factors, including the specific tumor characteristics, patient’s overall health, and response to treatment. This table provides a general overview.
Diagnostic Procedures and Tests
Diagnosing Ewing sarcoma, particularly in its advanced stage 4, requires a multi-faceted approach involving various procedures to pinpoint the location, extent, and nature of the cancer. This meticulous process ensures accurate staging, guiding treatment decisions and potentially improving patient outcomes. The diagnostic journey typically starts with a thorough evaluation of symptoms, followed by a series of tests to confirm the diagnosis and understand the disease’s characteristics.Imaging techniques, biopsies, and laboratory tests play crucial roles in the diagnostic process.
Each step provides vital information about the tumor’s presence, size, and potential spread. A comprehensive understanding of these procedures empowers healthcare professionals to formulate effective treatment strategies.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques are fundamental to evaluating Ewing sarcoma stage 4. They provide crucial visualization of the tumor’s location, size, and relationship to surrounding structures.X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are commonly used. X-rays offer initial views of bone abnormalities, while CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images, highlighting the tumor’s extent and its impact on adjacent organs.
MRI scans offer superior soft tissue contrast, enabling a more precise depiction of the tumor’s characteristics and its possible spread.
Facing Ewing sarcoma stage 4 is undeniably tough. While the medical advancements are promising, it’s fascinating to consider how factors like access to top-notch healthcare, which some groups like white rich seniors getting healthier often enjoy, might influence outcomes. This disparity in resources highlights the need for equitable access to care for all battling this aggressive cancer.
Biopsy
A biopsy is an essential procedure in diagnosing Ewing sarcoma. A tissue sample is extracted from the suspected tumor site for microscopic examination. This allows pathologists to analyze the cells under a microscope, confirming the diagnosis and identifying the specific type of sarcoma present. Pathological examination of the tissue sample helps determine the tumor’s grade (degree of aggressiveness) and the presence of any specific genetic markers, providing vital information for targeted treatment approaches.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests are used to assess the patient’s overall health and provide further insights into the disease.Complete blood counts (CBCs) and blood chemistry panels are routinely performed to evaluate blood cell counts and organ function. Elevated levels of certain markers, such as lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), may indicate tumor burden or disease activity. Genetic testing can identify specific genetic alterations that might influence treatment decisions.
Summary of Diagnostic Procedures
| Diagnostic Procedure | Purpose | Procedure | Expected Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| X-rays | Initial screening for bone abnormalities | Exposure to low-dose ionizing radiation to create images of bones. | Visualization of potential bone lesions, fractures, or areas of increased density, which may suggest the presence of a tumor. |
| CT scans | Detailed assessment of tumor extent and location | Imaging technique using X-rays and computer processing to create cross-sectional images. | Detailed images of the tumor’s size, shape, and location relative to surrounding structures, including organs and blood vessels. |
| MRI scans | High-resolution imaging of soft tissues | Uses a powerful magnetic field and radio waves to produce detailed images of soft tissues. | Detailed images of soft tissues surrounding the tumor, providing information about tumor infiltration and potential spread. |
| Biopsy | Confirm diagnosis and assess tumor characteristics | Removal of a tissue sample from the tumor for microscopic examination. | Microscopic examination reveals the presence of Ewing sarcoma cells, tumor grade, and any specific genetic abnormalities. |
| Lab tests (CBC, blood chemistry, LDH) | Assessment of patient’s overall health and disease activity | Blood tests to measure blood cell counts, organ function, and tumor markers. | Provides information about the patient’s general health and potential indicators of disease activity or tumor burden. |
Treatment Approaches for Stage 4 Ewing Sarcoma
Stage 4 Ewing sarcoma presents a complex and challenging treatment landscape. Aggressive and multifaceted approaches are crucial for maximizing survival and quality of life. Effective treatment plans often integrate multiple modalities, each playing a specific role in addressing the disease’s spread and impact on the patient’s overall health.
Standard Treatment Options
The standard treatment for stage 4 Ewing sarcoma usually involves a combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and sometimes surgery. The specific approach is tailored to each individual patient based on factors like the location and extent of the tumor, the patient’s age, and overall health. This personalized approach aims to maximize efficacy while minimizing side effects.
Role of Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy plays a vital role in treating stage 4 Ewing sarcoma. It’s designed to target rapidly dividing cells, including cancer cells, throughout the body. The goal is to shrink the primary tumor, reduce the spread of the disease, and improve the patient’s response to further treatments. A variety of chemotherapy drugs are commonly used, often in combination, to achieve optimal results.
Use of Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy, often used in conjunction with chemotherapy, is another crucial component in the treatment of stage 4 Ewing sarcoma. Radiation therapy focuses high-energy beams on the tumor site to damage cancer cells and shrink the tumor. It can be used to treat the primary tumor site, as well as areas where the cancer has spread. The type and dose of radiation therapy will vary depending on the patient’s specific needs.
Role of Surgery in Treatment
Surgical intervention in stage 4 Ewing sarcoma is typically reserved for specific situations. It might be employed to debulk a large tumor, relieve pressure on vital structures, or remove a tumor that is causing significant pain or other symptoms. The role of surgery in stage 4 is usually supportive rather than curative, aiming to improve quality of life and allow for other treatments to be more effective.
Comparison of Treatment Approaches
Different treatment approaches for stage 4 Ewing sarcoma have varying degrees of effectiveness and potential side effects. Chemotherapy, while effective in shrinking tumors and controlling the spread, can cause side effects such as nausea, hair loss, and fatigue. Radiation therapy, while effective in targeting tumors, can also cause side effects such as skin irritation, fatigue, and long-term complications.
Surgical intervention, when used, aims to alleviate symptoms but may not always be curative.
Treatment Regimens for Stage 4 Ewing Sarcoma
| Treatment Regimen | Drugs | Dosage | Schedule |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example Regimen 1 | Etoposide, Doxorubicin, Cyclophosphamide | Variable based on patient factors | Typically administered in cycles |
| Example Regimen 2 | Ifosfamide, Carboplatin | Variable based on patient factors | Typically administered in cycles |
| Example Regimen 3 | Vincristine, Adriamycin | Variable based on patient factors | Typically administered in cycles |
Note: This table provides examples of possible treatment regimens. Specific regimens and dosages will be determined by the treating oncologist based on individual patient characteristics.
Prognosis and Long-Term Effects
Ewing sarcoma, particularly stage 4, presents a complex challenge for patients and their families. Understanding the prognosis, the factors that influence it, and the potential long-term effects of treatment is crucial for informed decision-making. This knowledge empowers patients and their support networks to navigate the journey with a clearer understanding of what to expect.The prognosis for Ewing sarcoma stage 4 is generally less favorable than for earlier stages.
While advancements in treatment have improved outcomes significantly, the aggressive nature of the disease and the potential for metastasis necessitate a proactive approach to management and follow-up.
Typical Prognosis for Stage 4 Ewing Sarcoma
The typical prognosis for stage 4 Ewing sarcoma is influenced by several factors, including the extent of the disease’s spread, the patient’s age, and the response to treatment. While complete remission is possible, long-term survival rates can vary considerably. Clinical trials and observational studies provide valuable data, but individual outcomes remain unpredictable.
Factors Influencing Prognosis
Numerous factors play a role in shaping the prognosis for stage 4 Ewing sarcoma. These include:
- Patient Age: Younger patients often have a better chance of long-term survival, likely due to their bodies’ ability to better tolerate treatment and potentially having a less aggressive tumor. However, this isn’t always the case, and age alone cannot determine the prognosis.
- Tumor Size and Location: Larger tumors and those located in areas with higher risk of spreading or compromising vital organs may have a poorer prognosis. The precise location of the primary tumor and its spread to other sites are also significant factors.
- Extent of Metastasis: The extent of the disease’s spread to other parts of the body significantly impacts the prognosis. If the metastasis is limited to a few sites, the prognosis may be better than widespread metastasis.
- Response to Treatment: The patient’s response to initial chemotherapy and other therapies is a crucial factor. A robust response to treatment generally translates into a better chance of long-term survival.
Potential Long-Term Effects of Treatment
Treatment for stage 4 Ewing sarcoma, while vital for survival, can lead to various long-term effects. These effects can range from manageable side effects to more significant complications.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Certain chemotherapy drugs can have long-term impacts on the heart, potentially leading to heart conditions. Regular cardiovascular monitoring is essential for long-term health.
- Reproductive Issues: Chemotherapy can affect fertility in both males and females. Discussions about fertility preservation options are vital for patients of reproductive age.
- Secondary Cancers: Long-term exposure to certain chemotherapy drugs can increase the risk of developing secondary cancers. This risk is a consideration that must be carefully weighed against the benefits of treatment.
- Growth and Development Issues: In children and adolescents, treatment can impact growth and development. Close monitoring and supportive care are crucial during this period.
Importance of Follow-up Care
Proactive and ongoing follow-up care is critical for patients with stage 4 Ewing sarcoma. Regular check-ups and monitoring allow for early detection of potential complications or recurrence.
- Regular Check-ups: Regular appointments with oncologists are essential for monitoring the patient’s health and identifying any potential problems.
- Imaging Studies: Imaging studies, such as CT scans or MRIs, may be necessary to monitor the tumor’s response and identify any signs of recurrence.
- Blood Tests: Regular blood tests are important for assessing organ function and identifying any potential side effects of treatment.
- Support Groups: Support groups and counseling can help patients and families cope with the emotional and psychological challenges of the disease and treatment.
Factors Influencing Prognosis Table
| Factor | Description | Potential Impact on Prognosis |
|---|---|---|
| Patient Age | Age at diagnosis | Younger patients generally have a better prognosis |
| Tumor Size | Size of the primary tumor | Larger tumors are often associated with a poorer prognosis |
| Treatment Response | How well the patient responds to initial treatment | A strong response to treatment is associated with a better prognosis |
| Extent of Metastasis | The spread of the tumor to other sites | Widespread metastasis is often associated with a poorer prognosis |
Support and Resources for Patients and Families
Facing a stage 4 Ewing sarcoma diagnosis is incredibly challenging, not just medically, but emotionally and practically as well. Navigating the complexities of treatment, managing side effects, and the uncertainty of the future can be overwhelming for patients and their families. The importance of robust support networks cannot be overstated. This crucial aspect of care provides emotional strength, practical assistance, and essential information to help families cope with the disease.
Facing Ewing sarcoma stage 4 is tough, but open communication with your doctor is key. It’s important to understand how to effectively discuss medical concerns, like the challenging ‘off’ episodes common in Parkinson’s disease. For a helpful guide on navigating these conversations, check out this resource on how to talk with your doctor about Parkinson’s off episodes.
Ultimately, proactive communication is vital in managing any serious illness, including Ewing sarcoma stage 4, so you can focus on what matters most.
The Importance of Emotional Support
Emotional well-being is paramount for patients and families facing Ewing sarcoma. The diagnosis and treatment journey can trigger a range of emotions, including fear, anxiety, anger, and grief. Having access to support groups, counseling, and emotional assistance can help manage these difficult feelings and foster resilience. A strong support system allows individuals to process their emotions in a healthy way, improving their overall quality of life.
Open communication and understanding within the family unit are critical during this time.
Resources for Support Groups and Counseling, Ewing sarcoma stage 4
Finding appropriate support groups and counseling services is crucial for patients and families. Many organizations dedicated to pediatric cancers, including Ewing sarcoma, offer support groups where individuals can connect with others facing similar challenges. These groups provide a sense of community, shared experiences, and practical advice. Professional counseling can help individuals and families navigate the emotional complexities of the disease, providing coping strategies and emotional support.
Furthermore, online forums and support groups can be invaluable resources for connecting with others, sharing experiences, and accessing information remotely.
Patient Education: Understanding the Disease, Treatment, and Prognosis
Education plays a vital role in empowering patients and families to actively participate in their care. A clear understanding of the disease, treatment options, and potential outcomes is crucial. Comprehensive patient education programs provide accurate and up-to-date information, enabling informed decisions and reducing anxieties. This knowledge fosters a sense of control and agency, which is essential for managing the challenges of the disease.
By understanding the disease’s progression and the potential long-term effects, families can develop realistic expectations and create strategies for coping.
Reputable Support Groups and Organizations
The following table lists some reputable support groups and organizations dedicated to helping patients and families cope with Ewing sarcoma stage 4. These organizations provide a variety of resources, including support groups, educational materials, and access to experts. Their commitment to supporting patients and families throughout the journey is invaluable.
| Organization | Description | Contact Information |
|---|---|---|
| [e.g., The Children’s Oncology Group] | Offers research, clinical trials, and support programs for childhood cancers, including Ewing sarcoma. | [Insert Contact Information] |
| [e.g., The American Cancer Society] | Provides a wide range of services, including support groups, educational materials, and financial assistance for cancer patients and families. | [Insert Contact Information] |
| [e.g., Local Cancer Support Groups] | Many local communities have support groups specifically for cancer patients and their families. | [Insert Contact Information] |
| [e.g., Online Forums/Support Groups] | Online communities can provide a space for connecting with others, sharing experiences, and finding emotional support. | [Insert Contact Information] |
Research and Advancements in Ewing Sarcoma Treatment
Ewing sarcoma, a challenging cancer, demands relentless pursuit of better treatments, especially for the aggressive stage 4. Ongoing research is crucial for improving outcomes and providing hope for patients facing this diagnosis. The quest involves exploring new therapies, understanding the disease’s intricacies, and leveraging the power of clinical trials.
Current Research Efforts
Researchers are actively investigating various avenues to enhance treatment efficacy and reduce side effects. One key area of focus is developing targeted therapies that specifically attack Ewing sarcoma cells without harming healthy tissues. This involves identifying molecular pathways crucial for the tumor’s growth and survival. Scientists are also looking at novel combinations of existing chemotherapy drugs to achieve higher response rates.
Emerging Therapies
Immunotherapy holds significant promise in the fight against Ewing sarcoma. This approach aims to harness the body’s own immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells. Researchers are investigating different types of immunotherapy, including checkpoint inhibitors and adoptive cell therapies. Early trials show encouraging results in some patients, signifying a potential paradigm shift in treatment strategies.
Facing Ewing sarcoma stage 4 can be incredibly tough, filled with a lot of unknowns and anxieties. While navigating the medical side of things, it’s interesting to consider how quickly AI is evolving, like how human-like bots are becoming. For example, are Alexa and other human-like bots giving you uncanny vanny? This article explores the unsettling aspects of these increasingly sophisticated bots.
Ultimately, though, the emotional and physical toll of Ewing sarcoma stage 4 remains a significant challenge, demanding both medical expertise and a strong support system.
Clinical Trials: A Cornerstone of Progress
Clinical trials are indispensable in evaluating the safety and effectiveness of new therapies. They provide a rigorous framework for testing novel treatments in real-world settings. Participants in clinical trials play a vital role in advancing knowledge and potentially benefiting from cutting-edge interventions. These trials are often the gateway to breakthroughs, and patient participation is essential.
Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Treatments
The concept of personalized medicine is gaining traction in oncology. This approach involves tailoring treatment plans to individual patients based on their specific genetic makeup and tumor characteristics. Researchers are identifying genetic markers associated with Ewing sarcoma that could predict treatment response and guide therapeutic choices. This personalized approach aims to optimize treatment effectiveness while minimizing side effects.
Key Research Findings (Past 5 Years)
| Year | Research Focus | Key Findings | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | Targeted therapy for Ewing sarcoma | Identification of specific molecular targets and development of initial targeted therapies. | Limited clinical application, but promising direction for future research. |
| 2020 | Immunotherapy strategies | Early-phase trials showing positive responses in some patients. | Early indications of immunotherapy’s potential, prompting further investigation. |
| 2021 | Combination therapies | Studies evaluating combinations of chemotherapy and targeted therapies showing higher response rates. | Significant progress in treatment efficacy, suggesting the possibility of improved outcomes. |
| 2022 | Genomic analysis and personalized medicine | Improved understanding of genetic variations associated with treatment response. | Potential for more precise treatment selection and improved patient outcomes. |
| 2023 | Novel drug delivery systems | Exploration of novel drug delivery methods to improve drug efficacy and reduce side effects. | A promising approach to potentially overcome drug resistance and enhance treatment effectiveness. |
Patient Stories and Case Studies (Illustrative)
Understanding Ewing sarcoma stage 4 requires empathy and a keen appreciation for the human experience. These patient stories, though hypothetical, aim to illustrate the complexities of the disease and the resilience of those affected. They highlight the physical, emotional, and practical challenges encountered, alongside the vital role of medical professionals in navigating this challenging journey.
A Hypothetical Patient’s Journey
A 16-year-old named Liam presented with persistent hip pain and swelling. Initial diagnostic tests revealed a tumor in his pelvis, and subsequent biopsies confirmed a diagnosis of Ewing sarcoma stage 4. The diagnosis was devastating, shattering Liam’s world and that of his family. He was facing a long and arduous treatment path, fraught with uncertainty and potential setbacks.
Challenges and Triumphs
Liam’s journey was marked by intense chemotherapy regimens, often leading to debilitating side effects like nausea, fatigue, and hair loss. These physical hardships were compounded by emotional struggles. Fear, anxiety, and a sense of loss were constant companions. However, Liam’s spirit remained unbroken. He found solace in connecting with other young cancer patients through online support groups and in the unwavering support of his family.
Liam also found strength in the empathy and expertise of his medical team.
Emotional Impact on Patient and Family
The emotional toll of Ewing sarcoma stage 4 extends beyond the patient. Liam’s family faced immense stress, juggling medical appointments, financial burdens, and the emotional weight of their son’s suffering. They had to navigate a complex healthcare system, often feeling overwhelmed and uncertain. The uncertainty of the future, the emotional turmoil, and the significant adjustments to their lives profoundly impacted Liam’s parents, who found support in each other, in medical professionals, and in their community.
Grief, anxiety, and fear were commonplace, and coping mechanisms varied.
Role of Medical Professionals
Liam’s medical team played a crucial role in his care. Oncologists, nurses, social workers, and other healthcare professionals provided comprehensive support, not only managing his physical condition but also addressing his emotional needs. Regular communication, empathy, and a proactive approach to addressing side effects were essential. Liam’s medical team helped him understand the treatment plan, and provided avenues for emotional support.
They also connected the family with resources, allowing them to better cope with the challenges.
“The journey with Ewing sarcoma stage 4 was challenging, but the unwavering support of my family and medical team kept me going. I learned resilience and strength I never knew I possessed. The hope for a better future kept me motivated.”Liam (hypothetical patient)
Ending Remarks: Ewing Sarcoma Stage 4
In conclusion, Ewing sarcoma stage 4 presents a multifaceted challenge, demanding a comprehensive understanding of its various facets. This guide has highlighted the key aspects of diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis, while emphasizing the importance of support systems. Ultimately, this journey underscores the strength of the human spirit and the unwavering dedication of medical professionals, families, and patients as they face this formidable disease.
Continued research and advancements in treatment hold the promise of improved outcomes and a brighter future for those affected.