Following insulin price money trail, we delve into the complex financial landscape surrounding this vital medication. From historical price trends to the intricate supply chain, we explore the factors driving insulin costs and their far-reaching impact. This investigation examines the role of manufacturers, distributors, and government regulations, and ultimately analyzes the burden on patients and healthcare systems.
This exploration unveils the diverse stages of insulin production, from raw materials to the final product. We analyze the different types of insulin, their pricing variations, and the market forces impacting their cost. Comparing prices across countries and highlighting the profit margins at each stage of the supply chain provides a clear picture of the financial implications.
Insulin Price Fluctuations
Insulin, a life-saving medication for millions, has seen significant price fluctuations over the years. Understanding these trends is crucial for patients, healthcare providers, and policymakers alike. The rising costs of insulin have become a significant concern, prompting investigations into the underlying factors driving these price increases. This exploration will delve into the historical patterns, various types, market forces, and global disparities in insulin pricing.The fluctuating costs of insulin are a complex issue, influenced by a variety of interconnected factors.
These include advancements in technology, market competition, and the inherent complexities of the pharmaceutical industry. Analyzing these elements provides a clearer picture of the challenges and opportunities surrounding insulin pricing.
Historical Overview of Insulin Price Trends
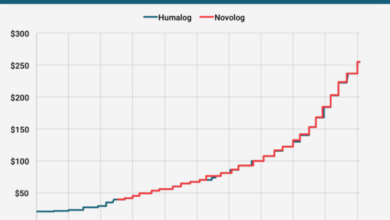
Insulin prices have experienced notable increases over time, creating substantial financial burdens for many patients. Early insulin was often produced using animal sources, which impacted costs and availability. Technological advancements led to the development of human insulin, and subsequently, newer, more sophisticated formulations. These advancements, while improving efficacy and convenience, often came with increased production costs. The shift from animal-derived to human insulin formulations and subsequent innovations played a role in price changes.
Different Types of Insulin and Their Price Variations
Various types of insulin cater to different needs and treatment regimens. Rapid-acting insulins are designed for quick absorption and are often more expensive than longer-acting varieties. The complexity of production processes and the specific formulations influence the price differences. The need for specialized manufacturing techniques and advanced research often contributes to the variation in price. Different types of insulin, like rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting, exhibit varying degrees of price fluctuations.
This variation is partly due to the differences in manufacturing processes, the specific ingredients, and the required regulatory approvals.
Impact of Market Forces on Insulin Pricing
Market forces, including supply and demand dynamics and competition among manufacturers, have a considerable impact on insulin pricing. Limited competition in the insulin market can lead to higher prices, especially when there are few alternatives available. Demand for insulin is relatively inelastic, meaning that even if prices increase, the demand remains high due to the necessity of the medication.
The balance between supply and demand, coupled with competitive pressures, ultimately shapes the market price. The lack of competition and the necessity of the medication contribute to the high prices.
Insulin Prices Across Different Countries
| Country | Average Insulin Price (USD) |
|---|---|
| United States | ~500 – ~1000 |
| Canada | ~200 – ~500 |
| United Kingdom | ~100 – ~300 |
| Germany | ~150 – ~400 |
Note
* Prices are approximate and can vary based on specific insulin types and quantities purchased.
Insulin Manufacturers and Their Product Ranges
| Manufacturer | Insulin Product Range |
|---|---|
| Novo Nordisk | NovoLog, Levemir, Humalog, and more |
| Sanofi | Lantus, Apidra, and others |
| Lilly | Humulin, and others |
Note
* This table is not exhaustive and there are other manufacturers and insulin products available.
Money Trail of Insulin Production

Insulin, a life-saving medication for millions, has a complex production and distribution process. Understanding the financial aspects of this process is crucial for comprehending the factors influencing insulin prices. This exploration delves into the various stages, players, and financial transactions involved in bringing insulin from raw materials to the patient.The insulin supply chain is intricate, involving multiple players with varying degrees of influence over the final price.
From the agricultural production of the raw materials to the retail pharmacy where patients purchase the medication, numerous financial transactions occur. Examining these transactions helps us understand the pressures and incentives within the industry.
Raw Material Acquisition
The production of insulin starts with the procurement of raw materials. These materials, often derived from agricultural products, are crucial to the insulin production process. The price of these raw materials can fluctuate significantly depending on market conditions, crop yields, and global demand. This volatility can directly impact the cost of insulin production.
Insulin Production
The production process itself involves sophisticated biotechnologies. Insulin is typically produced using genetically modified microorganisms, often in large-scale fermentation tanks. The production facilities are highly specialized and require significant investment in equipment and personnel. Operating costs, including labor, utilities, and research and development, contribute significantly to the overall production cost.
Manufacturing and Quality Control
Following production, the insulin undergoes rigorous quality control procedures. These tests ensure the medication’s purity, potency, and safety. This step adds to the cost of production due to the need for specialized equipment, trained personnel, and stringent regulatory compliance.
Following the insulin price money trail can be tricky, but it’s crucial for understanding the market forces at play. One aspect that often gets overlooked is the impact on the quality of diet for older adults, which has unfortunately declined in recent years. This is directly related to the rising cost of healthy options, as detailed in this insightful article about improving dietary habits for seniors: quality of diet for older adults has declined heres how to fix it.
Ultimately, understanding these interconnected factors is key to following the insulin price money trail effectively.
Distribution and Logistics
Once the insulin is manufactured and approved, it is distributed to wholesalers and retailers. This stage involves complex logistics, including warehousing, transportation, and handling. Transportation costs, storage costs, and distribution channels impact the price of insulin at the retail level.
Following the insulin price money trail is definitely a rabbit hole. It’s fascinating how these things intertwine, but also concerning. Meanwhile, recent studies suggest that Celebrex might be safer for the heart than previously thought, which is good news for those who need it. This article delves deeper into that, and I’m still trying to figure out the exact implications for the insulin price hike.
Digging into the specifics is key to understanding the whole situation.
Retail Pricing and Sales
Insulin is typically sold to patients through pharmacies. Pharmacies set their retail prices, which often include markups for their services. These markups vary depending on the pharmacy’s overhead and profit goals. Retailers play a crucial role in making insulin accessible to patients, but their pricing strategies can influence the final cost.
Pricing Strategies of Different Manufacturers
Different insulin manufacturers employ varying pricing strategies. Some manufacturers focus on maintaining a consistent price across their product lines, while others might adjust pricing based on market conditions. The decision to offer discounts or incentives for volume purchases can also significantly affect the overall price for various patients and healthcare systems.
Profit Margins at Each Stage
Profit margins vary significantly across the different stages of insulin production and distribution. Manufacturers often face high initial investments in research and development and production facilities, which can lead to lower profit margins in the initial years. Wholesalers and retailers often have more predictable and stable profit margins. A detailed breakdown of these margins would require specific data from each company and is not readily available in public sources.
Financial Transactions in the Supply Chain
The financial transactions in the insulin supply chain are complex. From the initial purchase of raw materials to the final sale to the patient, numerous payments and transfers occur. These transactions are tracked through various financial systems, ensuring transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain. Tracking these transactions can provide a clearer understanding of the overall cost structure of insulin.
Government Regulations and Policies
Governments worldwide play a crucial role in shaping the insulin market, impacting both the price and accessibility of this life-saving medication. Regulations surrounding insulin production, distribution, and pricing can significantly affect patients’ ability to afford necessary treatment. These policies, including price controls and subsidies, often reflect a balance between ensuring affordability and maintaining market incentives for pharmaceutical companies.The intricate web of government regulations influences the availability and cost of insulin, ultimately affecting patients’ health outcomes.
Different countries have adopted varying approaches, reflecting their unique socio-economic contexts and healthcare priorities. Policies and regulations regarding insulin pricing and access demonstrate the diverse approaches governments employ to tackle the complex issue of high medication costs.
Insulin Pricing Regulations in Different Countries
Different countries have implemented various policies to regulate insulin pricing, reflecting differing healthcare priorities and economic contexts. These regulations often involve price controls, subsidies, or a combination of both, aimed at balancing affordability and pharmaceutical industry incentives. The effectiveness of these policies in achieving both goals varies.
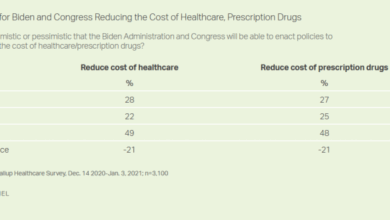
Impact of Policies and Subsidies on Insulin Accessibility and Affordability
Government subsidies and price controls are crucial in making insulin accessible to vulnerable populations. Subsidies directly reduce the cost of insulin for patients, while price controls place a cap on the maximum price a pharmaceutical company can charge. The effectiveness of these measures in increasing affordability varies based on factors such as the size of the subsidy, the level of price control, and the overall economic context of the country.
For example, in countries with robust social safety nets and extensive healthcare programs, subsidies can play a significant role in ensuring wider access.
Regulations Regarding Insulin Manufacturing, Distribution, and Pricing
Regulations regarding insulin manufacturing, distribution, and pricing vary across countries. These regulations aim to ensure quality, safety, and fair pricing. For instance, stringent quality control standards are applied during the manufacturing process, while regulations on distribution channels ensure efficient supply to pharmacies and patients. Price regulations, such as price caps, often target specific categories of insulin or specific patient groups to make treatment more affordable.
Role of Price Controls or Caps on Insulin Costs
Price controls or caps on insulin costs aim to curb the excessive prices charged by pharmaceutical companies. These measures can significantly reduce the cost of insulin for patients, improving affordability and accessibility. However, price controls can sometimes affect the profitability of pharmaceutical companies, potentially impacting their investment in research and development of new insulin therapies. It is a balancing act to ensure both affordability and the sustainability of the pharmaceutical industry.
Table of Insulin Pricing Policies in Different Regions
| Region | Policy Type | Description | Impact on Affordability |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Market-based pricing | Insulin prices are largely determined by market forces. | Insulin is often unaffordable for many patients. |
| Canada | Combination of subsidies and negotiation | Government negotiates prices and provides subsidies for certain patient groups. | Insulin is more affordable than in the US, but some patients may still face challenges. |
| European Union | National pricing policies | National governments implement price controls and regulations. | Insulin is generally more affordable in most EU countries compared to the US. |
Impact on Patients and Healthcare Systems
The escalating cost of insulin is having a profound and multifaceted impact on both patients and healthcare systems globally. This financial burden isn’t simply a matter of individual hardship; it reverberates throughout the entire system, affecting resource allocation, treatment adherence, and even long-term public health outcomes. Understanding these interconnected effects is crucial for developing effective solutions.
Financial Burden on Patients
The rising cost of insulin is a significant financial strain on patients with diabetes. Many individuals, particularly those with limited incomes, struggle to afford the necessary medication to manage their condition. This financial pressure can lead to significant distress and potentially compromise their ability to adhere to treatment plans, ultimately affecting their health and well-being. This often translates into delayed or missed doses, potentially leading to serious complications.
Insulin is a vital medication, and its affordability directly impacts the quality of life for people living with diabetes.
Impact on Healthcare Systems
Healthcare systems are facing considerable challenges in managing the escalating costs of insulin. Increased costs translate into reduced resources available for other essential healthcare services. This necessitates difficult decisions regarding resource allocation, potentially impacting preventative care, diagnostic tools, and treatment options for other conditions. Hospitals and clinics may need to adjust their budgets to accommodate the rising costs, potentially impacting the services they can provide.
The strain on healthcare systems is not just financial; it’s also a challenge in terms of managing the growing demand for insulin.
Impact on Patient Adherence to Treatment Plans
The cost of insulin directly impacts patient adherence to their prescribed treatment plans. When medication becomes unaffordable, patients may delay or skip doses to save money. This can lead to uncontrolled blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of severe complications such as diabetic retinopathy, kidney disease, and cardiovascular problems. The importance of consistent insulin administration cannot be overstated.
This lack of adherence often stems from the financial burden rather than a lack of understanding or motivation to follow the treatment plan.
Potential Long-Term Consequences on Public Health
High insulin costs have the potential for significant long-term consequences on public health. Uncontrolled diabetes, driven by poor adherence due to affordability issues, can lead to a higher prevalence of severe complications. This translates into increased healthcare costs for the public sector, as well as a decreased quality of life for those affected. This ultimately impacts the entire healthcare system, demanding more resources and creating a cycle of escalating costs.
The long-term consequences are substantial and demand immediate attention.
Average Cost of Insulin per Unit (Estimated)
| Country | Estimated Average Cost per Unit (USD) |
|---|---|
| United States | $200 – $400 |
| United Kingdom | $50 – $100 |
| Canada | $100 – $200 |
| Germany | $50 – $100 |
| India | $10 – $30 |
Note: These figures are estimates and can vary significantly based on specific types of insulin and pharmacy choices.
This table illustrates the significant price disparities in insulin costs across different countries. The wide range reflects variations in national healthcare policies, pharmaceutical pricing regulations, and market dynamics.
Alternative Insulin Sources and Delivery Methods: Following Insulin Price Money Trail
The rising demand for insulin, coupled with concerns over affordability and accessibility, has spurred considerable research into alternative insulin sources and delivery methods. Traditional insulin, derived from animal sources or produced through genetic engineering, has been the cornerstone of diabetes management for decades. However, limitations exist in terms of cost, availability, and potential side effects, making the search for alternatives crucial.
Following the insulin price money trail is definitely a rabbit hole, isn’t it? It’s fascinating to see how much is involved, and a new nonprofit, new nonprofit to nurture diversity in diabetes did , is working hard to address the impact of diabetes on diverse communities. This highlights the broader issue of access and affordability, which is deeply connected to the insulin price conundrum.
It’s a complex web, and tracing that money trail gets increasingly complicated.
Innovations in this field hold the promise of more personalized and effective treatments.
Potential Alternatives to Traditional Insulin Sources
The quest for alternative insulin sources encompasses exploring plant-based insulin production and synthetic insulin analogs. Plant-based insulin, though not yet widely adopted, offers a potentially sustainable and cost-effective alternative. Synthetic insulin analogs, engineered to mimic human insulin more closely, are also being investigated. These efforts aim to reduce reliance on animal-derived insulin and potentially offer improved efficacy and reduced side effects.
Alternative Insulin Delivery Methods
Alternative delivery methods aim to improve patient compliance and convenience. Insulin pumps, for example, provide continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion, mimicking the natural release of insulin in healthy individuals. This technology can lead to more precise glucose control, reducing the frequency of injections and improving overall quality of life. However, insulin pumps require significant user training and can be costly.
Insulin Pumps: Benefits and Drawbacks
Insulin pumps, a prevalent alternative delivery method, offer several benefits. They provide continuous insulin delivery, minimizing the need for multiple daily injections. This continuous delivery allows for more precise glucose control, leading to potentially better glycemic management. Improved glucose control can have positive implications for long-term health outcomes.However, drawbacks also exist. Insulin pumps require significant user training and education.
This training is crucial for proper pump operation and troubleshooting. The devices themselves can be expensive, and maintenance costs, including supplies and regular check-ups, need to be factored into the total cost of care.
Research and Development in Alternative Insulin Therapies
Ongoing research in alternative insulin therapies includes exploring inhaled insulin, oral insulin formulations, and even gene therapy approaches. Inhaled insulin offers a convenient alternative to injections, potentially improving patient adherence. Oral insulin formulations aim to eliminate the need for injections altogether. Gene therapy approaches, while still in the early stages of development, hold the potential to cure diabetes by addressing the underlying cause of the disease.
Financial Implications of Adopting New Insulin Technologies
The adoption of new insulin technologies brings significant financial implications. The development, manufacturing, and distribution of new therapies require substantial investments. Furthermore, the costs associated with training healthcare providers and educating patients must also be considered. Insurance coverage and reimbursement policies will play a crucial role in the accessibility and affordability of these new treatments.
Cost Comparison Between Traditional Insulin and Alternative Delivery Methods
A direct cost comparison between traditional insulin and alternative delivery methods is complex. The cost of traditional insulin varies significantly based on type and dosage. Insulin pumps and other advanced delivery methods are typically more expensive upfront. However, long-term cost savings are potentially achievable due to improved glucose control and reduced complications. The long-term cost analysis requires considering the cost of healthcare complications that might be avoided with better glucose control.
Comprehensive cost-effectiveness studies are necessary to evaluate the long-term financial implications of different insulin therapy options.
Ethical Considerations

The exorbitant cost of insulin has created a profound ethical crisis, impacting the lives of millions worldwide. This crisis forces a fundamental re-evaluation of the relationship between pharmaceutical companies, healthcare systems, and patients, particularly those with chronic illnesses. The ethical implications extend beyond simple economics, touching on fundamental principles of fairness, access, and human dignity.High insulin prices raise significant ethical concerns.
The exorbitant costs disproportionately affect vulnerable populations, including those with low incomes, limited insurance coverage, and those living in underserved communities. This inequitable access to life-saving medication directly challenges the fundamental principles of social justice. The very act of denying access to necessary treatment raises ethical questions about the value we place on human life and well-being.
Ethical Implications of High Insulin Prices
High insulin prices have far-reaching consequences, extending beyond the immediate financial burden on patients. The chronic stress associated with the high cost of insulin can negatively impact mental health and overall well-being. This stress can manifest as anxiety, depression, and decreased quality of life. It further impacts patients’ ability to afford other essential healthcare needs. Moreover, the high cost of insulin can exacerbate existing health disparities and create a two-tiered healthcare system, with those who can afford insulin receiving better care than those who cannot.
Social Justice Issues Related to Insulin Affordability
The issue of insulin affordability directly intersects with social justice concerns. The inability to access life-saving medication based on socioeconomic status creates a significant social injustice. This highlights a failure to uphold the basic human right to healthcare. The ethical imperative demands equitable access to essential medications, regardless of income or background. This is a crucial societal issue that requires systemic solutions to ensure equitable access.
Perspectives of Patient Advocacy Groups on Insulin Pricing
Patient advocacy groups consistently voice concerns about insulin pricing. These groups often advocate for policies that lower costs, increase access, and promote fairness in the insulin market. They highlight the moral obligation of pharmaceutical companies to ensure affordability and emphasize the importance of patient well-being. They also advocate for government regulation to control excessive pricing. For example, the advocacy group “Diabetes Action” has consistently campaigned for policies to lower insulin costs.
Ethical Responsibilities of Pharmaceutical Companies in Relation to Insulin Pricing
Pharmaceutical companies hold a crucial ethical responsibility in relation to insulin pricing. Their primary ethical obligation is to ensure that insulin remains affordable and accessible to all who need it. They should prioritize patient well-being over maximizing profits. Companies should also engage in transparency and explain the cost structure of insulin production. This includes detailing the research and development costs, manufacturing expenses, and pricing strategies.
They should consider the long-term impact of their pricing strategies on patients’ health and well-being.
Ethical Dilemmas Surrounding the Patenting of Insulin, Following insulin price money trail
The patenting of insulin presents ethical dilemmas. Patenting a fundamental biological process raises concerns about monopolies and access to essential treatments. The exclusive rights granted by patents can restrict competition and lead to artificially inflated prices, making life-saving medication inaccessible to many. The ethical imperative demands a reevaluation of patenting policies for essential medications, particularly those vital for treating chronic illnesses.
Public Awareness and Advocacy
The escalating cost of insulin has sparked a critical need for public awareness and advocacy efforts. Patients with diabetes, facing astronomical medication expenses, are increasingly reliant on support networks to navigate the complexities of this healthcare crisis. Advocacy groups play a vital role in educating the public about the issue and influencing policymakers to address the problem.Patient advocacy groups are essential in raising awareness about insulin affordability, and shaping public opinion on the issue.
Their efforts often include direct engagement with policymakers, public education campaigns, and collaborations with other organizations. This ongoing advocacy is crucial to driving meaningful policy changes and ensuring that those with diabetes have access to affordable medication.
Advocacy Group Initiatives
Patient advocacy groups employ various strategies to influence policy changes regarding insulin pricing. These strategies range from lobbying government officials to organizing public demonstrations and contacting media outlets to raise awareness. The groups often work closely with healthcare professionals and patient support organizations to build a unified voice for change.
Strategies to Influence Policy Changes
Advocacy groups leverage several tactics to affect policy decisions regarding insulin costs. These include direct engagement with legislators, presenting data on the impact of high insulin prices, and organizing grassroots campaigns to mobilize public support. Public pressure, through letters, petitions, and demonstrations, can significantly impact policy decisions.
Public Education Initiatives
Patient advocacy groups actively educate the public about the high cost of insulin and its impact on patients’ lives. They often organize workshops, seminars, and online resources to provide information about affordable insulin options, and the importance of advocating for change. By sharing personal stories and highlighting the financial burden, these groups aim to foster empathy and encourage broader support for policy reforms.
Patient Advocacy Organizations and Initiatives
| Organization | Key Initiatives |
|---|---|
| Diabetes Action | Advocating for lower insulin costs, and patient assistance programs; actively lobbying policymakers. |
| The American Diabetes Association | Developing educational materials on insulin affordability, supporting policy changes, and collaborating with advocacy groups. |
| Patient Advocates for Affordable Insulin | Organizing public awareness campaigns, and engaging in direct advocacy with pharmaceutical companies. |
| National Association of Chronic Disease | Supporting patient access to affordable insulin through policy changes, and lobbying for increased financial assistance. |
Public Perception of Insulin Pricing
Public perception of insulin pricing is characterized by growing concern and anger regarding the escalating costs of insulin. The disparity between the cost of insulin and other essential medications fuels this sentiment. The lack of transparency in pricing practices further exacerbates public frustration. Many individuals are increasingly aware of the financial burden insulin poses on patients and their families.
Consequently, public pressure is mounting for more affordable options and greater accountability in the pharmaceutical industry.
Last Point
In conclusion, the insulin price money trail reveals a complex interplay of factors, from production to patient access. High prices place a significant financial burden on patients and strain healthcare systems. While alternative sources and delivery methods show promise, the ethical implications of high costs and the need for public awareness and advocacy remain critical. Addressing this issue requires a multi-faceted approach involving manufacturers, policymakers, and patient advocates.