Gallstones could be a warning sign of pancreatic cancer. These small, hard deposits in the gallbladder can sometimes be linked to the development of pancreatic cancer, a serious disease affecting the pancreas. Understanding the potential connection between these two conditions is crucial for early detection and treatment. This post explores the potential relationship, examining symptoms, diagnostic considerations, and potential risk factors.
Gallstones, often formed from hardened bile, commonly cause discomfort and pain. Pancreatic cancer, on the other hand, frequently displays subtle symptoms in its early stages, making it challenging to distinguish from other ailments. This article will present key differences in symptoms and diagnostic methods.
Introduction to Gallstones and Pancreatic Cancer: Gallstones Could Be A Warning Sign Of Pancreatic Cancer
Gallstones, hardened deposits formed in the gallbladder, are a common ailment affecting millions worldwide. These stones typically develop when substances like cholesterol or bilirubin crystallize within the gallbladder. While often asymptomatic, gallstones can cause significant pain and discomfort, especially when they block the cystic duct or common bile duct. Understanding their formation and potential symptoms is crucial for preventative measures and timely intervention.
Pancreatic cancer, on the other hand, is a more serious condition characterized by the uncontrolled growth of malignant cells within the pancreas. Early detection is paramount for successful treatment, and unfortunately, early symptoms are often vague and easily misinterpreted. This post explores the potential link between these two conditions, examining the shared symptoms, types of gallstones, and the existing research on their correlation.
Gallstone Formation and Symptoms
Gallstones typically form when the chemical balance within the gallbladder is disrupted. Factors such as excess cholesterol, rapid weight loss, pregnancy, certain medications, and genetics can contribute to their formation. Common symptoms include sudden, intense pain in the upper right abdomen, often radiating to the back or shoulder, nausea, vomiting, and fever. The severity and frequency of symptoms can vary greatly depending on the size and location of the stones.
Pancreatic Cancer Characteristics and Early Indicators, Gallstones could be a warning sign of pancreatic cancer
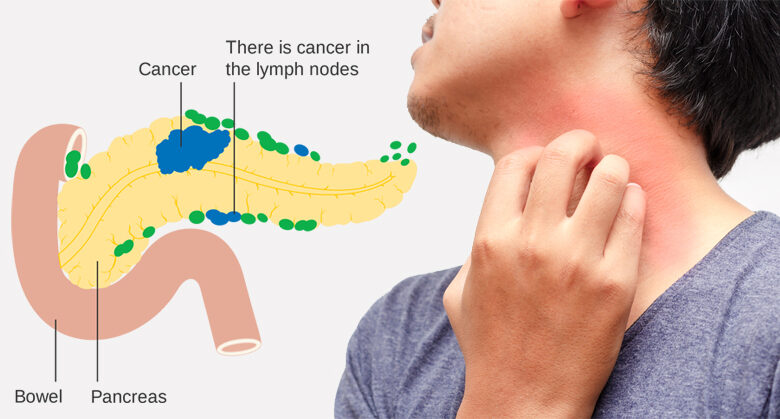
Pancreatic cancer is often aggressive and notoriously difficult to detect early. The pancreas, located behind the stomach, plays a vital role in digestion and hormone production. Tumors can develop within the pancreas, obstructing the flow of digestive enzymes or interfering with hormone production. Early symptoms are often subtle and nonspecific, making diagnosis challenging. These can include unexplained weight loss, persistent upper abdominal pain, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), fatigue, and changes in bowel habits.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be indicative of other conditions, necessitating further investigation.
Potential Relationship Between Gallstones and Pancreatic Cancer
While a direct causal link between gallstones and pancreatic cancer isn’t definitively established, some research suggests a potential association. Studies have investigated whether certain types of gallstones might increase the risk of pancreatic cancer. However, the results are not conclusive, and more research is needed to fully understand this potential relationship. The potential mechanisms are complex and not yet fully elucidated.
Comparison of Gallstone and Pancreatic Cancer Symptoms
| Symptom | Gallstones | Pancreatic Cancer |
|---|---|---|
| Pain | Sudden, intense, upper right abdominal pain, often radiating to the back or shoulder | Persistent, often dull upper abdominal pain, or pain that spreads to the back |
| Jaundice | Rarely a primary symptom, but may occur with blockage | Common symptom, often a late sign |
| Weight Loss | Possible, but usually not a prominent symptom | Often a significant, early indicator |
| Nausea/Vomiting | Common | Possible, but less common than weight loss |
| Fever | Possible | Rare |
Gallstone Types and Potential Links to Pancreatic Cancer
| Gallstone Type | Potential Link to Pancreatic Cancer |
|---|---|
| Cholesterol stones | Some studies suggest a potential association, but the evidence is not conclusive. |
| Pigment stones | The relationship is less well-studied compared to cholesterol stones. |
| Mixed stones | The potential link is likely similar to that of cholesterol stones. |
Potential Mechanisms Linking Gallstones to Pancreatic Cancer
The connection between gallstones and pancreatic cancer, while not fully understood, suggests potential biological pathways that warrant further investigation. Emerging research highlights the possibility of shared risk factors and inflammatory responses contributing to the development of both conditions. This exploration delves into the potential mechanisms, including the role of bile duct inflammation, oxidative stress, and genetic predisposition.The presence of gallstones can lead to chronic inflammation within the biliary system, potentially impacting the pancreas through various pathways.
This inflammation, if persistent, could create a microenvironment conducive to cellular changes and potentially, cancer development. This raises the critical question of how these seemingly disparate conditions might be linked.
Bile Duct Inflammation and Blockage
Gallstones, particularly if they obstruct the bile ducts, can lead to significant inflammation. This blockage disrupts the normal flow of bile, causing it to back up and potentially injure the surrounding tissues. The resulting inflammation in the bile ducts can spread to adjacent tissues, including the pancreas, which shares a close anatomical relationship. This inflammatory cascade may contribute to cellular damage and alterations that could ultimately contribute to pancreatic cancer development.
Chronic inflammation, a known risk factor for various cancers, could play a significant role in the observed association.
Inflammatory Responses Associated with Gallstones
Gallstones often trigger an inflammatory response within the biliary system. This inflammatory response involves the activation of immune cells and the release of inflammatory mediators. The resulting chronic inflammation can damage pancreatic tissues and potentially increase the risk of genetic mutations. Furthermore, the inflammatory mediators released could potentially promote the growth of pre-cancerous cells within the pancreas.
Studies have shown that chronic inflammation is associated with increased oxidative stress, a potential contributing factor to cancer development.
Potential Genetic Factors
Certain genetic predispositions may increase an individual’s susceptibility to both gallstones and pancreatic cancer. Individuals with a family history of either condition might carry genetic variations that influence the development of both. These genetic variations could affect the body’s ability to process bile, potentially increasing the risk of gallstone formation. They could also affect the mechanisms that regulate pancreatic cell growth and division, increasing the likelihood of pancreatic cancer.
Gallstones, while often benign, can sometimes be a subtle warning sign of pancreatic cancer. It’s a bit like how some seemingly minor health issues can point to more serious underlying problems. Interestingly, recent studies suggest that the Zika virus, while a concern, won’t likely travel far in the USA, as detailed in this article zika wont travel far in usa.
This doesn’t change the fact that gallstones warrant attention, especially if accompanied by other symptoms, as they could be an early indicator of a more serious condition like pancreatic cancer. It’s always a good idea to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
For instance, individuals with specific genetic polymorphisms might have a heightened response to inflammation, making them more vulnerable to the damaging effects of chronic inflammation.
Role of Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress, an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body’s ability to neutralize them, is implicated in various diseases, including cancer. Gallstones can contribute to oxidative stress within the biliary system and potentially in adjacent tissues, such as the pancreas. The oxidative stress induced by inflammation and bile duct obstruction may damage DNA, promote cellular mutations, and potentially contribute to pancreatic cancer development.
Studies have shown a correlation between oxidative stress and an increased risk of various cancers, emphasizing its potential role in this observed association.
Symptoms and Diagnostic Considerations
Understanding the symptoms of gallstones and pancreatic cancer is crucial for early detection and appropriate treatment. Distinguishing between the symptoms of these two conditions can be challenging, highlighting the importance of a comprehensive medical evaluation. Accurate diagnosis relies on a combination of patient history, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests.The symptoms of gallstones often mimic other digestive issues, making accurate identification a challenge.
A thorough medical evaluation is essential to pinpoint the underlying cause of the symptoms. This process involves careful consideration of the patient’s medical history, current symptoms, and risk factors for both gallstones and pancreatic cancer. This comprehensive approach is vital for determining the appropriate diagnostic path.
Symptoms of Gallstones
Gallstones typically cause pain in the upper right or middle abdomen, often described as sharp, cramping, or a dull ache. The pain may radiate to the back or shoulder blade. Other common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, and bloating. These symptoms are often intermittent and may resolve on their own, making diagnosis difficult. The severity and frequency of symptoms can vary significantly from person to person.
Symptoms of Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer symptoms can be vague and often appear later in the disease’s progression. Common symptoms include persistent upper abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), and dark urine. These symptoms can be subtle and easily overlooked, leading to delayed diagnosis. In some cases, patients may experience no noticeable symptoms in the early stages.
Gallstones, often a minor annoyance, could actually be a subtle warning sign of pancreatic cancer. It’s a sobering reminder of how easily health issues can mask more serious problems. This highlights the importance of regular check-ups, and the potential for alternative treatments like those involving stem cells, as seen in the recent case of three women blinded in unproven stem cell treatment.
three women blinded in unproven stem cell treatment serves as a stark reminder to be cautious and seek evidence-based medical solutions rather than unproven ones. Ultimately, knowing the potential for a gallstone issue to be a sign of a larger problem like pancreatic cancer, underscores the importance of careful medical attention.
It is important to remember that these symptoms can also be associated with other conditions.
Diagnostic Methods for Gallstones
Several methods are available for diagnosing gallstones, ranging from non-invasive imaging techniques to more invasive procedures. Ultrasound is a common initial diagnostic tool. It uses sound waves to create images of the gallbladder and surrounding structures, allowing for visualization of gallstones. Computed tomography (CT) scans and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can also be used to further assess the gallbladder and surrounding organs.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a more invasive procedure that involves inserting a tube with a camera through the mouth and into the bile and pancreatic ducts. This procedure allows for direct visualization of the ducts and can be used for both diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnostic Methods for Pancreatic Cancer
Diagnosing pancreatic cancer involves a multi-step approach, incorporating various imaging and laboratory tests. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a valuable tool that combines endoscopic visualization with ultrasound, allowing for detailed examination of the pancreas. CT scans and MRI are frequently used to assess the extent of the disease and evaluate for metastasis. Blood tests, such as tumor markers, may also be helpful in certain cases, although their accuracy is limited.
Biopsy, the removal of a tissue sample for microscopic examination, is often necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Comparison of Diagnostic Procedures
| Characteristic | Gallstones | Pancreatic Cancer |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Diagnostic Method | Ultrasound | CT Scan or EUS |
| Imaging Techniques | Ultrasound, CT, MRI | CT, MRI, EUS |
| Invasive Procedures | ERCP (in some cases) | ERCP, Biopsy |
| Importance of Biopsy | Rarely needed | Essential for confirmation |
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection and timely intervention are crucial for successful management of both gallstones and pancreatic cancer. Prompt diagnosis allows for appropriate treatment and potentially better outcomes. Early intervention in gallstone cases often involves lifestyle modifications and medication. In cases of pancreatic cancer, early detection allows for surgical intervention and/or targeted therapies. The earlier these conditions are detected, the greater the chances of successful treatment and improved patient outcomes.
Risk Factors and Prevention
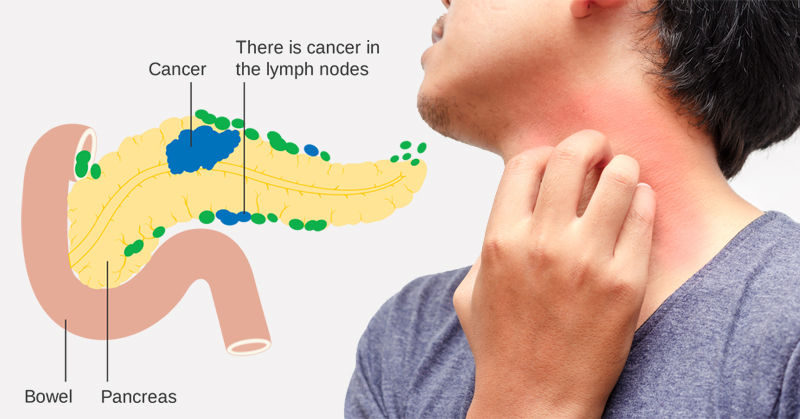
Gallstones and pancreatic cancer, while distinct diseases, can share some overlapping risk factors. Understanding these factors and adopting preventative measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing either condition. A proactive approach to lifestyle and dietary choices is crucial in minimizing the risk of these potentially serious health concerns.
Risk Factors for Gallstones
Gallstones are formed when substances in bile, such as cholesterol and bilirubin, become concentrated. Several factors contribute to this concentration, increasing the risk of gallstone formation. These include a family history of gallstones, obesity, rapid weight loss, pregnancy, certain medications, and a diet high in saturated and trans fats. Women are also more prone to developing gallstones than men.
Moreover, older age can be a contributing factor. The combination of several of these factors can significantly increase the likelihood of gallstone formation.
Risk Factors for Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer is a particularly aggressive disease, often diagnosed at a late stage. Several risk factors contribute to its development. Smoking is a significant risk factor, with heavy smokers experiencing a substantially elevated risk compared to non-smokers. A family history of pancreatic cancer is another important risk factor. Certain genetic conditions, such as Lynch syndrome and familial atypical mole-melanoma syndrome, are also linked to an increased risk.
Additionally, a diet high in processed foods, red meat, and saturated fats, and a history of diabetes and chronic pancreatitis can increase the risk.
Lifestyle Modifications to Reduce Risk
Adopting a healthier lifestyle can significantly decrease the risk of both gallstones and pancreatic cancer. Weight management is a cornerstone of prevention for both conditions. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular exercise can reduce the risk of developing gallstones and can also help manage other risk factors for pancreatic cancer. A balanced diet low in saturated and trans fats, and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is recommended for both conditions.
Dietary Recommendations for Prevention
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in mitigating the risk of gallstones and pancreatic cancer. Dietary changes are key to preventing both. Minimizing processed foods, red meats, and saturated fats is essential. Increasing intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is equally important. Dietary fiber is a significant component of a healthy diet and can contribute to reducing the risk of gallstones and pancreatic cancer.
Furthermore, controlling blood sugar levels through dietary adjustments is vital, particularly for those with diabetes. Consuming adequate protein and essential nutrients is also important.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Prevention
Regular physical activity is crucial for overall health and can significantly lower the risk of both gallstones and pancreatic cancer. Maintaining a healthy weight through exercise and a balanced diet is essential. Quitting smoking, if applicable, is another vital lifestyle adjustment. Furthermore, regular check-ups with healthcare providers are crucial for early detection and prompt treatment. Managing stress through relaxation techniques can also contribute to overall well-being.
Preventive Measures Summary
| Preventive Strategy | Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Maintaining a healthy weight | Reduces risk of gallstones and pancreatic cancer by managing related risk factors. |
| Regular exercise | Improves overall health, controls weight, and lowers risk. |
| Balanced diet (low in processed foods, red meat, saturated fats, high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains) | Reduces risk factors for both conditions. |
| Quitting smoking | Dramatically reduces the risk of pancreatic cancer. |
| Managing blood sugar levels (especially for those with diabetes) | Lowers risk for both conditions. |
| Regular medical check-ups | Allows for early detection and prompt intervention. |
| Stress management | Contributes to overall well-being and potentially reduces risk. |
Case Studies and Patient Experiences (Illustrative)
Navigating the complexities of digestive health can be daunting, especially when faced with symptoms mimicking those of serious illnesses. The potential for misdiagnosis, particularly when distinguishing between gallstones and pancreatic cancer, adds another layer of emotional and practical challenges. This section explores illustrative case studies, highlighting patient experiences and the diagnostic hurdles involved.
While gallstones might seem like a minor issue, they could actually be a warning sign of something more serious, like pancreatic cancer. Thinking about what to wear during labor might seem completely different, but understanding your body’s signals is key, whether it’s discomfort or something more serious. It’s important to remember that various factors can contribute to these symptoms, and consulting a doctor is crucial for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.
So, if you’re experiencing persistent gallstone issues, don’t hesitate to seek medical attention to rule out any potential complications. what to wear during labor might not be on your mind right now, but prioritizing your health is key to avoiding serious health concerns like pancreatic cancer. Ultimately, staying informed about potential health issues like gallstones is vital for proactive well-being.
Misdiagnosis and Delayed Diagnosis
Many individuals initially experience symptoms that resemble those of pancreatic cancer, leading to unnecessary anxiety and potentially delaying the appropriate diagnosis and treatment for gallstones. This can be particularly distressing as delays in diagnosis can significantly impact treatment outcomes. The initial presentation of symptoms can be subtle and often overlap with other conditions, making accurate diagnosis challenging. For example, persistent upper abdominal pain, jaundice, and weight loss can be symptoms of both gallstones and pancreatic cancer, making early differentiation crucial.
Emotional Impact of Potential Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis
A suspected pancreatic cancer diagnosis can evoke a wide range of emotional responses, including fear, anxiety, and grief. Patients may grapple with uncertainty about their future, and the emotional toll can be significant. The diagnostic process itself can be emotionally taxing, involving numerous tests and consultations, each adding to the overall uncertainty. Moreover, the prospect of a potentially aggressive and life-altering disease can impact mental well-being.
The emotional support provided by healthcare professionals and loved ones plays a crucial role in navigating this difficult time.
Illustrative Scenarios
Differentiating between gallstones and pancreatic cancer can be challenging due to overlapping symptoms. A patient presenting with episodic right upper quadrant pain might initially be suspected of having gallstones. However, if the pain is persistent and accompanied by jaundice and weight loss, the possibility of pancreatic cancer must be considered. The patient’s medical history, including family history of pancreatic cancer or previous gastrointestinal issues, plays a crucial role in the diagnostic process.
The complexity of these cases underscores the importance of thorough investigations and a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis. A meticulous review of the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies are essential for arriving at an accurate diagnosis.
Real-World Case Studies
| Patient History | Diagnosis | Treatment Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| A 55-year-old female with a history of intermittent right upper quadrant pain, now experiencing persistent pain, jaundice, and significant weight loss. Family history of gallstones. | Gallstones causing pancreatitis, with a possible secondary pancreatic lesion. | Cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal) and close monitoring for any pancreatic complications. |
| A 62-year-old male with a history of digestive issues, presenting with severe epigastric pain, nausea, and unexplained weight loss. | Pancreatic cancer, initially misdiagnosed as gallstones. | Extensive diagnostic testing and surgery for tumor removal; aggressive chemotherapy and radiation therapy, leading to a moderate response. |
| A 48-year-old female with a history of gallstones, experiencing persistent, severe upper abdominal pain radiating to the back. | Acute pancreatitis related to gallstones. | Conservative management, including pain medication, intravenous fluids, and close monitoring. No evidence of pancreatic cancer. |
The table above presents illustrative examples. Each case requires careful consideration of individual factors and a multidisciplinary approach.
Public Health Implications and Awareness
The potential link between gallstones and pancreatic cancer demands a proactive public health approach. Raising awareness is crucial to empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and seek timely medical intervention. Early detection and prevention strategies can significantly impact the course of these diseases.
Importance of Public Health Campaigns
Public health campaigns are essential to educate the public about the potential connection between gallstones and pancreatic cancer. These campaigns should emphasize the importance of regular check-ups, particularly for individuals with a history of gallstones. Clear and accessible information about risk factors, symptoms, and preventive measures can empower individuals to take control of their health. Using easily understandable language and visuals in campaigns can greatly improve their impact.
Role of Medical Professionals in Education
Medical professionals play a critical role in educating patients about the risks associated with gallstones and their potential connection to pancreatic cancer. Doctors, nurses, and other healthcare providers should proactively discuss the risks with patients during routine checkups, especially those with a history of gallstones. They should emphasize the importance of early detection and the need for follow-up care.
This proactive approach empowers patients to make informed choices and take preventive measures.
Need for Early Screening and Diagnostic Procedures
Early screening and diagnostic procedures are vital for both gallstones and pancreatic cancer. Early detection significantly increases the chances of successful treatment and positive outcomes. Regular checkups and imaging, such as ultrasound, can aid in early diagnosis. For individuals at higher risk, such as those with a family history of either condition, more frequent screenings may be warranted.
It is important to emphasize that these procedures are not just for individuals exhibiting symptoms but should be part of a proactive approach to health management.
Support Groups and Resources
Support groups and resources are crucial for patients and families dealing with gallstones and pancreatic cancer. These resources provide emotional support, practical guidance, and access to information. Patient advocacy groups, online forums, and support networks can offer a sense of community and shared experience. Such resources offer invaluable emotional support and provide access to information, fostering a sense of shared experience and coping strategies.
Potential Impact of Early Detection Programs
Visual Representation: A hypothetical bar graph showcasing the impact of early detection programs on disease outcomes.The x-axis would represent time (e.g., years) and the y-axis would represent the percentage of patients with a successful outcome. Two separate lines would be displayed: one representing the outcome for individuals with early detection and the other for those without. The line representing early detection would show a significantly higher percentage of successful outcomes over time compared to the line without early detection.
This visualization clearly illustrates the benefits of early intervention. The graph would emphasize the importance of early screening and detection in improving patient outcomes.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, the potential link between gallstones and pancreatic cancer warrants careful consideration. While more research is needed to fully understand the complex mechanisms involved, early detection and proactive healthcare are essential. This discussion highlights the importance of recognizing potential symptoms and seeking medical evaluation when concerns arise. Knowing the risk factors and preventive measures can empower individuals to take control of their health.