Gene therapy for cancer welcomed with reservations, a promising yet cautiously approached frontier in medicine. This approach aims to modify genes to combat cancer, offering potentially life-saving treatments. However, the path isn’t without hurdles. Significant research, ethical considerations, and public perception are all critical factors that need to be considered.
Different gene therapy methods, from gene editing to oncolytic viruses, hold the potential to revolutionize cancer care. Early clinical trials have shown promising results in specific cancers, but the long-term safety and effectiveness of these therapies are still being evaluated. A critical look at the various vectors used, their advantages and disadvantages, provides insight into the challenges and limitations of current gene therapy methods.
Introduction to Gene Therapy for Cancer
Gene therapy holds immense promise for revolutionizing cancer treatment, offering a potentially more precise and targeted approach compared to traditional methods. It aims to modify a patient’s genes to either directly kill cancer cells or enhance the body’s natural defenses against them. This innovative field, while still under development, is witnessing significant advancements, leading to clinical trials and potential breakthroughs.The fundamental principle behind gene therapy for cancer is to manipulate the genetic material within cells.
While gene therapy for cancer is getting a cautiously optimistic reception, it’s still early days. There are a lot of unknowns, and some valid concerns. Interestingly, studies suggest that coffee might protect your liver, potentially offering another avenue for disease prevention and treatment. coffee might protect your liver This is fascinating, and hopefully will open new doors in the future.
Ultimately, the promise of gene therapy for cancer is exciting, but needs further rigorous testing and research.
This manipulation can involve introducing new genes, correcting faulty genes, or silencing specific genes to disrupt cancer cell growth and survival pathways. The goal is to trigger the body’s natural mechanisms to combat cancer cells while minimizing harm to healthy cells.
Gene Therapy Approaches for Cancer Treatment
Gene therapy encompasses a range of approaches, each with its own mechanisms and potential applications. These approaches utilize various vectors to deliver therapeutic genes to target cells. Key methods include gene editing, oncolytic viruses, and immunotherapy.
Gene Editing Techniques
Gene editing technologies, like CRISPR-Cas9, allow for precise modifications to a cell’s DNA. These techniques enable scientists to correct mutations that contribute to cancer development or introduce genes that stimulate the immune system to recognize and eliminate cancer cells. For instance, CRISPR-Cas9 can be used to disable oncogenes, genes that promote uncontrolled cell growth, or enhance the expression of tumor suppressor genes, which normally regulate cell division.
Oncolytic Viruses
Oncolytic viruses are viruses modified to selectively infect and destroy cancer cells while leaving healthy cells unharmed. These viruses exploit vulnerabilities in cancer cells to replicate and spread, ultimately triggering the death of these cancerous cells. A key aspect of this approach involves tailoring the virus to target specific cancer types. This targeted destruction can help to limit the spread of the cancer and improve treatment outcomes.
Immunotherapy via Gene Therapy
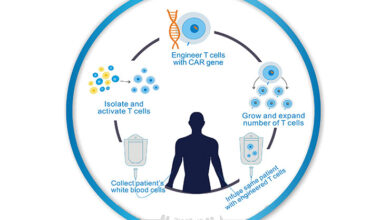
Immunotherapy, a branch of cancer treatment, enhances the body’s immune response to fight cancer cells. Gene therapy plays a crucial role in this area by modifying immune cells to recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively. For example, T cells can be engineered to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) that allow them to recognize and kill cancer cells bearing specific antigens.
Successful Clinical Trials
Numerous clinical trials have explored the use of gene therapy for various cancer types. Some successful examples include trials using oncolytic viruses to treat melanoma and other solid tumors. Other trials focus on using gene editing technologies to enhance the efficacy of immunotherapy. Further research and trials are essential to expand the application of gene therapy across different cancer types and patient populations.
Gene Therapy Vectors
| Vector Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Retroviruses | High efficiency in gene transfer to dividing cells | Integration into host genome can lead to insertional mutagenesis and potential activation of oncogenes |
| Adenoviruses | High efficiency in gene transfer to non-dividing cells; large payload capacity | Immune response and potential for toxicity |
| Adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) | Low immunogenicity; efficient transduction in non-dividing cells; stable integration into the host genome | Limited payload capacity compared to adenoviruses |
| Liposomes | Non-viral; less immunogenic | Lower efficiency of gene transfer compared to viral vectors |
Different vectors offer varying levels of efficiency in delivering therapeutic genes to target cells. The choice of vector depends on several factors, including the target cell type, the desired therapeutic outcome, and the potential for adverse reactions.
Current Status and Progress

Gene therapy for cancer, while promising, faces hurdles in its journey to widespread clinical application. Early trials showed encouraging results, but the path to effective and safe treatment is still under development. Current advancements focus on refining existing techniques and exploring novel approaches to overcome limitations.Significant progress has been made in understanding the intricate mechanisms of cancer development and the unique vulnerabilities of tumor cells.
This knowledge is driving the design of more targeted and potent gene therapies. However, ensuring safety and efficacy across diverse patient populations remains a considerable challenge.
Advancements and Breakthroughs
Significant strides have been made in developing viral vectors, the delivery vehicles for therapeutic genes. Modified viruses, like adeno-associated viruses (AAVs), are now more efficient and safer than earlier generations, allowing for more precise targeting and reduced immune responses. CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology is revolutionizing the field, enabling the precise modification of genes within tumor cells. This precision can lead to targeted disruption of oncogenes and activation of tumor suppressor genes.
Researchers are also exploring non-viral delivery methods, like nanoparticles, to improve safety and reduce potential side effects.
Challenges and Limitations
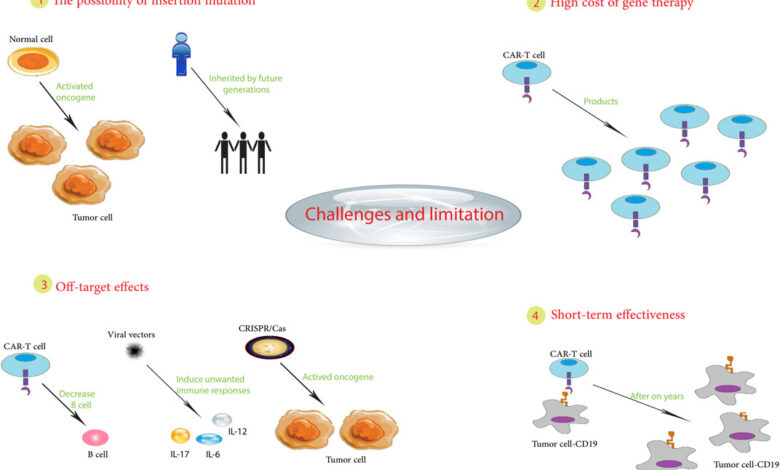
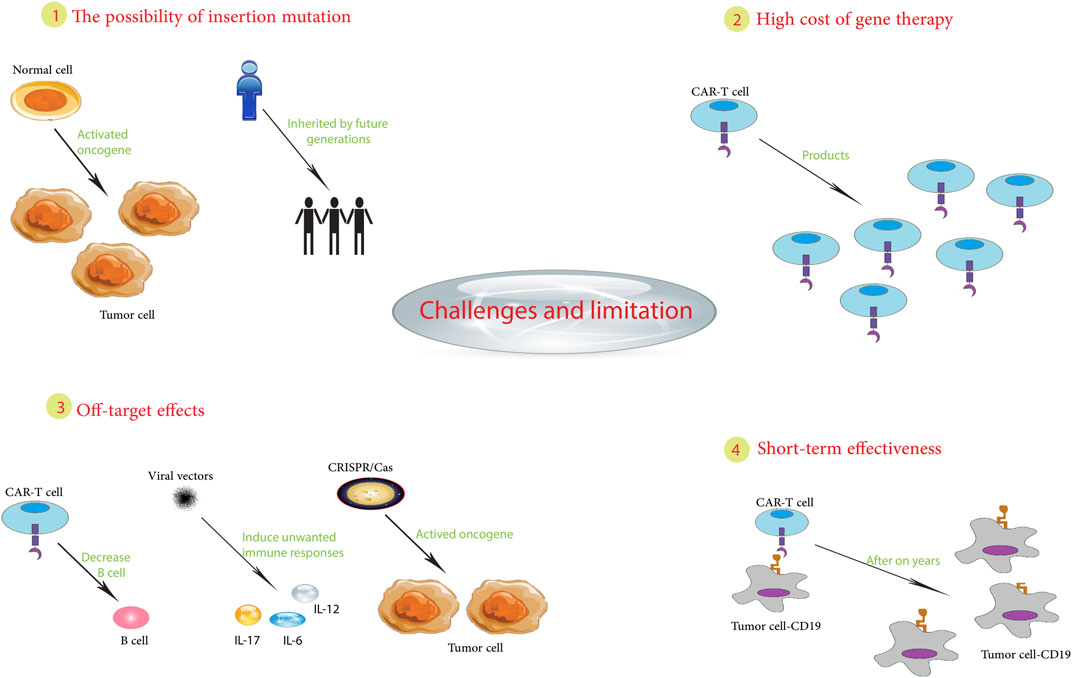
Despite advancements, gene therapy faces considerable challenges. Off-target effects, where the therapeutic gene modifies unintended genes, remain a concern. Immune responses to the therapy and the difficulty in achieving consistent and widespread gene delivery within tumors also limit effectiveness. Furthermore, the high cost of gene therapy development and manufacturing, along with the complexities of regulatory approvals, pose significant barriers to widespread clinical adoption.
Comparative Analysis of Gene Therapy Approaches
Various gene therapy approaches show varying levels of effectiveness and safety. Viral vectors, while efficient, can trigger immune responses and present challenges in targeting specific cells. Non-viral methods offer greater safety but may be less efficient in delivering genes to target cells. Gene editing techniques, like CRISPR-Cas9, hold immense potential but require further refinement to minimize off-target effects and ensure precise targeting.
The choice of approach depends on the specific type of cancer and the patient’s characteristics.
Ongoing Research and Development Efforts
Active research is focused on improving the efficiency and safety of gene therapy methods. Scientists are investigating novel vector designs, optimizing gene delivery mechanisms, and developing strategies to enhance immune responses to cancer cells. Further research into the long-term effects of gene therapy and developing strategies to overcome the challenges of tumor heterogeneity is also crucial. There is also a significant focus on personalized medicine approaches to tailor gene therapies to individual patient needs.
Key Milestones in the History of Gene Therapy for Cancer
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1990s | Early clinical trials using viral vectors for gene therapy began. |
| 2000s | Development of safer and more efficient viral vectors, such as AAVs. Understanding of tumor heterogeneity and the complexities of cancer became more apparent. |
| 2010s | CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology emerged as a powerful tool for precise gene modification. More focus on personalized approaches and developing strategies to overcome limitations. |
| 2020s | Ongoing research and development in non-viral delivery methods, and the exploration of new targets for gene therapy are ongoing. Clinical trials continue with a focus on safety and efficacy in diverse patient populations. |
Public Reception and Ethical Considerations
Gene therapy, while offering a potential cure for cancer, faces a complex interplay of scientific advancements and public perception. The public’s understanding and acceptance of such revolutionary treatments are crucial for their successful implementation. Ethical concerns, including potential risks, long-term consequences, and regulatory frameworks, must be carefully addressed to ensure responsible development and use.
Public Perception of Gene Therapy
Public perception of gene therapy is often a mix of excitement and apprehension. While many see the potential for curing previously incurable cancers, there’s also a healthy dose of concern regarding the unknown long-term effects and the potential for unintended consequences. This uncertainty is often amplified by media portrayals, which can sometimes oversimplify complex scientific processes. A balanced and informed public discussion is vital to fostering trust and acceptance.
Ethical Concerns Surrounding Gene Therapy
The ethical implications of gene therapy in cancer treatment are profound. Concerns arise from the potential for germline modifications, the equitable access to these therapies, and the potential for misuse. There’s a critical need for robust ethical guidelines and regulatory oversight to prevent unintended harm and ensure responsible application. This requires careful consideration of the potential for societal disparities in access and the long-term consequences of genetic manipulation.
Potential Risks and Long-Term Consequences
Gene therapy, while promising, comes with inherent risks. Off-target effects, immune responses, and the potential for cancer recurrence are all possibilities. Long-term monitoring of patients is essential to identify and mitigate these risks. Case studies of gene therapy applications in other diseases provide valuable insights into potential complications and the need for rigorous pre-clinical testing and ongoing post-treatment surveillance.
The need for long-term follow-up and extensive research into potential adverse effects is crucial for public confidence and safety.
Regulatory Frameworks and Guidelines
Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in overseeing the development and use of gene therapies. These frameworks aim to balance innovation with safety. The specific regulations vary across jurisdictions, but generally involve stringent testing procedures, ethical review boards, and ongoing monitoring of treated patients. Robust regulatory frameworks are essential for ensuring the safety and efficacy of gene therapies while allowing for careful advancement of the field.
Ethical Principles Guiding Gene Therapy Research
Ethical principles are essential for guiding gene therapy research and clinical trials. A clear framework helps to navigate the complex considerations.
| Ethical Principle | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Beneficence | The therapy should maximize benefits and minimize harm to patients. |
| Non-maleficence | The therapy should not cause harm or unintended consequences. |
| Justice | Access to the therapy should be equitable and fair, considering socioeconomic factors and geographical location. |
| Respect for persons | Patients’ autonomy and rights must be respected, including informed consent and the right to refuse treatment. |
| Transparency and accountability | Research should be conducted openly, with data transparency, and appropriate accountability for researchers and institutions. |
Reservations and Concerns Regarding Gene Therapy
Gene therapy, while promising, faces considerable reservations from both healthcare professionals and patients. These concerns stem from the complex nature of the technology, its potential side effects, and the ethical implications involved in altering the human genome. Understanding these reservations is crucial for navigating the path toward responsible and effective gene therapy implementation.The significant potential benefits of gene therapy must be weighed against the considerable uncertainties and challenges that remain.
This involves careful consideration of potential risks and the need for rigorous testing and safety protocols. Addressing these concerns proactively is essential to build public trust and encourage wider adoption of this transformative medical approach.
Specific Reservations of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals, including oncologists and geneticists, have specific reservations about gene therapy protocols. These professionals often highlight the complexities of gene delivery systems, the potential for off-target effects, and the need for long-term monitoring. Concerns also exist about the availability of resources and the potential for unequal access to these potentially expensive treatments. The need for extensive clinical trials and rigorous safety testing is paramount for their comfort in recommending gene therapy.
While gene therapy for cancer is getting a cautiously optimistic reception, it’s a bit like finally finding a great new skincare routine during quarantine. Just like trying out a new face mask or a different moisturizer, we’re cautiously optimistic about the potential, but also aware of the unknown. This new approach, like my newly discovered beauty routine in quarantine , needs careful monitoring and rigorous testing to ensure its safety and effectiveness.
Ultimately, gene therapy still faces hurdles to becoming a truly reliable treatment, much like a new beauty product that may not live up to the hype.
Potential Hurdles to Widespread Adoption
Several hurdles hinder the widespread adoption of gene therapy. The high cost of development, production, and administration is a major concern. The need for specialized expertise in gene therapy, including scientists, clinicians, and technicians, further complicates implementation. The ethical considerations surrounding germline gene editing also raise significant barriers. The complex regulatory frameworks required to ensure safety and efficacy are another obstacle.
Comparison of Stakeholder Opinions
Researchers often emphasize the potential of gene therapy to revolutionize cancer treatment and other diseases, while acknowledging the significant scientific challenges. Clinicians are concerned about the safety and efficacy of specific gene therapies in real-world settings, demanding robust clinical trial data. Patients, facing life-threatening illnesses, often view gene therapy with hope but also with caution, seeking transparent information about potential risks and benefits.
Concerns Regarding Off-Target Effects and Immune Responses
Off-target effects, where the gene therapy modifies unintended genes, pose a significant concern. The potential for immune responses against the delivered gene or the modified cells also needs careful consideration. Careful design and testing of gene therapies are crucial to minimize these risks. A crucial factor is the development of advanced delivery systems that target the desired cells with high precision and avoid off-target modifications.
The immune response to the introduced genetic material or the modified cells is another important concern. The immune system may recognize the modified cells as foreign, leading to rejection or inflammation. Research is ongoing to develop strategies to minimize or control these immune responses.
Influence of Reservations on Gene Therapy Protocols
The reservations and concerns regarding gene therapy profoundly influence the development and implementation of gene therapy protocols. Rigorous preclinical testing, including extensive in vitro and in vivo studies, is performed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of gene therapies. Stringent clinical trial protocols are implemented to monitor potential side effects and long-term outcomes. Furthermore, continuous research into advanced gene delivery systems, improved targeting mechanisms, and immune modulation strategies is necessary to overcome the hurdles.
The development of biomarkers to detect potential off-target effects and immune responses also contributes to a more robust and safer approach.
Future Directions and Potential Applications
Gene therapy for cancer, while still facing challenges, holds immense promise for the future. Early successes, coupled with ongoing research, suggest a potential paradigm shift in cancer treatment, moving beyond traditional approaches to more precise and targeted therapies. This exploration into future directions will illuminate the exciting possibilities and potential hurdles in the field.The ongoing evolution of gene editing technologies, coupled with a deeper understanding of the complex mechanisms driving cancer development, is paving the way for more effective and personalized treatments.
Researchers are exploring innovative strategies to enhance the efficacy and safety of gene therapies, ultimately aiming to improve patient outcomes.
While gene therapy for cancer is getting some cautious support, it’s interesting to see how similar advancements in other areas, like diabetes, are fostering change. A new nonprofit, new nonprofit to nurture diversity in diabetes did , is making strides in ensuring diverse communities have access to better resources. This highlights the need for similar considerations when implementing gene therapy; it’s not just about the technical advancements, but also the impact on all communities.
This cautious welcome of gene therapy for cancer remains, emphasizing the importance of equitable access and careful consideration.
Expanding Therapeutic Targets
Gene therapy is not limited to targeting oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Researchers are actively investigating the role of other genes involved in the tumor microenvironment, such as those regulating angiogenesis (blood vessel formation), immune response, and metastasis. This expanded focus allows for more comprehensive targeting of cancer cells, and potentially the entire tumor ecosystem. For instance, therapies targeting immune checkpoint inhibitors may be combined with gene therapy approaches to enhance anti-tumor immunity.
Novel Gene Editing Tools
The advent of CRISPR-Cas9 and other advanced gene editing technologies has revolutionized the field. These tools offer unparalleled precision in targeting specific genes, allowing researchers to precisely modify or correct faulty genetic material. This precision is crucial in minimizing off-target effects and maximizing therapeutic efficacy. Scientists are also exploring how these technologies can be used to deliver therapeutic genes directly to tumor cells, maximizing treatment specificity and reducing side effects.
Immunotherapy Integration
Combining gene therapy with immunotherapy holds significant potential. Gene therapy can be used to enhance the immune system’s ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells, creating a powerful synergy between the two approaches. Researchers are exploring ways to engineer immune cells, such as T cells, to express therapeutic genes that target specific cancer antigens. This integration aims to boost the immune response, making it more effective in eliminating tumors.
Personalized Medicine
Gene therapy has the potential to pave the way for personalized cancer treatments. By analyzing a patient’s specific genetic profile, gene therapy can be tailored to address unique genetic mutations driving the cancer. This precision approach allows for more effective treatment targeting, minimizing off-target effects and maximizing therapeutic efficacy. This personalized approach has the potential to lead to improved outcomes for patients with a variety of cancers.
Challenges and Opportunities
Developing and implementing gene therapies for cancer presents both challenges and opportunities. The need for rigorous safety testing and clinical trials to ensure efficacy and minimize side effects remains a priority. Furthermore, the high cost of developing and delivering these therapies could create barriers to access for some patients. However, the potential to revolutionize cancer care and provide more effective and targeted treatments is undeniable.
The continued development of more efficient delivery systems and reduced production costs will be critical for wider accessibility.
Projected Future Impact
| Aspect | Projected Future Impact |
|---|---|
| Efficacy | Increased efficacy and precision of cancer treatment, leading to higher remission rates and improved survival outcomes. |
| Safety | Continued improvements in gene editing technologies and delivery systems will enhance safety profiles and reduce off-target effects. |
| Accessibility | Decreased costs and improved scalability of gene therapy production and delivery systems will increase accessibility to a wider range of patients. |
| Personalized Treatment | Tailored gene therapies based on individual genetic profiles will optimize treatment strategies and maximize efficacy. |
| Combination Therapies | Integration of gene therapy with other treatment modalities, such as immunotherapy, will create synergistic effects and enhance overall treatment outcomes. |
Case Studies and Examples: Gene Therapy For Cancer Welcomed With Reservations
Gene therapy for cancer, while promising, faces significant hurdles. Real-world applications and outcomes provide valuable insights into its efficacy and limitations. Understanding specific case studies, trial results, and the applicability to different cancer types helps us evaluate the current state and future potential of this innovative approach.
Early Success Stories and Challenges, Gene therapy for cancer welcomed with reservations
Early gene therapy trials demonstrated some remarkable successes in treating certain cancers, particularly hematological malignancies. These successes often involved modifying immune cells to target tumors more effectively. However, these initial triumphs also highlighted the complex nature of gene delivery and the unpredictable behavior of the modified cells within the patient’s body. Long-term follow-up is crucial to assess the sustained efficacy and potential side effects of gene therapy interventions.
Specific Cancer Types and Gene Therapy Applicability
| Cancer Type | Gene Therapy Approach | Efficacy | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leukemia (specifically acute lymphoblastic leukemia – ALL) | Modifying T cells to target leukemia cells | Positive results in some clinical trials, leading to remission in some patients | High cost, potential for immune-related side effects, and variability in response across patients. |
| Lymphoma | Genetically engineering immune cells to recognize and destroy lymphoma cells | Some promising outcomes in clinical trials, with noticeable tumor reduction in certain cases | Challenges in achieving consistent, long-term remission and the need for more tailored approaches for different lymphoma subtypes. |
| Solid Tumors (e.g., lung cancer, melanoma) | Delivering genes to suppress tumor growth or enhance immune responses | Early results show promise but are often less impressive compared to hematological malignancies. | Significant obstacles in delivering genes effectively to solid tumors and managing the complex interactions of tumor cells with the surrounding tissues. |
Illustrative Gene Therapy Trials and Outcomes
Several clinical trials have explored different gene therapy approaches for various cancers. For instance, trials using CAR T-cell therapy have yielded positive outcomes in treating leukemia and lymphoma, demonstrating the potential of engineering immune cells to target tumors. However, the long-term effectiveness and potential side effects remain crucial areas of investigation. Furthermore, challenges in efficiently delivering genes to solid tumors have hindered progress in treating these more complex cancers.
Factors Influencing Treatment Outcomes
Various factors impact the success of gene therapy, including the specific cancer type, the patient’s overall health, the gene therapy approach used, and the efficiency of gene delivery. Careful patient selection and ongoing monitoring are crucial for optimizing treatment outcomes. Furthermore, the complexity of the tumor microenvironment and the inherent variability in patient responses require ongoing research to improve the accuracy and efficacy of gene therapy protocols.
Future Considerations
The field of gene therapy for cancer is continuously evolving. Research into safer and more effective gene delivery methods, personalized gene therapy approaches tailored to individual patient needs, and enhanced understanding of the tumor microenvironment are crucial for advancing this innovative treatment modality. Continued clinical trials and rigorous research are necessary to translate promising preclinical findings into tangible clinical benefits for cancer patients.
Societal Impact of Gene Therapy
Gene therapy, while promising in its potential to revolutionize cancer treatment, carries significant societal implications that extend far beyond the individual patient. Its potential to alter the course of diseases, including cancer, presents complex ethical, economic, and social considerations that demand careful consideration. Understanding these implications is crucial for navigating the path toward responsible and equitable implementation of this transformative technology.The societal impact of gene therapy for cancer spans a wide spectrum, affecting healthcare systems, access to care, and the very fabric of our social and cultural norms.
The potential for substantial economic gains and societal benefits must be weighed against the potential for widening health disparities and ethical dilemmas.
Economic Impact on Healthcare Systems
The high development and manufacturing costs associated with gene therapies, coupled with the potential for long-term treatment requirements, pose significant economic challenges to healthcare systems. Estimates suggest that gene therapies could potentially dramatically increase healthcare costs in the short term, potentially creating substantial financial burdens for patients and insurance providers. However, the potential for long-term cost savings due to reduced need for extensive and expensive conventional treatments remains a key consideration.
Moreover, the development of gene therapies and related infrastructure could stimulate economic growth in related industries, such as pharmaceutical manufacturing and biotechnology research.
Impact on Access to Care and Equitable Distribution
A critical concern regarding gene therapy is the potential for widening disparities in access to care. The high cost of gene therapy could create a two-tiered healthcare system, where only those with significant financial resources have access to these potentially life-saving treatments. Ensuring equitable access is crucial, requiring innovative financing mechanisms, government subsidies, and potential price controls. Addressing this issue will be paramount in avoiding a situation where the promise of gene therapy is limited to a select few.
Potential Social and Cultural Consequences
The ability to alter an individual’s genetic makeup raises profound social and cultural questions. Concerns regarding genetic modification and its potential impact on future generations warrant careful consideration and open dialogue. The potential for the use of gene therapy for enhancing traits beyond treating disease also raises ethical concerns, potentially creating social stratification based on access to genetic enhancements.
Open discussion and public engagement are crucial in addressing these concerns and ensuring that the application of gene therapy aligns with societal values.
Role of Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns play a vital role in shaping societal acceptance and understanding of gene therapy. Effective communication about the benefits, risks, and limitations of gene therapy is essential to fostering informed public discourse. Transparency and honesty in presenting information about the technology are crucial to avoid misinformation and speculation. These campaigns should aim to address ethical concerns, explain the process, and Artikel the potential societal implications, thereby promoting a balanced and nuanced understanding of this complex technology.
Closing Summary
Gene therapy for cancer, despite initial enthusiasm, faces reservations stemming from potential risks, ethical concerns, and public perception. Ongoing research and development, coupled with careful consideration of ethical principles and regulatory frameworks, are crucial for navigating the path towards broader adoption. The future of gene therapy hinges on addressing these reservations and ensuring equitable access to potentially life-altering treatments.
Case studies and societal impact analyses further highlight the complex interplay between scientific advancements and societal acceptance.