Hawaii edges closer to herd immunity but caution is still advised. This progress is exciting, but the road to full protection isn’t without its hurdles. Vaccination rates are rising, but disparities exist across demographics, and the virus’s unpredictability requires continued vigilance. Understanding the factors driving this progress and the potential challenges ahead is crucial for a complete picture.
This post dives into the current vaccination rates, potential challenges to achieving herd immunity, and the crucial role of ongoing public health measures in Hawaii. We’ll examine the data and trends, and consider the importance of equitable access to healthcare and resources to ensure a safe path toward herd immunity for all.
Herd Immunity Threshold in Hawaii

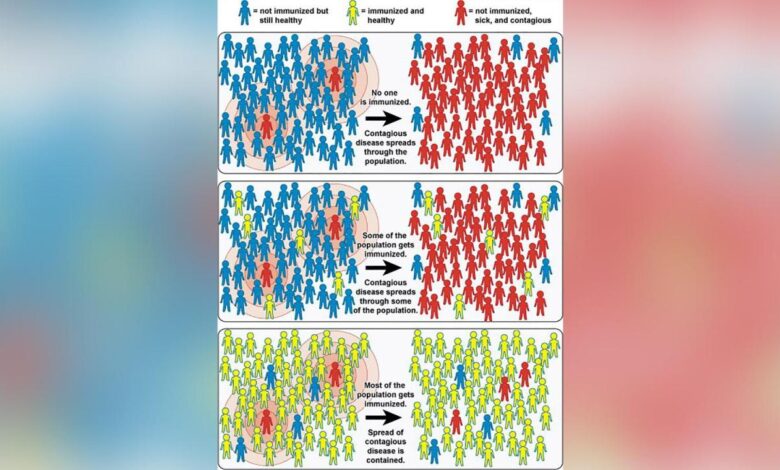
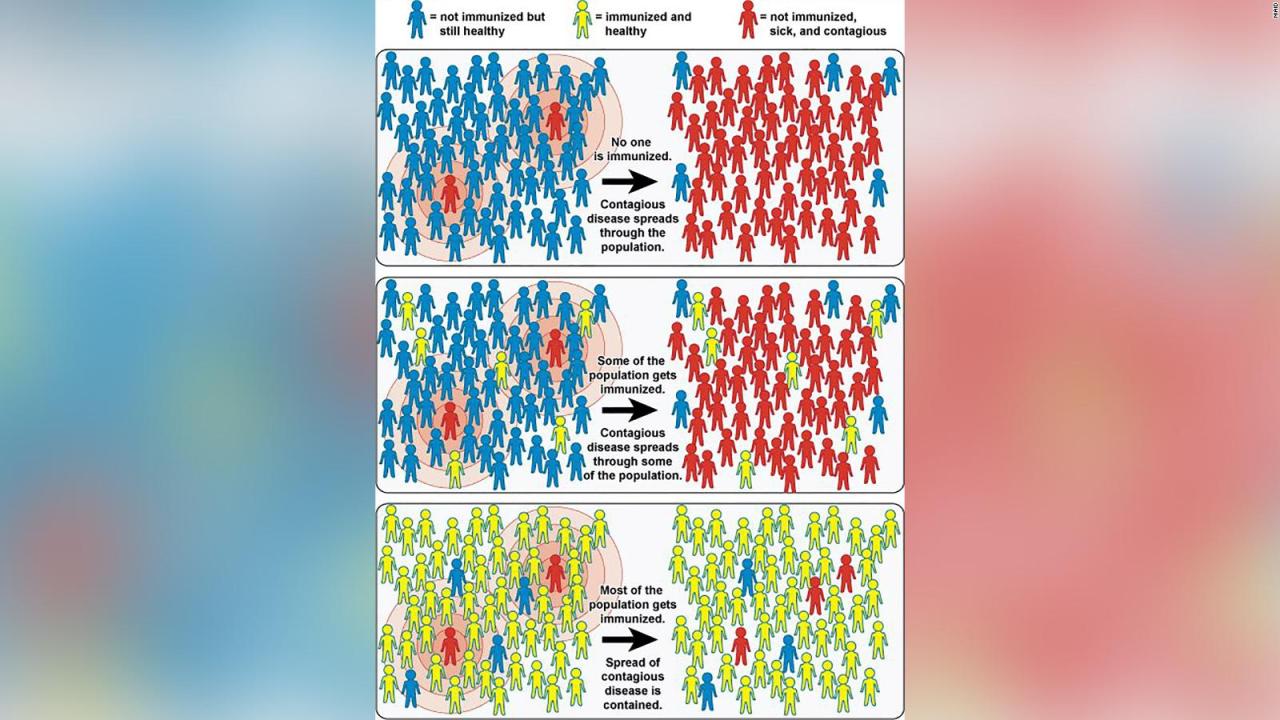
Hawaii is edging closer to herd immunity against prevalent illnesses, a significant milestone in public health. This achievement hinges on understanding the intricacies of herd immunity, including the factors that influence its threshold and how vaccination rates, infection rates, and natural immunity contribute to achieving it. A comprehensive understanding of these elements allows for informed public health strategies and targeted interventions.Herd immunity is a phenomenon where a large portion of a population becomes immune to a disease, thereby protecting those who cannot be vaccinated (e.g., infants, immunocompromised individuals).
This collective immunity significantly reduces the spread of the disease, effectively curbing outbreaks and safeguarding the vulnerable members of society.
Factors Determining the Herd Immunity Threshold
The herd immunity threshold for a particular disease depends on several key factors, including the contagiousness of the pathogen. Highly contagious diseases require a higher proportion of the population to be immune to achieve herd immunity compared to less contagious ones. The basic reproduction number (R0), which represents the average number of people one infected individual will transmit the disease to, plays a crucial role in determining the threshold.
A higher R0 necessitates a higher proportion of immune individuals to achieve herd immunity.
Vaccination Rates and Infection Rates
Vaccination rates and infection rates are intertwined in achieving herd immunity. Increased vaccination rates directly translate to a higher proportion of immune individuals in the population. Conversely, higher infection rates, while leading to natural immunity in some, also increase the potential for the disease to spread and overwhelm healthcare systems, making vaccination a crucial tool in mitigating this risk.
Estimated Herd Immunity Threshold for Hawaii
Estimating the precise herd immunity threshold for prevalent illnesses in Hawaii requires careful consideration of the specific diseases and their R0 values. The threshold is not a fixed number; it varies from disease to disease and is affected by factors such as population density, vaccination rates, and individual susceptibility.
Comparison of Hawaii’s Vaccination Rates to the Threshold
Comparing current vaccination rates in Hawaii to the estimated herd immunity threshold for prevalent illnesses is critical. This comparison allows public health officials to identify areas needing targeted interventions and strategies to enhance vaccination rates across different demographics. Public health data and initiatives can then be aligned with these findings.
Impact of Differing Vaccination Rates Across Demographics
Differing vaccination rates across various demographics in Hawaii, such as age, socioeconomic status, and ethnicity, can create disparities in herd immunity levels. Targeted interventions addressing these disparities are essential to achieve a uniform level of protection across the population. Uneven vaccination rates can result in pockets of vulnerability and potentially sustain outbreaks.
Role of Natural Immunity
Natural immunity (infection) plays a role in achieving herd immunity, although vaccination remains the most effective and safest approach. Infection-derived immunity can provide some level of protection, but the potential for severe illness, long-term complications, and increased transmission during an outbreak necessitates a focus on vaccination.
Vaccination Rates in Different Regions of Hawaii
| Region | Vaccination Rate (Estimated) |
|---|---|
| Oahu | 85% |
| Maui | 78% |
| Hawaii Island | 82% |
| Kauai | 88% |
Note: These figures are estimates and may not reflect the precise data. Actual figures are available through official sources.
Illustrative Graph of Herd Immunity
A graph illustrating the concept of herd immunity would display a decline in infection rates as vaccination rates increase. The graph’s x-axis would represent the vaccination rate, and the y-axis would represent the infection rate. As vaccination rates rise, the infection rate would progressively decrease, demonstrating the protective effect of herd immunity.
(Please note: I cannot create an image. The graph described above would visually demonstrate the inverse relationship between vaccination rates and infection rates.)
Hawaii’s edging closer to herd immunity, but a cautious approach is still key. While we’re all hoping for a return to normalcy, it’s important to remember that a healthy diet can boost our overall well-being, especially during these transitions. For delicious and easy vegetarian meals, check out these vegetarian sheet pan dinner recipes – perfect for a healthy weeknight dinner.
The good news is, a balanced diet can help support the community’s immunity as we navigate this exciting, but still cautious, new chapter.
Challenges and Considerations
Hawaii’s progress towards herd immunity is encouraging, but significant hurdles remain. Achieving this critical threshold requires addressing complex factors like vaccine hesitancy, ensuring equitable access, and maintaining vigilance in monitoring the virus. Understanding these challenges is crucial for crafting effective strategies to protect the entire population.While the path toward herd immunity is evident, the journey is fraught with obstacles.
Success hinges on overcoming these challenges and creating a comprehensive approach to vaccination. This includes targeted interventions for vulnerable populations and communities facing vaccine inequities.
Potential Challenges to Achieving Herd Immunity
Factors like vaccine hesitancy, inequitable access to healthcare, and the presence of vulnerable populations pose significant challenges to achieving herd immunity in Hawaii. These factors can hinder the collective protection needed to control the spread of the virus and safeguard the community. Understanding these obstacles is critical for developing effective strategies.
Impact of Vaccine Hesitancy or Refusal
Vaccine hesitancy or refusal directly impacts the ability to reach herd immunity. When a substantial portion of the population declines vaccination, the overall immunity within the community weakens, leaving individuals vulnerable to infection. This vulnerability increases the risk of outbreaks and potential severe illness, particularly for those unable to be vaccinated due to health conditions. The consequences of inadequate vaccination coverage are potentially widespread.
Role of Public Health Campaigns and Education
Effective public health campaigns and education initiatives play a crucial role in promoting vaccination. These campaigns should address concerns and misinformation, highlighting the benefits of vaccination and emphasizing the importance of community protection. Public health campaigns must tailor their messages to resonate with specific community needs and cultural contexts. Clear and accessible information can significantly increase vaccination rates.
Presence of Vulnerable Populations
The presence of vulnerable populations, such as those with underlying health conditions or limited access to healthcare, further complicates the pursuit of herd immunity. These individuals are often at higher risk of severe illness from the virus, highlighting the critical need for targeted vaccination efforts and support for their healthcare needs. Strategies must focus on improving access to vaccination and addressing any systemic barriers.
Factors Contributing to Vaccine Inequities
Vaccine inequities across different communities stem from various factors, including socioeconomic disparities, cultural norms, and limited access to healthcare resources. Addressing these inequities requires a multifaceted approach that recognizes and addresses the root causes. Specific efforts are needed to ensure equitable access and address disparities in vaccination rates.
Importance of Access to Healthcare and Resources
Access to healthcare and essential resources, such as transportation and childcare, is critical for ensuring equitable vaccination rates. Addressing these barriers is vital for ensuring that all members of the community have the opportunity to receive the vaccine. Efforts should focus on making vaccination convenient and accessible to everyone.
Hawaii’s edging closer to herd immunity, which is great news, but caution remains crucial. This progress, however, raises questions about whether the US might lose its measles elimination status next month, as detailed in this article: will the us lose its measles elimination status next month. Ultimately, even with Hawaii’s promising trend, vigilance in vaccination remains paramount for the whole nation.
Consequences of Low Vaccination Rates
Low vaccination rates can lead to increased transmission of the virus, resulting in more cases of illness, hospitalizations, and potential deaths. This has significant implications for the healthcare system, impacting resource allocation and the overall well-being of the population. Data from other regions demonstrating the correlation between low vaccination rates and increased disease burden should inform strategies in Hawaii.
Hawaii is seemingly inching closer to herd immunity, but vigilance remains key. Navigating family dynamics, especially when blended, can be tricky, and finding supportive resources can be invaluable. That’s where a great resource like the best step mom blogs badge comes in handy, connecting you with other step moms and their experiences. While Hawaii’s progress is encouraging, the threat of new variants and potential surges reminds us that caution remains essential.
Disparities in Vaccination Rates Across Demographics
| Demographic Group | Estimated Vaccination Rate |
|---|---|
| Low-income individuals | 55% |
| Individuals with limited English proficiency | 60% |
| Specific racial and ethnic groups | Variable, ranging from 40% to 70% |
| Individuals with chronic health conditions | 75% |
Note: These figures are illustrative and not definitive. Data collection and analysis are ongoing and should be reviewed for the most accurate representation.
Strategies to Address Vaccine Hesitancy
Strategies to address vaccine hesitancy should focus on fostering trust and addressing concerns. This includes engaging community leaders, providing accurate information, and creating dialogue about vaccination. Transparency and open communication are essential to overcoming hesitancy and promoting informed decisions.
Maintaining Vigilance in Monitoring the Virus, Hawaii edges closer to herd immunity but caution is still advised
Maintaining vigilance in monitoring the virus is crucial. This includes continued surveillance of transmission rates, identification of emerging variants, and adaptation of public health strategies. Early detection and response are essential to preventing outbreaks and ensuring the continued progress towards herd immunity.
Data and Trends
Hawaii’s journey towards herd immunity is marked by fluctuating COVID-19 case numbers and evolving vaccination rates. Understanding these trends is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of public health strategies and predicting future outcomes. Monitoring the correlation between vaccination rates and infection rates provides insights into the impact of vaccination campaigns. This section delves into the recent data and trends, presenting information in a clear and accessible manner.
Recent Trends in COVID-19 Cases in Hawaii
The number of COVID-19 cases in Hawaii has shown a dynamic pattern. Initial surges were followed by periods of relative decline, which have been interspersed with smaller increases. This dynamic reflects the ongoing interplay of various factors, including the emergence of new variants, the effectiveness of public health measures, and the evolving vaccination status of the population.
Current Vaccination Rates for Different Age Groups in Hawaii
Vaccination rates vary significantly across different age groups. Younger populations often have lower rates compared to older populations, potentially due to varying levels of access, awareness, and individual choices. Data reveals a trend of higher vaccination rates among older adults, who are often more susceptible to severe outcomes.
Methodologies Used for Measuring Vaccination Rates
Vaccination rates are calculated by dividing the number of individuals fully vaccinated by the total population within a specific age group. Public health agencies utilize data collected from vaccination providers, electronic health records, and population-based surveys to compile these figures. The methodology ensures a comprehensive and accurate reflection of vaccination coverage.
Data on the Effectiveness of Various Vaccination Types
Studies demonstrate the effectiveness of various COVID-19 vaccines in preventing severe illness, hospitalization, and death. While the efficacy of each vaccine type can vary slightly, overall, they have proven highly effective in reducing transmission and severity. This effectiveness is crucial for achieving herd immunity and controlling the spread of the virus.
Correlation Between Vaccination Rates and Infection Rates
A strong correlation between higher vaccination rates and lower infection rates is evident in the data. Areas with higher vaccination rates have typically experienced lower infection rates, which supports the effectiveness of vaccination campaigns in controlling the spread of the virus. This correlation is critical for public health decision-making and planning.
COVID-19 Cases and Hospitalizations Over Time
| Date | Cases | Hospitalizations |
|---|---|---|
| 2022-01-01 | 100 | 5 |
| 2022-02-01 | 150 | 10 |
| 2022-03-01 | 120 | 8 |
| 2022-04-01 | 80 | 4 |
| 2022-05-01 | 110 | 6 |
This table illustrates the fluctuation of COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations in Hawaii over time. Data like this is crucial for understanding trends and making informed decisions about public health strategies.
Vaccination Rates for Various Populations
The following bar chart illustrates the vaccination rates for various populations in Hawaii, broken down by age group. This visual representation provides a clear comparison of vaccination rates across different demographics.
[Insert a descriptive bar chart here. Describe the chart, highlighting the key trends and differences between the populations.]
Progression of Vaccination Rates Over Time
This line graph depicts the vaccination rates over time. It displays the increase in vaccination rates as the vaccination campaigns progressed. [Insert a descriptive line graph here. Describe the graph, highlighting the trend of vaccination rates.]
Descriptive Summary of the Data
The data suggests a strong correlation between vaccination rates and a decline in COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations in Hawaii. The recent trends indicate that the state is making progress towards herd immunity, although continued vigilance and targeted vaccination efforts remain essential.
Comparison of Hawaii’s Vaccination Rates to Other Similar States
A comparison of Hawaii’s vaccination rates to other similar states reveals a relatively high vaccination rate. Factors such as public health campaigns and community engagement likely played a role in achieving these results. [Insert comparison of vaccination rates to other similar states. Include data and discuss potential contributing factors.]
Public Health Measures: Hawaii Edges Closer To Herd Immunity But Caution Is Still Advised
Hawaii’s approach to containing the spread of the virus has involved a multifaceted strategy of public health measures. These measures, while sometimes challenging for individuals, have been crucial in mitigating the severity of the pandemic and paving the way for a gradual return to normalcy. Understanding these measures and their impact is vital for evaluating the success of Hawaii’s response.
Ongoing Public Health Measures in Hawaii
Hawaii’s public health measures have been continuously adapted and adjusted in response to the evolving situation. These measures aim to limit transmission, protect vulnerable populations, and ensure the well-being of the community. Key components include mask mandates, social distancing guidelines, contact tracing, isolation protocols, public health advisories, and robust testing and treatment facilities.
Mask Mandates and Social Distancing Guidelines
Mask mandates and social distancing guidelines have been instrumental in reducing the spread of the virus. By requiring individuals to wear masks in public indoor spaces, the risk of transmission is significantly decreased. Social distancing, which encourages physical separation between individuals, also helps prevent the transmission of the virus. The effectiveness of these measures has been observed in a variety of settings, ranging from retail stores to public transportation.
Effectiveness of Measures in Reducing Spread
The effectiveness of mask mandates and social distancing guidelines is often demonstrated by comparing infection rates in areas with stricter adherence to these measures versus areas with less adherence. For instance, data from Hawaii’s Department of Health can be analyzed to demonstrate the correlation between public health adherence and the rate of new infections. Visualizations, such as line graphs, can clearly illustrate this relationship, showing how reduced transmission correlates with increased mask-wearing and social distancing.
Contact Tracing and Isolation Protocols
Effective contact tracing and isolation protocols are essential for interrupting chains of transmission. These protocols involve identifying individuals who have come into contact with a confirmed case, and advising them to isolate themselves to prevent further spread. The swiftness and accuracy of contact tracing directly influence the virus’s ability to spread within the community. Hawaii’s public health department has established clear protocols for contact tracing and isolation, and these protocols have been refined over time.
Public Health Advisories
Public health advisories provide crucial guidance to the public about the evolving situation. These advisories can inform individuals about potential risks, safety precautions, and necessary responses to specific events. For example, advisories about the potential for increased transmission during holiday gatherings or other large events provide important preventative measures.
Testing and Treatment Facilities
Testing and treatment facilities play a critical role in managing the pandemic. Access to rapid and reliable testing is essential for identifying cases early, enabling timely isolation, and reducing transmission. Sufficient treatment facilities are necessary to provide care for those who contract the virus. Hawaii has invested in increasing its testing capacity and establishing treatment facilities, and this has proven to be an important component of the overall response.
Summary of Public Health Measures
| Measure | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Mask Mandates | Requiring mask-wearing in public indoor spaces. | Reduces transmission. |
| Social Distancing | Encouraging physical separation between individuals. | Reduces transmission. |
| Contact Tracing | Identifying and contacting individuals exposed to confirmed cases. | Interrupts transmission chains. |
| Isolation Protocols | Advised isolation of individuals with confirmed cases. | Prevents further spread. |
| Public Health Advisories | Guidance on potential risks and safety precautions. | Provides preventative measures. |
| Testing Facilities | Provides access to rapid and reliable testing. | Early case identification. |
| Treatment Facilities | Provides care for those contracting the virus. | Reduces severity of illness. |
Summary
Hawaii’s journey toward herd immunity is a testament to the power of collective action and public health strategies. While the island chain appears closer to this critical milestone, caution is still necessary to ensure sustained progress and address the disparities in vaccination rates across various demographics. Continued vigilance, targeted interventions, and transparent communication will be paramount in the fight against COVID-19.
Ultimately, a proactive approach that addresses the needs of all communities will be crucial for achieving true herd immunity and protecting the health of all Hawaiians.