How dangerous is rat lungworm disease? This article delves into the complexities of this parasitic infection, examining its various facets from its life cycle to the impact it has on human and animal health. We’ll explore the symptoms, diagnosis, prevention strategies, and treatment options, providing a comprehensive overview of this potentially serious illness.
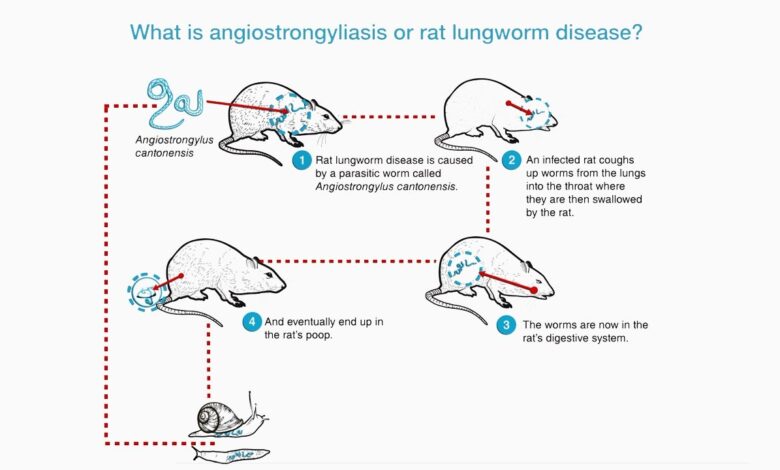
Rat lungworm disease, caused by the parasite
-Angiostrongylus cantonensis*, is a significant public health concern. The parasite’s life cycle involves rodents, which serve as intermediate hosts, making understanding the environmental factors crucial for prevention. The infection can affect a wide range of species, from rodents to humans, with varying degrees of severity.
Rat Lungworm Disease

Rat lungworm disease, a parasitic infection, is a significant health concern for both animals and humans. This debilitating illness is caused by a specific nematode, and its life cycle involves multiple stages and hosts. Understanding the disease’s intricacies, including its causative agent, life cycle, and common infection sites, is crucial for prevention and effective treatment.The infection is often contracted through the consumption of contaminated food or water.
Proper sanitation and awareness of potential sources are critical to minimizing the risk of transmission.
Causative Agent
The causative agent of rat lungworm disease is the nematodeAngiostrongylus cantonensis*. This parasitic roundworm is a significant public health concern, particularly in regions where rats and other rodents are prevalent.
Life Cycle
The life cycle ofAngiostrongylus cantonensis* involves several distinct stages. The parasite typically begins its life cycle within a snail or slug. After ingestion by a rodent, the parasite matures in the rodent’s lungs. The infection can then be transmitted to humans or other susceptible hosts through the consumption of infected rodents.
Common Locations of Infection
Infection with rat lungworm commonly occurs in the central nervous system (CNS) and other areas, including the lungs. The location of infection influences the symptoms and severity of the disease.
Susceptibility of Different Species
| Species | Susceptibility | Symptoms | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Humans | Medium | Headache, nausea, vomiting, fever, seizures, and potentially severe neurological complications. Symptoms can range from mild to severe depending on the location and extent of infection. | Moderate to Severe |
| Rats | High | Typically asymptomatic or exhibit mild symptoms; serve as a primary reservoir for the parasite. | Mild |
| Snails/Slugs | High | Serve as intermediate hosts, harboring the parasite in their tissues. | Mild (for the intermediate host) |
| Dogs | Medium | Symptoms include vomiting, diarrhea, and respiratory issues. | Moderate |
| Cats | Low | Less frequently affected compared to other species. Symptoms may include fever, lethargy, and anorexia. | Mild |
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Unveiling the cryptic nature of rat lungworm infection often hinges on recognizing its diverse symptoms and employing accurate diagnostic methods. Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial for managing the infection effectively and mitigating potential complications. The following sections delve into the multifaceted aspects of symptom presentation and the diagnostic procedures used to identify this parasitic disease.
Symptoms of Rat Lungworm Infection
The clinical presentation of rat lungworm infection can vary significantly, encompassing a broad spectrum of symptoms, making it challenging to diagnose initially. Patients may experience a range of respiratory issues, including persistent coughs, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Gastrointestinal problems, such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort, are also frequently reported. Additionally, neurological manifestations, like headaches, dizziness, and seizures, can occur, depending on the severity and location of the infection.
Rat lungworm disease, unfortunately, can be pretty serious. While it’s not as widely discussed as some other health concerns, it’s crucial to understand its potential dangers. Interestingly, despite vocal anti-vaccine movements, more Americans are embracing the measles vaccine, highlighting the importance of informed health decisions. This positive trend in vaccine acceptance, as seen in this recent study , suggests a growing understanding of the value of preventative measures.
Still, rat lungworm disease requires vigilance and proactive measures to prevent infection.
Some individuals may present with only mild symptoms, while others experience more severe, life-threatening complications.
Distinguishing Rat Lungworm from Other Diseases
Accurate diagnosis of rat lungworm infection necessitates distinguishing it from other diseases that share similar symptoms. Differentiating factors include the patient’s exposure history, particularly their interaction with potential sources of infection, such as contaminated soil or water. Consideration should also be given to the patient’s geographic location, as the prevalence of rat lungworm varies geographically. A comprehensive medical history, coupled with a thorough physical examination and appropriate diagnostic tests, can help in reaching a conclusive diagnosis.
Diagnostic Methods for Rat Lungworm Infection
Several diagnostic methods are employed to identify rat lungworm infection. These methods typically involve a combination of laboratory tests and imaging techniques. A crucial step is to collect a detailed patient history, including potential exposure to contaminated environments, to inform the diagnostic approach. This process often involves ruling out other possible conditions with similar symptoms.
Diagnostic Tests and Their Sensitivities, How dangerous is rat lungworm disease
The table below Artikels some of the diagnostic tests commonly used to identify rat lungworm infection, along with their respective sensitivities and specificities. Sensitivity indicates the test’s ability to correctly identify individuals with the infection, while specificity measures its ability to correctly identify those without the infection.
| Diagnostic Test | Method | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microscopy of Sputum/Stool Samples | Visual examination of samples for the presence of lungworm larvae | 50-70% | 90-95% |
| Serological Tests (ELISA) | Detection of antibodies specific to rat lungworm in patient serum | 80-90% | 95-98% |
| X-ray | Imaging of the lungs to detect potential abnormalities | 60-80% | 80-90% |
| CT Scan | Detailed imaging of internal organs to identify potential lungworm presence | 90-95% | 95-98% |
Diagnostic Flowchart
The following flowchart illustrates a simplified diagnostic process for rat lungworm infection. This is not a definitive guide and should be used in conjunction with expert medical advice.[Diagram of a flowchart would be placed here if possible. It should clearly depict the steps involved in the diagnostic process, from initial patient evaluation to confirmation of diagnosis. For example, the flowchart should show how patient history, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests lead to a diagnosis.
A detailed description of each step should be provided below the flowchart.]
Risk Factors and Prevention
Rat lungworm disease, while often preventable, poses a significant health risk. Understanding the factors that increase susceptibility and implementing preventative measures are crucial for protecting both human and animal populations. A proactive approach encompassing environmental control, personal hygiene, and responsible animal husbandry is essential to minimize the spread of this potentially dangerous parasite.Environmental factors play a critical role in the transmission of rat lungworm.
The lifecycle of the parasite involves intermediate hosts, primarily rodents, which shed the infective larvae into the environment. Contaminated water sources, soil, and vegetation can serve as vectors, increasing the risk of exposure for both humans and animals. The prevalence of rodent infestations in specific areas is also a significant indicator of the potential for exposure.
Environmental Risk Factors
Environmental conditions significantly influence the risk of rat lungworm infection. Areas with abundant food sources, inadequate sanitation, and a lack of rodent control measures create ideal breeding grounds for rodents and subsequently increase the likelihood of parasite transmission. Rodents often thrive in areas with high moisture content and readily available food sources. Accumulation of organic debris, such as discarded food, provides ideal conditions for rodent proliferation and thus the spread of the parasite.
These factors increase the environmental risk.
Personal Hygiene Practices
Maintaining proper hygiene is crucial in preventing rat lungworm infection. Avoiding direct contact with potentially contaminated soil, water, or vegetation is essential. Thorough handwashing after contact with soil or potentially contaminated environments is a critical preventative measure. Washing hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds after handling animals or touching potentially contaminated surfaces is vital in reducing the risk of infection.
Always wear protective gear, such as gloves and long sleeves, when working in areas known to have rodent infestations.
Preventive Measures for Humans
Preventive measures for humans focus on minimizing exposure to the parasite. This involves avoiding contact with contaminated soil, water, or vegetation, particularly in areas with known rodent infestations. Thorough handwashing and the use of protective gear, such as gloves and boots, are essential. Consulting with a healthcare professional about potential exposure or symptoms is crucial for early detection and treatment.
Preventive Measures for Animals
Preventing rat lungworm in animals hinges on controlling rodent populations and ensuring access to clean water and food. This includes routine inspection of animal enclosures and immediate removal of any potential rodent attractants. Regular veterinary check-ups and prompt treatment of any suspected infections are crucial. Rodent control measures in and around animal habitats are vital.
Rodent Control Strategies
Effective rodent control strategies are crucial for preventing rat lungworm transmission. These strategies should include a multi-pronged approach encompassing sanitation, exclusion, and trapping. Proper disposal of food waste and removal of potential nesting sites can significantly reduce rodent populations. Exclusion methods, such as sealing entry points to buildings, are vital to prevent rodents from accessing the premises.
Employing effective trapping techniques, coupled with monitoring and follow-up measures, can help manage rodent populations.
Treatment and Management
Rat lungworm disease, while often treatable, requires prompt and appropriate intervention. Early diagnosis and swift treatment are crucial to minimizing complications and improving patient outcomes. The effectiveness of different treatment approaches varies depending on the severity of the infection and the individual’s overall health.Effective treatment protocols typically involve a combination of supportive care and specific antiparasitic medications. The goal is to eliminate the parasite, reduce inflammation, and manage any resulting organ damage.
Proper supportive care, such as maintaining hydration and ensuring adequate nutrition, is essential for the body’s ability to fight the infection.
Treatment Options
Various anthelmintic drugs are effective against the lungworm parasite. These drugs work by targeting and destroying the parasites within the host’s body. Ivermectin is a common and widely used medication. Its efficacy against lungworm has been well-documented, making it a first-line treatment option. Other anthelmintics, such as albendazole, may also be prescribed, particularly in cases where ivermectin is not suitable or in combination with other therapies.
The selection of the appropriate medication depends on factors such as the severity of the infection, the patient’s overall health, and potential drug interactions.
Comparison of Treatment Approaches
The effectiveness of different treatment approaches varies based on several factors, including the stage of infection, the patient’s immune response, and the specific parasite load. Clinical trials and observational studies have shown that ivermectin is generally well-tolerated and highly effective in eliminating the parasite. While other anthelmintics may be equally effective, their use may be influenced by factors like potential side effects and drug interactions.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment are critical for favorable outcomes in rat lungworm disease. Prompt treatment can prevent the progression of the infection and limit the potential for severe complications. Delayed treatment can lead to significant organ damage, particularly in the lungs, and can result in chronic respiratory problems or other debilitating issues. The earlier the infection is addressed, the higher the likelihood of a complete recovery and the lower the risk of long-term consequences.
Potential Complications of Delayed Treatment
Delayed treatment of rat lungworm disease can result in a range of significant complications. These complications can affect various organ systems, particularly the lungs and central nervous system. For example, severe lung damage can lead to chronic respiratory problems, characterized by persistent coughing, shortness of breath, and reduced lung capacity. Furthermore, the infection can cause neurological issues, such as seizures, paralysis, or cognitive impairment.
In severe cases, delayed treatment can be life-threatening.
Treatment Protocols Summary
| Severity | Treatment Protocol | Duration | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild | Single dose of ivermectin or albendazole. Supportive care, including hydration and rest. | 1-2 weeks | Mild gastrointestinal upset (nausea, vomiting), headache. |
| Moderate | Multiple doses of ivermectin or albendazole, possibly combined with corticosteroids to reduce inflammation. Intensive supportive care. | 2-4 weeks | Increased risk of gastrointestinal upset, headache, dizziness. Possible allergic reactions to corticosteroids. |
| Severe | Hospitalization for intensive supportive care, including oxygen therapy, intravenous fluids, and multiple doses of ivermectin or albendazole, often combined with other therapies. Monitoring of vital signs and organ function is crucial. | 4-8 weeks or longer | Significant risk of severe gastrointestinal upset, allergic reactions, and potential organ damage. Careful monitoring is essential. |
Global Distribution and Prevalence
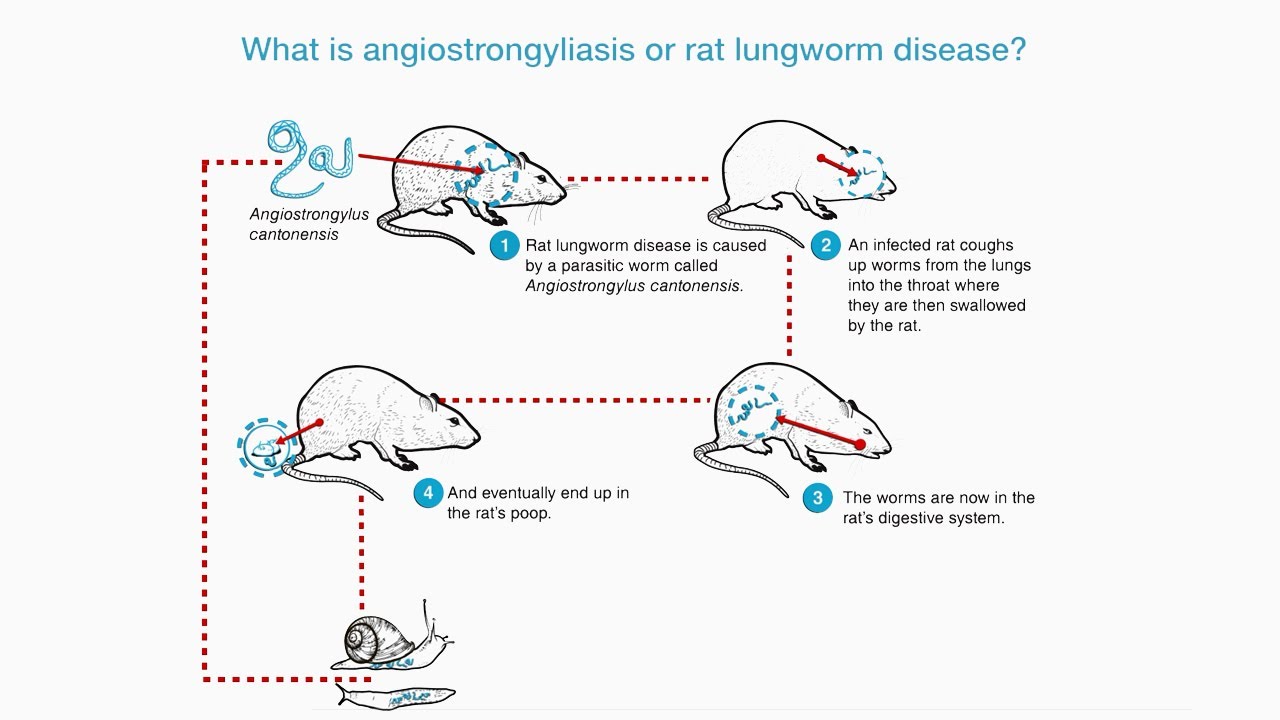
Rat lungworm disease, caused by the parasiteAngiostrongylus cantonensis*, isn’t confined to a single region. Its global spread has significant implications for public health, particularly in areas with high human exposure to infected intermediate hosts. Understanding its geographical distribution, prevalence rates, and contributing factors is crucial for effective prevention and control strategies.Geographical distribution ofAngiostrongylus cantonensis* is widespread, spanning various regions across the globe.
It’s not limited to a single continent or climate zone. The parasite thrives in diverse environments, indicating a potential for ongoing transmission in numerous locations. This necessitates a multifaceted approach to disease management across a variety of environments.
Geographical Distribution
The parasite’s distribution is extensive, found in tropical and subtropical regions, with reports extending into temperate zones. This global reach emphasizes the need for a globally coordinated response to mitigate the disease’s impact.
Prevalence Rates in Different Regions
Prevalence rates vary significantly across different regions. Higher prevalence is often observed in areas with a high density of intermediate hosts, like snails and slugs, and where human exposure to these hosts is prevalent. For instance, Southeast Asia has reported high prevalence rates, with specific countries experiencing considerable morbidity and mortality. The disease’s presence in areas like the Pacific Islands, the Caribbean, and parts of South America highlights the importance of adapting prevention strategies to local conditions.
Factors Contributing to the Spread
Several factors contribute to the spread of rat lungworm disease. High populations of rodents, particularly rats, are crucial intermediate hosts, often found in close proximity to human settlements. The presence of suitable intermediate hosts, such as slugs and snails, also plays a key role in the parasite’s life cycle. Human behavior, like consuming raw or undercooked food items, can increase risk.
Climate change can also influence the prevalence of the disease.
Impact on Public Health in Different Countries
The impact on public health varies based on the prevalence in a specific region and the existing healthcare infrastructure. Areas with high prevalence experience increased morbidity and mortality rates, putting a strain on healthcare systems and potentially affecting the overall economy. For example, regions in Asia with high rates of infection may require targeted public health campaigns and enhanced surveillance systems to effectively control the disease.
This emphasizes the importance of tailoring interventions to the specific context of each affected area.
Prevention Strategies
Prevention strategies should focus on reducing human exposure to infected intermediate hosts. This includes proper food handling practices, such as avoiding raw or undercooked food, and ensuring sanitation to control rodent populations and their habitats. Community awareness campaigns are crucial for educating the public about the disease and its prevention methods.
High Prevalence Areas Map
Unfortunately, I cannot create a map. However, high-prevalence areas are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions with a high density of intermediate hosts and where human exposure to these hosts is prevalent. Information on specific high-prevalence regions can be found in epidemiological studies and public health reports. The identification of these areas is crucial for developing targeted interventions and public health strategies.
Impact on Human Health
Rat lungworm disease, caused by the parasitic nematodeAngiostrongylus cantonensis*, poses a significant threat to human health. The infection, often acquired through consumption of contaminated food or water, can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe complications, and even death. Understanding the disease’s impact on human health is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.The severity of rat lungworm infection varies considerably.
While some individuals may experience only mild symptoms, others develop serious complications requiring extensive medical care. The long-term consequences of the infection can range from persistent neurological issues to permanent disability. The diverse range of potential outcomes underscores the importance of prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Rat lungworm disease is seriously concerning, especially for vulnerable populations. Imagine the terrifying prospect of a child facing such a threat. Thankfully, stories like the one detailing how doctors saved an infant with 3 weeks to live how doctors saved an infant with 3 weeks to live highlight the incredible advancements in medical care. This powerful reminder underscores just how critical it is to understand the dangers of this disease and the vital role of medical professionals in combating it.
Health Consequences for Humans
The infection primarily targets the central nervous system, leading to a range of neurological manifestations. Symptoms can include severe headaches, seizures, meningitis, and, in some cases, paralysis. The infection can also affect other organs, potentially leading to respiratory problems or inflammation in the heart or other organs.
Severity of Potential Complications
The complications of rat lungworm infection can be severe and life-threatening. Meningitis, characterized by inflammation of the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, can lead to permanent neurological damage. Hydrocephalus, an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain, can cause severe pressure buildup and irreversible brain damage. Encephalitis, inflammation of the brain itself, can result in long-term neurological deficits.
Long-Term Effects of the Infection
Long-term effects of rat lungworm infection can be substantial and debilitating. Individuals who experience severe complications may face permanent neurological damage, leading to problems with memory, concentration, and motor skills. Vision impairment, speech difficulties, and chronic pain are also potential long-term consequences. Recovery timelines can vary widely depending on the severity of the infection and the promptness of treatment.
Case Studies Illustrating the Disease’s Impact
Numerous case studies highlight the diverse range of symptoms and complications associated with rat lungworm infection. For example, a study in Southeast Asia documented several cases of individuals who developed severe meningitis, requiring intensive care and prolonged hospitalization. Another study in a South Pacific region reported cases of individuals with paralysis and other neurological deficits following infection. These cases underscore the need for better surveillance and prevention strategies in affected regions.
Socioeconomic Burden of the Disease
Rat lungworm infection imposes a significant socioeconomic burden on affected communities. The costs associated with medical treatment, hospitalization, and lost productivity due to illness and disability can strain healthcare systems and families. The impact on individuals’ ability to work and contribute to society can result in substantial financial losses for families and communities. The disease disproportionately affects vulnerable populations with limited access to healthcare resources.
Impact on Animal Health
Rat lungworm disease, while primarily affecting humans, isn’t without consequences for animal health. The parasitic nematode responsible for the disease,Angiostrongylus cantonensis*, can circulate within various animal populations, causing varying degrees of illness and potentially impacting livestock production. Understanding the impact on animal health is crucial for comprehensive disease management and control strategies.The parasitic nematodeAngiostrongylus cantonensis* doesn’t typically cause severe illness in animals.
However, it can lead to subclinical infections, where the animal shows no visible symptoms but still harbors the parasite. This can have long-term effects on the overall health and well-being of the animal population, particularly in vulnerable groups or during periods of stress. These subclinical infections can also impact the animal’s ability to fight off other diseases, making them more susceptible to secondary infections.
Affected Animal Species
Various animal species can be infected with rat lungworm. This includes a wide range of mammals, birds, and reptiles, although some species show a higher susceptibility or more prominent symptoms.
Rat lungworm disease, unfortunately, poses a serious threat to human health. While research into treatments is ongoing, the potential for advancements in regenerative medicine, like those explored in regenerative medicine has bright future , could pave the way for future breakthroughs in tackling this dangerous parasite. However, more research is still needed to fully understand the disease’s complexities and develop effective preventative measures.
- Rodents (rats, mice): These animals are the primary hosts and reservoirs for the parasite, meaning they carry the parasite and can spread it to other animals and humans.
- Dogs and cats: These domestic animals can be infected by consuming infected rodents or slugs/snails. Symptoms may range from mild to severe, depending on the level of infection.
- Other mammals: Other mammals, such as pigs, sheep, and goats, may be affected, although clinical cases are less common and often not readily recognized as rat lungworm.
- Birds: Birds, particularly certain species of poultry, can also be affected, but the clinical signs are often less severe compared to other animals.
Common Symptoms in Different Animal Species
The symptoms of rat lungworm infection can vary significantly depending on the affected animal species and the severity of the infection.
- Rodents: Subclinical infections are common in rodents. They often show no obvious signs of illness, but the parasite can be found in their lungs and other tissues.
- Dogs and cats: Common symptoms in dogs and cats include lethargy, loss of appetite, vomiting, and neurological problems, such as seizures or tremors. Some infected animals may exhibit respiratory difficulties or have a persistent cough.
- Other mammals: In other mammals, the symptoms are often non-specific and may include general weakness, loss of appetite, and mild respiratory issues. Some animals might also show signs of neurological problems.
- Birds: Symptoms in birds can include respiratory distress, weight loss, and lethargy. In severe cases, neurological problems can be observed.
Impact on Livestock Production
Rat lungworm infection in livestock can lead to decreased productivity and economic losses. The impact is generally less severe than in other animals, but it’s important to recognize its presence in livestock populations.
- Reduced Feed Intake: Infected animals may experience a decrease in appetite, leading to a reduced feed intake and slowing down growth rate.
- Reduced Milk Production: In dairy animals, the infection might affect milk production.
- Reproductive Issues: The infection can occasionally cause reproductive issues in affected animals, resulting in reduced fertility.
- Decreased Weight Gain: The disease can affect overall health, which directly translates to decreased weight gain in livestock.
Comparison of Impact on Different Animal Populations
The impact of rat lungworm infection varies considerably between different animal populations.
| Animal Population | Impact Description |
|---|---|
| Rodents | Generally subclinical infections; act as reservoirs and vectors. |
| Dogs and cats | Potentially severe; can exhibit neurological and respiratory symptoms; significant health concern. |
| Livestock | Generally less severe; potential for reduced feed intake, milk production, and reproductive issues; economic losses. |
| Wildlife | The impact on wildlife is less studied but is potentially significant in certain ecosystems. |
Emerging Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research into rat lungworm disease is crucial for understanding its complex lifecycle, improving diagnostic capabilities, and ultimately preventing human and animal infections. This includes investigating the specific environmental factors that contribute to the spread of the parasite and identifying the most vulnerable populations. Understanding the intricate interplay between the parasite, the intermediate host, and the definitive host is paramount for developing targeted control strategies.
Current Research Focuses
Research efforts are actively exploring the genetic diversity ofAngiostrongylus cantonensis*, the causative agent of rat lungworm disease. This knowledge is essential for understanding the parasite’s adaptation strategies and potential for evolution, which will allow for better prediction of its future behavior and the development of effective control measures. Researchers are also focusing on identifying specific molecular markers that can aid in rapid and accurate diagnosis, potentially leading to the development of diagnostic tests that are more sensitive and specific than existing methods.
Gaps in Current Knowledge
A significant gap in current knowledge lies in understanding the precise environmental conditions that promote the transmission of rat lungworm. The intricate relationship between temperature, humidity, and the presence of suitable intermediate hosts requires further investigation. Furthermore, the long-term effects of rat lungworm infection on human health, especially in vulnerable populations, remain unclear. More extensive longitudinal studies are needed to establish these effects and inform public health strategies.
Potential Research Areas for Future Studies
Future research should focus on developing improved diagnostic tools. This includes the development of rapid, point-of-care tests that can be used in resource-limited settings. Another area of investigation should focus on developing more effective preventive measures. This might involve exploring novel strategies for controlling the rodent population, optimizing sanitation practices, and identifying alternative intermediate hosts for the parasite.
Need for Improved Diagnostic Tools
Existing diagnostic methods for rat lungworm infection often lack sensitivity and specificity, leading to delayed or missed diagnoses. This necessitates the development of more reliable and accessible diagnostic tools. A key aspect of this development involves investigating the use of serological assays and molecular techniques for rapid and accurate identification of the parasite. The creation of a robust diagnostic tool, especially one suited for resource-limited settings, would dramatically improve the ability to detect and treat infections early.
Development of Effective Preventive Measures
Preventive measures for rat lungworm infection require a multifaceted approach. This includes the implementation of public health campaigns that promote proper food handling and hygiene practices, especially in areas with high rodent populations. The effective control of rodent populations through integrated pest management strategies is also essential. Finally, research into novel interventions, such as the development of vaccines or drugs targeting the parasite, holds promise for the future.
Effective implementation of these measures would reduce the risk of infection, and prevent outbreaks.
Ending Remarks: How Dangerous Is Rat Lungworm Disease
In conclusion, rat lungworm disease presents a multifaceted challenge requiring a comprehensive understanding of its biology, transmission, and impact on health. While prevention and early detection are crucial, ongoing research is vital to developing more effective treatments and strategies to mitigate the disease’s spread. The severity of the infection highlights the need for robust public health measures and improved awareness, especially in areas where the parasite is prevalent.
