How do you know if you have cervical cancer? This crucial question deserves careful consideration, as early detection is vital for successful treatment. Recognizing potential symptoms, understanding risk factors, and knowing the screening process are all essential steps in protecting your well-being. This comprehensive guide explores the key aspects of cervical cancer, from understanding symptoms to discussing treatment options and prevention strategies.
We’ll delve into the nuances of diagnosis, treatment, and support systems to provide a holistic view of this important health issue.
Cervical cancer, if detected early, is highly treatable. Symptoms can range from subtle changes to more pronounced indicators, making self-awareness crucial. This article will help you understand the signs to look for and what to do if you have concerns. We’ll also cover the importance of regular screenings, the role of risk factors, and the options available for treatment and support.
Recognizing Symptoms
Understanding the potential symptoms of cervical cancer is crucial for early detection and treatment. While some symptoms might be subtle or mimic other, less serious conditions, recognizing these indicators can be a vital step in seeking medical attention. Prompt diagnosis allows for more effective treatment and improved outcomes.
Potential Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
Recognizing potential symptoms is important for early detection. Symptoms can vary significantly between individuals, making self-awareness critical. Atypical or unusual symptoms should always be reported to a healthcare professional.
- Common Symptoms: Unusual vaginal bleeding, such as bleeding between periods, after sex, or after menopause. This bleeding can range from light spotting to heavier periods. Pain during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia) is another common indicator. Pelvic pain, though not specific to cervical cancer, can also be a sign, and is important to report.
- Less Common Symptoms: Persistent or unusual vaginal discharge, which may be different in color, odor, or consistency. Unexplained fatigue or weight loss can sometimes be linked to the disease, although these symptoms are often associated with other conditions.
Symptom Variability
The presentation of symptoms can differ greatly from person to person. Factors such as age, overall health, and the specific characteristics of the cancer can influence how symptoms manifest. Some individuals may experience no noticeable symptoms in the early stages, highlighting the importance of regular screenings.
Importance of Atypical Symptoms
Pay close attention to any vaginal discharge, bleeding, or pain that deviates from your usual pattern. Atypical symptoms, even if seemingly minor, could indicate a more serious underlying condition, including cervical cancer. Delaying medical attention for unusual symptoms can potentially hinder early detection and treatment.
Comparison of Symptoms
The following table provides a comparative overview of symptoms associated with cervical cancer and other, less serious conditions. It is crucial to remember that this table is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis.
| Symptom | Cervical Cancer | Other Conditions (e.g., Infections, Irritations) |
|---|---|---|
| Vaginal Bleeding | Intermenstrual, post-coital, post-menopausal bleeding | Menstrual irregularities, hormonal imbalances, infections |
| Vaginal Discharge | Unusual color, odor, or consistency | Bacterial vaginosis, yeast infections, other infections |
| Pelvic Pain | Persistent or worsening pain | Pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, ovarian cysts |
| Fatigue | Persistent tiredness | Stress, poor diet, other health issues |
Stages and Symptom Progression
The progression of cervical cancer symptoms can vary depending on the stage of the disease. Early-stage cervical cancer often presents with few or no noticeable symptoms, making regular screenings crucial.
| Stage | Potential Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Early Stage (Stages 0-IA) | Often asymptomatic or with subtle symptoms like abnormal bleeding or discharge |
| Intermediate Stage (Stages IB-IIA) | Increasing vaginal bleeding, possibly more frequent or heavier periods, pelvic pain, and possible back pain. |
| Late Stage (Stages IIB-IV) | Severe vaginal bleeding, persistent pelvic pain, fatigue, weight loss, leg pain, and potential spread to other parts of the body. |
Risk Factors and Predispositions
Understanding the factors that increase a person’s risk of developing cervical cancer is crucial for prevention and early detection. Knowing these predispositions allows for proactive measures and empowers individuals to make informed choices about their health. Early intervention is often key to successful treatment.Cervical cancer isn’t a random occurrence. A combination of genetic and environmental factors can influence a person’s likelihood of developing the disease.
While some risk factors are unavoidable, many are modifiable, offering opportunities for reducing the risk. This section delves into the key risk factors, focusing on the role of infections, lifestyle, age, and family history.
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
Sexually transmitted infections, particularly human papillomavirus (HPV), play a significant role in cervical cancer development. HPV is a common virus, and while many infections resolve on their own, some types can persist and increase the risk of abnormal cell growth in the cervix. Persistent HPV infections can lead to precancerous lesions that, if left untreated, can progress to invasive cervical cancer.
Role of Age
Age is another important factor. Cervical cancer is most often diagnosed in women between the ages of 35 and 55. This is partly due to the length of time it takes for precancerous cells to develop into cancer. Regular screenings become increasingly important as women age.
Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices, including smoking, can significantly impact cervical cancer risk. Smoking damages the body’s immune system, making it harder to fight off infections like HPV. Also, a diet low in fruits and vegetables may also play a role in increasing the risk of certain cancers. Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular physical activity can contribute to overall well-being and potentially reduce cancer risk.
Family History
Family history of cervical cancer can also be a contributing factor. If a close relative has had the disease, the individual may have a higher risk. This suggests a possible genetic predisposition. Understanding family history is crucial for assessing individual risk and tailoring screening recommendations.
HPV Infection and Cervical Cancer Development
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is a critical risk factor for cervical cancer. Specific types of HPV, known as high-risk types, can cause persistent infections that lead to cellular changes in the cervix. These changes, if not detected and treated, can progress to cancer over time. The majority of women with HPV infection will not develop cervical cancer, but regular screening is crucial for early detection and intervention.
“HPV is the most common sexually transmitted infection, and while most infections resolve on their own, persistent infections can increase the risk of cervical cancer.”
Importance of Regular Screenings and Preventative Measures
Regular cervical cancer screenings, such as Pap tests and HPV tests, are essential for early detection. These screenings can identify precancerous changes before they progress to cancer, allowing for timely treatment. Vaccinations against certain HPV types are also available, offering a preventative measure against infection. These measures significantly reduce the risk of developing cervical cancer.
Summary of Risk Factors
| Risk Factor | Potential Impact on Cervical Cancer Development |
|---|---|
| History of STIs (especially HPV) | Increased risk of persistent infection, leading to precancerous lesions. |
| Age (35-55) | Increased risk due to the time needed for precancerous cells to progress to cancer. |
| Smoking | Weakened immune system, potentially increasing the risk of infection and progression. |
| Family History | Possible genetic predisposition to developing cervical cancer. |
| Diet low in fruits and vegetables | Potential role in increasing the risk of various cancers. |
Screening and Diagnostic Procedures
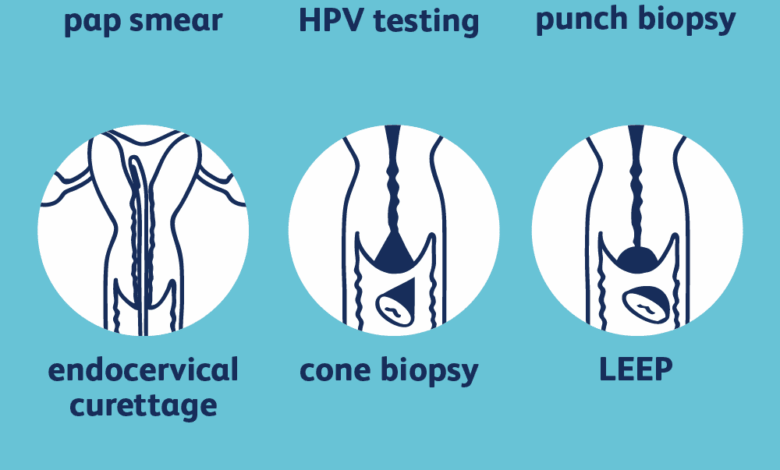
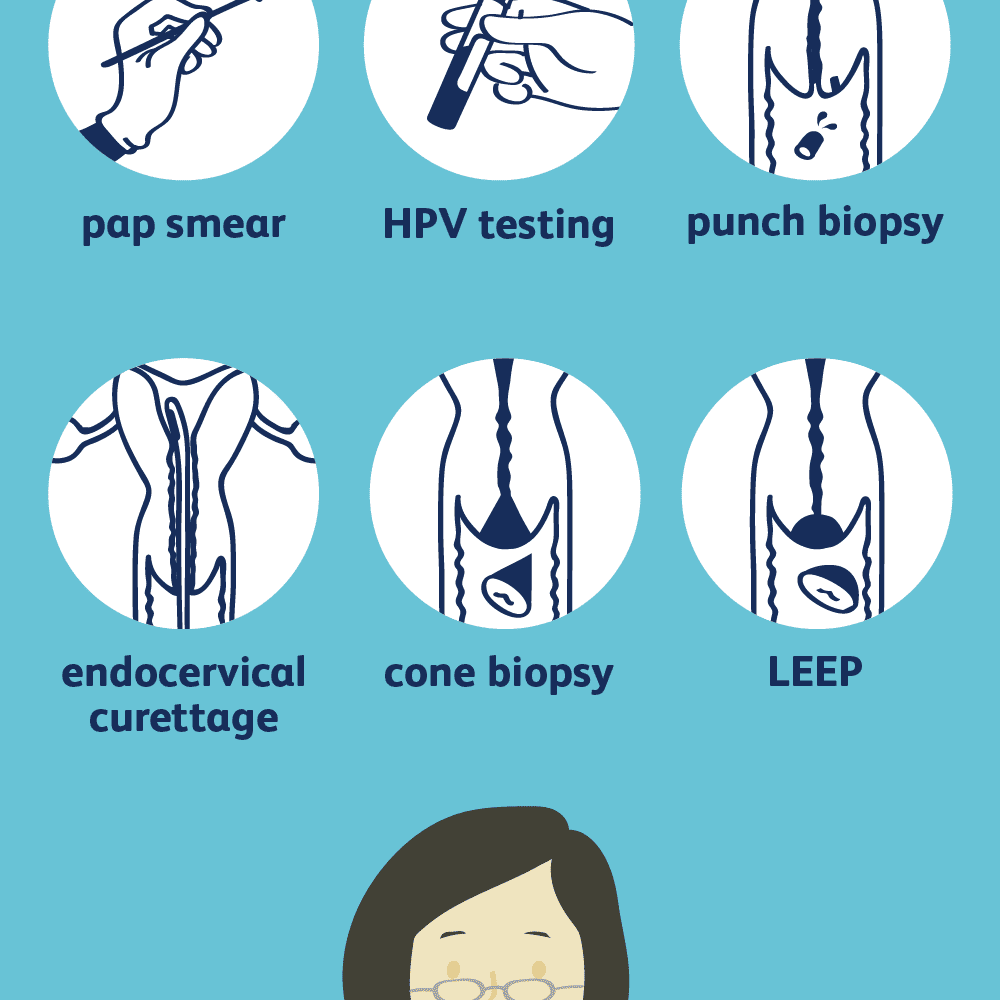
Knowing the potential risks and symptoms of cervical cancer is crucial, but early detection through screening is key to successful treatment. Effective screening methods, coupled with timely diagnostic procedures, significantly improve the chances of catching the disease in its early stages when treatment is most effective. This section will delve into the common screening procedures, including Pap tests, HPV tests, colposcopy, and explain the significance of abnormal results.
Common Screening Methods, How do you know if you have cervical cancer
Cervical cancer screening aims to detect precancerous changes or cancerous cells before they cause noticeable symptoms. Two primary screening methods are widely used: the Pap test and the HPV test. Both tests are vital in identifying potential issues early on, thereby enabling timely intervention and improving treatment outcomes.
- Pap Test (Pap Smear): This test examines cells collected from the cervix for abnormalities. A sample of cells is gently scraped from the cervix using a small brush or spatula, then examined under a microscope for any signs of precancerous changes or cancer. This procedure is typically painless and quick, taking only a few minutes. The Pap test is a fundamental tool in early detection, as precancerous cells often exhibit no symptoms.
Figuring out if you have cervical cancer can be tricky, but regular check-ups are key. Symptoms can be subtle, or sometimes there aren’t any at all. That’s why advancements in medical research, like rethinking a cure for diabetes rethinking a cure for diabetes , are so crucial. Ultimately, staying informed and proactive about your health is the best way to catch potential problems early.
This includes getting screened for cervical cancer as recommended by your doctor.
A sample is collected by a healthcare provider and sent to a lab for analysis.
- HPV Test: Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a common sexually transmitted infection. Certain types of HPV can increase the risk of cervical cancer. The HPV test directly identifies the presence of high-risk HPV types in cervical cells. This test is more specific for detecting the virus associated with cervical cancer than a Pap test. The HPV test is often used in conjunction with a Pap test, particularly for women at higher risk or those with abnormal Pap test results.
Colposcopy
Colposcopy is a procedure used to examine the cervix and vagina in detail. A colposcope, a specialized instrument with a magnifying lens, is used to visualize the tissues. This allows for a more thorough assessment than a Pap test, especially when abnormalities are detected.
- Procedure: A colposcopy typically involves the application of a vinegar solution or iodine to the cervix and vagina. These solutions highlight any abnormal areas that might not be readily visible. The colposcope is then used to examine the affected regions in detail. Biopsies may be taken from these areas to confirm the presence of abnormal cells and determine the severity of the condition.
- Significance: Colposcopy plays a critical role in diagnosing cervical cancer by enabling the visualization and evaluation of abnormal cells. It allows healthcare providers to identify the extent of the abnormality and guide further testing, such as biopsies. If abnormal cells are found, colposcopy helps determine the best course of action, ranging from monitoring to treatment.
Significance of Abnormal Results
Abnormal results from screening tests, such as an abnormal Pap test or HPV test, indicate the presence of potentially precancerous or cancerous cells. It’s crucial to understand that these abnormal results do not automatically mean a diagnosis of cervical cancer. Further evaluation, typically including colposcopy and possibly biopsies, is necessary to determine the extent and nature of the abnormality.
Screening Tests Comparison
| Screening Test | Accuracy Rate | Potential Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Pap Test | High, typically 70-90% | Can be affected by inflammation or infection in the cervix, leading to false negatives. May miss small precancerous changes. |
| HPV Test | High, typically 80-95% | Doesn’t always correlate directly with the development of cervical cancer. Some women with HPV infections may never develop cancer. |
Early Detection and Prevention
Cervical cancer, while treatable, is far more manageable when detected early. Proactive measures and vigilance play a crucial role in reducing the risk and improving outcomes for women. Early detection allows for prompt intervention, often leading to less invasive treatments and a higher chance of complete recovery.Regular check-ups and screenings are fundamental in the fight against cervical cancer.
Understanding the importance of these preventative steps, alongside lifestyle modifications and vaccination, empowers women to take control of their health.
Importance of Regular Check-ups and Screenings
Regular check-ups and screenings are essential for women of reproductive age. These screenings help identify precancerous changes in the cervix, enabling early intervention and prevention of cancer development. Early detection of abnormalities allows for timely treatment, often preventing the need for more aggressive procedures later. This proactive approach is crucial in reducing the overall impact of cervical cancer.
Strategies for Reducing Risk Through Lifestyle Modifications
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle significantly reduces the risk of developing cervical cancer. A balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, coupled with regular exercise, supports overall well-being and strengthens the body’s natural defenses. Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption are also crucial components of a preventative strategy. These lifestyle choices have a positive impact on various aspects of health, including a reduced risk of developing cervical cancer.
HPV Vaccine and its Role in Prevention
The human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine is a critical tool in preventing cervical cancer. HPV is a sexually transmitted infection that can lead to cervical cancer. The vaccine significantly reduces the risk of contracting HPV and, consequently, developing cervical cancer. Vaccination is highly effective, especially when administered at a young age. It’s recommended for both boys and girls to protect against a range of HPV-related cancers.
Preventative Measures and Effectiveness
| Preventative Measure | Effectiveness | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Regular Pap Smears | High | Detects precancerous changes, allowing for early intervention. |
| HPV Vaccination | High | Significantly reduces the risk of HPV infection and subsequent cervical cancer. |
| Healthy Lifestyle (Diet, Exercise, Smoking Cessation) | Moderate to High | Supports overall health, strengthens the immune system, and reduces risk factors. |
| Regular Pelvic Exams | Moderate | Allows for a comprehensive assessment of reproductive health and identification of any abnormalities. |
Understanding Treatment Options
Navigating cervical cancer treatment can feel overwhelming. The good news is that advancements in medical science have provided a range of effective options. Choosing the right path depends on several factors, including the stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and personal preferences. This section will delve into the various treatment approaches, their potential side effects, and the importance of personalized care.Treatment options for cervical cancer vary significantly based on the stage of the disease.
Early-stage cancers often respond well to less invasive procedures, while advanced cancers may require a more comprehensive approach. The ultimate goal is to eliminate the cancerous cells while minimizing harm to healthy tissue.
Treatment Modalities for Cervical Cancer
Different treatment modalities are used depending on the stage of the cancer and the patient’s overall health. Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy are common approaches. Understanding these options is crucial for informed decision-making.
Surgical Treatments
Surgical interventions for cervical cancer range from simple procedures to more extensive ones. Conization, a procedure where a cone-shaped piece of tissue is removed from the cervix, is often used for early-stage cancers. A hysterectomy, the removal of the uterus, is another option, typically considered for more advanced cases. Radical hysterectomies, which remove the uterus, cervix, and surrounding tissues, are sometimes necessary for more aggressive tumors.
The specific surgical approach depends on the extent of the cancer and the patient’s reproductive goals.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells. External beam radiation therapy delivers radiation from a machine outside the body. Internal radiation therapy, or brachytherapy, involves placing radioactive materials inside the cervix or vagina. Radiation therapy can be used as a primary treatment, an adjuvant treatment (following surgery), or as palliative care to alleviate symptoms.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves using drugs to kill cancer cells. These drugs can be administered intravenously or orally. In the context of cervical cancer, chemotherapy is often used in conjunction with radiation therapy or surgery for advanced stages. The specific chemotherapy regimen depends on the cancer’s characteristics.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy is a relatively new approach that focuses on specific molecules involved in cancer growth. These therapies are often used in combination with other treatments for advanced stages.
Personalized Treatment Plans
A crucial aspect of cervical cancer treatment is the development of a personalized plan. Healthcare providers consider factors like the stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and personal preferences when creating a treatment strategy. This personalized approach ensures the best possible outcome for each individual.
Treatment Approaches for Different Stages
Treatment approaches differ significantly for early-stage and advanced-stage cervical cancer. Early-stage cancers may be treated with less invasive procedures, such as conization or a hysterectomy, while advanced cancers often require a combination of surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. The goal is to tailor the treatment plan to maximize efficacy and minimize side effects.
Potential Side Effects of Treatment
Each treatment modality carries potential side effects. Surgery may lead to bleeding, infection, or complications related to anesthesia. Radiation therapy can cause fatigue, skin irritation, and bowel or bladder problems. Chemotherapy can lead to nausea, hair loss, and other side effects. The severity of side effects varies from person to person.
Careful monitoring and management of side effects are crucial during and after treatment.
Comparison of Treatment Outcomes
| Treatment Option | Typical Outcomes (Early Stage) | Typical Outcomes (Advanced Stage) |
|---|---|---|
| Surgery (e.g., Conization, Hysterectomy) | High cure rates, lower chance of recurrence | Potentially curative in some cases, but higher chance of recurrence |
| Radiation Therapy | High cure rates, especially when combined with surgery | Can shrink tumors, but may not be curative |
| Chemotherapy | Used as an adjuvant treatment to increase cure rates | Often used in combination with other treatments to shrink tumors and control the disease |
Living with Cervical Cancer: How Do You Know If You Have Cervical Cancer
Navigating a cervical cancer diagnosis is a complex journey, impacting not only physical well-being but also emotional and social life. This stage requires resilience, support, and a proactive approach to maintaining overall health. Understanding the resources available and strategies for coping can significantly improve the quality of life during and after treatment.Facing a cervical cancer diagnosis can evoke a wide range of emotions, from fear and anxiety to anger and sadness.
It’s crucial to acknowledge and address these feelings openly and honestly. This includes seeking professional help when needed, connecting with support networks, and prioritizing self-care. The experience will be unique to each individual, and there is no one-size-fits-all solution. However, with the right support systems and coping mechanisms, individuals can navigate this challenging time with strength and hope.
Support Systems for Individuals with Cervical Cancer
Comprehensive support systems are vital for individuals diagnosed with cervical cancer. These systems include medical professionals, family, friends, and support groups. Connecting with others who understand the challenges and share similar experiences can provide invaluable emotional support and practical advice. Moreover, healthcare providers can offer guidance on treatment options, side effects management, and overall well-being.
Spotting unusual changes in your cervical cells can be a red flag, but figuring out if it’s something serious requires a visit to your doctor. While we’re on the topic of health concerns, have you ever wondered if the rise in food allergies is connected to our increasing consumption of junk food? It’s an interesting question that researchers are exploring.
Is junk food responsible for increase in food allergies could be a contributing factor, but ultimately, knowing if you have cervical cancer involves a thorough examination and professional diagnosis.
- Medical Professionals: Oncologists, gynecologists, and other medical professionals play a critical role in providing medical care, treatment plans, and emotional support. They can guide patients through the complexities of diagnosis and treatment and connect them with other support resources.
- Family and Friends: The love and support of family and friends are essential during this challenging time. Their understanding and encouragement can significantly impact the emotional well-being of the individual. Offering practical assistance, such as help with daily tasks, can also ease the burden of the illness.
- Support Groups: Support groups provide a safe space for individuals to share their experiences, receive emotional support, and connect with others facing similar challenges. These groups offer a sense of community and understanding, fostering a supportive environment where individuals can feel heard and validated.
Emotional and Psychological Impact of a Cervical Cancer Diagnosis
A cervical cancer diagnosis can significantly impact mental well-being. Anxiety, fear, and depression are common responses. The experience can lead to feelings of isolation, loss of control, and uncertainty about the future. It is crucial to acknowledge and address these emotions with professional guidance and support networks. Open communication with healthcare providers and loved ones is vital.
- Seeking Professional Help: Mental health professionals, such as therapists or counselors, can provide support and guidance in managing the emotional and psychological challenges associated with a cancer diagnosis. Therapy can help individuals develop coping mechanisms, process their emotions, and navigate the uncertainties of the treatment process.
- Prioritizing Self-Care: Self-care activities, such as meditation, yoga, spending time in nature, or engaging in hobbies, can significantly reduce stress and improve emotional well-being. These activities can help individuals focus on positive aspects of their lives and promote emotional resilience.
Importance of Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is critical during and after cervical cancer treatment. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and sufficient rest are essential for supporting the body’s healing process and overall well-being. A healthy lifestyle can improve physical strength, reduce fatigue, and boost the immune system, helping individuals cope with the treatment’s physical and emotional challenges.
- Balanced Diet: A nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein is essential for providing the body with the necessary nutrients for healing and recovery. A balanced diet can help maintain energy levels and support the immune system during and after treatment.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or light exercises, can help manage stress, improve mood, and enhance physical strength. Exercise can be tailored to the individual’s physical capabilities and should be discussed with the healthcare team.
- Adequate Rest: Adequate sleep and rest are vital for the body’s healing process. Getting sufficient rest can help reduce fatigue and improve overall well-being during and after treatment.
Coping Strategies for Physical and Emotional Challenges
Developing coping strategies is essential for managing the physical and emotional challenges of cervical cancer. Strategies may include stress management techniques, relaxation exercises, and connecting with support networks. These strategies can help individuals navigate the uncertainties and challenges associated with the disease and treatment.
- Stress Management Techniques: Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or mindfulness practices can help manage stress and anxiety. These techniques can provide a sense of calm and control during a stressful period.
- Relaxation Exercises: Relaxation exercises, such as progressive muscle relaxation or guided imagery, can help reduce physical tension and promote relaxation. These techniques can help individuals cope with physical discomfort and emotional distress.
- Connecting with Support Networks: Connecting with family, friends, support groups, and mental health professionals can provide invaluable emotional support. Sharing experiences and connecting with others who understand the challenges can significantly impact emotional well-being.
Available Support Groups and Resources
Numerous support groups and resources are available for individuals diagnosed with cervical cancer. These resources provide practical guidance, emotional support, and information on navigating the various aspects of the disease and treatment.
Knowing if you have cervical cancer can be tricky, but regular checkups are key. It’s important to remember that sometimes, subtle changes can indicate potential issues, and that’s why understanding your body is crucial. Just like recognizing signs of gray area drinking during the pandemic, which you can learn more about here , paying attention to unusual symptoms is vital.
Ultimately, seeking professional medical advice is the best way to know for sure if you need to be concerned about cervical cancer.
| Organization | Description | Contact Information |
|---|---|---|
| American Cancer Society | Provides information, support, and resources for cancer patients and their families. | [Link to ACS website] |
| National Cervical Cancer Coalition | Focuses on prevention, early detection, and treatment of cervical cancer. | [Link to NCC website] |
| [Local Cancer Support Groups] | Offer support groups and resources specific to local communities. | [Contact information for local groups] |
Illustrative Cases
Navigating the complexities of cervical cancer often requires understanding how the disease progresses, how it’s diagnosed, and what treatment options are available. Case studies offer valuable insights into the challenges and triumphs of this journey. This section will explore illustrative cases, focusing on the diagnostic process, treatment approaches, and the crucial role of patient education in managing the disease.Understanding the progression of cervical cancer, the various diagnostic paths, and the diverse treatment approaches is vital for patients and their families.
The experiences of individuals facing this challenge highlight the importance of early detection and proactive management strategies.
A Case Study Illustrating Progression
A 35-year-old woman presented with abnormal vaginal bleeding, a common symptom often overlooked. Initial Pap smears revealed atypical cells, prompting further investigation. Colposcopy, a procedure that allows for visualization of the cervix, confirmed the presence of cervical dysplasia, a precancerous condition. The patient was advised on treatment options, including cryotherapy, laser ablation, or surgical excision. She opted for cryotherapy, a procedure that freezes and destroys abnormal tissue.
Follow-up Pap smears showed improvement, but a subsequent visit revealed a recurrence of abnormal cells, prompting a cone biopsy. The results confirmed the presence of invasive cervical cancer. This case highlights the importance of regular screenings and prompt follow-up when abnormal cells are detected. It also underscores the possibility of progression from precancerous to cancerous stages.
The Diagnostic Journey
The diagnostic journey for cervical cancer typically involves a combination of screenings and procedures. A Pap smear, a routine screening test, is often the initial step. Abnormal results lead to further investigations, such as colposcopy, which allows for a closer look at the cervix. Biopsies, small tissue samples, are then taken for laboratory analysis. This analysis can confirm the diagnosis and determine the stage of the cancer.
Different imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans, might be used to assess the extent of the disease and its spread. The diagnostic process aims to accurately determine the presence and extent of the cancer, allowing for informed treatment planning.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options for cervical cancer vary depending on the stage and extent of the disease. Surgical procedures, such as a hysterectomy, might be necessary to remove the affected tissues. Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells. Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including the patient’s overall health, the stage of the disease, and personal preferences.
The goal is to eradicate the cancer and minimize potential side effects.
Importance of Patient Education
Patient education plays a crucial role in managing cervical cancer. Educating patients about the disease, its treatment options, and potential side effects empowers them to actively participate in their care. This knowledge fosters a sense of control and promotes adherence to treatment plans. Patients who are well-informed are better equipped to ask questions, understand their options, and make informed decisions about their care.
Impact of Early Detection
Early detection significantly impacts treatment outcomes. A case study of a 28-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical cancer at an early stage demonstrates the positive effect of early intervention. Detected through routine screening, the cancer was localized and treated with a minimally invasive procedure. The patient experienced a full recovery and returned to her normal life. This example highlights the potential for a complete cure when the disease is detected and treated promptly.
Illustrative Case (Without Specific Patient Data)
A patient presented with abnormal vaginal bleeding and a history of HPV infection. Initial Pap smears showed atypical squamous cells. Colposcopy revealed cervical dysplasia, and a biopsy confirmed the presence of cervical cancer. The patient was assessed for the extent of the disease. Given the early stage, a cone biopsy was deemed appropriate.
Follow-up procedures and regular monitoring were recommended to ensure the cancer did not recur. This case demonstrates the common diagnostic path for cervical cancer, highlighting the importance of diligent follow-up and proactive management.
Closure
In conclusion, understanding how to recognize the signs of cervical cancer, identifying risk factors, and embracing preventive measures are paramount to protecting your health. Regular screenings, combined with a healthy lifestyle, significantly reduce the risk. Early detection dramatically improves treatment outcomes. Remember, knowledge empowers you. If you have any concerns, consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
