How social isolation loneliness can affect heart health cognitive abilities – How social isolation and loneliness can affect heart health and cognitive abilities sets the stage for this exploration, revealing the hidden toll of disconnection on our well-being. This discussion dives deep into the physiological and psychological impacts of isolation, from its effect on cardiovascular health to its influence on cognitive functions like memory and attention. We’ll examine the underlying mechanisms connecting social disconnection to physical and mental decline, and importantly, offer strategies for mitigating these harmful effects.
Modern life often pressures us towards individual pursuits, potentially leaving us feeling disconnected and alone. This can lead to a cascade of negative consequences. The article will explore how a lack of social interaction affects our heart, impacting blood pressure, inflammation, and sleep. We’ll also delve into how isolation and loneliness can impact cognitive function, from memory to executive function, potentially contributing to age-related decline.
This isn’t just about feeling sad; it’s about understanding how a lack of connection impacts our physical health and mental sharpness. Ultimately, the goal is to raise awareness and offer solutions.
Introduction to Social Isolation and Loneliness: How Social Isolation Loneliness Can Affect Heart Health Cognitive Abilities
Social isolation and loneliness, while often used interchangeably, represent distinct but interconnected experiences. Social isolation refers to a lack of social connections and interactions, often due to circumstances like geographic location, limited mobility, or social withdrawal. Loneliness, on the other hand, is the subjective feeling of being alone or lacking companionship, even when surrounded by others. This feeling can stem from a perceived lack of meaningful connections, despite having social interactions.
Both conditions are increasingly prevalent in modern society, impacting individuals’ well-being in significant ways.The increasing pace of life, urbanization, and the rise of technology have contributed to a growing sense of detachment and isolation. Many individuals find themselves juggling multiple responsibilities, leading to less time for social connections. While technology facilitates communication, it can also create a sense of superficiality, failing to replace the genuine intimacy and support found in face-to-face interactions.
This disconnect has far-reaching consequences for mental and physical health.
Defining Social Isolation and Loneliness
Social isolation is the objective absence of social connections. Loneliness, conversely, is the subjective feeling of isolation, even when in the presence of others. Crucially, an individual can be socially isolated but not lonely, and vice versa. For example, a person living alone might feel connected to their community through online forums, mitigating feelings of loneliness. Conversely, someone with a large social circle might still experience profound loneliness if those connections lack depth and intimacy.
Prevalence of Social Isolation and Loneliness
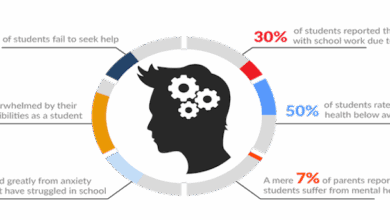
The prevalence of social isolation and loneliness is a significant public health concern. Studies show that a substantial portion of the population reports feeling lonely or socially isolated, impacting various demographic groups, including the elderly, young adults, and individuals experiencing unemployment or significant life transitions. These feelings are not limited to any specific socioeconomic group. For instance, a recent survey found a concerning correlation between loneliness and mental health issues among university students, highlighting the need for interventions and support systems.
Long-Term Consequences on Well-being
The long-term consequences of social isolation and loneliness extend beyond emotional distress. Research suggests a strong link between these conditions and a heightened risk of various health problems, including cardiovascular disease, weakened immune function, and cognitive decline. Chronic loneliness can also contribute to mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety. Prolonged isolation and loneliness have been associated with a higher risk of premature mortality, emphasizing the critical importance of addressing these issues.
Feeling isolated and lonely can really take a toll on your heart health and cognitive abilities, making you more vulnerable to various health issues. It’s crucial to prioritize social connections for overall well-being. For example, understanding the potential dangers of giving antacids to infants is equally important for their health and development, as improper medication use can lead to adverse effects.
Learning about the specific risks associated with giving antacids to infants can be found here: why you shouldnt give antacids to infants. Ultimately, nurturing strong social connections and avoiding harmful substances like unnecessary antacids in infants are key to promoting optimal health and well-being.
Comparison of Physiological and Psychological Impacts
| Characteristic | Social Isolation | Loneliness |
|---|---|---|
| Physiological Impacts | Increased blood pressure, elevated cortisol levels, weakened immune response, increased risk of cardiovascular disease, and potentially accelerated aging. | Increased risk of inflammation, higher levels of stress hormones, weakened immune system, and potential exacerbation of existing health conditions. |
| Psychological Impacts | Reduced social engagement, feelings of detachment, difficulty forming close relationships, and potentially a decline in overall well-being. | Sadness, hopelessness, feelings of worthlessness, depression, anxiety, and increased susceptibility to mental health challenges. |
This table highlights the interconnected nature of social isolation and loneliness, illustrating how both can negatively impact both physical and mental health.
Impact on Heart Health
Social isolation and loneliness are not just emotional burdens; they can have profound and detrimental effects on our physical health, particularly our cardiovascular system. The human body is intricately connected, and emotional well-being significantly influences physiological processes. This connection is particularly evident in the heart’s response to chronic feelings of isolation and loneliness.The relentless stress associated with social isolation and loneliness triggers a cascade of physiological responses that can damage the heart and blood vessels.
These negative impacts are often subtle but can accumulate over time, increasing the risk of serious cardiovascular problems. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial to developing effective preventative strategies.
Physiological Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Impact
Chronic social isolation and loneliness activate the body’s stress response system, which releases hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones, while beneficial in short bursts, can be detrimental when persistently elevated. Sustained high levels of these hormones can lead to increased blood pressure, inflammation, and an elevated heart rate. This constant state of physiological arousal takes a toll on the cardiovascular system, making individuals more susceptible to heart disease.
Elevated cortisol levels also interfere with the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar, potentially contributing to metabolic syndrome, a significant risk factor for heart disease.
Social Connection and Blood Pressure Regulation, How social isolation loneliness can affect heart health cognitive abilities
Strong social connections are associated with better blood pressure regulation. Studies suggest that individuals with robust social support networks tend to have lower blood pressure readings compared to those who are socially isolated. The presence of a supportive social network may act as a buffer against stress, thereby influencing the body’s physiological response to stressors and potentially mitigating blood pressure fluctuations.
This effect is likely due to the reduced stress and anxiety levels associated with strong social support.
Social isolation and loneliness can really take a toll on your health, impacting everything from your heart health to your cognitive abilities. It’s a serious issue, and unfortunately, rising prescription drug costs can add another layer of difficulty. For example, out of pocket costs go up when prescription drug prices rise , making it harder for people to afford the medications they need to manage conditions stemming from isolation, which further exacerbates the negative effects on heart health and cognitive function.
Ultimately, addressing these interconnected issues is crucial for overall well-being.
Influence on Inflammation and Heart Disease
Social isolation and loneliness are linked to increased levels of inflammation in the body. Inflammation is a natural bodily response to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can contribute to the development of various diseases, including heart disease. The constant stress response triggered by isolation and loneliness can lead to a persistent state of low-grade inflammation, damaging blood vessels and promoting the buildup of plaque, a crucial factor in atherosclerosis.
The chronic inflammation may also interfere with the body’s natural repair mechanisms, leading to more damage.
Preventative Measures for Maintaining Heart Health
Maintaining a strong social network is crucial in mitigating the negative cardiovascular impacts of social isolation and loneliness. Engaging in activities that foster social connections, such as joining clubs, volunteering, or participating in group activities, can significantly reduce feelings of isolation. Cultivating meaningful relationships with family and friends is equally important. Furthermore, prioritizing stress-reducing activities like exercise, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques can help manage the physiological effects of chronic stress.
Importance of Sleep Quality
Adequate sleep is vital for cardiovascular health. Social isolation and loneliness can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to poor sleep quality. Sleep deprivation can increase the risk of high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and irregular heartbeats, all of which are significant risk factors for heart disease. Prioritizing sleep hygiene, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and seeking professional help if sleep disturbances persist are important steps in maintaining heart health in the face of social isolation.
Ways Social Isolation and Loneliness Can Lead to Heart-Related Issues
| Aspect | Impact on Heart Health |
|---|---|
| Chronic Stress Response | Increased blood pressure, elevated heart rate, and persistent inflammation |
| Impaired Blood Pressure Regulation | Higher risk of hypertension and cardiovascular events |
| Inflammation | Damage to blood vessels, plaque buildup, and increased risk of atherosclerosis |
| Sleep Disruption | Higher risk of high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and irregular heartbeats |
| Weakened Immune System | Increased susceptibility to infections, further stressing the cardiovascular system |
Impact on Cognitive Abilities

Social isolation and loneliness aren’t just emotionally draining; they can significantly impact cognitive function. Our brains, like our bodies, thrive on connection and engagement. When we disconnect from others, we put our mental well-being at risk, and this can manifest in a range of cognitive challenges. This section will delve into how social isolation and loneliness affect various cognitive functions, highlighting the importance of social interaction for maintaining cognitive health, particularly as we age.Our minds are intricately linked to our social lives.
Social interaction isn’t just about emotional well-being; it plays a crucial role in keeping our cognitive abilities sharp. Maintaining strong social connections is vital for cognitive reserve, the brain’s ability to adapt and compensate for damage or decline. This reserve is like a mental cushion, protecting against age-related cognitive decline and other potential cognitive challenges.
Cognitive Functions Affected
Social isolation and loneliness can negatively impact several cognitive functions. These include memory, attention, and executive function. The brain’s intricate networks require stimulation from social interaction to function optimally. Without this engagement, these networks can weaken, leading to cognitive impairments.
The Role of Social Interaction in Cognitive Reserve
Social interaction plays a pivotal role in maintaining cognitive reserve. Engaging in conversations, sharing experiences, and participating in social activities stimulate various brain regions, contributing to the growth and strengthening of neural connections. This enhanced neural network complexity acts as a buffer against cognitive decline. Active participation in social groups and maintaining meaningful relationships help to bolster this cognitive reserve.
Impact on Memory, Attention, and Executive Function
Social isolation and loneliness can negatively affect memory, attention, and executive function. Memory, which encompasses both short-term and long-term storage, can suffer as a result of reduced mental stimulation. Attention, the ability to focus on tasks, can be hampered by feelings of isolation and loneliness, leading to decreased concentration. Executive functions, which include planning, problem-solving, and decision-making, can also be compromised when social engagement is limited.
This can manifest as difficulty in organizing thoughts, managing time, or adapting to new situations. For example, an individual struggling with loneliness may have trouble remembering appointments or focusing on work tasks.
Loneliness and Age-Related Cognitive Decline
Loneliness is a significant risk factor for age-related cognitive decline. Studies have shown a correlation between chronic loneliness and an increased risk of developing dementia and other cognitive impairments. The lack of social stimulation can lead to a decline in cognitive abilities, potentially accelerating the process of age-related decline. Maintaining strong social connections is crucial in mitigating this risk.
Social isolation and loneliness can significantly impact heart health and cognitive abilities, leading to a range of negative outcomes. Thankfully, taxpayers fund research for drugs taxpayers fund research for drugs aimed at addressing these issues, but much more research is needed to fully understand and combat the devastating effects of social isolation and loneliness on our well-being.
Social engagement helps keep the mind active and engaged, potentially slowing down the progression of age-related cognitive decline.
Social Engagement and Mitigating Age-Related Cognitive Decline
Social engagement is a powerful tool in mitigating age-related cognitive decline. Participating in social activities, whether it’s joining a book club, volunteering, or simply spending time with loved ones, can stimulate the brain, maintain cognitive function, and reduce the risk of cognitive impairment. By fostering a sense of belonging and connection, we can help safeguard our cognitive health as we age.
Table: Impact of Social Isolation and Loneliness on Cognitive Functions
| Cognitive Function | Impact of Social Isolation/Loneliness |
|---|---|
| Memory | Reduced short-term and long-term memory capacity; difficulty remembering appointments or events |
| Attention | Difficulty concentrating; reduced focus on tasks |
| Executive Function | Impaired planning, problem-solving, and decision-making; difficulty adapting to new situations |
| Cognitive Reserve | Weakening of the brain’s ability to adapt and compensate for damage or decline; increased vulnerability to cognitive decline |
Underlying Mechanisms
Social isolation and loneliness are not merely emotional states; they trigger a cascade of biological responses that profoundly impact our physical and mental well-being. These responses, often occurring subconsciously, can have long-term consequences for heart health and cognitive function. Understanding the underlying mechanisms provides crucial insight into how these seemingly intangible experiences translate into tangible health risks.These mechanisms, encompassing hormonal fluctuations, inflammatory responses, and neurochemical changes, highlight the interconnectedness of mind and body.
Recognizing these processes is essential for developing effective strategies to mitigate the negative effects of social isolation and loneliness and fostering a more supportive and connected society.
Stress Hormone Release
Chronic social isolation and loneliness activate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, leading to a heightened release of stress hormones, particularly cortisol. This continuous elevation can damage various bodily systems, including the cardiovascular system. Sustained cortisol release weakens the body’s natural defenses, leading to an increased risk of chronic inflammation.
Inflammatory Response
The inflammatory response plays a pivotal role in the detrimental effects of social isolation and loneliness on health. Studies have demonstrated a correlation between prolonged social isolation and elevated levels of inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP). This chronic inflammation contributes to cardiovascular disease and negatively impacts cognitive function. The body’s natural healing processes are compromised, leading to an increased vulnerability to various diseases.
Neurochemical Pathways
The brain’s neurochemical pathways are profoundly affected by social isolation and loneliness. Decreased levels of neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, vital for mood regulation and cognitive function, are observed in individuals experiencing these conditions. These neurochemical imbalances can lead to a range of symptoms, from reduced motivation and focus to heightened anxiety and depression.
Oxytocin and Social Bonding
Oxytocin, often called the “love hormone,” plays a crucial role in social bonding and attachment. Lower levels of oxytocin, associated with social isolation, can contribute to feelings of loneliness and detachment. This hormone’s role in promoting trust and social interaction underscores the importance of social connection for overall well-being. Reduced oxytocin levels can also weaken the body’s immune response, increasing susceptibility to illness.
Sleep Disruption and Cognitive Function
Social isolation and loneliness often disrupt sleep patterns, leading to insomnia, sleep fragmentation, and poor sleep quality. Sleep deprivation significantly impairs cognitive function, including memory, attention, and decision-making. Chronic sleep deprivation exacerbates the effects of stress hormones and inflammatory responses, creating a vicious cycle impacting both mental and physical health.
Impact on the Immune System
Chronic stress, a hallmark of social isolation and loneliness, profoundly impacts the immune system. A weakened immune response increases vulnerability to infections and hinders the body’s ability to fight off diseases. This compromised immune function is closely linked to increased susceptibility to various illnesses and the slower recovery from injuries. Sustained exposure to stress can significantly diminish the body’s capacity to heal and resist diseases.
Strategies for Mitigation
Combating social isolation and loneliness requires a multifaceted approach that addresses individual needs and leverages community resources. Effective strategies are crucial in preventing the detrimental effects of these conditions on physical and mental well-being. This section details evidence-based interventions and support systems for fostering social connection and engagement.
Building Social Connections
Cultivating meaningful social connections is fundamental to combating loneliness and isolation. This involves actively seeking opportunities to interact with others, regardless of the existing social circle. Simple actions, such as joining a local book club, volunteering at a community center, or taking a class, can significantly enhance social interaction. Engaging in shared hobbies and interests, whether through formal groups or informal gatherings, can help individuals connect with like-minded people.
- Joining Social Groups: Participating in organized activities like sports teams, hiking clubs, or book clubs provides structured opportunities for interaction and shared experiences. These groups offer a sense of belonging and shared purpose.
- Volunteering: Contributing time and skills to a cause that resonates with an individual fosters a sense of purpose and connection with others. Volunteering often involves interaction with diverse individuals and groups.
- Taking Classes or Workshops: Learning new skills or exploring interests through classes or workshops allows individuals to connect with others who share similar passions and learn alongside them. This fosters a sense of community and shared learning.
- Reaching Out to Friends and Family: Maintaining and nurturing existing relationships is vital. Regular contact with loved ones, whether through phone calls, video chats, or in-person visits, strengthens social bonds and combats feelings of isolation.
Leveraging Community Support Systems
Community support plays a pivotal role in preventing social isolation and loneliness. Community organizations, local initiatives, and support groups provide structured environments for individuals to connect with others and access resources. These networks offer a sense of belonging and reduce feelings of isolation.
- Community Centers: Many community centers offer various programs and activities designed to foster social interaction and engagement, such as senior centers, community gardens, or recreational programs for children and families. These centers often provide opportunities for social interaction and a sense of belonging.
- Support Groups: Structured support groups, such as those for individuals dealing with specific conditions or life experiences, provide a safe space for individuals to share their struggles and find support from others facing similar challenges. These groups offer a sense of camaraderie and shared understanding.
- Local Organizations: Local organizations dedicated to social welfare or community development can offer resources and support to individuals experiencing social isolation and loneliness. These organizations can connect individuals with appropriate support services and community events.
- Faith-Based Communities: Religious or faith-based communities can provide a strong social support network for individuals, offering a sense of belonging and connection through shared beliefs and rituals. These communities often organize events and activities that foster social interaction.
Resources and Programs
Numerous resources and programs are available to support individuals experiencing social isolation and loneliness. These resources vary based on the specific needs and circumstances of individuals. Accessing these resources can be crucial in alleviating feelings of isolation and fostering social connections.
| Type of Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Senior Centers | Provide activities, meals, and social interaction opportunities for older adults, addressing loneliness and isolation in this demographic. |
| Mental Health Organizations | Offer counseling and support groups for individuals experiencing loneliness and isolation, which often stems from underlying mental health conditions. |
| Community Outreach Programs | Organize social events, workshops, and activities to promote social connection and engagement in the community. |
| Online Platforms | Offer virtual support groups and social networking opportunities for individuals who may find it challenging to connect in person. |
Promoting Social Support
Promoting social support and fostering positive social connections are essential strategies for mitigating social isolation and loneliness. Encouraging individuals to actively participate in social activities and building strong relationships within their communities are crucial steps towards creating a supportive environment. This involves addressing barriers to social participation and providing opportunities for individuals to connect with others.
Final Wrap-Up

In conclusion, the impact of social isolation and loneliness on heart health and cognitive abilities is profound and multifaceted. From cardiovascular issues to cognitive decline, the consequences are far-reaching. This discussion highlights the importance of fostering social connections, building strong support systems, and prioritizing mental and physical well-being. By understanding the underlying mechanisms and implementing preventative measures, we can strive to build a more connected and healthier society.