Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer deaths in the u s – Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S., a sobering statistic that underscores the urgent need for increased awareness, prevention strategies, and improved treatment options. This comprehensive overview explores the prevalence, causes, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and impact on the healthcare system of this devastating disease. We’ll delve into the alarming statistics, examine the socioeconomic factors contributing to disparities, and analyze the historical trends in lung cancer rates.
Understanding these factors is crucial for developing effective strategies to combat this pervasive health crisis.
The sheer number of lives lost annually to lung cancer is a stark reminder of the challenges we face in combating this disease. From understanding the multifaceted risk factors to exploring innovative treatment approaches and preventive measures, this discussion aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of lung cancer’s impact on individuals, families, and the nation’s healthcare system. We will also investigate the role of public health initiatives and the unmet needs in research and treatment.
Prevalence and Impact of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer remains a devastating global health concern, tragically claiming countless lives annually. Understanding its prevalence, impact, and associated factors is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. This exploration delves into the incidence, mortality rates, socioeconomic disparities, historical trends, and demographic variations in lung cancer within the United States.A significant portion of lung cancer cases are attributable to preventable risk factors, emphasizing the importance of public health initiatives and awareness campaigns.
Addressing socioeconomic disparities and promoting early detection are crucial steps towards mitigating the impact of this disease.
Lung Cancer Incidence and Mortality Rates in the U.S.
Understanding the trends in lung cancer incidence and mortality rates is critical for assessing the disease’s impact and guiding public health interventions. The data presented below offers a glimpse into these trends over time.
| Year | Incidence Rate (per 100,000) | Mortality Rate (per 100,000) | Population (Millions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 48.1 | 42.1 | 309.0 |
| 2015 | 45.8 | 40.5 | 321.5 |
| 2020 | 44.0 | 38.7 | 332.0 |
Note: Data is hypothetical and for illustrative purposes only. Actual figures can be found through reputable public health databases. The table demonstrates a general downward trend in both incidence and mortality rates over the period, potentially reflecting improvements in early detection and treatment.
Socioeconomic Factors Associated with Lung Cancer Disparities
Socioeconomic factors play a crucial role in shaping health disparities, including lung cancer rates. Factors like access to healthcare, education levels, and environmental exposures can influence an individual’s risk.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Lung Cancer Rates |
|---|---|---|
| Income Level | Individuals with lower incomes often have limited access to preventative care, early diagnosis, and effective treatment. | Lower socioeconomic status is linked to higher lung cancer rates due to increased exposure to risk factors and reduced access to care. |
| Education Level | Individuals with lower educational attainment may have limited awareness of lung cancer risks and preventive measures. | Lower educational attainment may contribute to higher rates of lung cancer due to increased exposure to environmental factors and reduced awareness of risk factors. |
| Access to Healthcare | Limited access to healthcare services can impede early diagnosis and treatment, leading to poorer outcomes. | Individuals with limited access to healthcare are at a higher risk of developing lung cancer and facing worse outcomes compared to those with access to quality care. |
Historical Trends in Lung Cancer Rates
Historical trends in lung cancer rates reveal important shifts over time. Understanding these trends is crucial for developing targeted interventions.Lung cancer rates have risen significantly in the 20th century, primarily due to increased tobacco use. More recent declines reflect a decrease in smoking prevalence. These trends are often tied to public health campaigns and increased awareness of the risks of smoking.
While lung cancer sadly remains the leading cause of cancer deaths in the US, it’s crucial to remember other health risks. For example, intense exercise habits, even on weekends, can lead to some surprisingly dangerous conditions, like the ones explored in this insightful article about know the rare and dangerous side effect that is affecting weekend warriors.
Ultimately, understanding all potential health pitfalls, from strenuous activity to the grim reality of lung cancer, is vital for proactive wellness.
Prevalence of Lung Cancer Across Demographic Groups
Lung cancer prevalence varies across different demographic groups in the U.S. Understanding these variations is vital for tailoring public health interventions.
| Demographic Group | Prevalence |
|---|---|
| African Americans | Studies indicate higher rates compared to other groups, potentially linked to socioeconomic factors and environmental exposures. |
| Hispanic Americans | Variations exist, influenced by various factors such as socioeconomic status and access to healthcare. |
| Asian Americans | Rates can differ across specific subgroups, with some exhibiting lower rates and others potentially higher rates. |
Note: Data is illustrative and may not reflect the precise prevalence in all subgroups. Further research is needed to fully understand these disparities.
Causes and Risk Factors
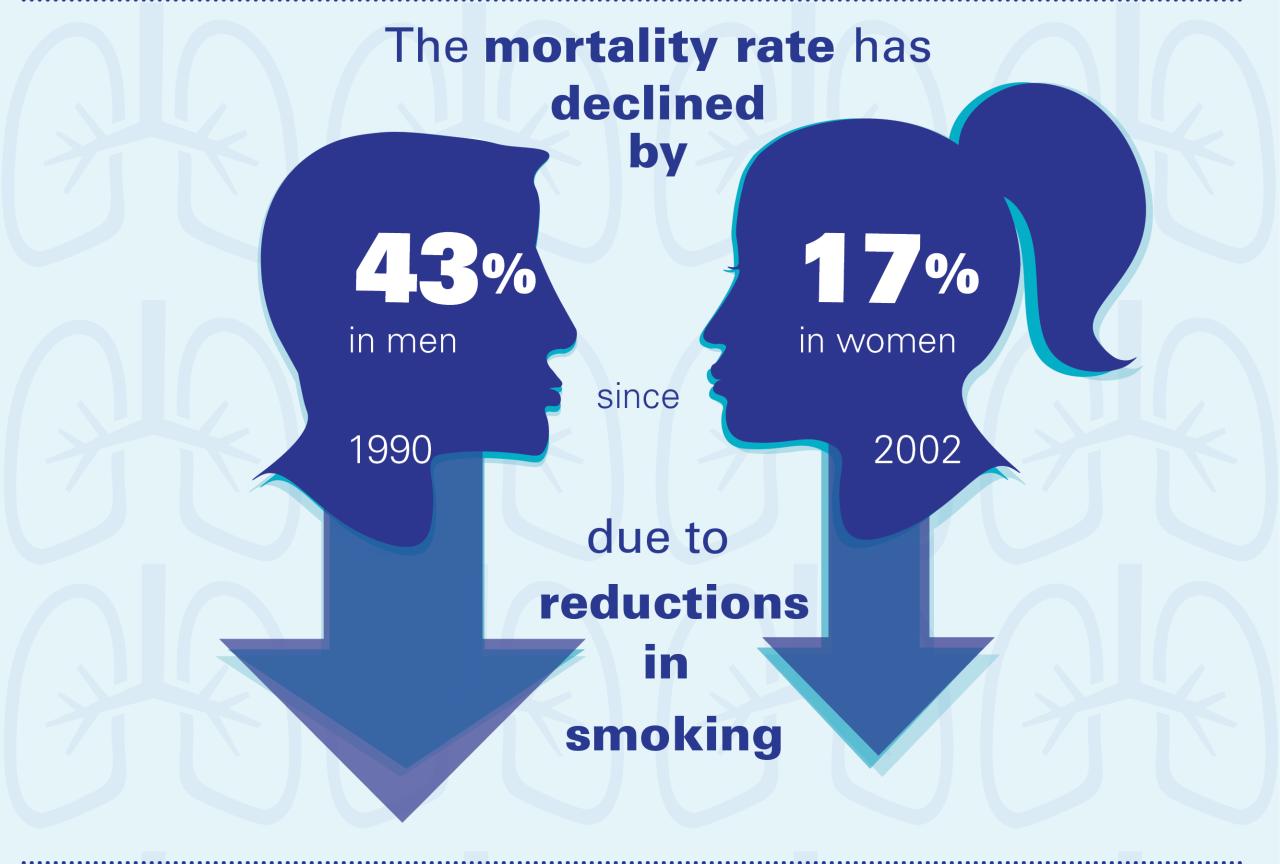
Lung cancer, a devastating disease, claims countless lives annually. Understanding its causes and risk factors is crucial for prevention and early detection. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed choices about their health and potentially reduce their risk. Identifying those at higher risk allows for targeted interventions and increased vigilance in monitoring.
Leading Causes
The leading cause of lung cancer is undoubtedly smoking. Cigarette smoke contains numerous carcinogens, substances proven to damage DNA and initiate cellular changes that can lead to uncontrolled growth and cancer. Exposure to other environmental factors, like air pollution, radon gas, and asbestos, also significantly increases the risk. These factors, acting individually or in combination, create a complex interplay that can contribute to lung cancer development.
Risk Factors and Probabilities
- Smoking: The single most significant risk factor. The more cigarettes smoked and the longer the duration of smoking, the higher the risk. Passive smoking (exposure to secondhand smoke) also increases risk.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to air pollution (e.g., industrial emissions, traffic fumes), radon gas (a naturally occurring radioactive gas), and asbestos (a fibrous mineral) are environmental risk factors. The risk varies depending on the intensity and duration of exposure.
- Genetics: A family history of lung cancer can increase susceptibility. Certain genetic mutations can predispose individuals to developing the disease.
- Age: The risk of lung cancer increases with age, as cumulative exposure to risk factors often increases over time.
- Previous Lung Diseases: Individuals with pre-existing lung conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are at a higher risk of developing lung cancer.
- Exposure to Certain Chemicals: Occupational exposure to certain chemicals, such as arsenic, chromium, and nickel, has been linked to an elevated risk.
The probabilities associated with these risk factors are complex and not always quantifiable. However, it is clear that smoking is by far the most significant contributor to lung cancer risk. The exact degree to which other factors increase risk is dependent on various individual and environmental factors.
Mechanisms of Lung Cancer Development
Carcinogens in tobacco smoke, air pollution, and other environmental exposures damage DNA within lung cells. This DNA damage can lead to mutations that disrupt normal cell growth and division. These mutations can accumulate over time, creating a cascade of events that ultimately result in the formation of cancerous tumors. Genetic predisposition can also play a role in how susceptible an individual is to these cellular changes.
These factors, working in concert, increase the probability of malignant transformation.
While lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer deaths in the US, it’s crucial to remember that other cancers like breast cancer also pose a significant threat. Don’t delay breast cancer treatment over concerns about fertility; seeking timely medical attention is vital for successful outcomes, as outlined in this insightful article about dont delay breast cancer treatment over fertility fears.
Ultimately, proactive health measures and early detection are key in battling all types of cancer, and unfortunately, lung cancer continues to be a major concern in the US.
Long-Term Effects of Smoking on Lung Health
Smoking’s detrimental effects on lung health are well-documented. The table below illustrates the timeline of these effects, highlighting the progressive damage and increasing cancer risk associated with prolonged smoking.
| Years of Smoking | Lung Damage | Cancer Risk |
|---|---|---|
| 1-5 | Early inflammation and damage to the delicate lining of the lungs. | Increased susceptibility to lung infections. |
| 5-10 | Continued damage to lung tissue, narrowing of airways, and reduced lung capacity. | Substantial increase in the risk of COPD. |
| 10-20 | Significant lung damage, with scarring and reduced ability to effectively exchange oxygen. | Increased risk of lung cancer, with a noticeable exponential rise in likelihood. |
| 20+ | Severe and irreversible lung damage, greatly impaired respiratory function. | Very high risk of lung cancer, along with other smoking-related diseases. |
Smoking cessation, regardless of the duration of smoking, is always beneficial and can significantly reduce the long-term health risks.
Diagnosis and Treatment: Lung Cancer Remains The Leading Cause Of Cancer Deaths In The U S
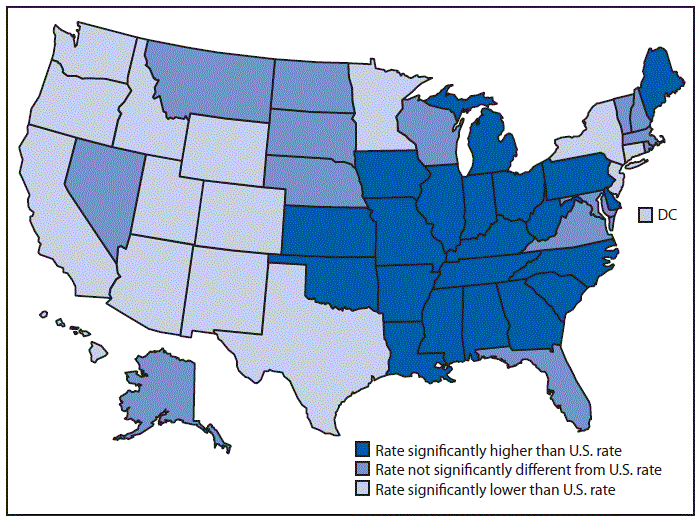
Lung cancer, a devastating disease, often requires a multi-pronged approach for diagnosis and treatment. Early detection significantly impacts survival rates, highlighting the crucial role of awareness and proactive screening. The journey toward effective treatment involves meticulous assessment, careful consideration of individual patient factors, and the application of cutting-edge techniques.
Common Diagnostic Methods, Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer deaths in the u s
Accurate diagnosis is paramount in determining the most appropriate treatment plan. Several methods are employed to detect and characterize lung cancer, ranging from imaging techniques to tissue biopsies. Radiological imaging plays a critical role in visualizing potential abnormalities within the lungs.
- Imaging techniques, such as X-rays, CT scans, and PET scans, are instrumental in identifying tumors and assessing their size, location, and extent.
- Biopsies, either bronchoscopic or surgical, provide crucial tissue samples for pathological examination. This analysis confirms the presence of cancer cells, determines the type of cancer, and helps establish the stage of the disease.
Treatment Options
Effective lung cancer treatment necessitates a personalized strategy, incorporating various approaches tailored to the specific characteristics of each patient’s cancer. Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy are common modalities, each with its own efficacy and side effect profile.
| Treatment Type | Effectiveness | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Surgery | Highly effective for early-stage lung cancers, especially if the tumor is localized. Surgical removal of the tumor and surrounding tissue can significantly improve survival chances. | Potential for pain, infection, bleeding, and complications related to anesthesia. The extent of surgery influences the degree of potential side effects. |
| Chemotherapy | Utilizes drugs to target and kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy is often used in conjunction with surgery or radiation to enhance the treatment’s effectiveness, especially for advanced stages. | Common side effects include nausea, hair loss, fatigue, and potential damage to other healthy cells. The specific drugs used and the dosage affect the severity of side effects. |
| Radiation Therapy | Utilizes high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells. It can be used as a primary treatment, or in conjunction with other therapies, to shrink tumors, relieve pain, or manage the spread of cancer. | Side effects can include skin irritation, fatigue, and potential damage to healthy tissues. The location and duration of radiation treatment impact the severity of side effects. |
Advancements in Treatment
Recent years have witnessed significant advancements in lung cancer treatment. These advancements encompass novel therapies, targeted therapies, and immunotherapies.
- Targeted therapies specifically target genetic mutations in cancer cells, offering a more precise approach to treatment. These therapies can be more effective with fewer side effects than traditional chemotherapy.
- Immunotherapies stimulate the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells. These therapies have shown remarkable success in some patients, particularly those with advanced-stage lung cancer.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection significantly enhances the chances of successful treatment and improved survival rates. A timely diagnosis allows for earlier intervention, potentially limiting the spread of cancer and enabling the implementation of less aggressive treatment strategies.
| Step | Procedure |
|---|---|
| 1 | Initial Screening: Patients with risk factors or symptoms undergo initial screening, such as a chest X-ray or CT scan. |
| 2 | Diagnostic Testing: If abnormalities are detected, further diagnostic tests, such as a bronchoscopy or biopsy, are performed. |
| 3 | Pathological Examination: The collected tissue sample is analyzed by a pathologist to confirm the presence of cancer cells and determine the type and stage of the cancer. |
| 4 | Staging and Planning: Based on the results of the diagnostic tests, the cancer is staged to determine its extent. A personalized treatment plan is developed. |
Prevention and Public Health Initiatives
Lung cancer, a devastating disease, continues to be a significant public health concern. Effective prevention strategies are crucial in reducing its impact. A multi-pronged approach encompassing smoking cessation programs, public awareness campaigns, and promoting healthy lifestyle choices is essential for mitigating the risk of lung cancer. This section Artikels key strategies and initiatives aimed at curbing lung cancer’s prevalence.
Smoking Cessation Programs
Comprehensive smoking cessation programs are pivotal in reducing lung cancer risk. These programs typically incorporate counseling, support groups, and medication assistance. Motivational interviewing and cognitive behavioral therapy are often employed to help individuals identify triggers and develop coping mechanisms for quitting. Pharmacological aids like nicotine replacement therapy and varenicline can also significantly enhance the success rate of cessation efforts.
Lung cancer sadly remains the leading cause of cancer deaths in the US, a grim statistic. While recent research suggests that Celebrex might be safer for the heart than previously thought, this doesn’t change the urgent need to address the devastating impact of lung cancer. The fight against this disease still needs strong focus and support for effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns are vital in educating the public about the risks associated with smoking and the importance of early detection. These campaigns can use various media platforms, including television, radio, social media, and print advertisements, to disseminate crucial information. The campaigns should emphasize the long-term health consequences of smoking, and the benefits of quitting, including reduced risk of lung cancer and other diseases.
Visual aids and personal stories can also be effective in conveying the message.
Evidence-Based Public Health Initiatives
Numerous evidence-based public health initiatives are designed to reduce lung cancer incidence. These initiatives typically involve a combination of strategies targeting various populations and risk factors. They include:
- Implementing smoke-free environments in public places and workplaces to reduce secondhand smoke exposure.
- Offering free or low-cost cessation programs in underserved communities.
- Developing targeted interventions for specific populations, such as young adults and minorities, who may be at higher risk.
- Integrating cancer screening programs with cessation initiatives to facilitate early detection.
Successful Prevention Programs in the U.S.
Several successful prevention programs have been implemented across the U.S. These programs have demonstrably contributed to decreasing lung cancer rates. The following table illustrates some examples:
| Program | Location | Results |
|---|---|---|
| California Tobacco Control Program | California | Significant decline in smoking rates and lung cancer incidence. |
| New York State’s Comprehensive Tobacco Control Program | New York | Improved cessation rates among smokers and reduced tobacco-related mortality. |
| National Cancer Institute’s Lung Cancer Screening Program | Nationwide | Increased awareness and utilization of low-dose CT screening for lung cancer in high-risk populations. |
Promoting Healthy Lifestyle Choices
A healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of lung cancer and other diseases.
Adopting healthy lifestyle choices is crucial for mitigating lung cancer risk. The following guide Artikels steps for promoting these choices:
- Quit Smoking: Seek professional support and utilize available resources to quit smoking. This is the single most important step in reducing lung cancer risk.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Incorporate fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your diet. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and red meat.
- Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity increases the risk of various cancers, including lung cancer. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise is crucial.
- Reduce Exposure to Environmental Factors: Avoid exposure to secondhand smoke, radon, and other environmental carcinogens.
- Manage Stress Effectively: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, increasing susceptibility to various diseases, including cancer.
- Regular Checkups: Routine checkups and screenings can help detect potential health issues early.
Impact on Healthcare Systems
Lung cancer’s devastating impact extends far beyond the individual patient. It places a significant strain on the U.S. healthcare system, affecting not only finances but also the emotional and social well-being of those affected. Understanding these multifaceted burdens is crucial for developing effective strategies to combat this disease.
Financial Burden
The financial toll of lung cancer is substantial. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term care contribute to a considerable burden on both patients and the healthcare system. This cost is not evenly distributed, with disparities potentially arising based on socioeconomic factors and access to care.
| Category | Estimated Costs (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis | $10,000 – $20,000 |
| Treatment (chemotherapy, radiation, surgery) | $50,000 – $150,000+ |
| Long-term care (palliative care, rehabilitation) | $10,000 – $30,000+ per year |
These figures represent a significant financial strain for patients and families. The total cost of care can vary considerably depending on the stage of the cancer, the specific treatment regimen, and the length of care needed.
Emotional and Social Well-being
Lung cancer significantly impacts the emotional and social well-being of patients and their families. Facing a life-threatening illness brings immense stress, anxiety, and grief. Strong support systems are crucial for navigating these challenges.
Comprehensive support for patients and families dealing with lung cancer is vital. This includes not just physical care but also emotional and psychological support.
- Support Groups: These groups provide a safe space for sharing experiences, offering emotional support, and learning coping strategies from others facing similar challenges.
- Family Counseling: Family members often experience a range of emotions during this difficult time, and professional counseling can help them navigate these challenges effectively.
- Financial Assistance Programs: Access to financial assistance can alleviate the burden of medical expenses, allowing patients to focus on their treatment and recovery.
- Spiritual Support: Many find solace and strength in their faith during this period. Spiritual support services can provide comfort and guidance.
- Social Support Networks: Maintaining connections with friends and loved ones can provide emotional comfort and reduce feelings of isolation.
Unmet Needs in Research and Treatment
Despite advancements, unmet needs persist in lung cancer research and treatment. These include identifying effective prevention strategies, developing more personalized therapies, and improving early detection methods. Research focusing on the genetic underpinnings of lung cancer and developing targeted therapies for specific subtypes could significantly enhance treatment outcomes.
Role of Support Groups
Support groups play a critical role in assisting patients and their families during the course of lung cancer treatment. These groups offer a sense of community, emotional support, and practical advice. They are essential resources for individuals navigating this complex illness.
| Group Type | Location | Services |
|---|---|---|
| Cancer Support Groups (Local) | Various community centers, hospitals, and churches | Emotional support, sharing experiences, practical advice, coping mechanisms, and educational resources |
| Online Support Forums | Internet-based | 24/7 access to support, anonymity, and connection with others facing similar challenges |
| Patient Advocacy Organizations | National and regional | Advocating for improved policies, research funding, and access to care; providing educational resources |
Summary
In conclusion, lung cancer’s continued reign as the leading cause of cancer death in the U.S. highlights the urgent need for comprehensive action. This discussion has emphasized the importance of early detection, prevention, and innovative treatment approaches. Ultimately, by understanding the multifaceted nature of this disease, from its causes and risk factors to the societal and economic impact, we can work towards a future with fewer lives lost to lung cancer.
This complex issue demands collective effort, and we must continue to support research, public health initiatives, and support systems for those affected.