
Men vs women media stereotypes sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail. From historical representations in literature and film to modern portrayals in various media genres, this exploration delves into how societal expectations are shaped and reflected in the images we consume. We’ll examine the evolution of these stereotypes, analyze their impact on individuals and society, and explore examples of media that challenge these traditional depictions.
The analysis will cover the historical development of these stereotypes across different eras and media types. It will also examine how modern media portrayals of men and women reinforce or challenge these preconceived notions. Further, we will explore the potential consequences of these stereotypes on individuals’ self-perception, career choices, relationships, and overall well-being. The exploration will also include examples of media that subvert these stereotypes, demonstrating how visual cues, language, and narratives can be utilized to challenge or reinforce gendered portrayals.
Historical Representations
The portrayal of men and women in media has evolved significantly throughout history, reflecting and shaping societal expectations and norms. These representations are not merely neutral observations; they actively construct and reinforce gender stereotypes, influencing how individuals perceive their roles and potential. Understanding this historical context is crucial to analyzing contemporary portrayals and their impact.The media’s influence on shaping gender roles is profound.
From literature and art to film and television, the characters and narratives we encounter constantly reinforce certain ideals. These ideals, while often seemingly harmless, can have far-reaching effects on personal aspirations and societal expectations.
Evolution of Media Portrayals
Different eras and media types have presented distinct portrayals of men and women. These portrayals are deeply intertwined with the prevailing social and cultural values of the time. The table below summarizes this evolution, highlighting key characteristics of the depicted genders.
| Era | Media Type | Key Characteristics of Portrayed Men | Key Characteristics of Portrayed Women |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ancient Greece | Literature, Art | Strong, physically capable, often warriors or leaders, focused on intellectual pursuits and public life. Often depicted in idealized forms. | Subservient, passive, associated with domesticity, beauty, and nurturing roles, often portrayed as objects of desire or inspiration. |
| Medieval Europe | Literature, Religious Art | Chivalrous, strong, protectors, often associated with religious ideals. Depicted as noble warriors. | Submissive, pious, devoted to their families, often depicted as symbols of purity and virtue, or as temptresses. |
| 18th and 19th Centuries | Literature, Novels, Early Film | Strong, independent, often depicted as adventurers or explorers, embodying the ideals of masculinity. Portrayed as rational and capable in the public sphere. | Often depicted as fragile, dependent, focused on beauty and domesticity, associated with emotional sensitivity. Portrayed as needing protection or guidance. |
| Early 20th Century | Film, Radio | Often depicted as strong, silent types, capable and resourceful, embodying traditional masculinity. Frequently involved in action-oriented roles. | Often depicted as glamorous, sophisticated, but also subordinate to men. Frequently confined to domestic roles, embodying a stereotypical image of femininity. |
| Mid-20th Century | Television, Film | Continued focus on strong, action-oriented roles. The “breadwinner” image was reinforced. | Often depicted as housewives or secretaries, perpetuating traditional gender roles. The portrayal of women as objects of male desire persisted. |
| Late 20th and Early 21st Centuries | Film, Television, Internet | Shifting portrayals, with increasing diversity of roles, including more emotional and vulnerable characters. Increased focus on men in non-traditional roles. | Increased representation in professional and leadership roles, showcasing women in more diverse and complex capacities. However, gender stereotypes still persist in certain media. |
Societal Factors Contributing to Stereotypes
Several societal factors contributed to the development and perpetuation of gender stereotypes in media.
- Cultural norms and values: Prevailing cultural norms and values influenced how men and women were portrayed in media. Traditional gender roles often dictated the types of characters created and the narratives explored.
- Economic structures: Economic structures often dictated the types of jobs available to men and women, which in turn shaped their representation in media. Men were frequently depicted in positions of power and authority, while women were often confined to roles associated with domesticity.
- Political ideologies: Political ideologies influenced the representation of men and women in media. Certain ideologies emphasized specific gender roles and reinforced existing stereotypes.
- Technological advancements: Technological advancements in media production have led to greater opportunities for diverse representations of men and women. However, the use of these technologies can still reinforce stereotypes.
Modern Media Portrayals
Modern media, encompassing television, film, online platforms, and news outlets, continues to shape our perceptions of men and women. While significant strides have been made in challenging traditional stereotypes, harmful representations persist. Understanding these contemporary portrayals is crucial to recognizing the subtle biases embedded in popular culture and fostering a more equitable understanding of gender roles.Contemporary media often reflects and reinforces existing societal norms and expectations.
However, the nature of these portrayals can vary greatly depending on the genre and intended audience. This analysis examines how men and women are depicted across different media platforms, highlighting common themes and stereotypes.
Examples of Current Media Portrayals
Contemporary media often presents men and women in ways that reflect and sometimes exacerbate existing gender stereotypes. Action films frequently cast men as the sole protagonists, often portrayed as physically strong and emotionally stoic. Women in these films are frequently relegated to supporting roles, sometimes hyper-sexualized or depicted as damsels in distress. In romantic comedies, women are often portrayed as seeking a partner who embodies the traditional masculine ideal, while men are depicted as pursuing romantic interests with a focus on physical attractiveness and status.
Comparison Across Genres
The depiction of men and women varies significantly across genres. News reporting, for instance, often presents men in leadership roles and women in more supportive roles, reflecting historical gender imbalances. In contrast, some reality television programs might showcase both men and women in more egalitarian roles, although this representation can be complex and nuanced.
Ugh, those annoying gender stereotypes in media! It’s so frustrating how often men and women are portrayed in such limited ways. I’m trying to be more conscious of that, and it’s actually made me appreciate finding new healthy options, like the ones I’ve been loving lately, especially in favorite healthy finds 2. It’s a great reminder that we can all find healthier, more diverse ways to nourish our bodies, and by extension, challenge these outdated media portrayals.
I’m definitely trying to make better food choices and promote healthier images for everyone.
Common Themes and Tropes
Several recurring themes and tropes emerge in contemporary media portrayals of men and women. Men are often associated with strength, independence, and ambition, while women are frequently linked to nurturing, emotional expressiveness, and domesticity. These portrayals, while sometimes positive, can also perpetuate limiting expectations and hinder genuine representation.
Gendered Portrayal in Different Media Genres
| Genre | Typical Male Roles | Typical Female Roles |
|---|---|---|
| Action Films | Protagonist, strong, physically capable, emotionally stoic, focused on action | Supporting character, damsel in distress, often hyper-sexualized, physical attractiveness prioritized |
| Romantic Comedies | The romantic lead, often successful and physically attractive, pursuing a romantic interest | The romantic interest, often seeking a partner who embodies the traditional masculine ideal, often presented in a more emotional and nurturing role |
| News | News anchors, reporters, political figures, typically in leadership roles | Reporters, news anchors, sometimes in supporting roles, often focusing on human interest or social issues |
| Reality Television | Varying, sometimes presented in more egalitarian roles but also can reinforce existing gender stereotypes | Varying, sometimes presented in more egalitarian roles but also can reinforce existing gender stereotypes |
Impact of Stereotypes
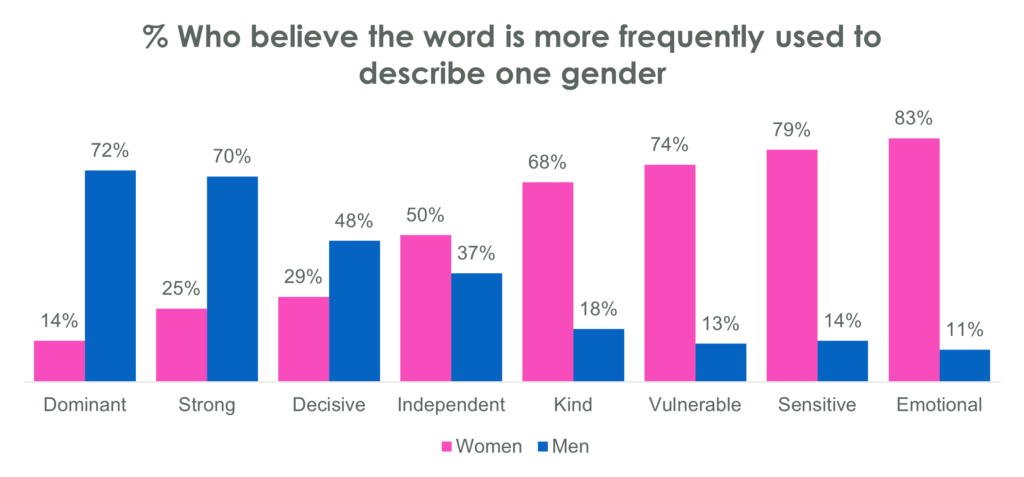
Media stereotypes, deeply ingrained in our collective consciousness, have far-reaching consequences, influencing not just how we perceive the world but also shaping individual lives and societal structures. These persistent portrayals, often based on oversimplified and inaccurate generalizations, can lead to significant negative impacts on individuals and society as a whole. The impact is not merely superficial; it can affect career choices, relationships, and overall well-being, creating and perpetuating societal inequalities.The internalization of these stereotypes can lead to a dissonance between self-perception and societal expectations.
Individuals may feel pressured to conform to prescribed roles, limiting their aspirations and opportunities. This can manifest in a variety of ways, from choosing careers that align with stereotypical expectations to experiencing difficulties in relationships based on preconceived notions.
Impact on Self-Perception
Internalizing stereotypes can significantly affect how individuals view themselves and their capabilities. A woman might feel discouraged from pursuing a career in STEM if she consistently sees women underrepresented in those fields. Conversely, a man might feel constrained in expressing emotions if he believes that displaying vulnerability is not masculine. These perceptions can impact self-esteem and confidence, leading to a diminished sense of self-worth.
This can have cascading effects on personal choices, such as career paths and relationship dynamics.
Impact on Career Choices
Stereotypes can limit career choices, particularly for individuals who are perceived to fit a specific mold. For example, women are often steered towards traditionally “feminine” professions, such as teaching or nursing, while men might be discouraged from pursuing careers in fields like childcare or social work. This bias often results in limited career progression opportunities and wage gaps, hindering overall economic growth.
Impact on Relationships
Stereotypes can also influence interpersonal relationships, creating unrealistic expectations and potential conflicts. For instance, if a man is expected to be the sole provider in a relationship, it can lead to stress and pressure, potentially hindering the development of healthy emotional connections. Conversely, if a woman is expected to primarily handle domestic responsibilities, it can strain the relationship dynamic.
Impact on Mental Health
The constant pressure to conform to stereotypes can negatively impact mental well-being. Individuals who feel constantly judged or pressured to act in ways that contradict their true selves may experience anxiety, depression, or other mental health challenges. For example, the pressure on women to maintain a certain physical appearance or to excel in traditional “female” roles can contribute to body image issues and feelings of inadequacy.
Impact on Societal Inequalities
Stereotypes contribute to societal inequalities by creating and perpetuating biases in various aspects of life. This includes wage gaps, limited opportunities in leadership roles, and unequal representation in various fields. These inequalities have far-reaching effects, impacting not only individuals but also broader societal structures and economic development.
Table: Potential Impact of Stereotypes, Men vs women media stereotypes
| Aspect of Life | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Career | Limited career choices, unequal pay, fewer opportunities for leadership positions. |
| Relationships | Unrealistic expectations, strained dynamics, conflict over roles and responsibilities. |
| Mental Health | Anxiety, depression, low self-esteem, body image issues, and feelings of inadequacy. |
| Society | Perpetuation of biases, wage gaps, limited opportunities for marginalized groups, hindering economic growth. |
Media Representation and Social Change
Media representations aren’t just reflections of society; they actively shape our understanding of gender roles and expectations. The images, narratives, and stereotypes portrayed in various media outlets profoundly influence how individuals perceive themselves and others. This influence is especially powerful because media messages are often implicitly accepted as accurate portrayals of reality.The impact of media on societal attitudes is bidirectional.
Ugh, those gender stereotypes in the media are so frustrating, aren’t they? It’s like women are constantly portrayed as needing to be skinny and perfect, while men are often seen as the strong, silent type. But, focusing on healthy habits like cutting out 200 calories a day and exercising can help you stay heart healthy is key to feeling good about yourself regardless of what the media tries to tell us.
These unrealistic expectations can really impact our self-esteem, and it’s important to remember that true strength and beauty come in many forms. We need to challenge these harmful portrayals and embrace a more balanced view of ourselves and others.
As societal norms and expectations evolve, media representations often reflect these shifts. Conversely, media portrayals can also contribute to the reinforcement or alteration of those norms. This dynamic interplay between media and society is crucial in understanding how gender roles evolve over time. The power of media to instigate change, however, is not always direct or immediately apparent; it often works through subtle shifts in public perception and cultural understanding.
How Media Representations Shape Societal Attitudes
Media portrayals significantly influence how individuals perceive and internalize gender roles. Consistent depiction of specific characteristics as associated with particular genders reinforces existing stereotypes and limits the scope of perceived possibilities for both men and women. For instance, media frequently portrays women in stereotypical roles like housewives or victims, while men are often depicted as strong, aggressive, or providers.
These pervasive portrayals contribute to the formation of rigid gender expectations. They influence self-perception, limiting opportunities and potential for both genders.
How Shifts in Media Portrayals Influence Broader Social Change
Changes in media portrayals often precede or coincide with broader social shifts in gender roles. As media increasingly features diverse and nuanced portrayals of men and women, it can foster a more inclusive understanding of gender identity and expression. For example, the growing presence of female characters in leadership roles in films and television shows can influence perceptions of women’s capabilities and suitability for positions of power.
Likewise, media representations that challenge traditional gender norms can lead to increased acceptance and understanding of alternative gender identities and expressions.
Examples of Media Campaigns Promoting Balanced Portrayals
Numerous media campaigns and initiatives have attempted to promote more balanced portrayals of gender. These efforts range from incorporating diverse characters in children’s programming to highlighting women in STEM fields. One prominent example is the #MeToo movement, which used social media to raise awareness of sexual harassment and assault, prompting significant conversations about gender power dynamics and challenging traditional media portrayals of women’s vulnerability.
The impact of such campaigns, though varied, underscores the potential for media to contribute to positive social change.
Historical Trajectory of Changing Gender Roles in Media
| Year | Media Type | Depiction of Gender Roles |
|---|---|---|
| 1950s | Television | Women primarily depicted in domestic roles, men as breadwinners; stereotypical representations were common. |
| 1970s | Films | Some films began to challenge traditional gender roles, showing women in more diverse professional and personal capacities, though these were still often exceptions rather than the norm. |
| 1980s | Television | Increasing visibility of women in professions and careers; however, traditional gender roles remained prevalent. |
| 1990s | Video Games | Stereotypes continued in many video games, but also saw some progression, especially with female characters in action roles. |
| 2000s-Present | All Media | Significant increase in diversity and complexity of gender representations across various media platforms. Female characters are increasingly depicted in diverse roles, challenging traditional norms and stereotypes. Men are also increasingly portrayed with diverse emotional and personal characteristics. |
Visual Representation of Gender

Visual representation in media plays a crucial role in shaping societal perceptions of men and women. It’s not just about what’s said, but how it’s shown – the imagery, the body language, the very clothes characters wear. These visual cues, often subtle, reinforce or challenge existing gender stereotypes, influencing how we understand and interact with the world around us.The visual language of media, from film and television to advertising and social media, subtly communicates messages about appropriate behavior, expectations, and even physical attributes for each gender.
Media often portrays men and women in stereotypical ways, painting overly simplified pictures of each gender. This can be problematic, creating narrow expectations and limiting possibilities. Interestingly, this same sort of simplification seems to be at play in the fascinating concept of “bigfoot unity connected diabetes system,” a study exploring the unexpected connections between these seemingly disparate ideas.
bigfoot unity connected diabetes system Perhaps these kinds of seemingly unrelated concepts highlight the broader issue of oversimplification in our media portrayals of men and women. Ultimately, it’s crucial to remember that diverse and nuanced portrayals of people are far more realistic and helpful than those confined to rigid stereotypes.
These messages, whether intentional or not, often contribute to the reinforcement or subversion of pre-existing societal norms and stereotypes.
Visual Cues in Media
The ways in which men and women are visually presented in media often reinforce established gender roles. Clothing choices, body language, and even the settings in which characters are placed can contribute to a specific gendered portrayal. For example, a woman in a media portrayal might be consistently dressed in a way that emphasizes her femininity, while a man might be presented in a manner that suggests strength and dominance.
Examples of Gendered Portrayals
Consider the typical portrayal of women in advertising. Frequently, women are shown in stereotypical roles, like homemakers or caretakers, often focusing on their appearance or relationship to men rather than their professional achievements. This contrasts with the portrayal of men, who are often depicted in positions of power, leadership, or action. Body language also contributes to these portrayals.
Women might be shown with a more passive demeanor, while men might exhibit more assertive or dominant postures.
Visual Language in Media
| Visual Element | Typical Portrayal | Intended Message |
|---|---|---|
| Clothing | Women are frequently shown in clothing that emphasizes femininity, such as dresses, skirts, and high heels. Men are often depicted in clothing that suggests strength or authority, like suits or business attire. | Reinforces traditional gender roles and expectations. Suggests appropriate appearance for each gender. |
| Body Language | Women are sometimes portrayed with a more submissive or passive body language, such as folded arms or avoiding eye contact. Men are often shown with assertive or dominant body language, like expansive postures and direct eye contact. | Communicates different levels of confidence and power associated with each gender. |
| Setting and Environment | Women are sometimes portrayed in domestic settings, like kitchens or homes. Men are often depicted in professional settings, like offices or outdoor spaces. | Reinforces societal expectations about where each gender “belongs” and their typical roles. |
| Facial Expressions | Women are sometimes shown with expressions of vulnerability or emotional distress. Men are often depicted with expressions of confidence or stoicism. | Connects gender to specific emotions, perpetuating stereotypes. |
Implications for Audiences: Men Vs Women Media Stereotypes
Media portrayals of men and women, both historically and currently, shape societal perceptions and expectations. These representations, often steeped in stereotypes, can have profound and lasting effects on individuals and society as a whole. Understanding these implications is crucial for fostering a more equitable and inclusive environment.The impact of media stereotypes on audiences is multifaceted, ranging from subtle biases to potentially harmful internalizations.
Different age groups, with varying cognitive and emotional development, react differently to these portrayals. The potential for these stereotypes to contribute to gender bias in various contexts, from education to the workplace, is significant and requires careful consideration.
Potential Effects on Children
Children are particularly vulnerable to the influence of media portrayals. They are still developing their understanding of gender roles and often rely on media for social cues. Exposure to stereotypical representations can lead to the internalization of these roles, limiting their self-perception and potential life choices. For example, a child consistently seeing women portrayed solely as caregivers or men as the sole breadwinners may develop a narrow view of appropriate gender roles.
This can influence their aspirations, choices, and behaviors.
Potential Effects on Adolescents
Adolescents face significant pressure to conform to social norms, making them particularly susceptible to the influence of media portrayals. Stereotypes can affect their self-esteem and body image, particularly for girls, who often are presented with unrealistic beauty standards. The portrayal of gender roles in romantic relationships and social interactions can influence their expectations and choices regarding relationships and social dynamics.
This can contribute to harmful social behaviors or unrealistic expectations about romantic partnerships.
Potential Effects on Adults
Adults, while potentially more critical, can still be influenced by ingrained stereotypes. Media portrayals can reinforce existing biases and influence their perceptions and judgments in personal and professional settings. Adults exposed to biased media portrayals may inadvertently perpetuate gender stereotypes in their own interactions and decision-making processes. This includes behaviors like implicit bias in hiring or promotion decisions, or unequal distribution of household responsibilities.
Gender Bias in Various Settings
Media stereotypes contribute to gender bias in a wide array of settings. In education, stereotypes can influence teachers’ expectations and interactions with students. In the workplace, they can contribute to unequal pay, promotion opportunities, and representation in leadership roles. In healthcare, stereotypes can affect the diagnosis and treatment of illnesses and conditions, leading to disparities in care.
Media portrayals play a critical role in shaping societal attitudes and expectations.
Implications Table
| Audience Type | Possible Interpretations | Potential Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Children | Internalization of narrow gender roles, limited self-perception, restricted aspirations | Limited life choices, potential for gender bias in future interactions |
| Adolescents | Reinforcement of social norms, pressure to conform, potential impact on self-esteem and body image | Development of unrealistic expectations about relationships, potential for gender bias in social interactions |
| Adults | Reinforcement of existing biases, influence on perceptions and judgments in personal and professional settings | Potential for perpetuation of gender stereotypes in interactions and decision-making |
Last Recap
In conclusion, this exploration of men vs women media stereotypes highlights the profound impact media has on shaping our understanding of gender roles. The analysis reveals how these stereotypes, often perpetuated across generations, influence individual perceptions and societal expectations. However, the examination also reveals the emergence of media that challenges these traditional portrayals, offering a glimpse of a more nuanced and inclusive future where gender roles are not confined by limiting stereotypes.
Ultimately, understanding the historical context, modern depictions, and the impact of these stereotypes is crucial for fostering a more equitable and representative media landscape.
