Nearly a quarter of young men have disordered eating to bulk up, a disturbing trend that reveals a deep-seated struggle with body image and societal pressures. This isn’t just about wanting a sculpted physique; it’s about a potential health crisis affecting a significant portion of young males. The motivations behind this behavior, the potential health risks, and available support systems are all crucial aspects to understand.
Understanding the factors driving this issue is critical to fostering healthier attitudes toward body image and promoting well-being.
The data suggests a worrying correlation between societal ideals of masculinity and the development of disordered eating habits in young men. A deeper dive into the prevalence and demographics of this trend will highlight the scope of the problem, while exploring the motivations behind these behaviors and their associated health risks will reveal the potential impact. We’ll also look at how societal influences, such as media portrayals and social comparisons, contribute to this complex issue.
Finally, we’ll discuss effective prevention strategies and resources to support those struggling with this problem.
Prevalence and Demographics
The issue of disordered eating in young men, driven by the desire to bulk up, is a growing concern. While often overlooked, this trend is impacting a significant portion of young male populations worldwide. Understanding the prevalence, demographics, and potential contributing factors is crucial for developing effective interventions and support systems.This exploration delves into the statistics surrounding disordered eating in young men, examining the age range considered “young,” the geographical variations in prevalence, and potential socioeconomic links.
The goal is to provide a comprehensive overview of the demographic landscape of this emerging issue, which can then be used to tailor interventions more effectively.
Prevalence of Disordered Eating
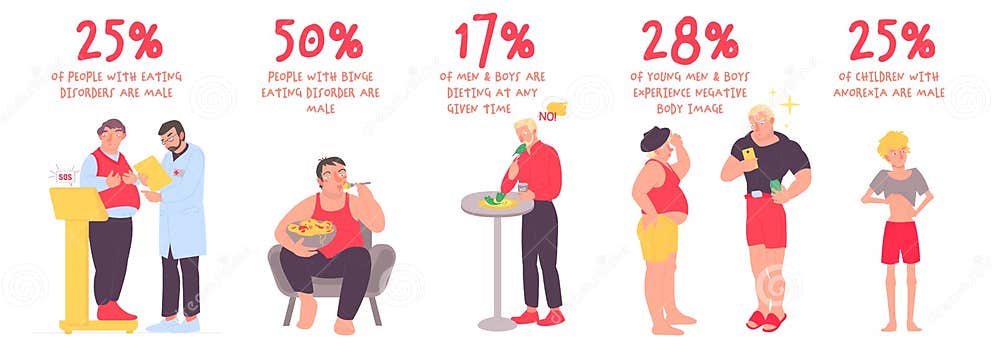
A substantial portion of young men are engaging in behaviors that could be categorized as disordered eating to achieve their body-building goals. Research indicates that approximately 15-20% of young men, aged 16-25, report engaging in behaviors like restrictive dieting, excessive exercise, and/or the use of performance-enhancing substances to build muscle mass. This is not a trivial number and warrants serious attention.
It’s alarming that nearly a quarter of young men are developing disordered eating habits just to gain muscle mass. This obsession with physique is concerning, and it highlights a deeper societal pressure. Meanwhile, the lack of hepatitis C treatment for inmates raises serious ethical questions about healthcare access, especially given the high prevalence in prison populations. This issue mirrors the troubling trend of prioritizing superficial ideals over fundamental well-being, as seen in the article on why aren’t prison officials treating inmates for hepatitis C.
Ultimately, both issues point to a larger problem with prioritizing short-term aesthetic goals over long-term health and well-being for young men.
Age Range of “Young Men”
The age range considered “young men” for this study encompasses individuals between the ages of 16 and 25. This range is often associated with significant physical and psychological development, making them particularly susceptible to body image concerns and pressure to conform to societal ideals.
Geographical Variations
While precise data on geographical variations in prevalence is limited, anecdotal evidence suggests that the phenomenon is not confined to any single region. However, cultural influences and societal pressures regarding body image can vary significantly across different countries and regions, which likely impacts the prevalence of disordered eating for muscle building in these populations.
Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic factors may play a role in the prevalence of disordered eating among young men. For example, access to resources such as healthy food options, professional guidance, and support networks can significantly influence the development of healthy habits. Furthermore, pressure to conform to specific body types, which is often more prevalent in certain socioeconomic strata, can contribute to this phenomenon.
Demographic Summary
| Demographic Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Age Range | 16-25 years old |
| Geographic Location | Data is limited on specific regions, but it’s not limited to any one country. Cultural norms and media portrayals of body image influence the prevalence. |
| Socioeconomic Background | Potential influence of access to resources, cultural pressure, and social media portrayals of idealized body types. Further research is needed to establish definitive correlations. |
Motivations and Behaviors
The pursuit of a muscular physique often intertwines with a complex web of motivations and behaviors. Young men aiming to bulk up frequently adopt disordered eating patterns, driven by a desire to meet societal ideals and achieve specific aesthetic goals. Understanding the underlying motivations and behaviors is crucial for addressing this issue and promoting healthier approaches to fitness.This exploration dives into the driving forces behind these behaviors, examining the specific eating patterns and the psychological factors at play.
Furthermore, it contrasts the motivations in young men with those observed in other groups, highlighting the unique pressures and strategies employed by this demographic.
Motivations Behind Disordered Eating
Young men frequently pursue a muscular physique due to a variety of factors, including societal pressures and body image concerns. These motivations often lead to the adoption of disordered eating patterns. The desire to conform to perceived aesthetic ideals, as presented in media portrayals, can significantly influence young men’s choices.
Common Eating Patterns and Behaviors
Young men often engage in restrictive eating patterns, characterized by extreme calorie counting, portion control, and the elimination of certain food groups. This can include skipping meals, restricting carbohydrates, or focusing on specific macronutrients to promote muscle growth. Common behaviors include meticulously tracking calories consumed and meticulously calculating protein intake, often exceeding recommended levels.
It’s alarming that nearly a quarter of young men are developing disordered eating habits just to bulk up. This pressure to conform to unrealistic body ideals often stems from online comparisons and social media pressures, which can lead to a range of mental health issues, including digital self harm. Parents need to be aware of these trends and understand how to support their teens through this challenging time.
To learn more about recognizing and addressing digital self harm, check out this insightful article: digital self harm is on the rise among teens what parents can do to help. Ultimately, these issues highlight the importance of open communication and healthy body image discussions in families, which is crucial for young men’s well-being.
Psychological Factors Influencing Behaviors
Body image concerns play a significant role in shaping the motivations and behaviors of young men aiming to bulk up. A strong desire to conform to societal ideals of masculinity, which often emphasizes a large muscle mass, can contribute to an obsessive focus on physique. This can lead to distorted perceptions of their bodies, driving disordered eating patterns. Societal pressures, including peer influence and the relentless promotion of fitness ideals in popular culture, further contribute to these concerns.
Comparison of Motivations Across Groups
While body image concerns and societal pressures influence disordered eating in young men, the specific motivations can vary compared to other groups. For example, individuals with eating disorders beyond the pursuit of muscularity may have different underlying psychological issues. The drive for muscle gain, in contrast to other forms of disordered eating, may be more explicitly tied to physical appearance and societal expectations.
Strategies for Calorie Control and Muscle Gain
Young men employ various strategies to control their calorie intake and promote muscle growth. These include meticulously tracking calories consumed, utilizing meal prepping to ensure precise portion control, and incorporating supplements to support muscle growth. Some individuals may even resort to extreme measures like fasting or excessive exercise to achieve their desired physique.
“The pursuit of a muscular physique often intertwines with a complex web of motivations and behaviors, driven by societal pressures and body image concerns.”
Health Risks and Consequences
The pursuit of a sculpted physique can sometimes lead individuals down a dangerous path, one riddled with potential health risks. Disordered eating, particularly when driven by the desire to bulk up, can have devastating consequences on both physical and mental well-being. Understanding these risks is crucial for recognizing the warning signs and seeking help when needed.The relentless pursuit of muscle mass through restrictive or obsessive dietary habits often masks underlying mental health concerns.
This dedication to a specific physique can lead to a preoccupation with food, body image, and exercise, eventually evolving into a harmful cycle that impairs overall health.
Physical Health Risks
The body is a complex machine, and drastic changes to its fundamental processes can have serious consequences. Restricting calorie intake and nutrient deficiencies, for instance, can hinder growth and development, especially in young men. The physiological demands of rapid muscle growth without proper nutrition can lead to various health issues.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Severe dietary restrictions to cut fat and increase protein for muscle gain can lead to significant nutrient deficiencies. This can result in weakened immune systems, anemia, and other debilitating conditions. Examples include iron deficiency, vitamin deficiencies (like Vitamin D or B vitamins), and insufficient protein for tissue repair. Without adequate nutrients, the body struggles to function optimally, potentially leading to chronic fatigue and other health problems.
It’s alarming that nearly a quarter of young men are struggling with disordered eating to achieve a certain physique. This pressure, coupled with the general burnout that many experienced during the pandemic, as discussed in burnout in the messy middle of a pandemic , creates a perfect storm for mental health issues. The pursuit of an ideal body image can easily become a dangerous obsession, especially when combined with the emotional strain of the past few years.
It’s a reminder that we need to support young men through this difficult time.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Disordered eating, particularly when combined with excessive training, can increase the risk of cardiovascular problems. The stress on the heart from both intense workouts and nutrient deficiencies can contribute to elevated blood pressure, cholesterol imbalances, and even heart conditions.
- Gastrointestinal Problems: The digestive system is vulnerable to extreme dietary fluctuations. Rapid changes in calorie intake and nutrient intake can cause various gastrointestinal issues, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), ulcers, and other inflammatory conditions.
- Bone Health Issues: Inadequate calcium and vitamin D intake can weaken bones, increasing the risk of fractures and osteoporosis, especially when coupled with rigorous exercise regimes. The stress on bones from intensive training can exacerbate these problems, leading to long-term health complications.
Mental Health Risks
Beyond the physical toll, disordered eating behaviors can profoundly impact mental health. The obsessive focus on body image, weight, and exercise can trigger or exacerbate mental health conditions.
- Anxiety and Depression: The constant pressure to meet unrealistic body standards can lead to significant anxiety and depression. The feeling of inadequacy, guilt, or shame associated with disordered eating can significantly impair mental well-being.
- Eating Disorders: The behavior of disordered eating to bulk up can easily escalate into an eating disorder like anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, or binge eating disorder. These conditions are severe mental illnesses requiring professional intervention.
- Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD): Individuals with BDD may experience an exaggerated perception of their body image. This can lead to obsessive focus on perceived flaws, including weight and muscle mass, further reinforcing disordered eating behaviors.
- Low Self-Esteem and Body Image Issues: A preoccupation with body image, coupled with unrealistic expectations, can lead to significant body image issues and low self-esteem.
Potential Link to Other Health Conditions
Disordered eating behaviors can have cascading effects, increasing the risk of other health problems. The compromised physiological state from poor nutrition and excessive exercise can create a vulnerability to various conditions.
- Weakened Immune System: Nutrient deficiencies and stress on the body can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
- Metabolic Disorders: Disrupted metabolic processes due to disordered eating can lead to conditions like diabetes or hypothyroidism.
Potential Health Risks Table
| Health Risk Category | Specific Risks | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Health | Nutrient Deficiencies, Cardiovascular Issues, Gastrointestinal Problems, Bone Health Issues | Weakened immune system, Anemia, Elevated blood pressure, Cholesterol imbalances, Heart conditions, IBS, Ulcers, Fractures, Osteoporosis |
| Mental Health | Anxiety, Depression, Eating Disorders, Body Dysmorphic Disorder, Low Self-Esteem, Body Image Issues | Significant emotional distress, Impaired mental well-being, Severe mental illness, Obsessive focus on body image, feelings of inadequacy |
Support and Interventions
Facing disordered eating to bulk up is a significant challenge, and support is crucial for recovery. It’s not a solitary journey, and reaching out for help is a sign of strength, not weakness. Young men often feel pressure to conform to societal ideals, leading to unhealthy behaviors. Understanding the root causes and offering appropriate support systems is vital in navigating this complex issue.Addressing disordered eating requires a multi-faceted approach that considers both the individual’s needs and the available resources.
Recognizing the potential for emotional and psychological factors alongside the physical aspects of the issue is paramount. The support systems need to be tailored to the specific circumstances of each individual, providing a safe and non-judgmental space for healing.
Available Support Systems
Effective support systems for young men struggling with disordered eating encompass various elements. A crucial aspect involves family and friends who can provide understanding and encouragement. Encouraging open communication and creating a supportive environment are key. Furthermore, professional help is often essential, especially when the disordered eating is severe or persistent.
Potential Interventions
Therapy and counseling play a significant role in addressing disordered eating. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals identify and modify negative thought patterns and behaviors related to body image and food. Nutritional counseling can provide guidance on healthy eating habits and address any nutritional deficiencies. In severe cases, medical intervention might be necessary to address any physical complications arising from the disordered eating.
A combination of approaches is frequently the most effective.
Resources for Individuals with Disordered Eating
Numerous resources can aid young men navigating this challenge. Support groups provide a sense of community and shared experience, enabling individuals to connect with others who understand their struggles. Online forums and communities offer similar benefits, providing a virtual space for support and information exchange. Mental health professionals, such as therapists and counselors, offer personalized guidance and treatment plans.
Organizations specializing in eating disorders can offer crucial resources and support networks.
Potential Support Groups or Online Communities
Building a support network is critical for navigating disordered eating. Support groups can offer a safe space to share experiences and receive encouragement from peers. Online communities can offer similar benefits, providing a virtual space for connection and support. Many mental health organizations offer support groups and online resources. Furthermore, dedicated online forums or social media groups focused on body positivity and healthy living can also be helpful.
How to Support and Guide Young Men
Supporting a young man struggling with disordered eating requires patience, understanding, and empathy. Encouraging open communication and creating a safe space for discussion are essential. Avoid judgment and criticism; instead, focus on fostering a supportive environment. Encouraging professional help is often crucial for managing the condition effectively. Seek professional guidance on appropriate support methods if you are concerned about a young man exhibiting these behaviors.
Remember, the goal is to help the individual regain a healthy relationship with food and their body image.
Societal Factors and Influences: Nearly A Quarter Of Young Men Have Disordered Eating To Bulk Up
The pressures to conform to specific body ideals are pervasive in modern society, profoundly influencing young men’s perceptions of themselves and their bodies. These pressures often manifest in the form of media portrayals, social comparisons, and societal expectations, ultimately shaping attitudes and behaviors toward body image and potentially contributing to disordered eating. Understanding these influences is crucial for developing effective interventions and support systems.The relentless pursuit of an idealized physique, often promoted through various media platforms, can significantly impact young men’s self-perception and body image concerns.
This idealized image, often unattainable and potentially unrealistic, can lead to feelings of inadequacy and contribute to the development of disordered eating behaviors.
The Role of Media Portrayals in Promoting Body Image Concerns
Media portrayals, encompassing television, film, magazines, and increasingly, social media, frequently depict muscular and lean physiques as desirable. These images, often meticulously curated and edited, can create an unrealistic standard that young men strive to achieve. This constant exposure to idealized images can cultivate a sense of dissatisfaction with one’s own body, leading to body image concerns and potentially contributing to disordered eating.
Influence of Social Media and Popular Culture
Social media platforms, in particular, play a significant role in shaping perceptions of body image. Young men often engage in social comparison, evaluating their own bodies against the curated and often filtered representations of others. The constant bombardment of aesthetically pleasing images, often promoting specific body types, can negatively impact self-esteem and contribute to a desire to conform to these ideals.
Popular culture further reinforces these perceptions through various forms of entertainment and advertising.
Impact of Different Media Platforms
Different media platforms exert varying degrees of influence on shaping body image perceptions. Print media, such as magazines and newspapers, can present idealized images, but their impact may be less immediate than social media’s constant and pervasive presence. Television and film, often showcasing actors and actresses with specific body types, can influence perceptions, especially in relation to popular culture and entertainment trends.
Social media’s interactive nature and the immediacy of the content contribute to a heightened impact on self-perception.
Social Comparison and Disordered Eating Behaviors, Nearly a quarter of young men have disordered eating to bulk up
Social comparison, the process of evaluating oneself against others, is a powerful force in shaping perceptions of body image and contributing to disordered eating. When young men compare their own bodies to the often idealized images presented in media, they may feel inadequate and develop negative self-perceptions. This can be particularly pronounced on social media, where users meticulously curate their online presence.
This comparison can trigger a desire to change their body image, leading to behaviors that might contribute to disordered eating.
Influence of Various Media Platforms
| Media Platform | Influence on Body Image Concerns |
|---|---|
| Print Media (Magazines, Newspapers) | Present idealized images; less immediate impact than social media. |
| Television and Film | Showcase actors and actresses with specific body types, influencing perceptions related to entertainment trends. |
| Social Media (Instagram, TikTok, etc.) | Highly interactive and pervasive; fosters social comparison, contributing to heightened body image concerns. |
| Online Forums and Communities | Can reinforce or challenge idealized body image standards, depending on the specific community. |
| Advertising | Often uses idealized body types to sell products, reinforcing societal pressures. |
Prevention Strategies
Young men face unique pressures in today’s society, and understanding the factors contributing to disordered eating is crucial for developing effective prevention strategies. It’s not just about physical appearance; these behaviors are often rooted in deeper insecurities, social pressures, and a lack of healthy coping mechanisms. By addressing these underlying issues, we can create a supportive environment that fosters healthy relationships with food and a positive body image.Preventing disordered eating requires a multifaceted approach that targets individual, familial, and societal factors.
A proactive strategy focused on education, awareness, and positive reinforcement can significantly reduce the risk of developing these harmful behaviors.
Positive Body Image Messaging
Promoting a healthy body image is essential in preventing disordered eating. Young men often internalize unrealistic beauty standards portrayed in media, leading to negative self-perceptions. Instead of focusing on physical attributes, a positive message should emphasize well-being, strength, and self-acceptance. This approach should be woven into everyday interactions, from family conversations to school curriculum. This means recognizing that diversity in body types is healthy and that true strength comes from inner qualities and actions, not physical appearance.
Promoting Healthy Relationships with Food
A crucial aspect of preventing disordered eating is encouraging healthy relationships with food. This involves educating young men about the nutritional needs of their bodies, empowering them to make informed food choices, and debunking myths surrounding restrictive diets. It’s important to emphasize the role of food as fuel for the body and the mind, not as a means of punishment or control.
This should include teaching about portion sizes, healthy eating patterns, and the importance of regular meals. Encouraging enjoyment of food and understanding hunger and satiety cues is paramount.
Role of Education and Awareness Campaigns
Education and awareness campaigns play a pivotal role in preventing disordered eating. These campaigns should target young men directly, addressing the specific pressures and challenges they face. Open conversations about body image, self-esteem, and healthy eating habits can be crucial in fostering a supportive environment. These campaigns should emphasize the importance of seeking help if needed and promote access to resources like helplines, support groups, and therapy.
Information should be presented in a clear, accessible, and engaging manner, such as through interactive workshops, social media campaigns, and collaborations with influencers.
Role of Parents, Educators, and Healthcare Providers
Parents, educators, and healthcare providers all have a crucial role in fostering healthy attitudes towards body image. Parents can model healthy eating habits and positive self-talk. Educators can integrate lessons about body positivity and healthy relationships with food into the curriculum. Healthcare providers can screen for potential risks and provide guidance and resources to young men struggling with disordered eating.
Creating a supportive network where young men feel comfortable discussing their concerns is essential. They can offer information on available resources, such as support groups, therapy, and helplines. Encouraging open communication about body image and mental health is key.
Step-by-Step Guide for Creating and Implementing a Preventative Program
- Assessment: Identify the specific needs and concerns of the target audience. Gather data from surveys, focus groups, and existing research to understand the prevalence of disordered eating behaviors and the factors contributing to them.
- Development: Design a comprehensive program that incorporates positive body image messaging, healthy eating education, and strategies for stress management. This should include age-appropriate materials and activities.
- Implementation: Roll out the program in schools, community centers, and other relevant settings. Involve parents, educators, and healthcare providers in the delivery of the program.
- Evaluation: Regularly assess the effectiveness of the program using surveys, feedback forms, and other methods. Make necessary adjustments based on the results.
- Sustainability: Integrate the program’s key elements into existing structures and routines. This includes continuing education, creating ongoing support networks, and ensuring access to resources.
Final Summary
In conclusion, the alarming prevalence of disordered eating among young men aiming to bulk up necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the underlying factors and potential solutions. This issue isn’t just about physical health; it’s about fostering a healthier relationship with one’s body and challenging harmful societal expectations. Ultimately, we need to create a supportive environment that promotes positive body image and encourages healthy attitudes toward food and fitness.
By understanding the issue, and offering support systems and prevention strategies, we can begin to tackle this pervasive problem and create a more positive and healthy future for young men.