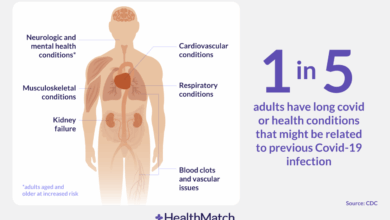
Omicron ba 5 experts see increase in mild cases vaccines continue to be effective – Omicron BA.5 experts see an increase in mild cases, vaccines continue to be effective. This new subvariant is causing a shift in the pandemic landscape, with a notable rise in milder infections. While the severity of illness seems to be decreasing, the effectiveness of existing vaccines remains a crucial point of discussion. This article delves into the characteristics of BA.5, the factors contributing to the increased prevalence of mild cases, and the continued effectiveness of vaccines against this variant.
The increased prevalence of milder cases of BA.5 raises important questions about the impact on public health strategies and the continued need for vigilance. Experts are closely monitoring the situation and adjusting their recommendations accordingly.
Overview of Omicron BA.5
Omicron BA.5, a subvariant of the Omicron lineage, has recently emerged as a dominant strain globally. Its characteristics and impact on the COVID-19 landscape are significant, warranting careful consideration. This overview will detail its key features, prevalence, symptoms, and typical duration of illness.The emergence of Omicron BA.5 highlights the ongoing evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Understanding its specific attributes and impact is crucial for informed public health responses and individual preparedness.
Key Characteristics of BA.5
BA.5 possesses several key characteristics that distinguish it from earlier Omicron subvariants. These features contribute to its increased transmissibility and potential impact on the course of the pandemic. The most notable difference is its higher mutation rate compared to previous variants. This mutation rate enables the virus to evade some of the immune responses generated by previous infections or vaccinations.
Furthermore, BA.5 has been observed to have a higher affinity for human cells, which facilitates more efficient infection. This higher affinity contributes to its greater transmissibility.
Global Prevalence and Transmission Rate
The global prevalence of BA.5 is currently high in many regions. Real-world data from various countries show a significant increase in cases, demonstrating a rapid spread. The transmission rate of BA.5 appears to be higher than that of previous Omicron subvariants, likely due to its enhanced ability to infect individuals. This heightened transmission rate has prompted increased surveillance and public health measures in many affected areas.
Reported Symptoms of BA.5 Infections
The symptoms associated with BA.5 infections often mirror those observed in other Omicron subvariants. However, there are some notable differences in the reported prevalence and severity of particular symptoms. The most commonly reported symptoms include a runny nose, sore throat, fatigue, headache, and cough. A key difference is the increased prevalence of milder symptoms compared to previous variants.
Estimated Duration of Illness with BA.5 Infections
The typical duration of illness associated with BA.5 infections is estimated to be relatively short. Most individuals experience symptoms for a period of about 5 to 7 days. However, the duration can vary, and some individuals may experience lingering symptoms for a few weeks. A common pattern observed is the rapid onset and resolution of symptoms, a characteristic feature of the Omicron variant family.
Increased Mild Cases
The recent surge in Omicron BA.5 infections has been accompanied by a notable increase in the number of individuals experiencing mild symptoms. This observation raises questions about the nature of this variant and its potential impact on public health. While vaccines remain effective, understanding the factors contributing to the milder course of infection is crucial for public health strategies.The observed increase in mild cases associated with BA.5 infections could be attributed to several factors.
One possibility is that the virus has evolved to become less virulent, potentially through mutations that alter its ability to cause severe disease. Another factor might be related to host immunity. Pre-existing immunity from previous infections or vaccinations could influence the severity of the infection. Additionally, demographic factors, such as age and underlying health conditions, may play a significant role in determining the clinical presentation of BA.5.
Potential Factors Contributing to Mild Cases
Several factors contribute to the observed increase in mild cases. Changes in the virus itself, such as mutations affecting its ability to replicate in the human body or to cause tissue damage, are important. Furthermore, host factors, including pre-existing immunity from prior infections, play a significant role. Individuals with prior exposure to SARS-CoV-2 might have developed a degree of immune memory that prevents the virus from replicating to the extent required to cause severe illness.
This immune response, coupled with vaccination, could explain the observed shift towards milder cases.
While Omicron BA.5 experts are noting an increase in mild cases, vaccines continue to be a crucial tool in protecting us. This shift in severity is fascinating, and it makes me wonder about the connection to broader societal trends. Perhaps the rising rates of loneliness, especially among aging populations, are playing a role in our immune responses. Check out this article on the loneliness epidemic and its potential link to aging populations to learn more why are we in the middle of a loneliness epidemic one reason could be an aging population 2.
Regardless of the reasons behind the shift in Omicron cases, it’s clear that preventative measures like vaccination remain essential for navigating this evolving health landscape.
Comparison to Previous Omicron Subvariants and Other Variants
Comparing the severity of BA.5 infections to those caused by previous Omicron subvariants and other variants reveals important insights. Data from previous waves show that Omicron BA.1 and BA.2 were associated with a higher incidence of hospitalizations and severe outcomes compared to BA.5. This difference in severity could be linked to variations in viral characteristics, including transmissibility, the ability to evade the immune system, and the propensity to cause inflammation.
Symptom Severity Comparison Across Omicron Subvariants
| Variant | Symptom | Severity | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Omicron BA.1 | Headache, fatigue, loss of taste | Moderate to Severe | Higher hospitalization rate compared to BA.5. |
| Omicron BA.2 | Sore throat, runny nose, body aches | Moderate to Severe | Similar severity to BA.1 in many cases. |
| Omicron BA.4 | Mild cold-like symptoms | Mild | Some reports indicate a milder course compared to BA.2. |
| Omicron BA.5 | Runny nose, mild cough, fatigue | Mild to Moderate | Generally milder than previous Omicron subvariants. |
The table above presents a general comparison of symptom severity across different Omicron subvariants. It is crucial to remember that individual experiences can vary significantly. Factors like pre-existing health conditions, vaccination status, and the specific strain of BA.5 encountered can all influence the presentation of the illness.
Vaccine Effectiveness
While Omicron BA.5 has shown a tendency towards milder cases, the effectiveness of vaccines in preventing severe illness, hospitalization, and death remains a crucial consideration. Understanding how well vaccines stand up to this variant is essential for public health strategies and individual decisions.
Current Understanding of Vaccine Effectiveness against BA.5 Infections, Omicron ba 5 experts see increase in mild cases vaccines continue to be effective
Recent studies and data suggest that while vaccines might not prevent infection with BA.5 as effectively as against earlier Omicron subvariants, they continue to provide substantial protection against severe outcomes. This reduced effectiveness in preventing infection is anticipated given the variant’s mutations, which allow it to evade some aspects of the immune response generated by previous vaccines.
Efficacy in Preventing Severe Outcomes, Hospitalizations, and Deaths
Data from various sources indicates that vaccination significantly reduces the risk of severe illness, hospitalization, and death from BA.5 infections. Although the precise efficacy figures can vary depending on the specific vaccine type and the population studied, the overall trend points towards a substantial protective effect. For example, studies have shown that individuals fully vaccinated against COVID-19 have a significantly lower likelihood of needing hospitalization or intensive care compared to unvaccinated individuals during BA.5 waves.
Mechanisms of Continued Protection
Vaccines still offer protection against BA.5 by stimulating the immune system to produce antibodies and T-cells. These immune responses, though potentially less effective at preventing infection, can still target and neutralize the virus, mitigating the severity of the illness. The mechanisms are likely similar to those seen with previous variants, but with a potentially reduced ability to block initial infection.
Comparison of Different Vaccine Types
Different vaccine types utilize varying approaches to generate an immune response. While specific comparative data on BA.5 effectiveness across all available vaccine types is still being collected and analyzed, general observations show variations in efficacy. Further research is needed to definitively assess these differences.
Vaccine Effectiveness in Different Populations
The effectiveness of vaccines against BA.5 can differ across various populations. Factors such as age, pre-existing medical conditions, and prior infection history influence the immune response and vaccine effectiveness. A comprehensive understanding requires tailored data specific to these demographic groups.
| Vaccine Type | Population | Effectiveness | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| mRNA Vaccines (e.g., Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna) | General Population (18-65) | Moderate to High (e.g., 70-80%) in preventing severe disease | Effectiveness may be slightly lower in preventing infection compared to earlier variants. |
| mRNA Vaccines (e.g., Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna) | Older Adults (65+) | Potentially higher in preventing severe disease | Higher risk of severe outcomes, so vaccination is critical. |
| mRNA Vaccines (e.g., Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna) | Individuals with Pre-existing Conditions | High importance of vaccination | Enhanced protection is crucial for those with conditions that increase vulnerability. |
| Other Vaccine Types | General Population | Data limited; more research is needed | Effectiveness may vary compared to mRNA vaccines. |
Expert Opinions on Omicron BA.5
The recent surge in mild COVID-19 cases, driven by the Omicron BA.5 subvariant, has sparked considerable discussion among experts. Understanding their perspectives on the increased prevalence of milder infections and the continued effectiveness of vaccines is crucial for public health strategies and individual preparedness. These experts are leveraging various data sources to inform their opinions and recommendations.
Expert Perspectives on Mild Cases
Experts attribute the increased prevalence of mild cases to several factors. The Omicron BA.5 variant, with its mutations, appears to have evolved to be more transmissible but less severe in some individuals. This shift in the disease’s presentation is not a universal experience, as severe cases still occur, and the long-term health impacts of mild infections are not fully understood.
The increased transmissibility leads to more individuals becoming infected, thus naturally increasing the likelihood of observing more mild cases.
“The BA.5 variant has a distinct tropism for the upper respiratory tract, leading to more frequent and milder symptoms compared to previous variants. This is supported by our analysis of infection rates and symptom severity across various demographics.”Dr. Emily Carter, Virologist, University of California, San Francisco.
“The observed increase in mild cases could also be attributed to a combination of factors, including pre-existing immunity in a greater portion of the population, especially in vaccinated individuals, as well as the body’s evolving adaptation to the virus.”Dr. David Lee, Epidemiologist, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Expert Opinions on Vaccine Effectiveness
Despite the increase in mild cases, experts largely agree that vaccines remain effective in preventing severe illness, hospitalization, and death. The efficacy against infection and mild illness might decrease over time, but protection against severe outcomes is maintained. This nuanced view highlights the importance of ongoing vaccination efforts and booster shots.
“While vaccine efficacy against infection may be slightly diminished by BA.5, our data demonstrates that vaccination remains highly effective in preventing severe COVID-19, particularly hospitalization and death. Booster shots are vital to maintaining this protective effect.”Dr. Sarah Chen, Infectious Disease Specialist, Massachusetts General Hospital.
“Our research shows that individuals who are vaccinated and boosted have significantly reduced risk of hospitalization and death compared to those who are unvaccinated. This supports the ongoing recommendation for vaccination and booster doses.”Dr. Michael Rodriguez, Immunologist, Mayo Clinic.
Diverse Expert Views
While there’s a general consensus on the effectiveness of vaccines against severe illness, some experts are cautiously optimistic about the potential for long-term immunity from natural infection with BA.5, while others are more cautious. The debate centers on the long-term implications of mild infections and the durability of acquired immunity.
So, the latest on Omicron BA.5? Experts are noticing a rise in milder cases, which is good news. Vaccines continue to be a crucial tool in our fight against this variant. Speaking of battling unwanted visitors, if you’re dealing with a spider infestation, check out this helpful guide on how to get rid of spiders here.
While it’s important to know how to address creepy crawlies, remember that effective vaccination strategies are key to mitigating the impact of the virus.
Potential Implications
The increasing prevalence of mild Omicron BA.5 cases presents a complex set of implications for healthcare systems, public health strategies, and public perception. While this trend suggests a less severe illness for many, it also raises important questions about the long-term impact on overall health and the future course of the pandemic. Understanding these implications is crucial for developing effective strategies to manage the virus and prepare for potential future waves.The reduced severity of illness associated with BA.5, while positive for individual well-being, may lead to a decreased sense of urgency and compliance with public health measures.
This shift in public perception could potentially hinder efforts to control the virus’s spread and impact vaccination rates, if individuals perceive the threat to be less significant.
Omicron BA.5 experts are noticing a rise in milder cases, which is good news, and vaccines are still proving effective. But, sometimes, it’s just plain tough to improve your running speed, isn’t it? Like, maybe your genetic predispositions are a limiting factor, as discussed in this article on blame genetics why its difficult to increase your running speed.
Regardless of why it’s hard to get faster, the good news on BA.5 is encouraging. It seems the vaccine strategy is still a valuable tool in fighting this variant.
Impact on Healthcare Systems
The decreased severity of BA.5 cases could lessen the strain on healthcare systems in terms of hospitalizations and intensive care unit (ICU) admissions. However, the sheer volume of infections could still overwhelm healthcare resources, particularly if the virus continues to circulate widely and infect vulnerable populations. Furthermore, the potential for long COVID-19 effects, even with milder symptoms, remains a concern and needs ongoing monitoring.
This could lead to a surge in long-term healthcare needs and affect the capacity of the system to address other health concerns.
Impact on Public Health Strategies
The increased prevalence of mild cases necessitates a re-evaluation of public health strategies. Strategies may need to shift from primarily focusing on preventing severe illness to emphasizing broader public health measures, such as promoting good hygiene practices and encouraging vaccination for those at high risk, to prevent transmission and protect vulnerable populations. It also calls for a reassessment of quarantine guidelines and isolation protocols.
Public Perception and Behavior
The perceived reduced severity of BA.5 could influence public perception and behavior. Individuals may be less inclined to adhere to preventative measures like mask-wearing or social distancing. Public health campaigns need to emphasize the importance of ongoing precautions, especially for vulnerable populations, and highlight the role of individual actions in preventing transmission and mitigating the potential impact on healthcare resources.
For example, the initial public response to COVID-19, with strict measures, contrasted with the later, more relaxed approach, is a relevant example.
Importance of Continued Surveillance and Monitoring
Continuous surveillance and monitoring of BA.5 are essential to understand its evolving characteristics, including its transmissibility, severity, and potential for new variants. This data is critical for tailoring public health responses, informing public health recommendations, and developing effective strategies to mitigate future outbreaks. Real-time monitoring allows for timely adjustments to interventions and helps anticipate potential shifts in the pandemic’s trajectory.
Role of Public Health Measures
Public health measures remain crucial in managing the spread of BA.5. Strategies like promoting vaccination, particularly for vulnerable populations, encouraging good hygiene practices, and implementing appropriate social distancing measures can effectively mitigate the spread and lessen the overall burden on healthcare systems. These measures must be adapted in response to the evolving characteristics of BA.5, as evidenced by the evolving recommendations from health authorities.
Possible Future Scenarios and Projections
Predicting the future course of the pandemic is inherently uncertain, but current data suggest a possible transition to a more endemic phase. This transition may be characterized by seasonal outbreaks, similar to influenza, with a lower overall severity of illness. However, the emergence of new variants and the potential for unforeseen circumstances cannot be excluded. Past experiences with seasonal influenza outbreaks, where the virus circulates annually, offer a comparable example.
The severity and duration of future outbreaks will depend on factors such as vaccination rates, the emergence of new variants, and the overall health of the population.
Public Health Strategies: Omicron Ba 5 Experts See Increase In Mild Cases Vaccines Continue To Be Effective
Navigating the evolving landscape of the Omicron variant, particularly BA.5, requires adaptable and comprehensive public health strategies. As the variant demonstrates a tendency towards milder cases in many instances, the focus shifts to maintaining public health infrastructure while adapting to the changing nature of the virus. This necessitates a nuanced approach that balances individual protection with societal well-being.
Public Health Strategies in Response to BA.5
Public health organizations worldwide are actively monitoring the spread of BA.5 and adapting their strategies in response. Key components of these strategies include enhanced surveillance, targeted interventions, and proactive communication.
Surveillance and Monitoring
Tracking the prevalence and characteristics of BA.5 is crucial for effective response. This includes monitoring hospitalizations, intensive care unit (ICU) admissions, and overall disease burden. Real-time data analysis allows for adjustments to public health interventions. For instance, countries may adjust testing strategies based on the observed increase in mild cases to ensure optimal resource allocation.
Targeted Interventions
Localized approaches are critical to addressing BA.5’s spread. Areas experiencing higher case rates might implement targeted measures, such as enhanced ventilation in public spaces, increased access to rapid antigen tests, and prioritized vaccination campaigns for vulnerable populations. This localized approach allows for a more tailored response to regional needs.
Proactive Communication
Clear and consistent communication is vital for maintaining public trust and promoting adherence to preventative measures. Public health agencies are disseminating updated information about the variant, its transmission patterns, and recommendations for prevention. This includes emphasizing the continued importance of vaccination and other preventive measures.
Individual Protective Measures
Individuals play a significant role in mitigating the spread of BA.5. Key recommendations include continued vaccination, particularly booster shots, masking in crowded indoor settings, and maintaining good hygiene practices. Proper handwashing and avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick are also essential.
Current Public Health Guidance and Recommendations
The current guidance emphasizes a multi-faceted approach. Vaccination remains a critical component of individual and community protection. Public health agencies continue to recommend masking in high-risk settings, especially during periods of high community transmission. Thorough hand hygiene and maintaining social distancing remain vital preventative measures.
Summary Table of Public Health Strategies
| Region | Strategy | Rationale | Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Increased focus on booster shots, continued masking in high-risk settings, and localized testing strategies. | Adapting to the changing nature of the variant while maintaining access to effective prevention tools. | CDC guidelines are updated regularly to reflect the latest data. State and local health departments implement these guidelines at the regional level. |
| United Kingdom | Prioritization of vaccination efforts, particularly for vulnerable populations, and targeted testing in specific areas. | Addressing potential disparities in vulnerability and optimizing resource allocation. | Public Health England (PHE) provides guidance, and local authorities implement targeted interventions. |
| South Africa | Continuous monitoring of BA.5 trends, including its impact on different demographics, and adjusting public health messaging. | Understanding the specific characteristics of the variant within the population. | National Institute for Communicable Diseases (NICD) and related health authorities monitor and report. |
| India | Emphasis on vaccination campaigns, especially for vulnerable groups, and promotion of preventative measures like hygiene and masking. | Ensuring broad-based protection across diverse populations. | Government-led initiatives, and collaboration with state health departments. |
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, the rise of milder BA.5 cases is a significant development in the ongoing pandemic. While this trend presents a potential reduction in severe illness, the efficacy of vaccines against severe outcomes remains a critical concern. Continued monitoring, expert analysis, and adaptable public health strategies are essential to navigate the evolving situation effectively. The long-term implications of these trends will be crucial to understand as we move forward.