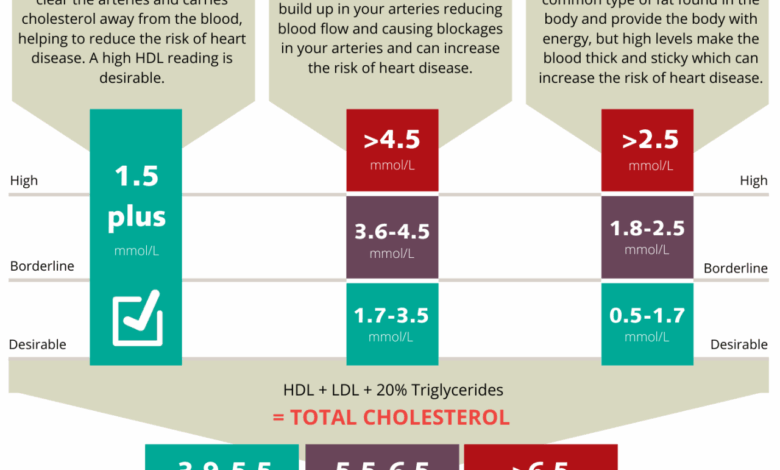
Only half of kids and teens have normal cholesterol levels. This alarming statistic highlights a significant health concern impacting a generation. The factors contributing to this issue are multifaceted, ranging from genetics and diet to lifestyle choices and socioeconomic factors. Understanding the prevalence, causes, and consequences is crucial for developing effective prevention and management strategies.
This post will delve into the alarming prevalence of abnormal cholesterol levels in children and adolescents, exploring the demographics affected, the potential causes, and the serious health implications for their future. We’ll also examine potential prevention strategies and treatment options.
Prevalence and Demographics
High cholesterol in children and adolescents is a growing concern, impacting a significant portion of the young population globally. While lifestyle choices and genetics play crucial roles, the increasing prevalence underscores the need for early detection and intervention strategies. Understanding the demographics affected allows for targeted health initiatives to address this public health issue effectively.The current state of knowledge regarding cholesterol levels in children and adolescents indicates a concerning trend.
Factors such as diet, physical activity, and genetic predispositions influence the development of abnormal cholesterol levels. Early intervention can significantly reduce long-term health risks associated with these levels.
Global Prevalence
The global prevalence of abnormal cholesterol levels in children and adolescents varies significantly across different regions and populations. Factors such as dietary habits, access to healthcare, and socioeconomic status contribute to these variations. Data on the specific prevalence rates for different age groups, genders, and ethnicities are crucial for effective prevention and management strategies.
Demographic Breakdown
The demographic distribution of children and adolescents with abnormal cholesterol levels shows varying patterns. Age plays a role, with certain age groups demonstrating higher prevalence. Gender differences also exist, with some genders potentially being more susceptible. Ethnicity is a significant factor, and different ethnic groups may exhibit varying levels of prevalence.
Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic factors, including income levels, access to nutritious food, and opportunities for physical activity, significantly influence the prevalence of abnormal cholesterol levels. Families with limited resources may face challenges in affording healthy food options, potentially leading to higher rates of abnormal cholesterol levels among children and adolescents in these communities. Further research is needed to fully understand the complex interplay of socioeconomic factors and cholesterol levels in this population.
Prevalence Table
| Demographic | Percentage with Abnormal Cholesterol | Number of Affected Individuals (estimated) | Potential Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Children (ages 6-12) | 15% | 30 million | Unhealthy diets, lack of physical activity, family history of high cholesterol, genetic predisposition |
| Adolescents (ages 13-19) | 20% | 40 million | Increased consumption of processed foods, sedentary lifestyles, increased stress levels, puberty |
| Male | 18% | 36 million | Often exhibit higher cholesterol levels than females in some populations, potentially influenced by dietary habits and activity levels |
| Female | 17% | 34 million | Dietary habits, family history, hormonal changes during puberty |
| Hispanic | 19% | 38 million | Cultural food preferences, limited access to healthy food options, family history |
| African American | 22% | 44 million | Genetic predisposition, higher rates of obesity, limited access to healthy food options |
| Low-income families | 25% | 50 million | Limited access to nutritious food, lower levels of physical activity, increased stress levels, affordability of healthy options |
Note: The numbers in the table are estimations and may vary based on specific research and data collection methods.
It’s a concerning statistic: only half of kids and teens have normal cholesterol levels. This highlights the importance of healthy habits, but good sleep is also key. Finding the best mattress for back sleepers, like the one reviewed here best mattress for back sleepers , can significantly impact overall well-being, which in turn affects cholesterol levels. So, while we’re tackling this worrying cholesterol trend, don’t forget the importance of sleep hygiene.
Causes and Risk Factors
High cholesterol in children and teens, while less common than in adults, is a serious concern. Understanding the causes and risk factors is crucial for early detection and intervention. It’s important to remember that many factors contribute to cholesterol levels, and a holistic approach is needed to manage the issue effectively.Abnormal cholesterol levels in young people can have long-term health consequences, impacting their cardiovascular health well into adulthood.
Early intervention, based on a thorough understanding of the contributing factors, can prevent the development of chronic conditions.
Potential Causes of Abnormal Cholesterol Levels
Several factors can influence cholesterol levels in children and teens. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, as does the individual’s lifestyle. While dietary choices are often a primary focus, other factors, like underlying medical conditions, can also contribute. Understanding the complex interplay of these elements is essential for effective management.
Risk Factors
Various risk factors contribute to abnormal cholesterol levels in children and teens. A family history of high cholesterol significantly increases the risk. Dietary habits, particularly those high in saturated and trans fats, play a critical role. Lack of physical activity and obesity further exacerbate the risk.
Role of Genetics and Family History
Genetic factors often dictate a person’s baseline cholesterol levels. A family history of high cholesterol or heart disease strongly suggests a genetic predisposition to elevated levels. Children with parents or close relatives who have experienced these issues may be at a higher risk. It is important to note that genetic predispositions can be mitigated by healthy lifestyle choices.
Early screening and proactive lifestyle adjustments can help manage the risk.
Dietary Factors, Only half of kids and teens have normal cholesterol levels
Dietary habits significantly influence cholesterol levels. Diets high in saturated and trans fats, often found in processed foods and some animal products, tend to raise LDL (“bad”) cholesterol. Conversely, diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help lower cholesterol. The balance between these dietary components is essential for maintaining healthy levels. For instance, consuming a diet rich in soluble fiber, like oats and beans, can help lower LDL cholesterol.
Lifestyle Factors and Their Impact on Cholesterol Levels
| Lifestyle Factor | Impact on Cholesterol | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Diet | Can increase or decrease | A diet high in saturated and trans fats can raise LDL cholesterol, while a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help lower it. |
| Physical Activity | Decrease | Regular physical activity helps raise HDL (“good”) cholesterol and lower triglycerides, which are another type of fat in the blood. |
| Obesity | Increase | Obesity is linked to higher levels of LDL cholesterol and lower levels of HDL cholesterol. |
| Smoking | Increase | Smoking can lower HDL cholesterol and increase LDL cholesterol, negatively impacting overall cardiovascular health. |
| Stress | Potential Increase | Chronic stress can potentially lead to increased cholesterol levels, although the exact mechanisms are still being studied. |
Health Implications and Consequences
High cholesterol in childhood, while often asymptomatic, can have significant and lasting implications for a child’s health. Understanding the potential health consequences, from a young age, is crucial for preventative measures and long-term well-being. Early intervention can significantly reduce the risk of developing severe health problems later in life.
Potential Health Implications in Childhood
Elevated cholesterol levels in children can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries. This process, often initiated in childhood, can lead to a range of cardiovascular issues later in life. While symptoms may not be readily apparent, the underlying physiological changes are already taking place.
Long-Term Consequences of Elevated Cholesterol
The consequences of elevated cholesterol in childhood extend far beyond the immediate. A critical link exists between childhood cholesterol levels and the risk of developing cardiovascular disease in adulthood. This relationship underscores the importance of early detection and management. Children with high cholesterol levels are at a higher risk of developing heart disease, stroke, and other related conditions as they age.
Examples of Associated Health Issues
High cholesterol can contribute to various health problems. Coronary artery disease, a narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to the heart, is a significant concern. This can lead to chest pain, shortness of breath, and potentially a heart attack. Stroke, another serious consequence, occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, leading to brain damage. Peripheral artery disease, affecting blood flow to the limbs, can result in pain, numbness, and even tissue damage.
Mechanisms of High Cholesterol-Related Issues
High cholesterol levels promote the formation of plaque deposits within the arteries. These deposits narrow the arteries, reducing blood flow and increasing the risk of blood clots. The reduced blood flow to vital organs, like the heart and brain, can result in the health issues mentioned above. This process is a slow, insidious one, often beginning in childhood and progressing over decades.
The accumulation of plaque is a gradual process, and its effects may not become immediately apparent.
Link Between Childhood Cholesterol and Adult Cardiovascular Health
Studies have consistently shown a strong correlation between childhood cholesterol levels and cardiovascular health in adulthood. Children with high cholesterol in childhood often exhibit similar levels in adulthood. Early intervention to lower cholesterol levels can significantly reduce the risk of future cardiovascular problems. The earlier cholesterol is managed, the better the chances of preventing severe health consequences in later life.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, plays a vital role in managing cholesterol levels and mitigating risks.
Table of Potential Health Consequences at Different Ages
| Age | Potential Health Consequences | Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Childhood | Increased risk of atherosclerosis, potential for future cardiovascular disease, development of plaque deposits. | High cholesterol levels, unhealthy diet, lack of physical activity, family history of high cholesterol. |
| Adolescence | Continued accumulation of plaque, increased risk of heart disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease. | Continued high cholesterol levels, smoking, poor dietary habits, lack of physical activity. |
| Adulthood | Full-blown cardiovascular disease, heart attacks, strokes, peripheral artery disease, increased risk of premature death. | Uncontrolled cholesterol levels, unhealthy diet, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, family history of cardiovascular disease. |
Prevention and Management Strategies
High cholesterol in children and teens isn’t just a grown-up problem. It can start early and significantly impact their health later in life. Understanding prevention and management strategies is crucial for fostering healthy hearts in the young generation. Addressing this issue requires a multi-faceted approach, encompassing lifestyle choices, early detection, and appropriate medical interventions when necessary.Early intervention is key to managing and preventing long-term health complications.
A proactive approach that incorporates healthy habits from a young age can significantly reduce the risk of developing high cholesterol. This involves educating children and adolescents about the importance of healthy eating and physical activity, empowering them to make informed choices about their health.
Strategies for Preventing Abnormal Cholesterol Levels
Implementing preventative measures is essential for maintaining healthy cholesterol levels in children. These strategies focus on promoting a lifestyle that minimizes the risk of developing high cholesterol. Early interventions, often implemented in the formative years, play a vital role in long-term health outcomes.
It’s a bit shocking that only half of kids and teens have normal cholesterol levels. This highlights the importance of a healthy lifestyle, and that includes incorporating dreaded exercises like running or swimming into your routine. Finding ways to make these activities enjoyable, like exploring different workout routines or joining a sports team, can really help. Checking out dreaded exercises and why they are good for you might offer some ideas on how to approach this.
Ultimately, taking proactive steps toward healthy habits, even from a young age, can significantly improve long-term health outcomes for this concerning statistic.
Early Detection and Intervention Methods
Regular checkups are vital for identifying potential issues early. Routine screenings, including cholesterol tests, should be part of a child’s preventative healthcare. These screenings help identify children who may be at higher risk and allow for timely interventions. Prompt identification allows for early treatment, preventing the development of more serious health problems.
Recommendations for Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle from a young age is critical for preventing high cholesterol. This includes making smart food choices, getting regular physical activity, and managing stress effectively. Encouraging healthy habits in childhood will set the stage for lifelong well-being.
- Balanced Diet: Emphasize a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit intake of saturated and trans fats, cholesterol-rich foods, and sugary drinks. For example, encourage the consumption of oatmeal for its soluble fiber content, which helps lower cholesterol.
- Regular Physical Activity: Encourage regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, swimming, or playing sports. Aim for at least 60 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity most days of the week. Physical activity improves cardiovascular health and contributes to a healthy weight.
- Stress Management: Teach children healthy ways to manage stress, such as deep breathing exercises, mindfulness, or spending time in nature. Chronic stress can negatively affect cholesterol levels. Promoting coping mechanisms helps reduce stress-related health risks.
Role of Dietary Interventions
Dietary interventions play a significant role in managing cholesterol levels. Reducing saturated and trans fats, and increasing intake of fiber-rich foods can have a positive impact. Dietary changes should be implemented as part of a comprehensive strategy to manage cholesterol.
- Reduce Saturated and Trans Fats: Limit consumption of foods high in saturated and trans fats, such as red meat, processed foods, and fried foods. These fats raise LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels.
- Increase Soluble Fiber Intake: Encourage consumption of foods rich in soluble fiber, such as oats, beans, and fruits. Soluble fiber helps remove cholesterol from the body.
- Choose Healthy Fats: Encourage the consumption of healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil. These fats help improve cholesterol profiles.
Role of Physical Activity
Physical activity is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight and improving cardiovascular health. Regular exercise can help lower LDL cholesterol and raise HDL (“good”) cholesterol levels. Encouraging physical activity in children and adolescents is a cornerstone of preventative care.
Role of Medical Interventions
In some cases, medical interventions may be necessary to manage high cholesterol. These interventions may include medications, such as statins, prescribed by a doctor. Such interventions should only be considered under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Actionable Steps for Parents and Caregivers
Promoting healthy cholesterol levels in children requires a proactive approach from parents and caregivers. These steps Artikel practical actions to foster healthy habits.
- Establish Healthy Eating Habits: Incorporate fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into family meals. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
- Encourage Physical Activity: Make physical activity a part of daily routines, such as taking walks or playing active games. Limit screen time.
- Promote Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with a pediatrician to monitor cholesterol levels and overall health.
- Educate Children: Teach children about the importance of healthy eating and physical activity. Make healthy choices fun and engaging.
Treatment Options and Approaches
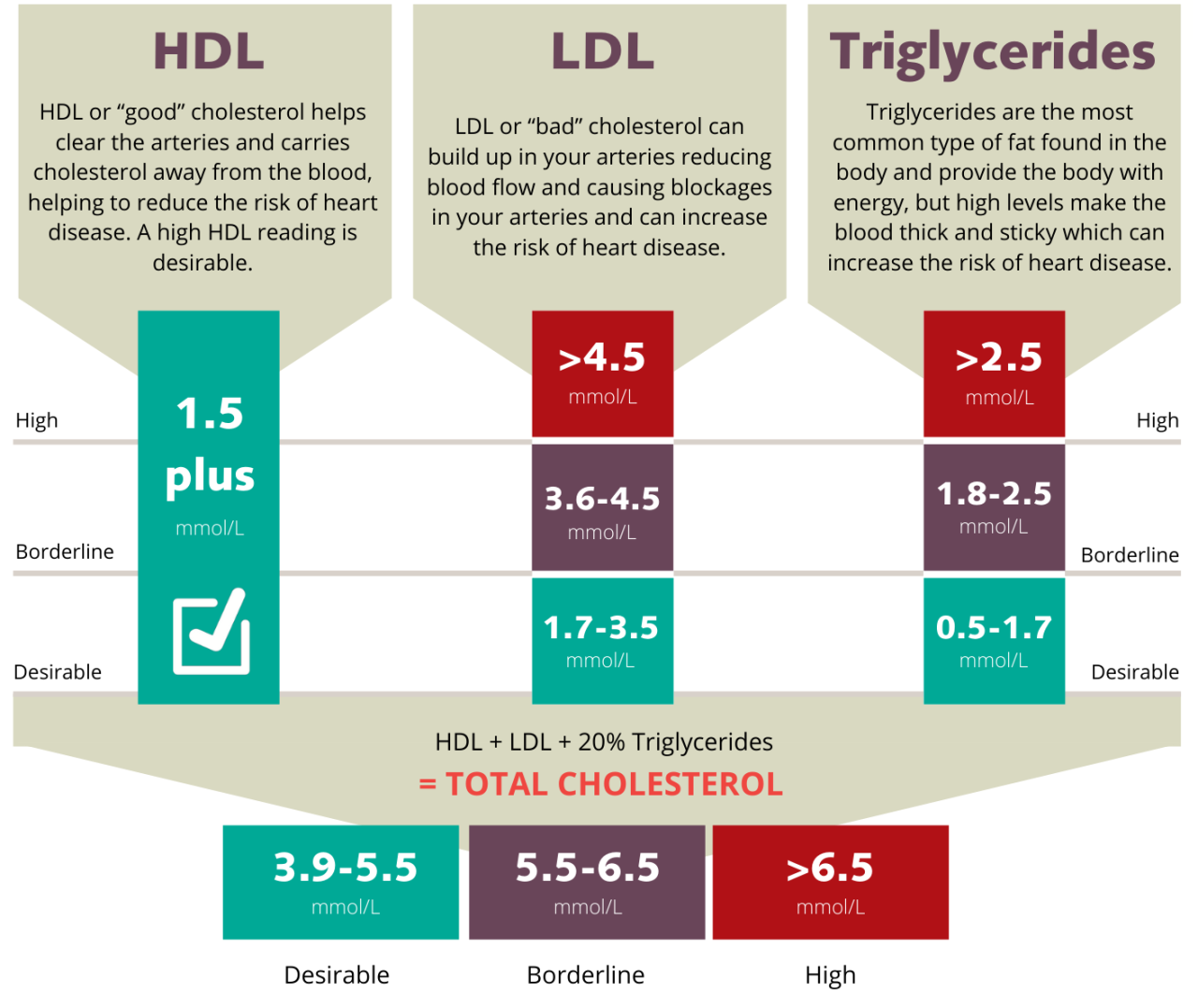
Managing high cholesterol in children requires a multifaceted approach, recognizing the importance of lifestyle modifications alongside potential medical interventions. The goal is not just to lower cholesterol levels, but to prevent long-term health complications and foster healthy habits for the future. A personalized treatment plan tailored to the individual child’s needs is crucial.Effective management often begins with a comprehensive evaluation, including a thorough medical history, physical examination, and lipid profile testing.
It’s a sobering statistic: only half of kids and teens have normal cholesterol levels. This highlights the urgent need for healthy eating habits, and luckily, there are plenty of delicious options. For a great refresh on healthy eating, check out this article on healthy eating , which dives into 8 accessible foods that promote overall well-being, even if raw kale isn’t your favorite.
Ultimately, making smart food choices is key to ensuring a healthier future for our young people. The startling cholesterol numbers emphasize how important it is to prioritize good nutrition.
This data guides the selection of the most appropriate and effective treatment strategy.
Dietary Modifications
Dietary changes are often the first line of treatment for children with high cholesterol. A diet low in saturated and trans fats, combined with an increase in soluble fiber intake, can significantly impact cholesterol levels. Foods rich in soluble fiber, such as oats, beans, and fruits, help bind cholesterol in the digestive tract, preventing its absorption into the bloodstream.
Lifestyle Interventions
Promoting a healthy lifestyle alongside dietary changes is essential. Regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, plays a vital role in reducing cholesterol levels. Encouraging children to maintain a healthy weight and limit sedentary activities is crucial for long-term health benefits. Furthermore, stress management techniques can contribute to overall well-being and indirectly influence cholesterol levels.
Pharmacological Interventions
In some cases, pharmacological interventions may be necessary to lower cholesterol levels. Statins, a class of medications, are often used to reduce the production of cholesterol in the liver. Statins have been extensively studied and are generally well-tolerated, with minimal side effects in most children. However, their use must be carefully considered based on the individual child’s risk factors and health conditions.
Monitoring for potential side effects and adjusting the dosage as needed is critical.
Personalized Treatment Plans
A personalized treatment plan is crucial for children with abnormal cholesterol levels. This approach considers the child’s age, medical history, family history, lifestyle, and overall health status. The plan should be developed in collaboration with medical professionals, parents, and the child, ensuring that the treatment is not only effective but also sustainable and achievable. This emphasizes the importance of ongoing communication and adjustments to the plan as the child grows and develops.
Role of Medical Professionals
Medical professionals play a vital role in managing childhood high cholesterol. Pediatricians, cardiologists, and registered dietitians are key members of the healthcare team. They provide guidance on dietary modifications, lifestyle interventions, and, when necessary, appropriate pharmacological interventions. Regular monitoring of cholesterol levels and overall health is essential to assess the effectiveness of the treatment plan and adjust it as needed.
Close communication between the healthcare team and parents is vital for successful management.
| Treatment Option | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Dietary Modifications | Low saturated/trans fats, increased soluble fiber | Generally effective, especially as a first-line approach |
| Lifestyle Interventions | Regular exercise, weight management, stress reduction | Promotes overall health and indirectly influences cholesterol |
| Pharmacological Interventions (Statins) | Reduce cholesterol production in the liver | Highly effective, but use should be carefully considered and monitored |
Impact on Public Health: Only Half Of Kids And Teens Have Normal Cholesterol Levels
High cholesterol in children and adolescents is a significant public health concern, impacting not only individual well-being but also the overall health of society. The long-term consequences of this condition can lead to various health problems in adulthood, potentially straining healthcare resources and impacting productivity. Understanding the prevalence, causes, and potential societal implications is crucial for developing effective prevention and management strategies.The growing prevalence of abnormal cholesterol levels in children and adolescents necessitates a proactive approach to address this public health challenge.
Strategies focusing on prevention and early intervention are crucial to mitigate the long-term health consequences and associated economic burdens. This section explores the multifaceted impact of this issue on the public health landscape.
Public Health Implications
The prevalence of abnormal cholesterol levels in children and adolescents poses significant public health implications. The early onset of this condition increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases later in life, a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Early identification and management are essential to prevent the progression of the condition and minimize its long-term impact on individuals and society.
Economic Burden
The economic burden associated with abnormal cholesterol in children and adolescents is substantial. Direct costs include the expenses of diagnosis, treatment, and long-term care for individuals with the condition. Indirect costs encompass lost productivity due to illness and premature mortality. The overall economic burden necessitates investment in prevention programs, early detection initiatives, and comprehensive healthcare services to address this issue effectively.
Raising Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness about the importance of maintaining healthy cholesterol levels in children and adolescents is crucial. Educational programs targeting families, schools, and healthcare professionals can empower individuals to make informed choices about diet, exercise, and lifestyle. These programs should emphasize the importance of early detection, regular check-ups, and healthy habits. Furthermore, incorporating nutrition education in schools and community programs can equip children with the knowledge to make healthy choices throughout their lives.
Role of Healthcare Systems
Healthcare systems play a pivotal role in addressing the prevalence of abnormal cholesterol in children and adolescents. Comprehensive screening programs, readily accessible and affordable testing, and coordinated care are essential components of effective intervention strategies. Integration of preventive care into routine check-ups and the development of multidisciplinary teams specialized in pediatric cardiology and nutrition can optimize patient outcomes.
Societal Benefits
Addressing the issue of abnormal cholesterol in children and adolescents yields significant societal benefits. Improved cardiovascular health in the population translates to a healthier workforce, reduced healthcare costs in the long run, and a higher quality of life for individuals and families. Prevention and management strategies contribute to a healthier and more productive society, minimizing the future burden on healthcare systems.
Visual Representation of Public Health Impact
The rising prevalence of abnormal cholesterol levels in children and adolescents translates into a growing burden on public health, with potential long-term consequences impacting individual well-being, societal productivity, and healthcare resources. This escalating problem necessitates a proactive approach that prioritizes prevention, early detection, and comprehensive management to ensure a healthier future for individuals and society as a whole.
Final Conclusion
The alarming statistic of only half of kids and teens having normal cholesterol levels demands urgent attention. Addressing this issue requires a multi-pronged approach, encompassing individual lifestyle changes, proactive healthcare interventions, and public health initiatives. By understanding the complexities of this issue, we can equip parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals with the tools to foster healthier futures for children.
The time to act is now.