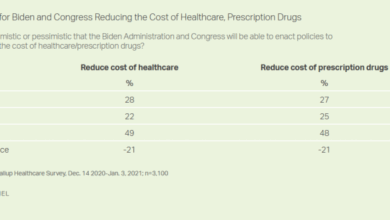
Out of pocket costs go up when prescription drug prices rise, leaving individuals and families struggling to afford necessary medications. This escalating issue impacts everyone from low-income families to high-net-worth individuals, highlighting the critical need for accessible and affordable healthcare. The burden isn’t just financial; it affects overall health and well-being, potentially hindering preventative care and leading to delayed or forgone treatment.
This exploration delves into the multifaceted problem of rising prescription drug costs, examining the ripple effects on individuals, healthcare systems, and the policies that shape this crucial aspect of healthcare. We’ll examine factors driving price increases, the role of pharmaceutical companies, and potential solutions to mitigate the financial strain on patients and the healthcare system as a whole.
Impact on Individuals and Households
Rising prescription drug prices are a significant financial burden for individuals and households, impacting their ability to access necessary medications and overall well-being. This escalating cost can have profound consequences, especially for those with chronic conditions or multiple health issues. The strain on household budgets can be substantial, forcing difficult choices and potentially compromising other essential expenses.Rising prescription drug prices translate directly into increased out-of-pocket costs for consumers.
This means that individuals are responsible for paying more for their medications, often leading to financial hardship. The impact is not uniform, and different factors like insurance coverage, income levels, and the specific drugs needed influence the severity of the burden.
Rising prescription drug costs are unfortunately leading to higher out-of-pocket expenses for many. It’s a frustrating reality, especially when considering the myriad of factors impacting health. Fortunately, a recent study has shed light on a potential solution for weight loss in individuals experiencing depression. This new approach, detailed in study finds best way to help people with depression lose weight , suggests a tailored strategy that could significantly improve overall well-being.
However, the rising cost of prescriptions continues to be a significant burden for many, making it harder to afford the necessary medications.
Financial Burden on Individuals
Prescription drug costs are a significant financial burden, often affecting individuals across all income brackets. The costs can be unpredictable and substantial, forcing individuals to make difficult choices regarding their health care. Individuals with pre-existing conditions or chronic illnesses face particularly high costs, as they often require more frequent and expensive medications.
Coping Mechanisms for Increased Costs
Individuals employ various strategies to manage the rising costs of prescription drugs. Some cut back on other expenses, delaying or foregoing necessary purchases. Others explore options like generic medications, which are often significantly cheaper. Seeking financial assistance programs, including those offered by pharmaceutical companies or non-profit organizations, is another common approach. Negotiating with insurance providers to lower prescription costs is also an increasingly explored avenue.
Impact Across Income Brackets
The impact of rising prescription drug costs varies significantly across different income brackets. For low-income individuals, the increased out-of-pocket costs can be devastating, potentially leading to medication non-adherence and adverse health outcomes. Even middle-income households may find it challenging to absorb these costs, particularly if they have multiple dependents or pre-existing conditions requiring extensive treatment. High-income individuals may experience less immediate financial hardship, but even they can face significant out-of-pocket costs, especially when considering the cumulative impact over time.
For example, a family with two children with asthma requiring inhalers and allergy medication will experience a higher out-of-pocket cost than a single individual with a simple condition.
Consequences on Health and Well-being
High out-of-pocket costs for prescription drugs can have significant consequences on overall health and well-being. Individuals may delay or forgo necessary medications, potentially leading to worsening health conditions. This can also lead to increased stress, anxiety, and other mental health issues. The financial strain can further limit access to preventative care, which can compound the impact of high prescription costs.
In extreme cases, patients may have to choose between affording medication and other basic necessities, such as food and housing.
Rising prescription drug costs inevitably lead to higher out-of-pocket expenses for patients. This is a real concern, especially when considering situations like using an older insulin pump, as detailed in the recent question “ask dmine new pump really old insulin” ask dmine new pump really old insulin. Ultimately, these increased costs can significantly impact the financial well-being of individuals and families.
Average Out-of-Pocket Costs by Age Group
| Age Group | Average Out-of-Pocket Cost (Estimated) |
|---|---|
| 18-25 | $100-$300 per year |
| 26-45 | $200-$500 per year |
| 46-65 | $300-$800 per year |
| 65+ | $500-$1500 per year |
Note
* These are estimated figures and can vary significantly depending on the specific prescription drug, insurance coverage, and individual circumstances.
Impact on Healthcare Systems
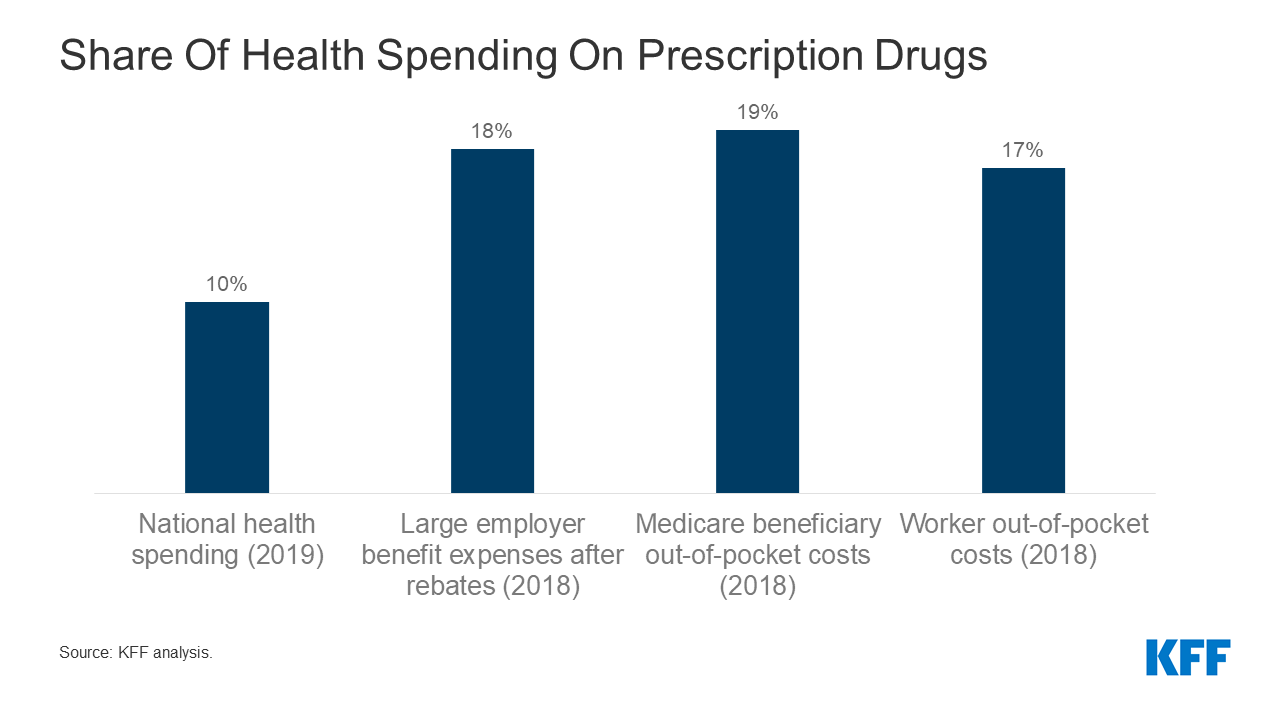
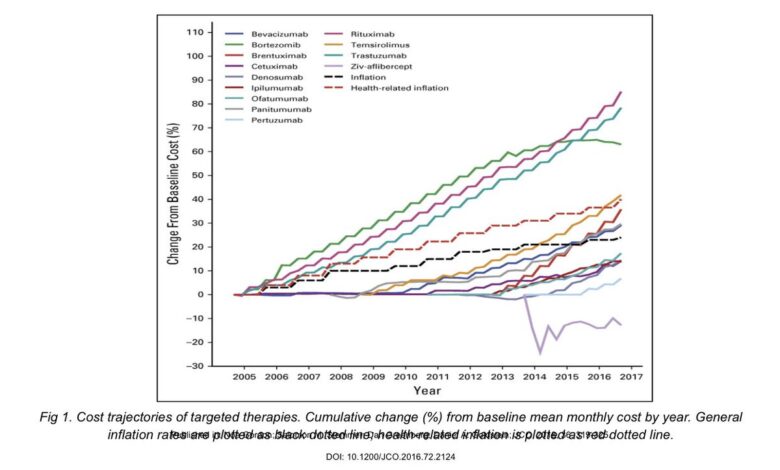
Prescription drug price increases ripple through the entire healthcare system, impacting providers, patients, and the overall cost of care. These escalating costs aren’t just a financial burden; they affect the quality and accessibility of healthcare services. The rising cost of medications forces adjustments in various facets of the system, from how providers manage their budgets to how patients utilize care.The escalating cost of prescription drugs significantly impacts healthcare providers.
Margin pressures are amplified as providers struggle to balance the increasing cost of medications with the need to maintain patient access. This often leads to difficult choices, such as limiting the number of medications they can offer or negotiating lower prices with pharmaceutical companies. These decisions, while necessary, can negatively affect patient care.
Impact on Healthcare Providers
Rising prescription drug prices strain healthcare providers’ budgets. They face the challenge of covering these increased costs while maintaining quality patient care. This financial pressure can lead to reduced reimbursements, limiting their ability to invest in new technologies or staff training. Consequently, healthcare providers might experience reduced profitability and a diminished capacity to invest in the most advanced medical care.
Impact on Healthcare Utilization
Increased out-of-pocket costs for medications directly influence patient utilization of healthcare services. Patients might delay or forgo necessary follow-up appointments, lab tests, or preventative care to manage their drug expenses. This can lead to a deterioration in health outcomes and potentially more expensive treatments in the long run. The decision to postpone necessary medical care can have significant implications for overall health.
Impact on Preventative Care
The rising cost of prescription drugs can discourage preventative care. When patients face significant out-of-pocket costs for medications, they may be less inclined to invest in preventative measures like screenings or vaccinations. This can lead to a delay in the diagnosis of chronic conditions, potentially resulting in more severe health problems and greater costs in the future. This is especially true for individuals with chronic conditions who rely on medications to manage their symptoms.
Relationship to Overall Healthcare Costs
The rising cost of prescription drugs is a significant contributor to the overall escalating cost of healthcare services. The direct link between drug prices and overall healthcare expenses is substantial. As the cost of medications increases, it drives up the cost of treatments, hospital stays, and other associated services. This interrelationship underscores the need for comprehensive solutions to address the escalating price of prescription drugs.
Correlation Between Prescription Drug Price Increases and Healthcare System Costs
| Year | Prescription Drug Price Increase (%) | Estimated Increase in Healthcare System Costs (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 5.2 | 3.8 |
| 2021 | 6.8 | 4.5 |
| 2022 | 7.5 | 5.2 |
| 2023 | 8.2 | 5.9 |
Note: These figures are illustrative and do not represent precise data. The correlation between prescription drug price increases and healthcare system costs is complex and influenced by various factors. These are estimated values based on observed trends.
Factors Driving Prescription Drug Price Increases
Prescription drug prices have been a persistent source of concern for individuals and healthcare systems alike. The escalating costs are driven by a complex interplay of factors, impacting both patient affordability and the overall financial health of healthcare. Understanding these drivers is crucial to developing effective solutions for containing costs and ensuring access to necessary medications.The rising cost of prescription drugs is a multifaceted issue, with various contributing factors.
These include research and development costs, manufacturing processes, marketing and distribution strategies, and the influence of government regulations. Ultimately, these factors contribute to the overall price tag consumers pay at the pharmacy.
Research and Development Costs
The pharmaceutical industry requires significant investment in research and development to discover and develop new drugs. This process is often lengthy and costly, involving clinical trials and regulatory approvals. The high costs associated with these activities are frequently cited as a justification for higher drug prices. However, the relationship between R&D investment and drug pricing is often complex and debated.
Manufacturing and Distribution Costs
Prescription drug manufacturing and distribution involve intricate processes, including quality control measures, packaging, and logistics. The cost of these procedures can vary depending on the complexity of the drug and the scale of production. In some cases, manufacturing costs might be comparatively low, while distribution costs could be higher due to specialized handling requirements. Overall, these factors contribute to the total cost of a drug, ultimately influencing its price.
Marketing and Promotion
Pharmaceutical companies spend substantial amounts on marketing and promotion to increase awareness and generate demand for their products. The marketing efforts, which include targeted advertising, promotional campaigns, and interactions with healthcare professionals, are crucial to market penetration and sales. However, the relationship between marketing expenses and drug prices is not always straightforward, as different marketing strategies can impact prices differently.
Government Regulations
Government regulations play a significant role in shaping prescription drug prices. These regulations, which encompass patent protection, regulatory approvals, and pricing controls, can affect both the development and pricing of medications. The impact of these regulations varies, with some potentially driving up costs while others aim to control them. Regulations, in general, can either increase or decrease drug prices, depending on the specifics of the policy.
Pricing Models
Different pricing models are used for prescription drugs, each with its own implications. Some models, such as value-based pricing, attempt to link drug prices to the clinical value or health outcomes they produce. Other models, such as cost-plus pricing, base prices on the cost of production plus a markup. The effectiveness of each pricing model in controlling costs and ensuring access to medication is a subject of ongoing debate and scrutiny.
Potential Solutions for Reducing Costs
A multitude of potential solutions exist to address the rising costs of prescription drugs. These include measures to improve the efficiency of drug development, enhance competition among pharmaceutical companies, and implement more transparent pricing models.
- Increased Competition: Encouraging competition among pharmaceutical companies can potentially drive down prices through greater innovation and cost-effectiveness. Promoting competition can foster a more dynamic market environment, potentially benefiting consumers.
- Value-Based Pricing: Transitioning to value-based pricing models, which link drug prices to their clinical value and health outcomes, may provide a more rational approach to pricing. This approach can potentially incentivize innovation in areas of high clinical need.
- Generic Drug Promotion: Promoting the use of generic drugs, which are typically significantly less expensive than their brand-name counterparts, can be a substantial cost-saving measure. Encouraging the availability of generic drugs can contribute to affordability and accessibility.
- Negotiated Prices: Implementing price negotiation strategies, where governments or large payers negotiate drug prices with pharmaceutical companies, could reduce costs. This strategy can be implemented to ensure reasonable and affordable prices.
- Streamlined Regulatory Processes: Streamlining the regulatory processes for new drug approvals can accelerate the introduction of new medications, potentially fostering competition and cost reduction.
Policy and Regulatory Responses
Prescription drug pricing has become a significant concern, impacting individuals and the healthcare system. Government intervention is necessary to address this issue, but the approach must consider various factors, including the complexities of the pharmaceutical industry and the potential consequences of different policy choices. Effective policies must balance affordability, innovation, and patient access.Policies designed to control prescription drug prices can vary greatly in scope and approach.
Rising prescription drug costs unfortunately translate to higher out-of-pocket expenses for everyone. It’s a tough pill to swallow, especially when you consider stories like NFL player Tevin Coleman’s experience parenting a child with sickle cell disease, which highlights the immense financial strain on families dealing with chronic illnesses. The increasing costs of medication for conditions like sickle cell are a major concern, and ultimately, this translates into a greater burden on individuals and families.
It’s a real issue that needs attention and solutions.
Some policies focus on direct price controls, while others emphasize market-based solutions or incentives for drug development. The success of any policy depends on its design, implementation, and the wider economic and political context.
Potential Government Policies
Various government policies aim to control prescription drug prices. These policies may involve direct price controls, negotiation of drug prices, and the use of price transparency. Negotiating drug prices with pharmaceutical companies can lower the cost of medications for consumers. Price transparency can allow consumers to compare drug prices and make informed decisions.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Policies
Examples of policies aimed at controlling prescription drug prices vary in their outcomes. Some countries have successfully negotiated lower drug prices through government-run programs. The success of these policies often hinges on factors such as the strength of the government’s negotiating position and the willingness of pharmaceutical companies to participate. Conversely, other policies have been less successful due to their limited scope or insufficient enforcement mechanisms.
Challenges and Limitations of Implementing Policies
Implementing policies to curb drug price increases faces numerous challenges. These include the complexities of the pharmaceutical industry, the protection of intellectual property rights, and the potential for negative impacts on innovation and drug development. Balancing the need to control costs with incentives for innovation is a key challenge. Drug companies often argue that price controls could discourage investment in research and development.
Alternative Approaches
Alternative approaches to address rising prescription drug costs include promoting generic drug use and increasing competition among pharmaceutical companies. Generic drug use can significantly reduce the cost of medications, while increased competition among pharmaceutical companies can lead to more affordable prices. Additionally, focusing on preventative care and lifestyle changes can reduce the need for expensive medications.
Drug Pricing Negotiations
Drug pricing negotiations involve complex processes and considerations. Negotiation tactics include setting price caps, negotiating with pharmaceutical companies for lower prices, and establishing formularies that restrict the types of drugs covered. The specific steps and procedures involved can vary based on the specific context of each negotiation.
| Policy Type | Description | Potential Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Price Controls | Setting maximum prices for drugs | Can reduce costs but may discourage innovation |
| Negotiation | Government negotiating with pharmaceutical companies for lower prices | Can lead to lower prices but depends on the negotiating power |
| Generic Drug Promotion | Encouraging use of cheaper generic versions | Can significantly reduce costs |
Consumer Awareness and Advocacy
Rising prescription drug costs are a significant concern for individuals and families. Understanding how to advocate for lower prices and taking an active role in the healthcare system can empower consumers to manage these costs effectively. This involves not only understanding your options but also actively engaging with the system to effect change.
Strategies for Consumer Advocacy
Consumers can take several steps to advocate for lower prescription drug costs. These strategies involve direct action, informed choices, and collective efforts. Understanding these strategies is key to making a meaningful impact.
- Direct Communication with Pharmacies and Insurance Companies: Consumers can contact their insurance companies and pharmacies directly to inquire about prescription drug costs and potential alternatives. Comparing prices and seeking cost-saving options is crucial. This direct communication can highlight the need for more affordable options.
- Utilizing Patient Assistance Programs: Many pharmaceutical companies and non-profit organizations offer patient assistance programs to help reduce the financial burden of medications. Researching and applying for these programs can significantly decrease out-of-pocket expenses.
- Joining or Supporting Consumer Advocacy Groups: Consumer advocacy groups play a vital role in advocating for lower prescription drug prices and improving access to affordable medications. Supporting these groups through donations or volunteer work can amplify their impact.
- Participating in Public Forums and Meetings: Participating in public forums, town halls, and meetings related to healthcare policy can provide an opportunity to voice concerns and advocate for change. This engagement helps policymakers understand the impact of high prescription drug costs on individuals and communities.
Examples of Consumer Advocacy Groups
Several consumer advocacy groups work to address prescription drug costs. These organizations offer support and resources to individuals and families. Their efforts aim to empower consumers and bring about positive change.
- AARP: The AARP advocates for affordable healthcare, including prescription drugs, for its members. Their advocacy efforts focus on policies that make medications more accessible and affordable for seniors.
- National Council on Aging: The National Council on Aging (NCOA) advocates for policies that improve the health and well-being of older adults. This includes advocating for lower prescription drug costs and ensuring access to needed medications.
- Consumers Union: Consumers Union, the policy and research arm of Consumer Reports, works to protect consumer interests, including affordable prescription drugs. Their research and advocacy aim to influence policy changes.
Importance of Patient Education Regarding Out-of-Pocket Costs
Understanding the various factors influencing prescription drug costs is crucial. This knowledge allows individuals to make informed decisions about their medications and healthcare choices. Patient education empowers individuals to actively manage their health and financial situations.
- Comparing Prescription Drug Prices: Consumers can compare prescription drug prices using online resources and by contacting pharmacies. Many online tools and websites compare prices for various medications, helping individuals find the most affordable option.
- Understanding Insurance Coverage: Knowing how insurance plans cover prescription drugs is vital. Consumers should review their plan details and understand co-pays, deductibles, and formularies to manage costs effectively.
How Consumers Can Compare Prescription Drug Prices
Comparing prescription drug prices is crucial for minimizing out-of-pocket expenses. A variety of methods can be employed to achieve this goal. Consumers should actively seek the best options available to them.
- Online Comparison Tools: Many websites and mobile applications allow consumers to compare prescription drug prices from different pharmacies. These tools consider factors such as insurance coverage and co-pays to provide a comprehensive comparison.
- Contacting Pharmacies Directly: Contacting pharmacies directly to request price quotes for specific medications can yield valuable information. This approach allows consumers to obtain tailored pricing information.
- Using Insurance Plan Information: Insurance plans often have formularies listing covered medications and their associated costs. Using this information enables consumers to assess the cost of medications within their coverage.
Potential Impact of Consumer Activism on Pharmaceutical Pricing
Consumer activism can significantly influence pharmaceutical pricing. A collective voice can lead to policy changes and increased awareness. A united front can push for fairer pricing and improved access to medications.
Future Trends and Projections
Prescription drug pricing is a complex issue with significant implications for individuals, healthcare systems, and the economy. Predicting future trends requires careful consideration of various factors, including technological advancements, new drug development, and policy changes. Understanding these potential trajectories is crucial for preparing for the challenges and opportunities ahead.
Projected Prescription Drug Price Increases
Forecasting precise price increases for prescription drugs is inherently challenging. Several factors influence these fluctuations, including patent expirations, manufacturing costs, market competition, and government regulations. While precise numbers are elusive, general upward trends are anticipated, especially in specialty medications and those treating complex conditions. Historical trends suggest that price increases often outpace inflation, a pattern that warrants ongoing attention.
This is further complicated by the varying price controls and regulatory environments across different countries.
Impact of Technological Advancements on Drug Pricing
Technological advancements are revolutionizing drug development and delivery. Biotechnology and gene therapies, for example, are poised to deliver highly effective treatments for previously incurable diseases. However, the high upfront research and development costs associated with these breakthroughs can translate into significantly higher prices for patients. The cost of producing and manufacturing new drugs also plays a critical role.
Long-Term Consequences of Unchecked Prescription Drug Inflation
Unchecked prescription drug inflation can lead to substantial financial hardship for individuals and families. Out-of-pocket costs can quickly erode household budgets, potentially leading to delayed or forgone care. This, in turn, can negatively impact public health outcomes and create a more inequitable healthcare system. Increased medication costs also impact the overall affordability and accessibility of healthcare. The long-term implications are far-reaching, impacting individual well-being and societal health.
New Drug Development and Out-of-Pocket Costs
New drug development is essential for treating emerging and existing diseases. The high investment in research and development for these innovative therapies frequently translates into high prices. This poses a significant challenge to patient affordability, necessitating the development of innovative financing strategies. However, the benefits of these new treatments can be immense. In the future, a greater emphasis on the cost-effectiveness of new drugs will likely be required.
Projected Out-of-Pocket Costs (Next 5 Years)
| Drug Class | Projected Out-of-Pocket Cost Increase (Estimated Average) |
|---|---|
| Anti-cancer medications | 10-15% annually |
| Specialty biologics | 8-12% annually |
| Chronic disease medications (e.g., diabetes, hypertension) | 5-8% annually |
| Antibiotics | 3-5% annually |
| Over-the-counter medications | 2-4% annually |
Note
* These are estimated projections, and actual increases may vary. Factors like market competition, regulatory changes, and economic conditions can significantly impact the final figures.
Case Studies
Prescription drug price increases have a significant impact on individuals, households, and healthcare systems. Understanding specific examples of these increases, their impact, and the driving forces behind them is crucial for developing effective policy responses. This section explores several case studies, highlighting the complexities of the pharmaceutical market.
Specific Examples of Price Increases, Out of pocket costs go up when prescription drug prices rise
Significant price increases for certain prescription drugs have drawn considerable attention. These increases often leave patients facing financial hardship and strain healthcare budgets. The examples below illustrate this reality.
- EpiPens: The price of EpiPens, an essential medication for treating severe allergic reactions, experienced substantial increases in recent years. This dramatic rise prompted significant public outcry and legislative scrutiny. The high cost of the drug has been a point of contention in recent years, and patients have voiced their concerns about affordability.
- Daraprim: The 2015 price increase for Daraprim, a drug used to treat parasitic infections, from $13.50 per tablet to $750 per tablet, sparked outrage and prompted a thorough investigation into pharmaceutical pricing practices. This extreme price increase drew considerable attention and criticism, highlighting the need for greater transparency and regulation.
- Heparin: The price of heparin, a blood thinner used to prevent blood clots, has seen considerable fluctuation. These price changes are linked to issues in the manufacturing and supply chain, as well as market pressures. This situation underscores the importance of understanding the various factors that contribute to price volatility in the pharmaceutical market.
Impact on Patients and Healthcare Systems
Price increases for prescription drugs directly impact patients’ ability to afford medications. These increases can lead to significant financial burdens for individuals and families, potentially impacting their overall health and well-being.
- Reduced adherence to medication regimens: Patients may struggle to afford medications, leading to reduced adherence to their prescribed treatment plans. This reduced adherence can result in worse health outcomes and higher healthcare costs in the long run. The inability to afford medications can negatively affect adherence to treatment plans.
- Strain on healthcare budgets: Higher prescription drug costs put a strain on healthcare systems, as insurance companies and government programs face increased expenses. This financial burden can lead to reduced funding for other critical healthcare services.
Reasons Behind Price Increases
Several factors contribute to the rising costs of prescription drugs. These factors often interact and create a complex pricing environment.
- Research and development (R&D) costs: Developing new drugs requires substantial investment in research and development. However, the relationship between R&D costs and drug prices is complex and often debated. A high R&D cost is not the only factor in pricing decisions.
- Patent protection: Patents grant pharmaceutical companies exclusive rights to manufacture and sell their drugs for a specific period, enabling them to recoup their investment. However, the length of patent protection is often linked to pricing strategies.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: Pharmaceutical mergers and acquisitions can result in increased drug prices due to consolidation of market power. Companies may use their increased market share to raise prices to maximize profits.
Pharmaceutical Mergers and Acquisitions
The impact of mergers and acquisitions on prescription drug pricing is significant. These events often lead to price increases due to consolidation of market power and reduced competition.
- Reduced competition: Mergers and acquisitions can lead to fewer competitors in the market, reducing competition and allowing companies to raise prices without facing significant pushback from other companies. This reduced competition allows companies to raise prices without facing the same pressures from competitors.
- Increased bargaining power: Larger companies often have increased bargaining power with insurance companies and government programs, allowing them to negotiate higher prices for their drugs. This increased leverage plays a significant role in pricing decisions.
Case Study Summary
| Drug | Price Increase | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| EpiPens | Significant increase over time | Financial burden on patients, reduced access to necessary medication |
| Daraprim | Extreme price increase | Public outrage, scrutiny of pricing practices |
| Heparin | Fluctuating prices | Challenges in affordability and supply chain reliability |
Final Wrap-Up: Out Of Pocket Costs Go Up When Prescription Drug Prices Rise
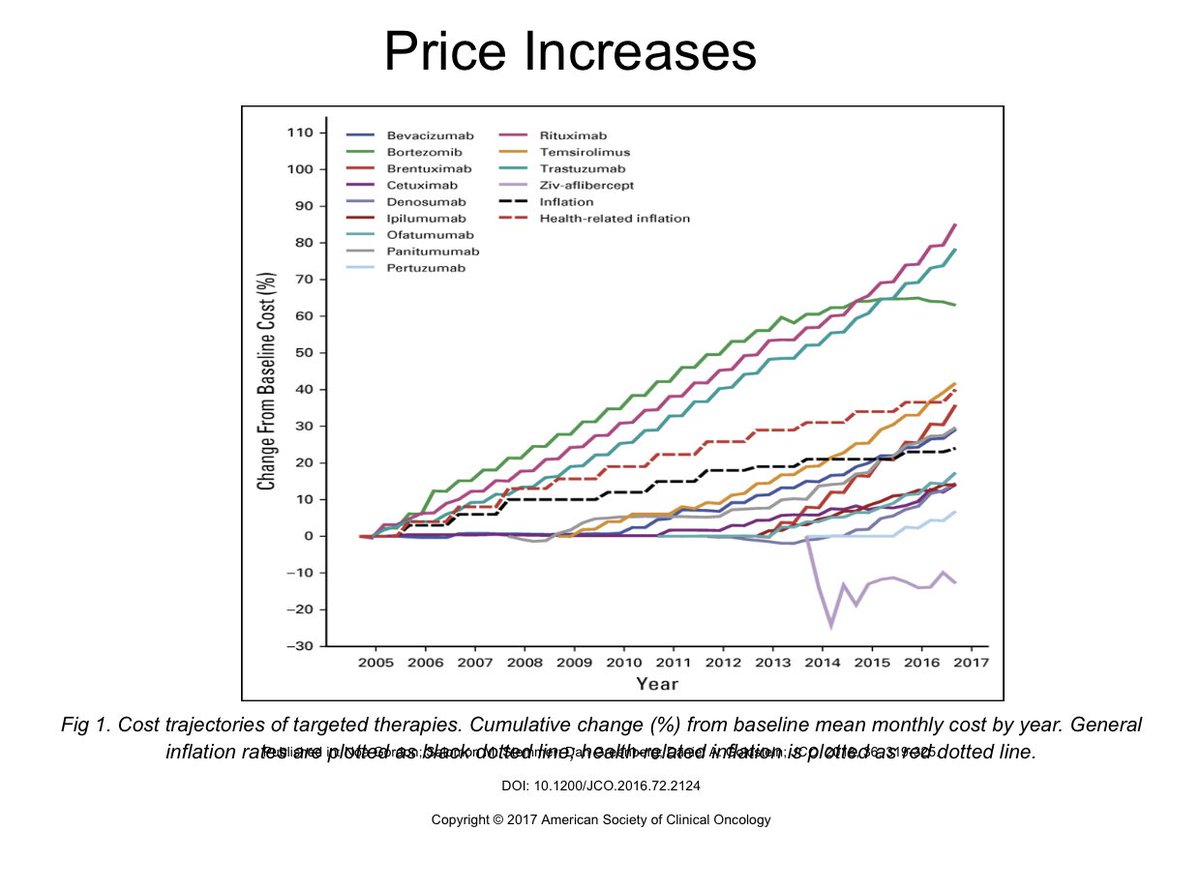
In conclusion, the escalating cost of prescription drugs is a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. The financial strain on individuals and the potential for reduced healthcare utilization demand urgent attention and innovative solutions. Understanding the various contributing factors, including pricing models, government regulations, and pharmaceutical company practices, is critical to developing effective strategies for controlling costs and ensuring access to essential medications for all.
Ultimately, proactive measures are necessary to prevent further escalation and safeguard the health and well-being of patients across all income brackets.