Postpartum anxiety what to know 2 delves into the complexities of this often-overlooked condition. We’ll explore the nuanced differences between normal postpartum mood fluctuations and the more serious symptoms of anxiety. This post aims to equip you with a comprehensive understanding, from identifying potential triggers and symptoms to building a supportive network and effective coping mechanisms.
This in-depth look at postpartum anxiety will provide you with actionable insights into managing this condition, while highlighting the importance of early intervention and seeking professional help when needed.
Understanding Postpartum Anxiety
Navigating the rollercoaster of emotions after childbirth can be challenging. While some mood fluctuations are normal, postpartum anxiety is a distinct condition that requires understanding and support. This article delves into the complexities of postpartum anxiety, exploring its symptoms, triggers, and important distinctions from typical postpartum adjustments. Recognizing the signs and seeking help early are crucial for a healthy recovery.Postpartum anxiety is a significant mental health concern that affects many new mothers.
Postpartum anxiety, what to know 2, often involves persistent worries and fears, different from the initial adjustment period. It’s fascinating how some things in nature, like mosquitoes, apparently remember who swats them and who smells good to them, as research shows. Understanding this kind of learned behavior might offer a parallel in how we approach coping strategies for postpartum anxiety.
It’s a complex topic, and seeking support is key for navigating these challenges.
It’s characterized by persistent and excessive worry, fear, and apprehension about the baby’s well-being, the mother’s ability to care for the infant, or general anxieties related to the transition to motherhood. This anxiety often interferes with daily life, impacting sleep, relationships, and overall well-being.
Symptoms of Postpartum Anxiety
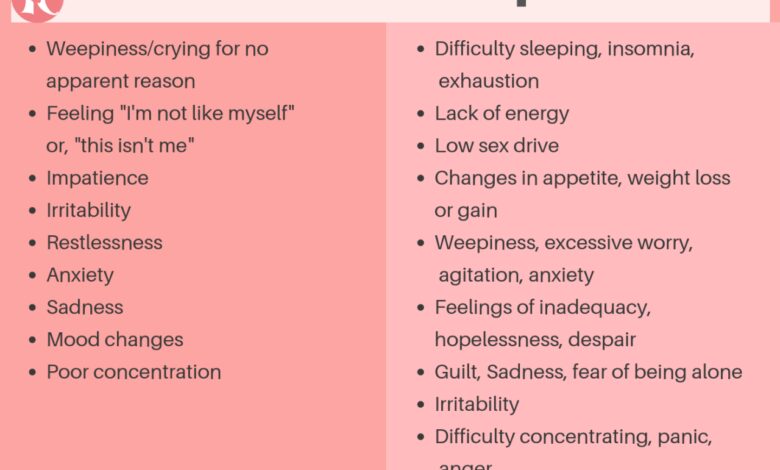
Postpartum anxiety manifests in various ways, and symptoms can vary from person to person. Recognizing these signs is key to seeking help. Common symptoms include excessive worry, irritability, restlessness, difficulty sleeping, and physical symptoms like headaches or stomach aches. Some mothers experience panic attacks, characterized by intense fear, rapid heartbeat, and shortness of breath. These symptoms can significantly impact a new mother’s ability to care for her baby and maintain healthy relationships.
Distinguishing Postpartum Anxiety from Normal Mood Fluctuations
The hormonal shifts after childbirth can lead to a range of emotions. While some fluctuations in mood are normal, postpartum anxiety is distinct. Normal postpartum mood swings tend to be less intense and shorter-lived, often linked to specific triggers like lack of sleep or changes in routine. Postpartum anxiety, however, involves persistent and overwhelming worry that significantly disrupts daily functioning.
Potential Triggers for Postpartum Anxiety
Numerous factors can contribute to postpartum anxiety. These triggers can be biological, psychological, or environmental. A significant contributing factor is hormonal changes, as fluctuating levels of hormones like estrogen and progesterone can affect mood. Additionally, pre-existing mental health conditions, such as anxiety or depression, can increase the risk of postpartum anxiety. Other triggers include stressful life events, relationship difficulties, financial strain, and a lack of social support.
Types of Postpartum Anxiety (If Any)
Postpartum anxiety is not categorized into specific types, but it can manifest in varying intensities and expressions. While not classified as different types, some mothers might experience a heightened level of anxiety centered around specific concerns, such as the baby’s health or their ability to be a good mother. A mother might have severe anxiety related to feeding or sleeping issues, for example.
The focus of the anxiety, while not a specific type, is still an important factor in understanding and addressing the condition.
Common Misconceptions about Postpartum Anxiety
Several misconceptions surround postpartum anxiety. One common misconception is that it’s a sign of weakness or a lack of maternal instincts. This is simply not true. Postpartum anxiety is a real medical condition that requires professional help. Another misconception is that it only affects mothers who have experienced a difficult pregnancy or delivery.
While these factors can contribute, postpartum anxiety can affect mothers of all backgrounds and experiences. It’s essential to understand that postpartum anxiety is a treatable condition, and seeking help is a sign of strength.
Importance of Early Detection and Intervention
Early detection and intervention are crucial for effective management of postpartum anxiety. Prompt intervention can help reduce the severity of symptoms and improve long-term outcomes. Seeking help from a healthcare professional as soon as concerns arise is vital. Symptoms may be subtle at first, but they can escalate rapidly if left unaddressed. The earlier professional help is sought, the better the chance of a swift and successful recovery.
Identifying Symptoms
Navigating the postpartum period is a journey filled with profound physical and emotional changes. Understanding the potential symptoms of postpartum anxiety is crucial for early intervention and support. Recognizing these signs, both subtle and overt, empowers individuals to seek help and embark on a path toward healing and well-being.Postpartum anxiety is not simply “baby blues”; it’s a distinct condition requiring professional attention.
Identifying its symptoms is the first step toward effective management and recovery.
Physical Symptoms of Postpartum Anxiety
Early identification of physical symptoms is vital for timely intervention. These symptoms, though often subtle, can significantly impact a new parent’s well-being.
| Symptom | Description | Subtle Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Rapid Heart Rate | A noticeably elevated heart rate, even without significant exertion. | Increased heart rate while resting or performing simple tasks. |
| Muscle Tension | Chronic muscle tension, particularly in the neck, shoulders, or back. | Frequent or persistent neck pain, shoulder pain, or back pain. Difficulty relaxing. |
| Sleep Disturbances | Difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing restless sleep. | Waking up frequently during the night, feeling exhausted despite sufficient sleep, or experiencing vivid nightmares. |
| Gastrointestinal Issues | Stomach aches, nausea, diarrhea, or constipation. | Changes in bowel habits or persistent stomach discomfort. |
| Headaches | Frequent or intense headaches. | Tension headaches, migraines, or other types of recurring headaches. |
Emotional Symptoms of Postpartum Anxiety
Emotional symptoms are often intertwined with physical discomfort. These symptoms can vary significantly from person to person, making recognition even more crucial.
| Symptom | Description | Subtle Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Excessive Worry | Constant or overwhelming worry about the baby’s well-being, health, or safety. | Intrusive thoughts about potential harm or danger. Overthinking everyday scenarios. |
| Irritability and Anger | Feeling easily irritated or experiencing outbursts of anger. | Frequent mood swings, heightened sensitivity to minor events, or feeling easily frustrated. |
| Fear and Panic | Experiencing sudden feelings of fear or panic. | Racing thoughts, difficulty concentrating, or feeling overwhelmed. |
| Difficulty Concentrating | Inability to focus on tasks or maintain attention. | Feeling mentally scattered, easily distracted, or experiencing mental fog. |
| Sadness or Hopelessness | Persistent feelings of sadness or hopelessness. | Loss of interest in activities, withdrawal from loved ones, or feeling emotionally numb. |
Behavioral Changes Suggesting Postpartum Anxiety
Recognizing behavioral shifts is essential in identifying postpartum anxiety. These changes often manifest as subtle adjustments in daily routines and interactions.
- Withdrawal from social interactions: A noticeable decrease in engagement with friends, family, or support networks.
- Increased avoidance of certain situations: A reluctance to leave the home, or participate in activities previously enjoyed.
- Difficulty managing daily tasks: Struggling with household chores, childcare, or personal hygiene.
- Excessive reassurance seeking: Constantly needing confirmation from others about the baby’s well-being.
- Difficulty sleeping: A significant disruption in sleep patterns, leading to fatigue and exhaustion.
Comparing Postpartum Anxiety and Postpartum Depression
Differentiating between postpartum anxiety and postpartum depression is crucial for appropriate treatment.
| Characteristic | Postpartum Anxiety | Postpartum Depression |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Symptom | Excessive worry, fear, and apprehension. | Persistent sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest. |
| Emotional State | Often characterized by nervousness, irritability, and panic. | Typically marked by feelings of worthlessness, guilt, and despair. |
| Sleep Patterns | Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. | Difficulty sleeping, excessive sleeping, or a combination of both. |
| Appetite | Potentially affected, but not typically a primary symptom. | Significant changes in appetite (either increased or decreased). |
Warning Signs for Escalation of Symptoms
Monitoring for escalating symptoms is vital. Uncontrolled anxiety can have serious consequences.
- Increased frequency and intensity of panic attacks: Panic attacks becoming more frequent or more severe.
- Thoughts of self-harm or harm to the baby: Thoughts of harming oneself or the child.
- Inability to cope with daily tasks: Complete inability to perform basic daily tasks.
- Withdrawal from support systems: Complete withdrawal from family, friends, or support groups.
- Inability to function: Inability to carry out everyday tasks.
Seeking Professional Help
When symptoms worsen, seeking professional help is crucial. A healthcare provider can offer a proper diagnosis and develop a personalized treatment plan.
Seeking professional help is a sign of strength, not weakness. Early intervention is key to managing postpartum anxiety effectively.
Risk Factors and Prevention

Understanding the potential risk factors for postpartum anxiety is crucial for proactive prevention and early intervention. Identifying these factors can empower individuals to take steps towards reducing their vulnerability and building resilience. This knowledge allows for targeted support and resources, fostering a healthier transition into parenthood.Postpartum anxiety, like other forms of anxiety, isn’t simply a matter of willpower or coping mechanisms.
It’s a complex interplay of biological, psychological, and social factors. Recognizing these factors can help us move beyond blaming the individual and towards creating supportive environments that promote mental well-being.
Potential Risk Factors
Various factors can increase the likelihood of developing postpartum anxiety. These range from pre-existing conditions to the unique challenges of the postpartum period. Acknowledging these risk factors allows for early identification and targeted interventions.
- Pre-existing mental health conditions: A history of anxiety disorders, depression, or other mental health challenges significantly increases the risk of postpartum anxiety. For example, someone with a history of generalized anxiety disorder may be more susceptible to developing postpartum anxiety due to the stress and hormonal changes of pregnancy and childbirth.
- Stressful life events: Major life stressors, such as financial difficulties, relationship problems, or job loss, can contribute to anxiety during the postpartum period. The added stress of caring for a newborn can exacerbate existing anxieties, making it challenging to cope.
- Complications during pregnancy or childbirth: Experiences such as preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, or a difficult delivery can significantly impact mental well-being and increase the risk of anxiety. For instance, a woman who experiences a prolonged or complicated labor may experience increased stress hormones, which can heighten anxiety.
- Lack of social support: Limited social support networks and a lack of emotional or practical assistance from family and friends can contribute to increased stress and anxiety during this time. The lack of a supportive network can lead to feelings of isolation and overwhelm.
Preventive Measures and Strategies
Taking proactive steps to reduce the likelihood of developing postpartum anxiety is crucial. These measures focus on building resilience and creating a supportive environment.
- Prioritizing mental health during pregnancy: Establishing a routine for self-care, including regular exercise, mindfulness practices, and stress-reducing activities, can help build coping mechanisms for the postpartum period. For example, attending prenatal yoga classes can help manage stress and promote relaxation techniques that can be beneficial post-delivery.
- Building a strong support system: Cultivating a network of trusted family members, friends, or support groups can provide emotional and practical assistance during the postpartum period. Having a network of individuals to lean on for emotional support and practical help is crucial for navigating the challenges of this period.
- Seeking professional help: Talking to a therapist or counselor during pregnancy or after delivery can help identify and address potential risk factors and develop coping strategies for anxiety. Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes and prevent the development of more severe anxiety.
- Managing lifestyle factors: Adequate sleep, a balanced diet, and regular exercise are vital for maintaining overall well-being and managing stress. For instance, establishing a sleep schedule and incorporating regular walks into the daily routine can significantly reduce stress and promote mental health.
Lifestyle Factors in Managing Anxiety
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle plays a critical role in managing anxiety during pregnancy and postpartum. The impact of sleep, diet, and exercise on mental well-being cannot be underestimated.
- Sleep: Prioritizing sufficient sleep is essential for managing stress and maintaining emotional stability. Aiming for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night can significantly improve mood and reduce anxiety.
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide essential nutrients to support overall well-being. Maintaining a healthy diet is important for supporting the body’s physical and mental health.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can help reduce stress, improve mood, and promote relaxation. Incorporating even moderate exercise into the daily routine can help reduce stress and promote overall well-being.
Importance of Social Support Systems
Strong social support networks provide crucial emotional and practical assistance during pregnancy and the postpartum period. A supportive environment can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing anxiety.
- Family and friends: Encouraging open communication with family and friends about concerns and anxieties can help foster a supportive environment. Talking to family and friends about feelings and concerns can significantly reduce feelings of isolation and provide valuable support.
- Support groups: Connecting with other parents experiencing similar challenges can provide a sense of community and shared understanding. Joining a support group can offer valuable insights and strategies from other parents who are facing similar experiences.
Coping Mechanisms
Developing healthy coping mechanisms is vital for managing stress during pregnancy and postpartum. These techniques can help individuals navigate the challenges of this period effectively.
- Mindfulness and relaxation techniques: Practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques can help manage stress and promote emotional regulation. Mindfulness practices can help reduce stress and promote emotional regulation.
- Stress management strategies: Employing stress-reducing techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or progressive muscle relaxation, can effectively manage stress. These techniques can help reduce stress levels and promote emotional regulation.
- Setting boundaries: Establishing clear boundaries with family, friends, and others can help manage expectations and prevent overwhelm. Setting boundaries can help to manage expectations and prevent feelings of being overwhelmed.
Seeking Help and Support
Navigating postpartum anxiety can feel isolating, but remember you’re not alone. Reaching out for help is a sign of strength, not weakness, and it’s crucial for your well-being and the well-being of your baby. This section details the resources available and the process of seeking professional support.Understanding that postpartum anxiety is a treatable condition is the first step toward recovery.
Many women experience these feelings, and seeking professional help is a vital part of the healing journey. It’s important to remember that early intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
Resources Available for Individuals
A variety of resources are available to provide support and guidance during this challenging time. These resources can offer crucial information, practical strategies, and a sense of community. Your primary care physician is an important initial point of contact.
- Support Groups: Postpartum support groups offer a safe space to connect with other mothers experiencing similar challenges. Sharing experiences and coping strategies with others who understand can be incredibly beneficial. These groups often provide a sense of community and validation.
- Online Forums and Communities: Online platforms dedicated to postpartum mental health can offer valuable support and resources. These platforms often allow for anonymous interaction and the sharing of experiences. However, it is crucial to remember that online support should not replace professional care.
- Local Organizations: Many local organizations offer support services specifically for mothers and families. These organizations can provide information on resources, referrals to therapists, and support groups in your area.
Support Groups and Their Potential Benefits
Support groups provide a vital network of understanding and shared experiences. These groups can offer a sense of belonging, emotional validation, and practical advice from mothers who have been through similar struggles. Connecting with others facing similar challenges can reduce feelings of isolation and offer encouragement during challenging times. For example, women may discover coping strategies, share insights into their experiences, and gain a sense of hope.
Professionals Who Can Offer Support
A multidisciplinary approach often yields the best results in managing postpartum anxiety. These professionals can provide a range of support, from diagnosis and treatment to guidance and emotional support.
- Therapists: Licensed therapists specializing in perinatal mental health can provide individual therapy to address the root causes of anxiety, develop coping mechanisms, and address any underlying emotional issues.
- Psychiatrists: Psychiatrists can diagnose postpartum anxiety and prescribe medication if deemed necessary. They are medical doctors with specialized training in mental health.
- Obstetricians/Gynecologists (OB/GYNs): OB/GYNs are crucial in providing initial screenings and referrals for mental health support.
- Counsellors: Counselors can offer support, guidance, and coping strategies for managing postpartum anxiety. They often provide a safe space for emotional processing and problem-solving.
Process of Seeking Professional Help
The process of seeking professional help is crucial for effective management of postpartum anxiety. Open communication with your healthcare provider is essential for a successful outcome. Firstly, discussing your concerns and symptoms is the first step. Following this, a comprehensive evaluation can be performed to understand the nature of your anxiety and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
- Initial Consultation: During the initial consultation, your therapist will assess your symptoms, medical history, and personal circumstances to determine the best course of action.
- Diagnosis and Treatment Plan: Based on the assessment, a diagnosis can be made, and a tailored treatment plan will be developed. This may include therapy, medication, or a combination of both.
- Ongoing Support: Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor progress, adjust the treatment plan as needed, and address any emerging concerns.
Treatment Options for Postpartum Anxiety
Several treatment options are available for postpartum anxiety. A combination of approaches often yields the most effective results. The choice of treatment depends on individual needs and preferences.
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Therapy (e.g., Cognitive Behavioral Therapy – CBT) | CBT helps identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors contributing to anxiety. It equips individuals with coping mechanisms and strategies to manage anxiety-provoking situations. |
| Medication (e.g., Antidepressants) | In some cases, medication may be necessary to manage the symptoms of postpartum anxiety. Antidepressants, under a doctor’s supervision, can help regulate neurochemicals in the brain, reducing anxiety levels. |
| Support Groups | Connecting with other mothers experiencing similar challenges can offer emotional support, practical advice, and a sense of community. |
Managing Postpartum Anxiety

Navigating the emotional landscape of the postpartum period can be challenging, especially when anxiety symptoms arise. This stage often brings a whirlwind of hormonal fluctuations, sleep deprivation, and the overwhelming responsibility of caring for a newborn. Understanding how to manage these anxieties is crucial for both the mother’s well-being and the child’s development.Effective management of postpartum anxiety requires a multifaceted approach, combining self-care strategies, therapeutic interventions, and strong support networks.
By incorporating relaxation techniques, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and fostering strong connections, mothers can navigate these challenges with greater ease and resilience.
Self-Care Strategies for Managing Anxiety Symptoms
Managing postpartum anxiety often begins with prioritizing self-care. These strategies are essential tools for mitigating anxiety and promoting overall well-being.
- Prioritizing sleep is paramount. Even short periods of rest can significantly reduce anxiety. Establish a consistent sleep schedule, even if it means taking naps when the baby naps, and create a calming bedtime routine for yourself.
- Nourishing your body with a balanced diet is essential. A nutritious diet supports physical and mental health. Include foods rich in vitamins and minerals, and limit processed foods, caffeine, and excessive sugar.
- Engaging in regular physical activity, even if it’s just a short walk, can release endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects. Find activities you enjoy and make them part of your routine.
- Taking breaks and setting boundaries is vital. Learn to say “no” to requests that overwhelm you. Don’t hesitate to ask for help with household tasks or childcare.
The Role of Relaxation Techniques and Mindfulness Practices
Mindfulness and relaxation techniques can significantly reduce anxiety symptoms. They provide tools to manage stress and promote emotional regulation.
Navigating postpartum anxiety can be tough, and understanding the different factors involved is key. While postpartum anxiety, what to know 2, focuses on specific coping strategies and resources, it’s important to consider the broader societal implications. For example, the potential ramifications of a Supreme Court decision on Roe v Wade could significantly impact women’s health choices, including access to reproductive healthcare, which in turn could exacerbate the challenges of postpartum anxiety and other mental health concerns.
Ultimately, support systems and resources for postpartum anxiety need to be readily available and accessible regardless of these external factors. what could happen in the u s if roe v wade is overturned
- Mindfulness practices, such as deep breathing exercises and meditation, help to focus on the present moment and reduce racing thoughts. Regular practice can cultivate a sense of calm and awareness.
- Progressive muscle relaxation involves systematically tensing and relaxing different muscle groups. This technique helps to release physical tension associated with anxiety.
- Yoga and tai chi combine physical postures, breathing techniques, and mindfulness, promoting both physical and mental well-being. These practices can be particularly helpful for managing stress and anxiety.
Importance of Healthy Lifestyle Choices for Overall Well-being
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is fundamental to managing postpartum anxiety. These choices impact both physical and mental health.
- Adequate hydration is crucial. Dehydration can exacerbate anxiety symptoms. Carry a water bottle and sip water throughout the day.
- Regular exposure to sunlight can help regulate mood and sleep patterns. Aim for at least 15-30 minutes of sunlight daily.
- Avoiding excessive screen time before bed can improve sleep quality, which is vital for managing anxiety.
Significance of Maintaining a Support Network
A strong support network is crucial for navigating postpartum anxiety. Having people to confide in and rely on can significantly reduce feelings of isolation and overwhelm.
Postpartum anxiety, what to know 2, often involves a complex interplay of physical and emotional factors. While research continues to shed light on these nuances, it’s fascinating to see how advancements in other fields, like gene therapy for cancer, are also generating cautious optimism. Gene therapy for cancer welcomed with reservations highlights the careful consideration needed when introducing new treatments.
Ultimately, understanding postpartum anxiety requires a multifaceted approach, considering both the individual and the broader societal context.
- Connecting with other mothers who have experienced similar challenges can provide valuable emotional support and practical advice.
- Talking to a trusted friend, family member, or therapist about your concerns can alleviate feelings of isolation and provide a safe space to express your emotions.
- Seeking professional help, such as therapy or counseling, can provide specialized support and guidance for managing anxiety.
Importance of Ongoing Support and Follow-up Care
Postpartum anxiety is often a temporary condition, but ongoing support and follow-up care are vital for a full recovery. These factors contribute to long-term well-being.
- Regular check-ins with your healthcare provider are important to monitor your progress and adjust treatment strategies as needed.
- Continuing therapy or counseling sessions can provide ongoing support and coping mechanisms for managing anxiety.
- Maintaining a strong support network and continuing to connect with others experiencing similar challenges can promote long-term recovery and resilience.
Building a Support System
Navigating postpartum anxiety can feel isolating, but you’re not alone. A strong support system is crucial for managing the challenges and fostering recovery. Building this network involves open communication, understanding the role of your loved ones, and actively seeking help when needed. This support system can be a lifeline during difficult times, providing encouragement, practical assistance, and a sense of belonging.A robust support network can make a significant difference in coping with postpartum anxiety.
This network extends beyond romantic partners and includes family, friends, and even professional support. Open communication and clear boundaries are key to fostering a supportive environment where you feel comfortable expressing your needs and anxieties.
Importance of Open Communication
Effective communication is vital in building a support system. Sharing your experiences with loved ones fosters understanding and empathy. It’s essential to express your feelings honestly and directly, rather than bottling them up. Avoid assuming your partner or family members understand your struggles without explicitly articulating them.
Examples of Effective Communication
“I’m feeling overwhelmed lately, and I’m worried about my ability to manage everything. Could we talk about ways we can share responsibilities?” is a direct and clear way to communicate your needs. Another approach is to be specific: “I’ve been having trouble sleeping and it’s making me feel anxious. Would you be willing to help with [childcare task] so I can get some rest?”
Role of Family and Friends
Family and friends play a critical role in providing emotional support. Their presence and understanding can significantly ease the burden of postpartum anxiety. Offering practical assistance, like helping with household chores or childcare, can be a huge relief. Listening without judgment and validating your feelings are equally important. Avoid offering unsolicited advice or minimizing your experiences.
Building Your Support System
| Category | Actions |
|---|---|
| Partner | Establish clear communication channels, schedule dedicated time for discussions, and identify shared responsibilities. |
| Family | Share your concerns with trusted family members, request specific help (e.g., grocery shopping, meal preparation), and openly discuss expectations. |
| Friends | Reach out to close friends for emotional support, arrange social activities, and schedule regular check-ins. |
| Support Groups | Join online or in-person support groups to connect with others experiencing similar challenges, share experiences, and gain valuable insights. |
| Professionals | Seek guidance from therapists or counselors specializing in postpartum mental health, discuss treatment options, and actively participate in therapy sessions. |
Potential Barriers and How to Overcome Them
Feeling ashamed or embarrassed about your struggles can prevent you from seeking support. Acknowledging these feelings as common and understandable is the first step. Remember that reaching out is a sign of strength, not weakness. If you’re worried about burdening your loved ones, focus on clearly articulating your needs and offering specific ways they can help. This can ease their concerns and demonstrate that you’re not expecting them to solve all your problems.
Don’t hesitate to set boundaries and let people know what you can and cannot handle.
Coping Mechanisms
Navigating postpartum anxiety can feel overwhelming, but understanding coping mechanisms can empower you to manage triggers and build resilience. These strategies are not a one-size-fits-all solution, and what works for one person may not work for another. Experiment with different techniques to find what resonates best with you and your unique situation. Remember, seeking professional support is crucial, and these coping mechanisms are meant to supplement, not replace, professional guidance.Effective coping mechanisms for postpartum anxiety involve a multifaceted approach.
This includes recognizing and managing stress, employing relaxation techniques, and actively challenging negative thought patterns. These strategies aim to foster a sense of calm and control, allowing you to navigate the challenges of this period with greater ease.
Managing Anxiety Triggers
Identifying and understanding your personal anxiety triggers is essential for developing effective coping strategies. Common triggers may include sleep deprivation, changes in your body image, or feelings of inadequacy. Keeping a journal to track your triggers and reactions can provide valuable insights into your patterns and help you anticipate potential challenges.
- Recognize and acknowledge your triggers. Understanding what situations or emotions tend to escalate your anxiety is the first step. Be patient and kind to yourself as you identify these patterns. It’s a process, not a destination.
- Develop a plan for coping with triggers. Having pre-planned responses for common anxiety triggers can reduce their impact. For example, if feeling overwhelmed, practicing deep breathing exercises or calling a trusted friend for support can be beneficial.
- Create a safe space. Designate a quiet, comfortable space in your home where you can retreat when feeling overwhelmed. This space can be a physical or mental sanctuary. Filling it with calming elements like soft lighting and calming scents can enhance its effectiveness.
Managing Stress and Overwhelming Feelings
Effective stress management is crucial for navigating postpartum anxiety. Techniques like deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness meditation can be highly effective.
- Deep breathing exercises. These simple exercises can help calm your nervous system by slowing your heart rate and reducing feelings of panic. Focus on slow, deep breaths, inhaling deeply through your nose and exhaling slowly through your mouth. Practice these exercises regularly, even when you don’t feel anxious.
- Progressive muscle relaxation. This technique involves tensing and releasing different muscle groups in your body. This process helps to release physical tension that often accompanies anxiety.
- Mindfulness meditation. This practice involves focusing on the present moment without judgment. By focusing on your breath, thoughts, and sensations, you can become more aware of your anxious feelings and develop techniques to manage them.
Relaxation Exercises and Mindfulness Practices
Relaxation and mindfulness practices are powerful tools for managing anxiety. Regular practice can significantly reduce anxiety levels and improve overall well-being.
| Exercise | Description |
|---|---|
| Deep Breathing | Inhale slowly through your nose, hold for a few seconds, and exhale slowly through your mouth. Repeat several times. |
| Progressive Muscle Relaxation | Tighten and release different muscle groups in your body, starting from your toes and working your way up. |
| Mindful Walking | Pay attention to the sensations in your body as you walk, noticing the ground beneath your feet and the movement of your limbs. |
| Mindful Eating | Pay attention to the taste, texture, and smell of your food. Savor each bite and appreciate the experience. |
Identifying and Challenging Negative Thought Patterns
Negative thought patterns can exacerbate anxiety. Identifying and challenging these patterns is crucial for managing anxiety. Cognitive restructuring techniques can be effective in replacing negative thoughts with more balanced and realistic ones.
- Identify negative thoughts. Become aware of the automatic negative thoughts that arise during anxious moments. Write them down to gain a clearer perspective.
- Evaluate the evidence. Assess the validity of these thoughts. Are they based on facts or assumptions? What evidence supports or contradicts them?
- Challenge the thoughts. Replace negative thoughts with more realistic and balanced perspectives. Consider alternative explanations or interpretations.
Relaxation and Well-being Activities
Engaging in activities that promote relaxation and well-being can be an important part of managing postpartum anxiety. Activities that encourage creativity, connection, and self-care are beneficial.
- Engage in hobbies. Pursue activities that bring you joy and relaxation, such as reading, listening to music, painting, or gardening. These activities can provide a welcome distraction from anxious thoughts.
- Spend time in nature. Connecting with nature can have a calming effect. Try going for a walk in a park, sitting by a lake, or simply spending time outdoors.
- Practice self-care. Prioritize activities that nourish your mind, body, and spirit. This could include taking a warm bath, getting a massage, or simply enjoying a quiet cup of tea.
Long-Term Well-being
Overcoming postpartum anxiety isn’t a sprint; it’s a marathon. While active treatment and support during the immediate postpartum period are crucial, maintaining long-term well-being requires ongoing effort and a proactive approach. This phase focuses on building resilience, fostering healthy habits, and integrating coping mechanisms into daily life to prevent future episodes and ensure a fulfilling life beyond the initial challenges.Successfully navigating the long-term effects of postpartum anxiety often requires a holistic strategy that integrates mental health support, self-care, and practical lifestyle adjustments.
This involves understanding the lingering impact of the condition, developing sustainable coping mechanisms, and nurturing a supportive environment. By addressing these factors, individuals can build a strong foundation for long-term well-being.
Strategies for Maintaining Mental Well-being, Postpartum anxiety what to know 2
Sustaining mental well-being after postpartum anxiety necessitates a multifaceted approach that encompasses self-care, support networks, and ongoing professional guidance. Consistent self-care practices are essential for managing stress and preventing relapse. These strategies, when integrated into daily routines, can build resilience and promote overall mental health.
- Prioritize self-care activities, such as engaging in hobbies, exercising regularly, and maintaining a balanced diet. These practices foster a sense of normalcy and help manage stress, crucial in preventing future anxiety episodes. For example, dedicating 30 minutes daily for reading or a short walk can significantly contribute to mental well-being.
- Establish a strong support network. This includes connecting with family, friends, or support groups who understand the unique challenges of postpartum life. Shared experiences and empathetic listening can offer invaluable emotional support. Seeking help from a trusted friend or family member is often the first step towards recovery.
- Regular mindfulness and relaxation techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, can effectively manage stress and anxiety levels. Practicing these techniques can be a powerful tool in managing the day-to-day challenges of motherhood.
Importance of Continued Self-Care and Support
Consistent self-care and a supportive environment are paramount for long-term recovery and preventing future anxiety episodes. They provide a foundation for resilience and a buffer against stress. The ongoing support system is vital in helping individuals navigate life’s challenges with greater ease and confidence.
- Self-care isn’t selfish; it’s essential. Taking time for oneself, even if it’s just 15 minutes, allows for a much-needed respite and helps in managing stress. Examples of self-care activities can include taking a warm bath, listening to music, or engaging in a hobby.
- Maintaining a support system, whether through family, friends, or professional support groups, is vital for emotional well-being. These connections provide understanding, encouragement, and a sense of belonging.
Role of Ongoing Therapy and Support Groups
Ongoing therapy and support groups play a vital role in long-term recovery from postpartum anxiety. They provide a safe space for processing emotions, developing coping strategies, and fostering a sense of community.
- Continuing therapy allows for addressing underlying issues, fine-tuning coping mechanisms, and adjusting strategies as needed. This sustained support is invaluable in preventing future anxiety episodes.
- Support groups provide a platform for sharing experiences and receiving encouragement from others facing similar challenges. These groups offer a sense of community and validation, which is critical for maintaining mental well-being.
Integrating Coping Strategies into Daily Life
Incorporating coping strategies into daily life is crucial for long-term management of postpartum anxiety. This proactive approach helps in managing stress and building resilience.
- Identifying triggers and developing strategies to manage them is a vital step. For instance, recognizing that overwhelming schedules can lead to anxiety allows for proactive planning and delegation.
- Creating a structured routine, including designated time for self-care and relaxation, helps in maintaining a sense of control and stability. Consistency is key in reducing anxiety levels.
Long-Term Impact of Postpartum Anxiety and Strategies for Recovery
Postpartum anxiety can have lasting effects, but recovery is possible. Addressing the underlying causes, developing coping mechanisms, and seeking ongoing support are key strategies.
- The long-term impact of postpartum anxiety can include difficulties with relationships, work performance, and overall well-being. However, with the right support and strategies, individuals can navigate these challenges effectively.
- Proactive strategies, including maintaining open communication with partners and seeking professional help when needed, are crucial in fostering recovery.
Last Point: Postpartum Anxiety What To Know 2
In conclusion, navigating postpartum anxiety requires a multi-faceted approach. By understanding the various factors contributing to anxiety, recognizing the symptoms, and building a robust support system, individuals can effectively manage their well-being and work towards long-term recovery. Remember, you’re not alone, and help is available. This post is intended to be a starting point for learning more and connecting with the resources you need.