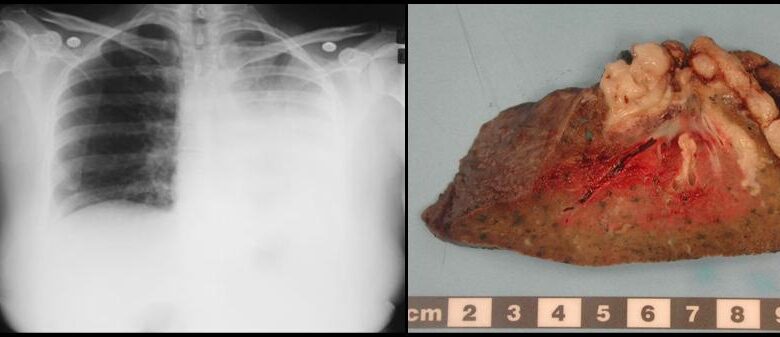
Pulmonary aspergillosis allergic bronchopulmonary type (ABPA) is a complex lung condition that requires careful understanding. This blog post delves into the intricacies of ABPA, exploring its presentation, diagnostic methods, treatment strategies, potential complications, and future research directions. We’ll uncover the immunological mechanisms driving ABPA and provide a comparative analysis to other forms of aspergillosis.
ABPA, characterized by allergic reactions to Aspergillus fungus, can lead to chronic lung inflammation and damage. Understanding the different aspects of this condition, from its initial presentation to long-term management, is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals. We’ll use tables and flowcharts to visualize key information and aid comprehension.
Introduction to Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA)
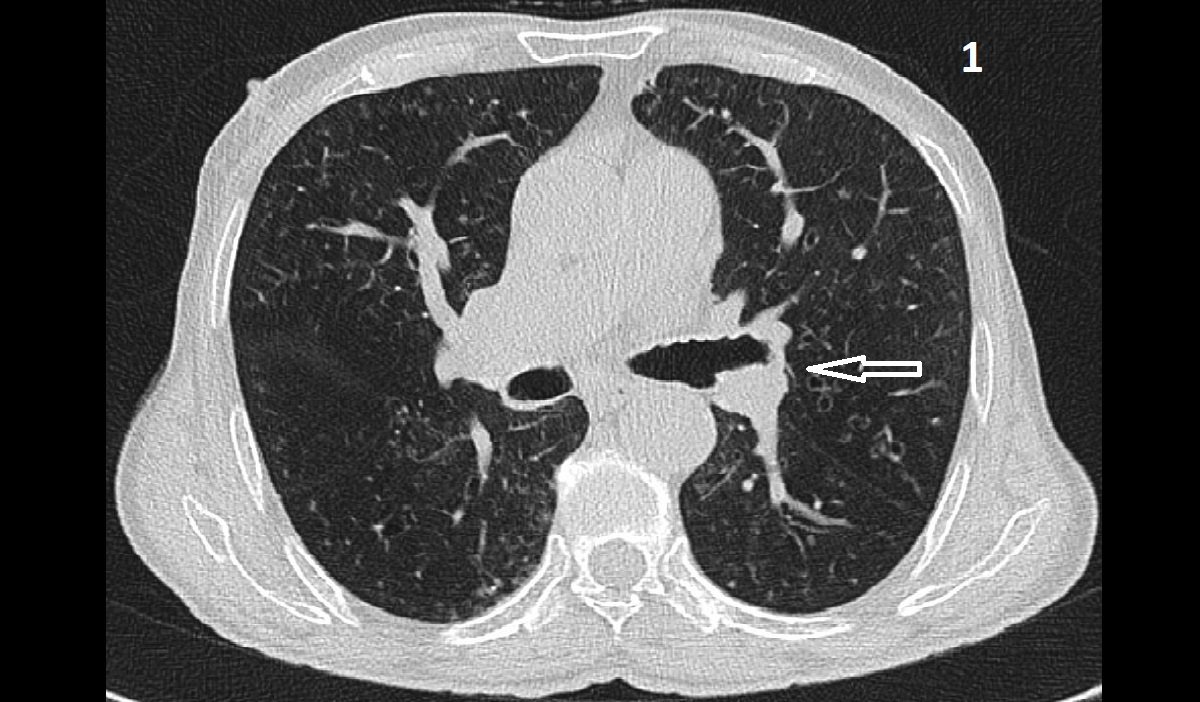
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) is a complex allergic lung disease that primarily affects individuals with pre-existing asthma or cystic fibrosis. It’s characterized by an exaggerated immune response to the presence ofAspergillus fumigatus*, a common fungus, leading to inflammation and damage within the airways. This immune reaction, rather than a direct infection, is the driving force behind the disease.ABPA typically presents with a chronic, fluctuating course, often marked by periods of exacerbations and remissions.
Symptoms can range from mild to severe, and the severity can vary considerably among patients. Understanding the immunological mechanisms and clinical manifestations is crucial for effective diagnosis and management.
Typical Presentation of ABPA, Pulmonary aspergillosis allergic bronchopulmonary type
ABPA often begins insidiously, with symptoms mimicking those of asthma or other respiratory illnesses. Initial presentations might include wheezing, cough, and shortness of breath. Over time, these symptoms can worsen and become more frequent, with exacerbations often triggered by environmental factors or infections. Patients may also experience chest tightness, fever, and fatigue. A key characteristic of ABPA is the development of bronchiectasis, a chronic dilation of the airways, which can contribute to persistent symptoms.
Immunological Mechanisms of ABPA
The development of ABPA is a complex interplay of immunological factors. The immune system of individuals with ABPA reacts abnormally to
Pulmonary aspergillosis, the allergic bronchopulmonary type, can be a real challenge to manage. Fortunately, research into new treatments for various conditions is ongoing, like this exciting new device that could make treatment easier for early stage breast cancer new device could make treatment easier for early stage breast cancer. While this new development is promising, it’s crucial to remember that effective management of pulmonary aspergillosis still relies on a multi-faceted approach, including medication and lifestyle adjustments.
- Aspergillus fumigatus* antigens, leading to a Th2-mediated response. This involves the overproduction of immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies specific to
- Aspergillus* antigens. The resulting inflammatory response involves eosinophils, neutrophils, and other immune cells, leading to airway inflammation and damage. The presence of pre-existing lung conditions, such as asthma or cystic fibrosis, likely plays a role in the susceptibility to developing ABPA.
Clinical Features of ABPA
| Feature | Description | Severity | Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | Wheezing, cough, shortness of breath, chest tightness, hemoptysis, fever, fatigue | Mild to severe, fluctuating | Bronchodilators, corticosteroids, antifungal therapy, and monitoring |
| Imaging | Bronchiectasis, patchy infiltrates on chest X-rays or CT scans | Variable | Imaging helps assess disease extent and response to treatment. |
| Laboratory Findings | Elevated IgE levels, eosinophilia, positive Aspergillus precipitins or skin tests | Often elevated | These markers help confirm the diagnosis. |
| Lung Function Tests | Reduced lung function, especially FEV1 and FVC | Variable | Tracking lung function is essential to monitor disease progression and response to treatment. |
Differential Diagnosis of Aspergillosis
| Feature | ABPA | Invasive Aspergillosis | Allergic Fungal Sinusitis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Underlying Condition | Asthma, cystic fibrosis | Compromised immune system | Nasal or sinus inflammation |
| Presentation | Chronic, fluctuating respiratory symptoms | Rapidly progressive, potentially life-threatening | Sinus symptoms, nasal polyps |
| Immunological Response | Th2-mediated hypersensitivity | Direct invasion and tissue damage | Allergic response to fungi in sinuses |
| Treatment | Antifungal therapy, corticosteroids | Aggressive antifungal therapy, supportive care | Corticosteroids, antifungals, surgery |
Diagnostic Criteria and Methods
Diagnosing allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) can be challenging, as its symptoms often overlap with other lung conditions. Accurate diagnosis hinges on a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. A comprehensive approach, considering the patient’s history, physical examination, and supporting evidence, is crucial for proper management.
Key Laboratory Findings
The diagnosis of ABPA relies heavily on laboratory findings that reveal the presence of an allergic response to
- Aspergillus* and the resulting inflammatory process in the lungs. Elevated immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels, particularly specific IgE to
- Aspergillus*, are frequently observed. This indicates an allergic sensitization. Furthermore, elevated eosinophil counts, a type of white blood cell associated with allergic reactions, are often present. The presence of circulating immune complexes, immune molecules formed in response to an antigen, can also be indicative of the disease process.
Imaging Findings
Chest X-rays and computed tomography (CT) scans play a vital role in assessing the structural changes in the lungs. Characteristic findings in ABPA include bronchiectasis, a widening and distortion of the airways, and areas of mucus plugging within the airways. These findings, visible on imaging, provide crucial evidence of the chronic inflammatory process in the lungs. Additionally, the presence of fleeting or persistent infiltrates, areas of inflammation in the lungs, might be observed.
These findings, when combined with other clinical and laboratory data, support a diagnosis of ABPA.
Immunological Tests
Immunological tests are crucial in determining the presence and extent of the allergic response. Specific IgE tests for
- Aspergillus* are highly sensitive and specific, confirming the patient’s allergic sensitization. These tests measure the levels of IgE antibodies directed against
- Aspergillus* antigens. Another important test is the measurement of total IgE levels, which often shows an elevation in patients with ABPA. Furthermore, detection of circulating
- Aspergillus* precipitins (antibodies) is important. The presence of these precipitins can indicate the patient’s immune response to the fungus.
Diagnostic Criteria
The diagnosis of ABPA is based on a combination of clinical features, laboratory findings, and imaging studies. A definitive diagnosis often requires meeting several criteria, which vary across different diagnostic guidelines. These criteria may include the presence of asthma, a positive skin test or serum IgE test forAspergillus*, radiographic evidence of pulmonary infiltrates, and elevated eosinophil counts. The specific criteria may vary between different guidelines and healthcare providers.
Pulmonary aspergillosis, the allergic bronchopulmonary type, can be a real challenge for managing. Proper food storage is crucial for everyone, but especially for those with diabetes. Knowing how to keep insulin and other diabetic medications at the right temperature is essential, and understanding why refrigerators are an important necessity for people with diabetes can be found here why refrigerators are an important necessity for people with diabetes.
This helps prevent complications and keep everything stable, ultimately improving overall health outcomes for those with this specific type of pulmonary aspergillosis.
Comparison of Diagnostic Tests
| Test | Methodology | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total IgE | Measures the overall level of IgE in the blood. | High | Moderate |
| Specific IgE to – Aspergillus* | Measures the level of IgE antibodies specifically directed against
|
High | High |
| Chest X-ray | Visualizes the lungs for signs of bronchiectasis, mucus plugging, and infiltrates. | Moderate | Moderate |
| CT scan | Provides detailed images of the lungs for better visualization of bronchiectasis, mucus plugging, and infiltrates. | High | High |
| Eosinophil count | Measures the number of eosinophils in the blood. | High | Moderate |
The table above provides a general comparison of diagnostic tests for ABPA, highlighting their methodologies and associated sensitivity and specificity. These values can vary based on the specific testing method and patient population.
Diagnostic Flowchart
(A visual flowchart depicting the diagnostic pathway for ABPA would be presented here. It would begin with a patient presenting with symptoms, followed by clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Each step would have branching possibilities, leading to either a confirmed diagnosis or further investigation, or a differential diagnosis.)
Treatment Strategies and Management
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond simply treating the symptoms. Effective management aims to control the inflammatory response, prevent exacerbations, and minimize long-term lung damage. This involves a combination of medications, lifestyle modifications, and ongoing monitoring.Successful treatment of ABPA hinges on understanding the interplay between the immune system, Aspergillus, and the airways. By addressing the underlying inflammatory processes, patients can achieve better control of their condition and improve their quality of life.
Treatment Goals for ABPA
The primary goals of ABPA treatment are to suppress the allergic inflammatory response, prevent further lung damage, control symptoms, and prevent exacerbations. This includes reducing fungal burden, improving lung function, and mitigating the risk of complications. Achieving these goals requires a personalized approach tailored to the individual patient’s needs and severity of the disease.
Role of Corticosteroids in ABPA Management
Corticosteroids play a central role in ABPA management. They are potent anti-inflammatory agents that help reduce the immune response triggered by Aspergillus. By decreasing inflammation in the airways, corticosteroids help improve lung function, alleviate symptoms, and prevent exacerbations. The dosage and duration of corticosteroid therapy are carefully adjusted based on the patient’s response and the severity of the disease.
High-dose corticosteroids are typically used during acute exacerbations, while lower doses are often maintained long-term to prevent relapses.
Comparison of Treatment Regimens
Various treatment regimens are employed for ABPA, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of regimen often depends on the severity of the disease, the patient’s response to previous treatments, and the presence of comorbidities. A common initial approach involves using oral corticosteroids in combination with antifungal agents. The antifungal agent is typically chosen based on its effectiveness against Aspergillus species and potential side effects.
Dealing with pulmonary aspergillosis allergic bronchopulmonary type can be tough, but hey, at least there are some seriously funny TikToks out there to help you through it! Seriously, check out these hilarious TikToks every parent needs while in quarantine for a much-needed laugh. While navigating the complexities of this condition, these videos offer a welcome distraction, and a reminder that even in challenging times, there’s always room for a good chuckle.
It’s important to remember that pulmonary aspergillosis allergic bronchopulmonary type still requires proper medical attention, but a little humor can certainly help lighten the load.
Alternative regimens may involve different antifungal medications or variations in corticosteroid dosing.
Antifungal Agents in ABPA Treatment
Antifungal agents are crucial in managing ABPA, especially when the infection is causing significant issues. The most commonly used antifungal agents include itraconazole and voriconazole. These drugs work by targeting the fungal cell structure and preventing its growth. Itraconazole is often the initial choice, but voriconazole can be a viable option, particularly in cases of resistance or intolerance to itraconazole.
The selection of an antifungal agent is dependent on several factors, including the specific Aspergillus species, the patient’s overall health, and potential drug interactions.
Potential Complications and Management
ABPA can lead to a range of complications, including recurrent exacerbations, progressive lung damage (bronchiectasis), and even respiratory failure. Prompt recognition and management of these complications are essential to prevent further deterioration. Regular monitoring of lung function, chest X-rays, and sputum analysis can help detect and address these issues early. Appropriate treatment for these complications often involves adjusting corticosteroid doses, adding antifungal medications, and implementing supportive care.
Importance of Long-Term Monitoring
Long-term monitoring is vital in ABPA management. Regular follow-up appointments, pulmonary function tests, and imaging studies help track disease progression, assess treatment effectiveness, and identify any potential complications early. This ongoing surveillance allows for timely adjustments to treatment strategies and helps prevent long-term lung damage.
Treatment Modalities Table
| Treatment | Mechanism of Action | Side Effects | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone) | Reduce inflammation in the airways | Increased risk of infections, osteoporosis, cataracts, hyperglycemia | Long-term use requires careful monitoring and gradual tapering |
| Antifungal agents (e.g., itraconazole, voriconazole) | Inhibit fungal growth | Nausea, vomiting, liver damage | Individual tolerance and potential drug interactions must be considered |
| Immunomodulators (e.g., azathioprine) | Modify the immune response | Bone marrow suppression, increased risk of infections | Reserved for severe cases with corticosteroid intolerance or resistance |
| Supportive care | Manage symptoms and prevent complications | Variable, depending on the specific intervention | Includes respiratory therapy, nutritional support, and oxygen therapy |
Complications and Prognosis
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) is a complex condition, and its impact on a person’s health extends beyond the initial symptoms. Understanding the potential complications and long-term prognosis is crucial for effective management and improving the quality of life for those affected. This section delves into the possible consequences of ABPA, focusing on the severity of disease, treatment adherence, and the overall impact on daily life.ABPA’s progression can vary significantly, with some individuals experiencing mild symptoms and others facing severe pulmonary damage.
The long-term effects of ABPA are often influenced by the extent of inflammation and the body’s response to treatment.
Potential Pulmonary Complications
The chronic inflammatory response in ABPA can lead to a range of pulmonary complications. These include the development of bronchiectasis, a condition where the airways become permanently widened and damaged. This damage can compromise the lungs’ ability to function effectively, leading to increased susceptibility to respiratory infections. In severe cases, extensive scarring and fibrosis can occur, resulting in irreversible lung dysfunction.
These complications can significantly impact the individual’s ability to breathe and participate in daily activities.
Systemic Effects of ABPA
Beyond the lungs, ABPA can manifest in other parts of the body. Systemic effects can include an increased risk of other respiratory infections, such as pneumonia. Additionally, individuals with ABPA might experience an elevated risk of developing other autoimmune disorders. Understanding these systemic effects is crucial for comprehensive management and prevention of secondary complications.
Long-Term Prognosis
The long-term prognosis for individuals with ABPA is variable and depends on several factors. Adherence to prescribed treatment plays a critical role. Regular monitoring, timely intervention for exacerbations, and consistent medication adherence can significantly improve outcomes and mitigate the progression of the disease. The severity of the initial disease presentation also influences the long-term outlook. Those with a milder form of ABPA often have a more favorable prognosis compared to individuals with a more severe presentation.
Impact on Quality of Life
ABPA significantly impacts the quality of life of those affected. The chronic respiratory symptoms, including coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath, can limit physical activity and participation in social and recreational activities. The emotional toll of a chronic illness, including anxiety and depression, should also be considered. The impact on daily life is influenced by the severity of the condition and the individual’s overall health.
Co-morbidities Associated with ABPA
Individuals with ABPA may have co-existing conditions, or co-morbidities, that can complicate their health status. These co-morbidities can include other respiratory conditions, such as asthma or cystic fibrosis, or allergic diseases, like allergic rhinitis. It is important to identify and manage these co-morbidities alongside ABPA for comprehensive care.
Frequency of Complications
| Complication | Frequency | Impact on Prognosis |
|---|---|---|
| Bronchiectasis | High | Significant, leading to irreversible lung damage |
| Respiratory Infections | Moderate | Can exacerbate existing lung damage |
| Systemic Autoimmune Disorders | Low | Potential for further health complications |
| Pulmonary Fibrosis | Variable | Severe cases can lead to irreversible lung dysfunction |
Prevention and Prevention Strategies: Pulmonary Aspergillosis Allergic Bronchopulmonary Type
Preventing allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) and its exacerbations requires a multifaceted approach. This involves understanding the risk factors associated with the development of ABPA, implementing preventive measures, and actively managing environmental triggers. By addressing these aspects, we can significantly reduce the burden of ABPA on patients and improve their quality of life.A crucial aspect of preventing ABPA is recognizing the interplay between predisposing factors and environmental exposures.
Early intervention and proactive management are key to minimizing the likelihood of ABPA development and reducing the frequency of exacerbations. Strategies that effectively target both aspects are essential for long-term control.
Potential Risk Factors for ABPA Development
Several factors increase the susceptibility to developing ABPA. These risk factors often intertwine and create a complex interplay. Understanding these risk factors is critical for identifying individuals at higher risk and implementing preventative measures.
- Cystic Fibrosis (CF): CF patients are at significantly higher risk due to impaired mucociliary clearance, which allows for the proliferation of Aspergillus. This is a well-established risk factor.
- Asthma: Individuals with severe, uncontrolled asthma are more susceptible. The chronic inflammation in the airways can create an environment favorable to Aspergillus colonization.
- Bronchiectasis: Patients with bronchiectasis have a history of airway damage, making them more prone to infection, including fungal infections.
- Prior Exposure to Aspergillus: Individuals with a history of exposure to Aspergillus may develop a hypersensitivity response, making them more susceptible to ABPA.
Preventive Measures
Implementing preventive measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of ABPA development and exacerbation.
- Optimal Asthma Control: Maintaining well-controlled asthma is crucial. This includes adhering to prescribed medications, monitoring symptoms regularly, and seeking prompt medical attention for exacerbations. Consistent adherence to prescribed medication regimens is essential.
- Immunomodulatory Therapies: In some cases, immunomodulatory therapies might be considered for individuals with a high risk of ABPA, especially in patients with CF. This approach focuses on modulating the immune response to minimize the inflammatory reaction.
- Early Diagnosis and Treatment: Prompt and accurate diagnosis of ABPA is essential. Early treatment with antifungal agents and corticosteroids can help control the disease and reduce the risk of exacerbations.
Strategies for Preventing ABPA Exacerbations
Managing ABPA exacerbations is crucial to minimize the impact on patients’ lives.
- Avoiding Environmental Triggers: Identifying and avoiding environmental triggers, such as mold and dust, can help prevent exacerbations. This includes maintaining a clean living environment and taking necessary precautions when exposed to potential allergens.
- Strict Adherence to Medication Regimens: Adhering to prescribed medications, including corticosteroids and antifungal agents, is critical for preventing exacerbations. Regular monitoring and adjustments to the medication regimen, as needed, are essential.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular follow-up visits and monitoring of lung function are crucial to detect early signs of exacerbation. This allows for prompt intervention and prevents the progression of the disease.
Environmental Control in ABPA Management
Controlling the environment can significantly reduce the risk of ABPA exacerbations. Environmental control strategies aim to minimize exposure to Aspergillus and other potential triggers.
- Mold Control: Reducing mold growth in the home and workplace is essential. This includes proper ventilation, regular cleaning, and addressing any water damage promptly.
- Dust Management: Minimizing dust accumulation through regular cleaning and the use of appropriate measures can help control the spread of dust mites and other allergens.
- Air Quality Monitoring: Monitoring indoor air quality and identifying sources of allergens can help create a healthier environment.
Table of Preventive Strategies and Effectiveness
| Strategy | Effectiveness | Practical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Optimal Asthma Control | High | Adhering to medication regimens, monitoring symptoms, and seeking prompt medical attention for exacerbations. |
| Early Diagnosis and Treatment | High | Regular follow-up visits, prompt initiation of appropriate treatment, and monitoring of disease progression. |
| Avoiding Environmental Triggers | Moderate | Identifying and eliminating triggers like mold, dust, and allergens. |
| Strict Adherence to Medication Regimens | High | Regular follow-up with healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans as needed. |
Research and Future Directions
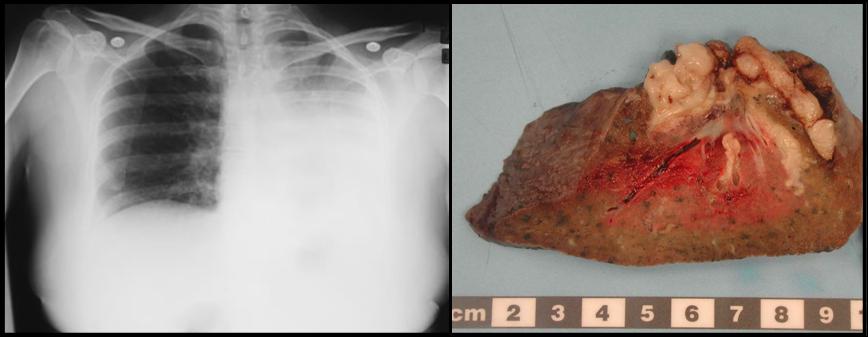
Understanding Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA) requires ongoing research to refine diagnosis, treatment, and preventative strategies. Current research trends are focused on developing more accurate diagnostic tools, improving treatment efficacy, and identifying novel therapeutic targets. This exploration of future directions underscores the significance of ABPA research, highlighting unmet needs and recent advancements.
Current Research Trends in ABPA
Research efforts in ABPA are increasingly multi-faceted, encompassing molecular diagnostics, biomarker discovery, and the investigation of novel therapeutic approaches. Studies are aiming to improve the sensitivity and specificity of existing diagnostic methods, and to identify biomarkers that can predict disease progression or response to treatment. This proactive approach is crucial for early intervention and tailored management plans.
Potential Areas for Future Research in ABPA
Future research in ABPA should concentrate on several key areas. Developing novel biomarkers for early diagnosis and monitoring disease activity is a crucial area. These biomarkers could significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of ABPA diagnosis, enabling earlier intervention and preventing exacerbations. Another important focus is the development of personalized treatment strategies. By understanding individual patient responses to treatment, tailored therapies can be designed to optimize outcomes and minimize adverse effects.
Moreover, further investigation into the underlying immunopathogenic mechanisms of ABPA will offer valuable insights into disease pathogenesis. Understanding the intricate interplay of immune cells and mediators involved in the disease process will provide new avenues for targeted therapeutic interventions.
Unmet Needs in ABPA Research and Management
Despite advancements, significant unmet needs remain in ABPA research and management. One key area is the development of standardized diagnostic criteria that are applicable across different populations and healthcare settings. Improved access to diagnostic resources and expertise is also vital in many regions, particularly in resource-limited settings. The lack of a definitive treatment strategy for severe or refractory cases is another significant challenge.
Further research is needed to address these limitations and improve patient outcomes.
Significance of ABPA Research
ABPA research holds immense significance for improving the lives of affected individuals. Early and accurate diagnosis allows for timely intervention, preventing exacerbations and long-term complications. Effective treatment strategies can reduce the burden of disease and improve quality of life. Research into the underlying mechanisms of ABPA can lead to the development of novel therapeutic approaches, potentially leading to breakthroughs in disease management.
Examples of Recent Advancements in ABPA Research
Recent advancements in ABPA research include the development of more sensitive diagnostic assays for detecting Aspergillus-specific IgE and IgG antibodies. These advancements have led to earlier and more accurate diagnosis, enabling timely initiation of treatment and reducing the risk of severe complications. Further research is focusing on the role of specific cytokines and immune cell profiles in ABPA pathogenesis.
Understanding these immune responses will pave the way for targeted therapies. The discovery of new drug targets is another exciting avenue of investigation, promising the development of more effective and safer treatments.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, pulmonary aspergillosis allergic bronchopulmonary type (ABPA) presents a multifaceted challenge in respiratory medicine. While significant advancements have been made in diagnosis and treatment, ongoing research and a comprehensive understanding of the underlying immunological mechanisms are vital. This discussion highlights the importance of early detection, personalized treatment strategies, and continuous monitoring to optimize patient outcomes and quality of life.
