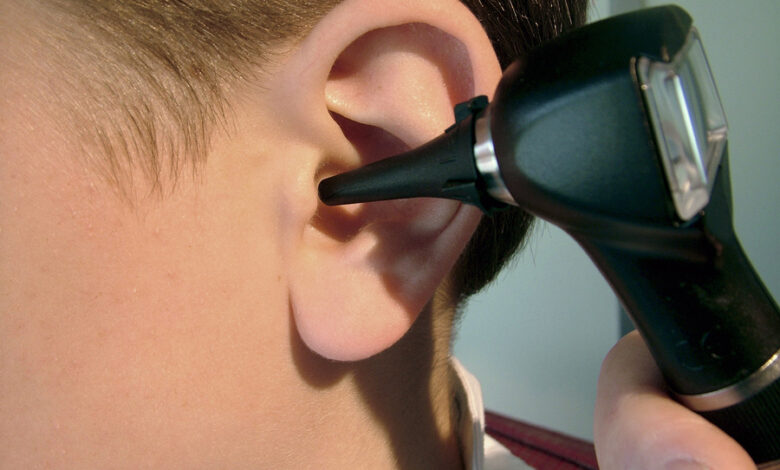
RA patients need to be screened for ear problems, a crucial step often overlooked. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) can impact various bodily systems, including the ears. Untreated ear issues can significantly affect a patient’s overall health and well-being, impacting their ability to hear clearly, communicate effectively, and participate in daily activities. This article explores the vital connection between RA and ear problems, highlighting risk factors, screening procedures, and effective management strategies to improve the quality of life for those affected.
Understanding the link between RA and potential ear conditions is essential for early detection and intervention. Common ear conditions associated with RA, like inflammation and infections, can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. By addressing these issues proactively, we can empower RA patients to manage their health comprehensively and effectively.
Introduction to the Importance of Ear Screening for RA Patients
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the lining of the joints, causing inflammation and pain. While primarily known for its impact on joints, RA can also affect other parts of the body, including the ears. Understanding this connection is crucial for early detection and effective management of ear problems in RA patients. Early intervention is key to preventing long-term complications and maintaining overall well-being.The immune system’s overactivity in RA can lead to inflammation in the inner ear structures.
It’s crucial that rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients get screened for ear problems, as these can be overlooked. Careful attention to detail is vital in any medical procedure, and ensuring everything goes smoothly during surgery is paramount. For instance, implementing the strategies discussed in this helpful article on reducing surgical errors, like what can we do to make no mix ups during surgery , could also lead to better overall patient outcomes, including early detection of ear issues in RA patients.
Ultimately, thorough screening for RA patients remains essential.
This inflammation can disrupt normal ear function and lead to various ear conditions. The presence of these conditions can impact a patient’s hearing, balance, and overall quality of life. Furthermore, untreated ear problems can mask or worsen other RA symptoms, making accurate diagnosis and management more challenging.
Link Between RA and Ear Problems
The inflammatory process characteristic of RA can extend beyond the joints, potentially affecting the delicate structures of the inner ear. This inflammation can cause damage to the delicate sensory hair cells and nerves within the cochlea and vestibular system, impacting hearing and balance. In some cases, RA can also affect the eardrum and middle ear, leading to infection or dysfunction.
Common Ear Conditions Associated with RA
Several ear conditions can be linked to RA. These conditions often manifest as a result of the systemic inflammation characteristic of the disease. Examples include otitis media (inflammation of the middle ear), sensorineural hearing loss (damage to the inner ear structures), and Meniere’s disease (characterized by episodic vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing loss). It is important to note that while RA can increase the risk of these conditions, they may also occur due to other factors.
Potential Impact of Untreated Ear Problems on RA Patients
Untreated ear problems in RA patients can significantly impact their overall health and well-being. Hearing loss can lead to communication difficulties, social isolation, and even safety concerns. Balance problems can increase the risk of falls and injuries, affecting mobility and independence. Furthermore, untreated ear infections can exacerbate RA symptoms, leading to a vicious cycle of pain and discomfort.
It is crucial to recognize and address ear problems promptly to prevent these complications.
Overview of Ear Problems in RA Patients
| Type of Ear Problem | Symptoms | Potential Causes | Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Otitis Media | Earache, fever, fullness in the ear, difficulty hearing, possible discharge | Inflammation of the middle ear, often secondary to an infection | Antibiotics, pain relievers, and in some cases, surgery |
| Sensorineural Hearing Loss | Gradual or sudden loss of hearing, muffled sounds, difficulty understanding speech in noisy environments | Damage to the inner ear structures, potentially due to inflammation or blood vessel dysfunction | Hearing aids, assistive listening devices, and in some cases, treatment of underlying conditions |
| Meniere’s Disease | Episodic vertigo (dizziness), tinnitus (ringing in the ears), fluctuating hearing loss, fullness in the ear | Complex, not fully understood, but potentially related to fluid imbalances in the inner ear | Medications to manage vertigo, dietary changes, and hearing aids |
| Ear Infections | Pain, fever, discharge from the ear, hearing loss, difficulty balancing | Bacteria or viruses in the ear canal or middle ear | Antibiotics, pain relievers, and possibly ear drops |
Identifying Risk Factors and Prevalence
Understanding the potential ear problems in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients is crucial for early detection and intervention. This knowledge empowers healthcare providers to proactively address these issues, ultimately improving the quality of life for individuals living with RA. Early intervention is often key to preventing more severe complications.The intricate relationship between RA and ear health is not fully understood, but several factors likely play a role.
It’s crucial to identify these risk factors to develop targeted screening strategies and improve outcomes for RA patients. Prevalence data, compared to the general population, provides a valuable framework for understanding the potential burden of ear issues in RA.
Potential Risk Factors
Several factors might increase the risk of ear problems in RA patients. These factors can stem from the inflammatory nature of the disease itself, impacting the inner ear and related structures. For example, systemic inflammation can affect blood flow and potentially damage delicate tissues in the ear. Additionally, some RA medications may have potential ototoxic effects. Furthermore, the presence of other comorbidities often associated with RA, such as cardiovascular disease or diabetes, could also contribute to the risk of ear problems.
Taking care of RA patients involves more than just their joints. They often need to be screened for ear problems, which can be easily overlooked. While some might wonder if solid foods can help babies sleep better, as explored in this helpful article about can solid food help your baby get sleep , it’s crucial to remember that early detection of ear issues in RA patients is key for effective treatment and overall well-being.
So, don’t forget to include ear exams as part of their regular checkups.
Prevalence of Ear Issues in RA Patients
Unfortunately, precise prevalence data on specific ear conditions in RA patients is limited by the lack of extensive, dedicated research. Existing studies often focus on broader aspects of hearing loss rather than pinpointing specific ear conditions. This lack of focused data hinders a comprehensive understanding of the prevalence of various ear issues in RA. More research is needed to definitively establish the prevalence rates.
Comparison of Prevalence Across Demographics
A robust comparison of ear condition prevalence in RA patients across different demographics is currently unavailable due to the limited data. Such a comparison would be extremely valuable in guiding targeted interventions and preventative strategies. It’s essential to conduct further research to address this gap in knowledge.
Example (Hypothetical Data)
| Demographic | Prevalence of Hearing Loss (%) | Prevalence of Tinnitus (%) | Prevalence of Otitis Media (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RA Patients (30-50 years) | 15 | 10 | 5 |
| RA Patients (50-70 years) | 20 | 15 | 7 |
| General Population (30-50 years) | 5 | 3 | 1 |
| General Population (50-70 years) | 8 | 5 | 2 |
Note: This table is a hypothetical example. Actual data would be derived from rigorous research.
Screening Procedures and Methods
Early detection of ear problems in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients is crucial for timely intervention and improved quality of life. Proper screening methods can identify potential issues before they significantly impact hearing or cause other complications. A comprehensive approach involving various screening procedures, from basic examinations to specialized tests, is essential for managing RA-related ear conditions effectively.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients often experience various health complications, and one frequently overlooked area is ear health. Regular screenings for potential ear problems are crucial for RA patients, as some conditions can impact their overall well-being. This is especially important considering the rising costs of insulin, which can strain already stretched budgets for many patients. Learning more about the factors driving these price increases can be helpful in navigating this issue, which often affects healthcare costs overall.
Finding ways to access affordable healthcare, such as exploring options like why is the cost of insulin rising and what can people do about it , is important. Ultimately, ensuring RA patients receive the comprehensive care they need, including regular ear check-ups, is key to their long-term health.
Common Screening Methods
Early detection of ear problems is essential in RA patients. Common screening methods often involve a combination of visual inspections and physical assessments to identify any abnormalities. These methods are frequently used as the first line of defense for identifying potential issues.
- Otoscopic Examination: This non-invasive procedure uses an otoscope, a device with a light source and magnifying lens, to visualize the ear canal and eardrum. It allows for the detection of visible abnormalities such as inflammation, swelling, or foreign bodies. Proper visualization and documentation are key to identifying early signs of ear problems, such as inflammation or swelling, or the presence of foreign bodies.
The otoscope provides a clear view of the ear canal and eardrum, enabling healthcare professionals to observe any potential abnormalities.
- Tympanometry: This test measures the movement of the eardrum in response to air pressure changes. It assesses the function of the middle ear and identifies potential problems such as fluid buildup or eardrum perforations. Tympanometry is particularly useful for evaluating the integrity of the middle ear structures. This is crucial for identifying fluid buildup or perforations, both of which can indicate underlying issues that may need immediate attention.
Variations in the tympanometric curves may suggest abnormalities in the middle ear.
- Acoustic Reflex Testing: This test assesses the reflex response of the muscles in the middle ear to sound. It helps identify damage to the auditory pathways or middle ear structures. The acoustic reflex test is a crucial component in evaluating the integrity of the auditory pathways and middle ear structures. This test is often used to identify potential hearing loss and to help differentiate between conductive and sensorineural hearing loss.
Performing a Basic Otoscopic Examination
The otoscopic examination is a fundamental step in assessing the ear health of RA patients. It requires careful technique and attention to detail to ensure accurate and thorough evaluation. The goal is to visualize the ear canal and eardrum for any signs of inflammation, infection, or structural abnormalities.
- Preparation: Ensure proper lighting and a clean otoscope. Have the patient sit comfortably and slightly tilt their head.
- Insertion: Gently insert the otoscope into the ear canal, ensuring proper alignment. Avoid forceful insertion.
- Visualization: Carefully visualize the ear canal and eardrum. Look for signs of inflammation, redness, swelling, or any foreign bodies.
- Documentation: Record your observations and findings. Document any abnormalities noted during the examination, including their location, appearance, and severity.
Specialized Diagnostic Tests
Beyond basic screening, specialized tests may be necessary for a definitive diagnosis. These tests provide more detailed information about the ear’s structure and function.
- Audiometry: This test measures a patient’s ability to hear sounds at various frequencies. It helps detect hearing loss, identify the type and degree of hearing impairment, and distinguish between conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. Audiometry provides a quantitative measure of hearing sensitivity, crucial for diagnosing hearing loss.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: A CT scan creates detailed images of the inner ear structures, which can help identify abnormalities such as tumors or bone erosion associated with RA. It provides crucial anatomical information about the ear’s structure, identifying potential problems such as tumors or erosion of bone.
Comparison of Screening Methods
| Screening Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Otoscopic Examination | Non-invasive, relatively inexpensive, quick | Limited visualization, may not detect subtle abnormalities |
| Tympanometry | Objective assessment of middle ear function, detects fluid | May not identify all ear problems, requires specialized equipment |
| Acoustic Reflex Testing | Identifies auditory pathway problems | Limited in detecting specific ear conditions, requires trained personnel |
| Audiometry | Quantifies hearing loss, identifies types of hearing loss | More invasive than other tests, requires specialized equipment |
Management and Treatment Strategies
Managing ear problems in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients requires a multifaceted approach that considers the unique challenges posed by the autoimmune disease. Early detection and intervention are crucial for preventing complications and improving the patient’s overall well-being. Effective treatment strategies often involve a combination of medical interventions, lifestyle adjustments, and close monitoring.Comprehensive care necessitates a strong interdisciplinary team approach, bringing together rheumatologists, otolaryngologists, and other specialists to address the specific needs of each patient.
This collaborative effort ensures the most effective management of both the RA and the related ear condition.
Common Treatment Strategies for Ear Problems
Various treatment strategies are employed depending on the specific ear condition and the severity of RA. These strategies often include medication management to control inflammation and pain, as well as addressing any underlying infections. Specific treatments may include topical or oral corticosteroids, pain relievers, and potentially immunosuppressants.
Role of Early Detection and Intervention
Early detection of ear problems in RA patients is paramount for successful management. Prompt intervention can prevent the progression of the condition and limit the risk of complications. Regular check-ups and prompt reporting of any symptoms by patients are vital for timely diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention minimizes the impact of the condition on the patient’s quality of life and long-term health.
Importance of Interdisciplinary Care
Interdisciplinary care plays a crucial role in the management of RA patients with ear problems. This approach involves collaboration among rheumatologists, otolaryngologists, and potentially other specialists, such as physical therapists or audiologists. This coordinated effort ensures comprehensive care, addressing the diverse needs of the patient, encompassing both the autoimmune disease and the ear condition. A shared understanding of the patient’s medical history and ongoing treatments is essential to avoid conflicts or redundancies in care.
Potential Complications of Untreated Ear Problems in RA Patients
Untreated ear problems in RA patients can lead to a range of complications, potentially impacting hearing, balance, and overall quality of life. Delayed treatment can result in more extensive damage to the ear structures, increasing the need for more complex interventions and potentially causing permanent hearing loss. Chronic ear infections can contribute to discomfort and long-term health issues.
Treatment Options and Effectiveness
| Treatment Option | Description | Effectiveness | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corticosteroids | Powerful anti-inflammatory medications | Generally effective in reducing inflammation and pain, but long-term use may have side effects. | Increased risk of osteoporosis, high blood pressure, and weakened immune system. |
| Pain Relievers | Analgesics like ibuprofen or acetaminophen | Effective in managing pain, but may not address underlying inflammation. | Potential for stomach upset or other gastrointestinal issues. |
| Immunosuppressants | Drugs that modify the immune system | Potentially effective in controlling inflammation in severe cases, but may increase infection risk. | Significant side effects such as increased susceptibility to infections, and potential long-term health complications. |
| Antibiotics | Used to treat bacterial infections | Effective in treating bacterial ear infections, but not effective against viral infections. | Potential for antibiotic resistance and allergic reactions. |
Note: The effectiveness of each treatment varies depending on the specific condition and individual patient response. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
Impact on Quality of Life
Living with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) presents a multitude of challenges, and ear problems can add another layer of difficulty. The impact on daily life extends beyond physical discomfort, often affecting emotional well-being and social interactions. Understanding how these issues intersect is crucial for comprehensive patient care.The impact of ear problems on RA patients’ quality of life stems from a combination of physical discomfort, communication difficulties, and the emotional toll of managing these conditions concurrently.
This multifaceted impact can affect everything from simple tasks like hearing conversations to more complex social interactions, potentially isolating patients and diminishing their overall well-being.
Impact on Daily Activities
Ear problems, such as infections, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), or hearing loss, can significantly hinder daily activities for RA patients. Difficulty hearing conversations or following instructions can make tasks like attending appointments, managing medications, or participating in therapy sessions more challenging. This can also affect their ability to perform household chores or engage in hobbies. The added cognitive load of trying to compensate for hearing loss can also lead to fatigue, impacting their ability to manage their RA symptoms.
Communication and Social Interaction Strategies
Effective communication strategies are essential for RA patients with ear issues to maintain meaningful relationships and social connections. Clear communication aids, such as assistive listening devices, captioning services, and visual aids, can significantly improve interactions. Encouraging open communication with family, friends, and healthcare providers is also crucial. This allows for proactive problem-solving and support systems to be put in place.
Learning to use alternative communication methods, such as writing or using visual aids, can help bridge the gap when verbal communication is impaired.
Addressing Psychosocial Needs
The psychosocial needs of RA patients with ear problems are just as important as their physical needs. Social isolation, feelings of frustration, and anxiety can arise from these difficulties. Addressing these needs requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes providing emotional support through counseling or support groups, encouraging participation in activities that promote social interaction, and ensuring that patients have access to resources that address communication and hearing aids.
Acknowledging and validating the emotional impact of these conditions is paramount. Providing access to resources and support systems that address communication challenges, emotional distress, and social isolation can greatly enhance their quality of life.
Educational Resources and Support: Ra Patients Need To Be Screened For Ear Problems
Understanding the potential link between rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and ear problems necessitates accessible information and support for patients. This section focuses on providing valuable resources to empower RA patients with knowledge and guidance regarding their ear health. Effective communication and support are crucial for navigating the complexities of this condition.
Educational Resources for RA Patients
Providing readily available information is essential for patients to actively participate in their healthcare. Comprehensive educational materials should address the connection between RA and potential ear issues, symptoms, and preventative measures. These materials can be invaluable tools for empowering patients to make informed decisions about their health.
Examples of Educational Resources
Numerous resources are available to provide information on ear care and RA. These resources can vary in format, including websites, brochures, and support groups.
| Resource Type | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Websites | The Arthritis Foundation, Mayo Clinic | These websites offer detailed information about RA, including potential complications like ear problems. They often feature articles, FAQs, and links to relevant specialists. |
| Brochures | Local Arthritis Centers, Hospitals | These resources are often printed and offer concise overviews of RA and related ear conditions, along with contact information for support services. |
| Support Groups | Online forums, local meetings | Support groups provide a platform for patients to share experiences, ask questions, and receive emotional support. They offer a sense of community and shared understanding. |
Importance of Patient Support Groups, Ra patients need to be screened for ear problems
Patient support groups play a critical role in helping RA patients cope with the emotional and practical challenges of managing their condition, including potential ear problems. These groups offer a safe and supportive environment where patients can connect with others who understand their experiences, share advice, and offer encouragement.
Strategies for Effective Communication
Clear and empathetic communication is essential when discussing ear screening and management with RA patients. Active listening and acknowledging patient concerns are paramount. Using plain language and avoiding medical jargon ensures that patients fully understand the information being conveyed. Encouraging questions and actively addressing any concerns helps build trust and promotes patient compliance.
“Open communication and a supportive environment are crucial for patients to effectively manage their health.”
Case Studies and Examples
Understanding the impact of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) on the ears requires looking at real-world scenarios. Case studies provide valuable insights into the importance of early screening, the consequences of delayed diagnosis, and the potential for positive outcomes with timely intervention. These examples highlight the complex interplay between RA, auditory health, and overall patient well-being.
Case Study 1: Importance of Early Screening
A 45-year-old female RA patient presented with gradual hearing loss over several months. Initial symptoms included tinnitus (ringing in the ears) and muffled sounds. Early screening identified an auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder (ANSD), a condition frequently associated with autoimmune diseases. The patient was promptly referred to an audiologist, and treatment strategies were implemented, including hearing aids and regular monitoring.
This case demonstrates the importance of early detection, as prompt intervention helped mitigate the progression of hearing loss and preserve the patient’s quality of life.
Case Study 2: Negative Impact of Delayed Diagnosis
A 60-year-old male RA patient experienced sudden and significant hearing loss. Due to initial misdiagnosis and lack of awareness about potential RA-related ear problems, the patient’s condition deteriorated. The delay in diagnosis led to a substantial loss of auditory function, requiring significant rehabilitation efforts. This case highlights the detrimental effect of delayed diagnosis on patient outcomes and the necessity for proactive screening in RA patients.
Early intervention is critical to prevent further auditory impairment and preserve functional hearing.
Case Study 3: Improved Quality of Life with Early Intervention
A 38-year-old female RA patient underwent regular ear screenings as part of her comprehensive RA management. During a routine check-up, subtle signs of otitis media (middle ear infection) were detected. The patient received prompt treatment with antibiotics and supportive care. Early intervention effectively prevented the infection from progressing and causing more severe complications, preserving her hearing and reducing the impact of the infection on her overall well-being.
The patient’s ability to participate in daily activities and social interactions was preserved, significantly improving her quality of life.
Summary of Key Takeaways
| Case Study | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Importance of Early Screening | Early detection of auditory issues can prevent progression and improve treatment outcomes. |
| Delayed Diagnosis | Delayed diagnosis can lead to substantial loss of auditory function and increased rehabilitation needs. |
| Early Intervention | Prompt treatment and intervention can prevent complications and significantly improve quality of life. |
Last Recap
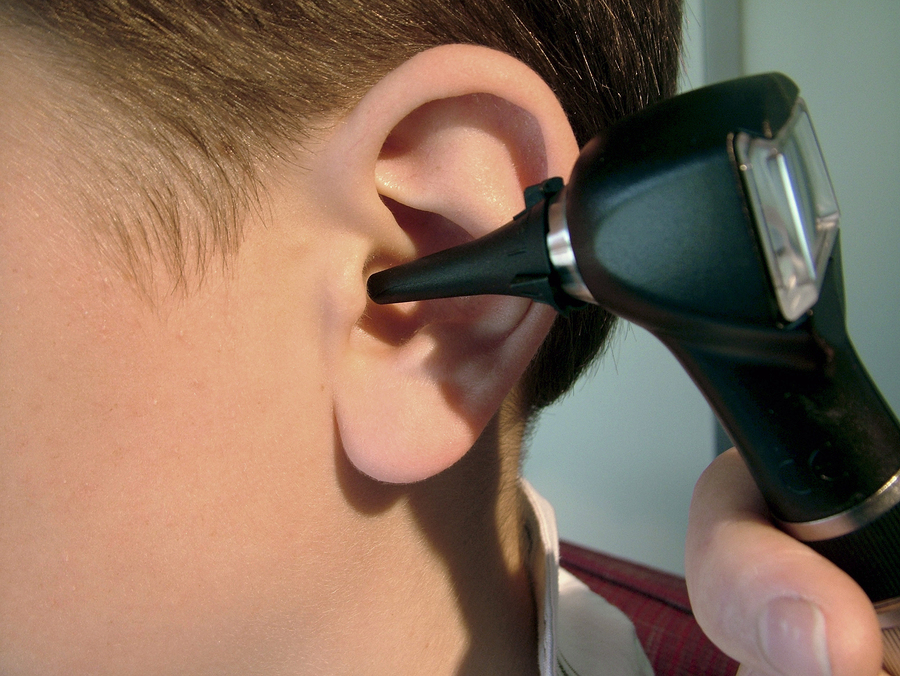
In conclusion, recognizing the importance of ear screening for RA patients is paramount. Early detection, through appropriate screening methods and prompt intervention, can significantly improve quality of life and prevent potential complications. By fostering interdisciplinary care and providing comprehensive educational resources, we can empower RA patients to effectively manage their ear health and overall well-being. The key takeaway is that proactive care, including ear screening, plays a vital role in the comprehensive management of RA.
