Relief ahead for traumatic brain injuries sets the stage for a detailed exploration of the challenges and potential solutions for those affected. This in-depth look delves into the different types of TBIs, from mild to severe, examining their causes, symptoms, and long-term impacts. We’ll explore current treatments and management strategies, highlighting the crucial role of rehabilitation, support systems, and mental health care.
The discussion will also delve into emerging research, innovative technologies, and promising avenues for future advancements in TBI treatment.
Understanding the diverse landscape of traumatic brain injuries, from diagnosis and assessment to current treatment options and emerging research, is crucial for comprehending the multifaceted nature of this condition. The evolving understanding of TBI recovery, with its emphasis on comprehensive care and support systems, underscores the importance of ongoing research and innovation in improving outcomes for TBI survivors.
Understanding Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBIs)
Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) are a serious concern affecting individuals of all ages. They result from a blow or jolt to the head or body, causing damage to the brain. Understanding the different types, causes, and effects of TBIs is crucial for prevention, early intervention, and appropriate care. This comprehensive look delves into the intricacies of TBIs, empowering readers with valuable knowledge.Traumatic brain injuries, ranging from mild to severe, can impact various aspects of a person’s life, including physical, cognitive, and emotional well-being.
The severity of the injury directly correlates with the extent of the damage and the subsequent consequences. Factors such as the force of the impact, the location of the injury, and the individual’s overall health all play a role in determining the long-term effects.
Types of Traumatic Brain Injuries
TBIs are categorized based on their severity. This categorization helps healthcare professionals determine the appropriate course of treatment and anticipate potential outcomes.
- Mild TBI: Often referred to as concussions, mild TBIs typically involve a brief loss of consciousness or altered mental status. Symptoms may include headaches, dizziness, confusion, and memory problems. Most individuals recover fully within a few weeks with proper rest and management. For example, a bump on the head during a sports game may result in a mild TBI, with recovery occurring within a few days.
- Moderate TBI: Moderate TBIs involve a longer period of unconsciousness or a more significant disruption in mental function. Symptoms may include more severe headaches, prolonged confusion, seizures, and difficulty with motor skills. Recovery can take several weeks or months, and some individuals may experience long-term cognitive or physical impairments. For instance, a car accident causing a moderate TBI could lead to temporary memory loss and difficulty concentrating for several weeks.
Finally, some promising research suggests relief ahead for traumatic brain injuries. While the road to recovery is often long and arduous, exploring the complex interplay of trauma and resilience, as seen in the powerful work of Arabelle Sicardi, arabelle sicardi beauty is terror and power , might offer new perspectives on healing. This could lead to more effective treatments and support systems for those facing these devastating injuries.
- Severe TBI: Severe TBIs involve a prolonged period of unconsciousness, lasting more than 24 hours, or a profound disruption in cognitive function. Symptoms may include loss of consciousness for a significant duration, severe cognitive impairments, physical disabilities, and lasting neurological problems. Recovery is often prolonged and may result in significant long-term physical and cognitive impairments. For instance, a severe fall from a significant height leading to a severe TBI could result in long-term neurological issues and the need for extensive rehabilitation.
Causes and Risk Factors of Traumatic Brain Injuries, Relief ahead for traumatic brain injuries
Various factors contribute to the occurrence of TBIs. Understanding these factors allows for the implementation of preventive measures and strategies to mitigate risks.
- Falls: Falls are a leading cause of TBIs, particularly in older adults and children. Factors such as slippery surfaces, poor lighting, and inadequate safety measures contribute to the risk of falls. For example, elderly individuals living alone may experience falls in their homes, leading to TBIs due to environmental hazards.
- Motor Vehicle Accidents (MVAs): MVAs are a significant cause of TBIs, with collisions and impacts often resulting in severe injuries. Factors such as speeding, drunk driving, and inadequate safety equipment increase the risk of severe TBIs. For example, a driver exceeding the speed limit and colliding with another vehicle can lead to serious TBIs for both drivers and passengers.
- Sports-Related Injuries: Participation in contact sports carries a risk of TBIs, with collisions and impacts during play potentially causing concussions and other head injuries. For example, a football player experiencing a head-on collision with another player may suffer a concussion, a mild TBI.
Physical, Cognitive, and Emotional Effects of TBIs
TBIs can affect various aspects of an individual’s life, including physical, cognitive, and emotional well-being.
- Physical Effects: These may include headaches, dizziness, balance problems, nausea, vision changes, and physical disabilities. For example, a person experiencing a TBI might experience difficulty with balance and coordination, leading to falls and other physical challenges.
- Cognitive Effects: These may include problems with memory, attention, concentration, processing speed, and executive functions. For example, an individual may have difficulty remembering recent events or following instructions.
- Emotional Effects: These may include changes in mood, irritability, anxiety, depression, and difficulty controlling emotions. For example, a person may experience increased frustration and anger due to cognitive impairments.
Long-Term Impacts of TBIs
The long-term effects of TBIs can significantly impact individuals and their families.
- Cognitive Impairments: These may persist long after the initial injury, affecting daily functioning and independence. For example, a person may experience persistent difficulties with memory and attention, impacting their ability to perform daily tasks.
- Physical Disabilities: Some individuals may experience long-term physical impairments, such as difficulties with motor skills and mobility. For example, a person may have persistent pain or difficulty walking, affecting their daily activities.
- Emotional and Behavioral Problems: Individuals may develop emotional or behavioral issues, impacting their relationships and overall well-being. For example, a person may experience increased irritability and difficulty controlling their emotions.
Diagnostic Processes for TBIs
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management and treatment of TBIs.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination assesses neurological function, including reflexes, coordination, and balance. For example, a healthcare professional may assess the patient’s reflexes and balance to evaluate neurological function.
- Neurological Tests: These tests evaluate cognitive abilities, memory, and processing speed. For example, a neuropsychological assessment may be performed to evaluate cognitive functions.
- Imaging Studies: Techniques such as CT scans and MRIs provide detailed images of the brain, helping to identify any structural damage. For example, a CT scan can detect any bleeding or swelling in the brain.
Comparison of TBI Types
| Type of TBI | Symptoms | Severity | Potential Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild TBI | Headache, dizziness, confusion, memory problems, nausea | Least severe | Full recovery within weeks |
| Moderate TBI | Prolonged unconsciousness, severe headaches, seizures, motor skill difficulties | Moderate severity | Partial recovery with potential long-term cognitive or physical impairments |
| Severe TBI | Prolonged unconsciousness (over 24 hours), profound cognitive impairment, physical disabilities | Most severe | Significant long-term physical and cognitive impairments, possible need for extensive rehabilitation |
Current Treatments and Management: Relief Ahead For Traumatic Brain Injuries

Navigating the complexities of a traumatic brain injury (TBI) requires a multifaceted approach. Effective treatment encompasses a range of medical interventions, rehabilitation programs, and crucial support systems. This journey often necessitates ongoing adjustments and adaptations to meet the evolving needs of the individual.Current medical interventions aim to stabilize the initial injury, minimize secondary damage, and address any resulting complications.
While there’s still a long road ahead for those dealing with traumatic brain injuries, a glimmer of hope shines through. Improved medical care in emergency rooms, like medical care in emergency rooms , is playing a crucial role in providing better initial support and potentially altering long-term outcomes. This proactive approach offers real relief for patients and their families facing this challenging journey.
Early diagnosis and prompt medical care are critical for positive outcomes. Therapies are tailored to the specific nature and extent of the injury, focusing on improving cognitive function, motor skills, and overall well-being.
Medical Interventions and Therapies
Medical interventions for TBI encompass a spectrum of treatments, from immediate stabilization to long-term management. These interventions often involve a combination of techniques to mitigate the impact of the injury. For instance, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the brain, while medication can help manage associated symptoms such as seizures or headaches. Ongoing monitoring and adjustments to treatment plans are vital to address any evolving needs.
Rehabilitation Programs
Rehabilitation programs are integral to the recovery process for TBI patients. These programs provide a structured environment for regaining lost skills and adapting to new limitations. Rehabilitation programs typically incorporate physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy, addressing the specific needs of each individual. The programs focus on improving functional abilities and enhancing independence.
Importance of Support Systems and Mental Health Care
The emotional and psychological impact of TBI cannot be underestimated. Support systems play a vital role in helping patients and their families cope with the challenges. Mental health care is essential for addressing anxiety, depression, and other emotional responses to the injury. Seeking professional help can empower individuals and their families to navigate the emotional complexities of recovery.
A strong support network, encompassing family, friends, and support groups, is crucial for encouragement and encouragement throughout the recovery process.
Physical Therapy Exercises
Physical therapy exercises are essential for regaining strength, flexibility, and motor skills. Specific exercises are designed to target areas affected by the injury. For example, exercises to improve balance and coordination are crucial for patients who have experienced impairments in these areas. These exercises should be tailored to the individual’s specific needs and abilities. The progression of exercises should be carefully managed by physical therapists to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Progressive resistance training, balance exercises, and range of motion exercises are examples of commonly used strategies.
Treatment Approaches for TBIs
| Treatment Approach | Effectiveness | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Pharmacological interventions (e.g., medications for pain, seizures, or cognitive impairments) | Can alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being. | May have side effects and may not address the underlying cognitive or physical impairments. |
| Surgical interventions (e.g., craniotomy for hematomas) | Can be life-saving in cases of severe TBI. | Involves risks and may not be suitable for all types of injuries. |
| Rehabilitation programs (e.g., physical, occupational, speech therapy) | Effective in restoring lost functions and improving independence. | Requires significant time and effort from the patient and can be costly. |
| Mental health support (e.g., counseling, therapy) | Crucial for managing emotional and psychological distress. | May not be accessible to all patients and may not be effective for everyone. |
Support Groups and Resources
Numerous support groups and resources are available for TBI survivors and their families. These groups provide a sense of community and shared experiences. Organizations specializing in TBI support offer valuable information, guidance, and practical resources to help patients and their families navigate the challenges of recovery. Examples include the Brain Injury Association of America and similar local organizations.
Online forums and support groups can also be invaluable sources of information and emotional support.
Emerging Research and Advancements
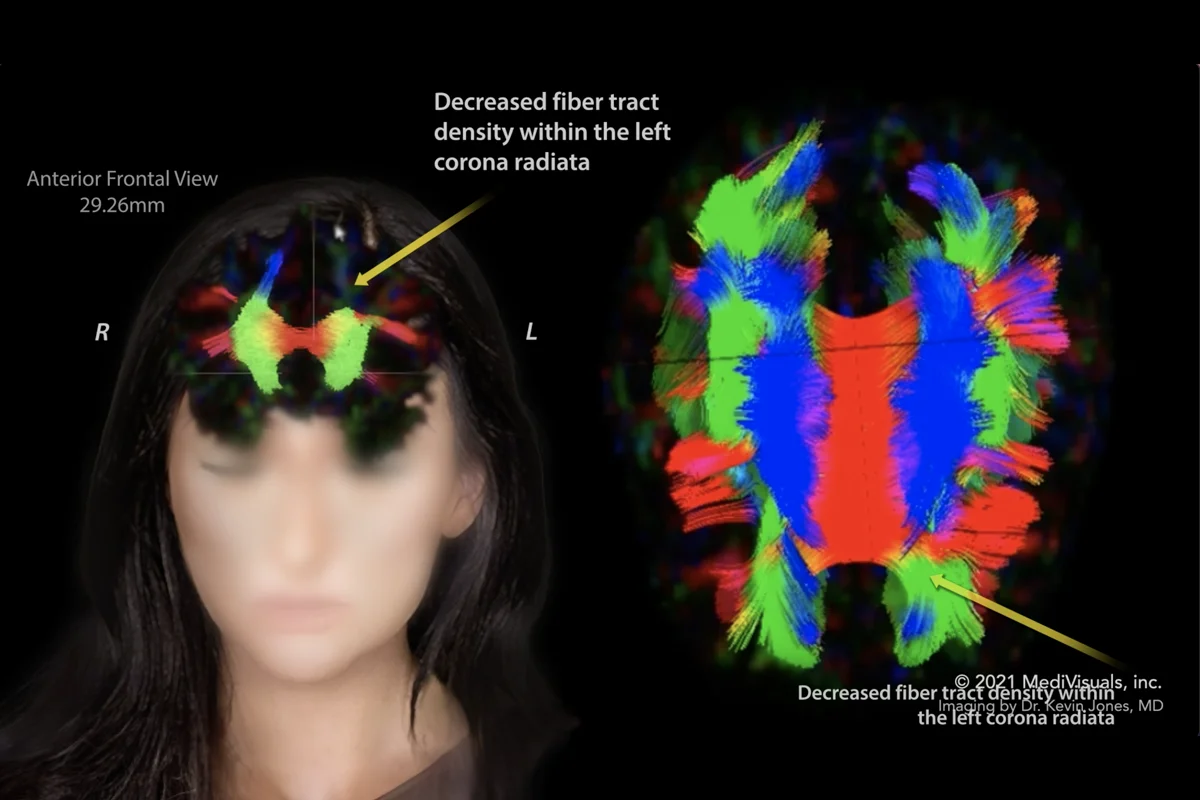
The landscape of traumatic brain injury (TBI) treatment is constantly evolving, driven by innovative research and technological advancements. These breakthroughs offer hope for improved outcomes and recovery for individuals affected by TBI. This exploration delves into recent progress, highlighting promising therapies and technologies poised to revolutionize the management of TBI.Recent breakthroughs in understanding the complex biological processes following a TBI are paving the way for more targeted and effective treatments.
Researchers are focusing on identifying specific molecular pathways and cellular mechanisms involved in the damage and subsequent recovery. This knowledge is critical for developing interventions that can address the root causes of TBI-related impairments.
Stem Cell Therapies
Stem cell therapies represent a cutting-edge approach to TBI recovery. These therapies aim to promote tissue repair and regeneration by introducing specialized cells that can differentiate into various cell types within the damaged brain tissue. Early clinical trials show promising results, with some patients experiencing improvements in cognitive function and motor skills. The potential for stem cell therapies to repair damaged neural circuits and reduce the long-term effects of TBI is substantial.
Innovative Technologies
Innovative technologies are being developed to enhance the diagnosis, monitoring, and rehabilitation of TBI patients. These include advanced imaging techniques that provide more detailed insights into the extent and location of brain damage, as well as real-time monitoring tools to track the progress of recovery. Neuro-modulation devices are being explored to stimulate specific brain regions, potentially promoting neural plasticity and facilitating recovery.
Rehabilitation Strategies
A variety of rehabilitation strategies are being investigated to optimize recovery outcomes. These strategies encompass physical, occupational, and speech therapies, tailored to address the specific needs of each patient. Cognitive rehabilitation programs are gaining prominence, focusing on improving attention, memory, and executive function. The development of personalized rehabilitation plans based on individual patient characteristics is becoming increasingly important.
Comparison of Treatments
| Treatment Type | Description | Potential | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Treatments | Existing therapies such as medications, surgery, and standard rehabilitation. | Effective for managing immediate symptoms and preventing further complications. | Limited ability to address underlying neural damage and long-term cognitive impairments. |
| Emerging Treatments | Stem cell therapies, advanced imaging, and neuro-modulation devices. | Potential to repair damaged neural circuits, enhance recovery, and improve cognitive function. | Requires further research, clinical trials, and regulatory approvals; potential safety concerns. |
A Novel Technology: Brain-Computer Interface (BCI)
A Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) is a novel technology that allows direct communication between the brain and an external device. In TBI rehabilitation, BCIs can assist patients in regaining lost motor functions by decoding brain signals related to movement intentions. Imagine a patient with limited hand movement; a BCI can translate their brain signals into commands for a robotic arm or a prosthetic device, allowing them to regain a degree of independence.
This technology has the potential to revolutionize the rehabilitation process for individuals with severe TBI, enabling them to regain lost functions and improve their quality of life. Preliminary studies demonstrate promising results in restoring lost motor functions in individuals with stroke, and the potential for TBI rehabilitation is significant. BCIs can also be used to monitor brain activity in real-time, providing valuable insights into the effectiveness of rehabilitation programs and identifying areas needing adjustment.
Relief and Support Systems
Navigating the aftermath of a traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a complex journey, demanding comprehensive support for both the individual and their family. Beyond medical care, a robust network of resources and assistance is crucial for successful recovery and reintegration into life. This support extends beyond the immediate crisis and encompasses long-term rehabilitation, emotional well-being, and financial stability.The path to recovery from a TBI often involves navigating a maze of medical procedures, therapies, and emotional challenges.
A well-structured support system, encompassing both formal and informal networks, can greatly enhance the quality of life for TBI survivors and their families. This support system should be adaptable and responsive to the evolving needs of the individual, considering the varied nature of TBI presentations and their impact on daily functioning.
Various Support Systems and Resources
A comprehensive support system for TBI survivors encompasses various levels of care, encompassing medical, psychological, social, and financial assistance. Early intervention is paramount, as it often dictates the trajectory of recovery. This includes access to skilled rehabilitation services, tailored to individual needs and progress.
Importance of Early Intervention and Quality Care
Early intervention in TBI cases is critical. Prompt access to quality medical care, including diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation, can significantly impact long-term outcomes. This involves a multidisciplinary approach, encompassing neurologists, physical therapists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, and psychologists. The sooner these specialized professionals can be involved, the sooner a tailored recovery plan can be developed and implemented. This personalized approach, often delivered in a multi-faceted manner, addresses the unique needs of each individual.
Role of Advocacy Groups
Advocacy groups play a vital role in raising awareness about TBI, advocating for better policies, and providing support to individuals and families affected by this condition. These organizations frequently offer educational resources, support groups, and networking opportunities. They also often actively participate in legislative efforts to improve the accessibility and quality of TBI care. Such advocacy efforts often lead to improvements in funding for research, development of innovative treatments, and the implementation of policies to enhance access to quality care for TBI patients.
Financial Assistance Programs
Financial assistance programs for TBI survivors and their families are available from various sources, including government agencies, non-profit organizations, and private foundations. These programs often cover expenses related to medical treatment, rehabilitation, and adaptive equipment. Information on eligibility criteria and application procedures is crucial for accessing these vital resources.
While there’s promising relief ahead for traumatic brain injuries, it’s crucial to be mindful of potential pitfalls when exploring alternative treatments like CBD. For example, many CBD products are unfortunately mislabeled, some even containing THC, which is important to understand before trying any. Checking out this article on cbd products often mislabeled some containing thc what to know can help you navigate this complex landscape and make informed decisions.
Ultimately, responsible research is key to finding the right path towards recovery from traumatic brain injuries.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Relief Programs
Assessing the effectiveness of relief programs involves a range of metrics. These include measuring improvements in functional abilities, quality of life, and emotional well-being. Regular evaluations, coupled with feedback from patients and families, are essential to ensure programs are meeting their intended goals. This includes monitoring the cost-effectiveness of different interventions, as well as tracking long-term outcomes and impact on various aspects of life.
A comprehensive approach should consider the individual’s progress, cost-effectiveness, and societal benefits.
Support Organizations for TBI Survivors
| Organization | Services | Contact Information |
|---|---|---|
| The Brain Injury Association of America (BIAA) | Information, support groups, advocacy, and resources. | (Phone number), (website) |
| National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) | Research, information, and clinical trials. | (Phone number), (website) |
| [Specific local TBI support group] | Local support groups, community resources, and peer-to-peer support. | (Phone number), (website) |
Prospects for the Future
The journey towards better outcomes for traumatic brain injury (TBI) patients is a complex and multi-faceted one, demanding a comprehensive approach encompassing improved prognosis, preventative measures, technological advancements, and optimized care models. This section delves into the potential for future improvements in managing TBI, exploring the role of public health initiatives, new technologies, diverse care models, and promising research avenues.
Potential Improvements in Prognosis and Outcomes
The prognosis for TBI patients varies significantly based on the severity and location of the injury. Factors like pre-existing health conditions and access to quality medical care also play crucial roles. Future advancements in diagnostic tools, such as more precise imaging techniques and biomarkers for early injury detection, promise to enhance the accuracy of prognosis. Furthermore, the development of personalized treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs will likely improve outcomes by addressing specific cognitive and physical impairments.
For example, targeted rehabilitation programs designed to strengthen specific cognitive functions, such as memory and attention, could yield more positive long-term results.
Role of Public Health Initiatives in Reducing TBI Incidence
Public health initiatives play a vital role in mitigating the incidence of TBI. Strategies aimed at reducing risk factors, such as improved road safety measures, enhanced safety protocols in workplaces and recreational settings, and public awareness campaigns promoting safer behaviors, can demonstrably reduce the number of TBI cases. A comprehensive approach, encompassing multiple sectors, is critical. For instance, increased funding for research into accident prevention technologies and implementation of stricter regulations regarding helmet use in high-risk activities could substantially decrease the occurrence of TBI.
Impact of New Technologies on Long-Term Care and Support
Technological advancements are poised to revolutionize long-term care and support for TBI patients. Virtual reality (VR) therapy, for instance, can provide immersive and engaging rehabilitation experiences, addressing cognitive deficits in a more effective manner than traditional methods. Telemedicine platforms enable remote monitoring and support, improving access to specialized care for patients in underserved areas. Furthermore, assistive technologies, such as communication aids and adaptive devices, can enhance the independence and quality of life for individuals with TBI.
For instance, personalized apps designed to track cognitive function and provide reminders can prove beneficial in maintaining independence and fostering engagement in daily activities.
Comparison of Different Models of Care and Areas Needing Improvement
Different models of care for TBI patients exist, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The effectiveness of a specific model often depends on the patient’s specific needs and the availability of resources. Integrated care models, combining medical, rehabilitation, and social services under one umbrella, demonstrate promise in providing holistic support. However, current models often struggle to address the complex social and emotional needs of patients and their families.
Improving access to mental health services and providing tailored support for caregivers are crucial areas for enhancement.
Key Challenges and Opportunities for Improving TBI Outcomes
| Challenges | Opportunities |
|---|---|
| Lack of standardized assessment tools across different healthcare settings | Development and implementation of standardized assessment protocols to ensure consistent and accurate evaluation of TBI patients |
| Limited access to specialized rehabilitation programs in some regions | Expanding access to specialized rehabilitation centers and training programs for healthcare professionals in underserved areas |
| Inadequate support systems for caregivers of TBI patients | Development of comprehensive caregiver support programs, including educational resources, emotional support groups, and respite care options |
| Difficulty in predicting long-term cognitive and functional outcomes | Advancements in diagnostic tools and biomarkers to improve the accuracy of long-term outcome prediction |
Promising Research Areas for Developing New Treatments and Therapies
Neuroprotective strategies aimed at minimizing neuronal damage following TBI represent a promising area of research. Developing targeted therapies that stimulate neuronal repair and regeneration hold significant potential for improving functional recovery. Further research into the underlying mechanisms of brain injury and the identification of novel therapeutic targets are crucial steps towards developing more effective treatments and improving the lives of individuals affected by TBI.
For example, stem cell therapies and gene therapies offer promising avenues for repairing damaged neural pathways and promoting neuronal growth.
Last Word
In conclusion, relief ahead for traumatic brain injuries is not just a hope but a tangible pursuit. By examining the various facets of TBI, from its diverse forms and effects to cutting-edge treatments and supportive resources, we gain a deeper understanding of the complex journey toward recovery. The future holds immense promise, with ongoing research and innovative approaches likely to lead to even better outcomes for TBI patients and their families.
Continued advocacy, improved access to care, and a supportive community will play a vital role in shaping a brighter future for those impacted by this condition.
