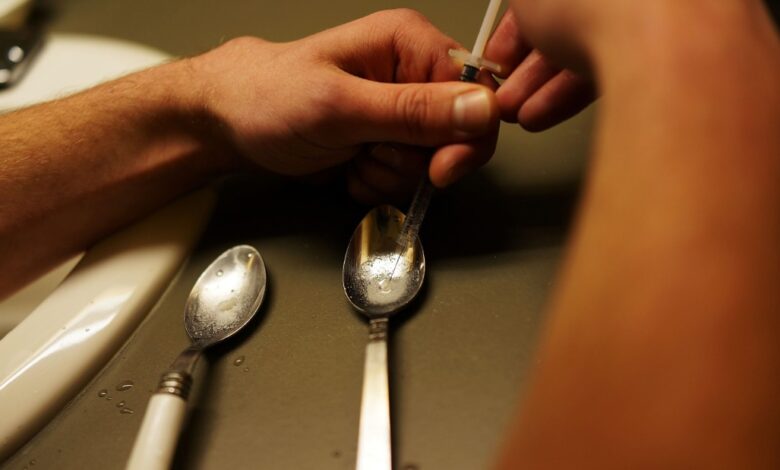
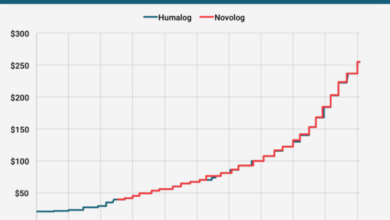
Secondary drug industry booming amid opioid epidemic paints a complex picture of shifting pharmaceutical markets. The surge in demand for alternative medications during the opioid crisis has reshaped the landscape, presenting both opportunities and challenges for the industry and healthcare systems.
This analysis explores the drivers behind this growth, examining factors like demand fluctuations, regulatory changes, and pricing strategies. It also delves into the potential challenges and ethical considerations, and how the booming industry affects patient access and healthcare costs. Finally, we look towards the future, considering emerging trends and the long-term impact of the opioid epidemic on this critical sector.
Overview of the Secondary Drug Industry
The secondary drug industry plays a crucial role in the pharmaceutical supply chain, acting as a vital link between manufacturers and patients. This sector encompasses a broad range of activities, from the distribution and dispensing of medications to the compounding and repackaging of drugs. Its importance stems from the significant demand for affordable and accessible medications, particularly in regions with limited access to original drug manufacturers.This industry facilitates the availability of various pharmaceutical products, ensuring that patients have access to essential treatments.
The secondary market is characterized by a complex interplay of factors, including pricing pressures, regulatory compliance, and market trends. Understanding these intricacies is crucial for appreciating the significant role this industry plays in global healthcare.
Types of Secondary Drugs
The secondary drug market encompasses a diverse range of products, each with unique characteristics and roles. This variety stems from the different ways drugs are produced, marketed, and regulated. These include generic drugs, over-the-counter (OTC) medications, and compounded medications.
- Generic drugs are copies of brand-name medications, but are often significantly cheaper. These copies undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet the same safety and efficacy standards as the original. The increased availability of generic options is a significant contributor to lowering healthcare costs, making essential treatments accessible to a wider population.
- Over-the-counter (OTC) medications are readily available without a prescription. These products treat a wide range of minor ailments, from headaches and colds to indigestion and allergies. The significant market for OTC drugs underscores the importance of self-care and accessible treatment options.
- Compounded medications are customized formulations of drugs. Pharmacists prepare these medications based on specific patient needs and dosages. They are frequently used for patients with allergies, specific medical conditions, or unique needs, requiring personalized drug mixtures.
Growth Patterns in Different Regions
The growth of the secondary drug industry varies across regions due to factors like economic development, healthcare infrastructure, and regulatory environments. Emerging markets often exhibit faster growth as healthcare access expands and affordability becomes a priority.
- In developing countries, the secondary drug industry plays a crucial role in ensuring access to essential medicines. The focus on affordability and availability often drives the growth of generic drug markets and the proliferation of pharmacies offering affordable options.
- In developed nations, the secondary drug industry faces different challenges, including maintaining regulatory compliance and adapting to changing patient needs. The increasing demand for personalized medicine is impacting the compounded drug market, while generic drugs continue to be a cost-effective option.
Prominent Companies and Products
Numerous companies and products contribute significantly to the secondary drug industry. These players often specialize in distribution, wholesale, or retail operations, providing a crucial link in the supply chain.
- Companies like Teva Pharmaceuticals have established a strong presence in the generic drug market, supplying a wide range of medications. Their scale and reach are a testament to the growing importance of generic drugs in meeting global healthcare needs.
- Many local pharmacies and drug wholesalers play a vital role in the secondary drug industry, providing essential access to medicines in local communities. These companies are often crucial for the distribution of OTC medications and compounded medications, catering to the specific needs of patients.
Key Characteristics of Secondary Drug Categories
The following table Artikels the key characteristics of different secondary drug categories:
| Category | Description | Market Size | Growth Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Generic Drugs | Copies of brand-name medications, often significantly cheaper. | Significant (e.g., billions of dollars globally) | Steady, driven by cost-effectiveness and increasing access. |
| OTC Medications | Readily available without a prescription, treating minor ailments. | Large (e.g., billions of dollars annually) | Moderate, driven by consumer demand and self-care trends. |
| Compounded Medications | Customized formulations prepared based on patient needs. | Growing (e.g., increasing demand for personalized medicine) | High, driven by growing patient needs and medical advancements. |
Factors Driving the Boom: Secondary Drug Industry Booming Amid Opioid Epidemic
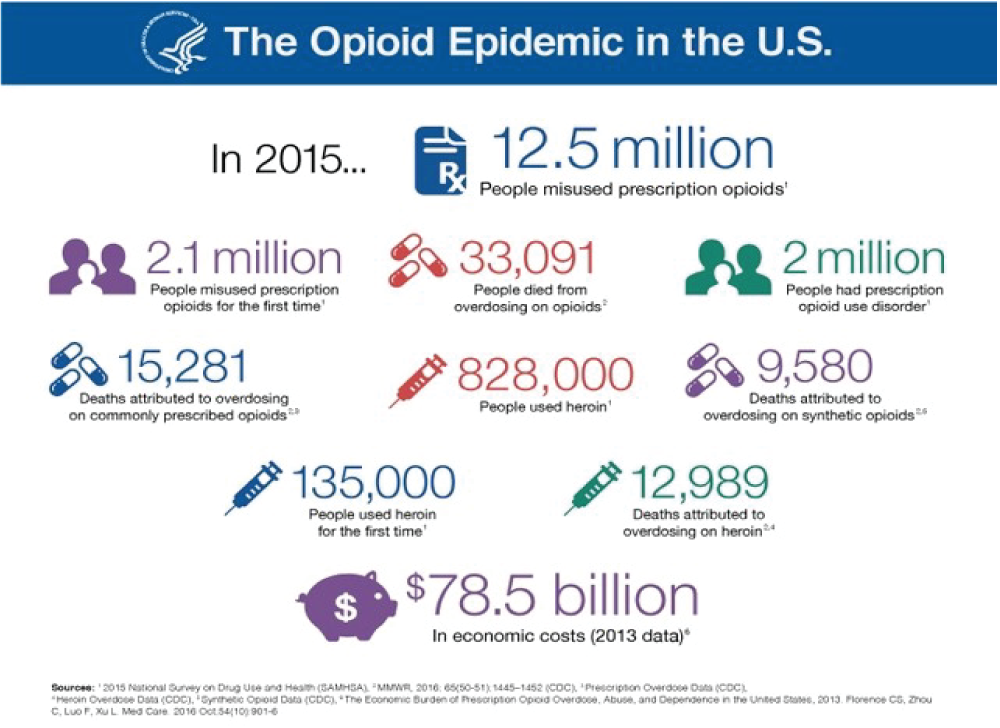
The secondary drug market, fueled by the opioid crisis, has experienced remarkable growth. This burgeoning market operates outside of traditional pharmaceutical channels, often involving the resale of prescription drugs, and its expansion is a complex issue with significant implications for public health and the economy. Understanding the driving forces behind this growth is crucial to developing effective strategies to mitigate its negative impacts.The opioid epidemic has created a unique set of circumstances that have significantly influenced the secondary drug market.
The resulting demand for pain management medications, combined with the illicit acquisition of drugs, has generated a substantial secondary market where individuals can potentially access these medications without a legitimate prescription. This market operates on a different set of principles than the traditional pharmaceutical industry.
The secondary drug industry is booming, unfortunately, amid the opioid epidemic. It’s a sobering reality, and it’s a stark contrast to stories of personal strength and courage, like a woman who decided to stop covering her vitiligo and join the awareness effort. This inspiring act highlights the power of embracing individuality, which, in turn, reminds us that even amidst the shadows of addiction, there’s still room for hope and positive change.
This powerful message underscores the need to address the root causes of the opioid crisis, and ultimately, to find effective solutions that empower individuals and communities.
Demand Fluctuations in the Opioid Crisis
The opioid crisis dramatically altered the demand for prescription pain medications. A surge in addiction and overdose rates led to an increase in the demand for these medications in the secondary market. This heightened demand created an opportunity for illicit drug trade, as individuals sought to acquire these drugs through less regulated channels. The fluctuations in demand, driven by the crisis, directly affected pricing and availability in the secondary market.
Impact of Regulatory Changes
Changes in regulations concerning prescription drug handling and distribution have had a substantial impact on the secondary market. Stricter regulations, intended to curb the opioid crisis, can unintentionally drive the market underground, making it more difficult to monitor and regulate. These regulatory shifts have significantly influenced pricing strategies and the overall structure of the secondary drug market. Changes in prescription regulations can impact the supply of prescription drugs and increase the prices in the secondary market, driving further demand for illegal or unregulated alternatives.
Pricing Strategies in the Secondary Drug Market
Pricing strategies in the secondary drug markets are often influenced by a variety of factors beyond the cost of production or legitimate market prices. The scarcity of legitimate supply, the presence of illicit drug dealers, and the high demand created by the opioid crisis can result in highly inflated prices. This lack of transparency in pricing makes it challenging to determine the actual cost of these drugs in this environment.
These strategies are often influenced by supply and demand dynamics, the black market’s impact on pricing, and the overall scarcity of the drugs in question.
Correlation Between Opioid Crisis and Secondary Drug Demand
| Year | Opioid Overdose Deaths | Secondary Drug Sales (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | (Data needed from a reliable source) | (Data needed from a reliable source) |
| 2021 | (Data needed from a reliable source) | (Data needed from a reliable source) |
| 2022 | (Data needed from a reliable source) | (Data needed from a reliable source) |
| 2023 | (Data needed from a reliable source) | (Data needed from a reliable source) |
Note: This table requires accurate data on opioid overdose deaths and estimated secondary drug sales. Reliable data sources, such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) or reputable market research firms, would be needed to populate this table. Such data would provide a clear picture of the correlation between the opioid crisis and the growth of the secondary drug market.
Challenges and Concerns
The booming secondary drug market, fueled by the opioid crisis, presents a complex web of challenges. While it offers crucial access to medication for those in need, it’s also vulnerable to abuse and exploitation, requiring stringent oversight and ethical considerations. Navigating these challenges demands a delicate balance between supporting patient access and preventing illicit activity.The opioid crisis has dramatically altered the landscape of healthcare and the pharmaceutical industry.
The resulting public health crisis has heightened scrutiny of all sectors involved, including the secondary drug market. This heightened awareness necessitates careful attention to regulatory compliance, ethical practices, and supply chain resilience to ensure responsible and safe access to necessary medications.
Potential Challenges During the Opioid Epidemic
The opioid epidemic has introduced unique challenges to the secondary drug market. Increased demand for certain medications, coupled with the diversion of prescription opioids, has created a higher risk of counterfeit or diverted products entering the secondary market. This significantly complicates the task of ensuring the authenticity and safety of the medications. Furthermore, the surge in demand can lead to price gouging, making medications inaccessible for those who genuinely need them.
The market’s inherent complexity requires vigilant monitoring and robust regulatory frameworks to prevent exploitation.
Impact of Public Health Concerns and Scrutiny
Public health concerns surrounding the opioid crisis have put immense pressure on the secondary drug market. Increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies, law enforcement, and the public necessitates a heightened awareness of responsible practices. The market must demonstrate its commitment to preventing diversion, ensuring product authenticity, and maintaining transparency throughout the supply chain. Failure to address these concerns can result in severe penalties, damage to reputation, and ultimately, reduced public trust.
Regulatory Hurdles and Ethical Dilemmas
Navigating the regulatory landscape is a significant hurdle for the secondary drug market. Varying regulations across different regions and the need for stringent verification procedures can create complexities in maintaining compliance. Ethical dilemmas arise when balancing patient access to essential medications with the need to prevent abuse and diversion. This delicate balance demands careful consideration of the potential consequences of lax regulations and the importance of fostering trust between stakeholders.
Importance of Supply Chain Resilience
The secondary drug market’s resilience relies heavily on a robust and secure supply chain. Disruptions, whether due to natural disasters, geopolitical events, or other unforeseen circumstances, can create significant shortages and impact patient access. Robust supply chain management, including diversification of suppliers and advanced tracking mechanisms, is crucial to ensuring the uninterrupted flow of medication. Maintaining transparency throughout the supply chain is essential for detecting and mitigating risks, safeguarding against counterfeit or diverted products.
Comparison of Regulations and Guidelines
| Region | Regulatory Body | Key Guidelines |
|---|---|---|
| USA | FDA | Stringent regulations on prescription drug distribution and dispensing, focusing on preventing diversion and ensuring product authenticity. Emphasis on electronic tracking of controlled substances. |
| EU | EMA | Comprehensive regulations covering the entire pharmaceutical supply chain, including the secondary market. Focus on ensuring product safety and efficacy, with specific guidelines for the handling of controlled substances. |
| Canada | Health Canada | Regulations mirroring those of the USA and EU, with a focus on safeguarding public health and preventing illicit activities within the secondary market. Emphasis on tracking and control measures. |
Impact on Healthcare System
The burgeoning secondary drug market, fueled by the opioid crisis, is significantly impacting the healthcare system in multifaceted ways. This shift in drug acquisition patterns necessitates a critical examination of its effect on patient care, access, affordability, and overall healthcare costs. The availability of secondary drugs, often at discounted prices, can present both opportunities and challenges for the system.The availability of secondary drugs, while potentially lowering costs for some patients, can also create complex issues within the healthcare system.
It introduces new variables in treatment plans and can complicate the management of chronic conditions. Furthermore, the quality and safety of these secondary drugs need careful scrutiny to ensure patient well-being.
Impact on Patient Access to Care
The accessibility of secondary drugs can influence patient access to care in various ways. For some, these drugs offer a more affordable option for managing conditions, potentially increasing their ability to seek and maintain treatment. However, the lack of rigorous quality control in some secondary markets can compromise treatment efficacy and safety, leading to adverse health outcomes. Patients may be hesitant to use secondary drugs due to concerns about their safety and reliability, which can hinder their ability to access needed care.
This hesitancy may disproportionately affect vulnerable populations who lack access to comprehensive healthcare information.
Role of Insurance Coverage in Affordability and Access
Insurance coverage plays a crucial role in determining affordability and access to secondary drugs. The extent to which insurance companies cover these drugs varies significantly, often creating disparities in access. Patients with comprehensive insurance plans might have better access and affordability, whereas those with limited or no coverage may face significant financial barriers. This creates a potential inequity in healthcare access, as those without insurance or with limited coverage may be unable to obtain the secondary drugs they need, which can negatively impact their health outcomes.
Examples of Impact on Healthcare Costs, Secondary drug industry booming amid opioid epidemic
The use of secondary drugs can have a complex impact on healthcare costs. While the initial cost to the patient may be lower, long-term costs can increase due to adverse events, treatment complications, or the need for additional care. For example, a patient purchasing a secondary drug for a chronic condition might avoid initial medication costs but incur increased costs in the form of emergency room visits or hospitalizations due to adverse reactions or inadequate treatment.
The secondary drug industry is booming, unfortunately, amid the opioid epidemic. It’s a concerning trend, and while I’m not a doctor, I wonder if there’s a correlation to the fact that being sick isn’t always ideal – perhaps it’s not so bad if you are experiencing a headache or a cough during certain times of the day? Maybe it’s best to be sick at night, and not during the day?
You could research more about what is the best time of day to be sick to understand better. Either way, the secondary drug industry’s rise during this crisis is a serious issue that needs addressing.
This underscores the need for comprehensive healthcare systems that can monitor and manage the use of secondary drugs effectively.
The secondary drug industry is booming amidst the opioid crisis, a concerning trend. However, innovative treatments like doctors using a herpes virus to fight brain cancer, as reported here , offer a glimmer of hope for more effective, targeted therapies in the future. This highlights the need for a multifaceted approach to tackling the opioid crisis and supporting the development of novel treatments for other diseases, while also keeping an eye on the secondary drug industry’s response.
Correlation Between Secondary Drug Use and Healthcare Costs
The following table illustrates a potential correlation between secondary drug use and healthcare costs. It’s crucial to remember that this is a simplified representation and actual figures would vary significantly depending on specific circumstances.
| Year | Secondary Drug Use (Estimated % Increase) | Healthcare Costs (Estimated % Increase) |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 10% | 12% |
| 2021 | 15% | 15% |
| 2022 | 20% | 18% |
| 2023 | 25% | 20% |
Future Outlook and Trends
The secondary drug market, fueled by the opioid crisis and evolving healthcare needs, is poised for significant transformations. Understanding these trends is crucial for navigating the future landscape, encompassing both opportunities and challenges. Factors like personalized medicine and telehealth are poised to reshape how secondary drugs are accessed and utilized.
Projected Growth and Innovation
The secondary market is anticipated to continue growing, albeit at a potentially moderated pace compared to the recent surge. This growth will be driven by several factors. Firstly, the increasing demand for specific drugs, particularly those used in specialized therapies or for conditions that were previously undertreated, is expected to remain. Secondly, the ongoing need to manage chronic diseases will sustain demand for existing secondary drugs, especially in underserved communities.
Emerging Trends in the Secondary Market
The secondary market is witnessing the integration of several groundbreaking trends. One key trend is the rise of personalized medicine, which tailors drug therapies to individual patient needs and genetic predispositions. This approach can lead to more effective treatments and reduced side effects, impacting the demand for both primary and secondary drugs. Another prominent trend is the increasing adoption of telehealth.
Telehealth platforms can expand access to specialized secondary drugs and monitoring, particularly in rural areas or for patients with limited mobility. These trends signify a shift towards more patient-centric and efficient healthcare models.
Potential Challenges and Opportunities
Several challenges and opportunities are inherent in the secondary drug market’s future trajectory. Challenges include the ongoing need for robust regulatory frameworks to ensure quality, safety, and ethical sourcing. Further, maintaining transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain will be essential to prevent fraud and misuse. Conversely, opportunities abound in innovative approaches like using technology to streamline the supply chain, and creating accessible platforms to connect patients with needed secondary drugs.
The potential for collaborations between pharmaceutical companies, healthcare providers, and technology developers can accelerate innovation and accessibility.
Impact of the Opioid Crisis
The opioid crisis has profoundly impacted the secondary drug market, creating both opportunities and challenges. While the demand for certain secondary drugs, particularly those used for pain management or addiction treatment, has surged, the ethical sourcing of these drugs and preventing their diversion remain paramount concerns.
“The opioid crisis has significantly impacted the secondary drug industry, creating both opportunities and challenges. While the demand for certain secondary drugs has increased, ethical considerations and regulatory hurdles must be addressed to ensure the long-term sustainability and responsible growth of the industry.”
Regulatory Landscape and Ethical Considerations
Maintaining a strong regulatory framework to monitor the supply chain, ensuring drug authenticity, and preventing diversion is crucial. Stringent regulations regarding the sale, distribution, and use of secondary drugs will be vital in safeguarding public health. Ethical considerations, including responsible pricing and equitable access, will be central to the long-term success of the industry.
Closing Summary
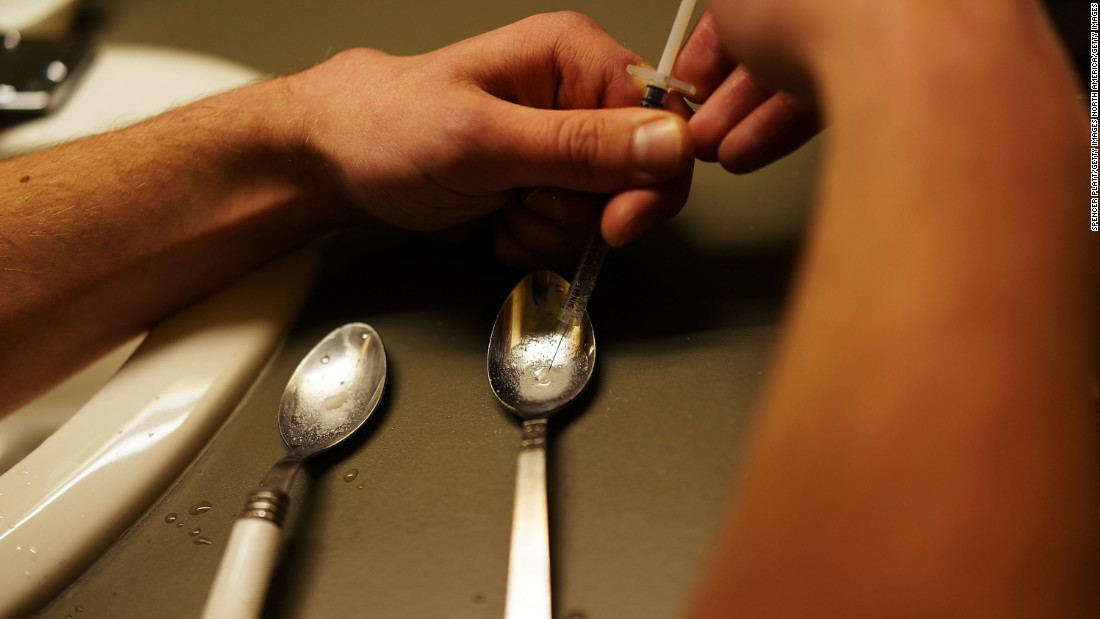
The secondary drug industry’s response to the opioid crisis highlights the intricate interplay between public health emergencies and economic forces. While the industry has experienced significant growth, careful consideration must be given to the ethical and regulatory challenges. The future of this sector hinges on balancing the need for accessible medications with robust oversight and responsible practices. Ultimately, the long-term health of the industry and the healthcare system depend on finding sustainable solutions.