Summer camps tightening rules on vaccinations is a significant development impacting families and the summer camp industry. The new regulations are prompting a lot of discussion, weighing the importance of public health against individual choices. Camp administrators, parents, and health officials are all navigating a complex landscape of evolving policies, potential impacts on enrollment, and the ethical considerations surrounding mandatory vaccinations.
This article explores the historical context of vaccination policies in summer camps, the rationale behind tightening these rules, and the multifaceted impact on various stakeholders. It also delves into public responses, legal and ethical considerations, alternative solutions, and future projections for vaccination policies in the summer camp sector.
Background on Vaccination Policies in Summer Camps
Summer camps, a cherished part of childhood, have historically played a significant role in fostering social and developmental growth. However, the safety and well-being of campers necessitate careful consideration of health protocols, especially regarding vaccinations. Vaccination policies in summer camps have evolved significantly over time, driven by public health concerns and evolving scientific understanding.Vaccination requirements in summer camps have demonstrably improved public health by reducing the transmission of preventable diseases.
The policies reflect a crucial balance between safeguarding campers and maintaining a supportive, inclusive environment. This evolution has been shaped by public health organizations and, importantly, adapting to new knowledge and challenges.
Historical Overview of Vaccination Requirements
Early summer camps often lacked formal vaccination requirements. However, the increasing recognition of the importance of vaccination against contagious diseases led to the gradual implementation of policies. The 1950s saw the rise of organized vaccination programs, which influenced the development of early vaccination guidelines for camps. The 1980s and 1990s witnessed a rise in concerns about vaccine-preventable diseases and the introduction of more stringent policies.
Common Vaccination Policies Across Regions/Countries
Vaccination requirements for summer camps vary significantly across different regions and countries. In some regions, a comprehensive list of required vaccinations is mandated, while others might have more flexible approaches. For instance, some countries might prioritize vaccinations based on local disease prevalence, while others maintain a more standardized approach across all camps.
Evolution of Vaccination Policies Over Time
Vaccination policies in summer camps have undergone substantial change. Initial policies focused primarily on protecting campers from common childhood diseases. As medical knowledge advanced, the scope of required vaccinations broadened to include newer vaccines and to address emerging public health threats. This evolution demonstrates a commitment to public health and a responsiveness to the changing epidemiological landscape.
The inclusion of new vaccines like those for HPV and Meningitis reflects this adaptability.
Role of Public Health Organizations in Shaping Policies
Public health organizations play a critical role in establishing and updating vaccination guidelines for summer camps. These organizations conduct research, monitor disease trends, and provide recommendations to camp administrators and government bodies. They offer expert advice on vaccination schedules and safety protocols, ensuring compliance with evidence-based best practices. For example, the CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) plays a pivotal role in recommending and updating vaccination schedules.
Comparison of Vaccination Requirements for Different Age Groups
| Age Group | Required Vaccinations |
|---|---|
| Infants (0-1 years) | Hepatitis B, Rotavirus, Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, Haemophilus influenzae type b, Pneumococcal disease, Polio, Measles, Mumps, Rubella |
| Toddlers (1-3 years) | Hepatitis B, Rotavirus, Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, Haemophilus influenzae type b, Pneumococcal disease, Polio, Measles, Mumps, Rubella |
| Preschoolers (3-5 years) | Hepatitis B, Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, Haemophilus influenzae type b, Pneumococcal disease, Polio, Measles, Mumps, Rubella, Varicella, Hepatitis A (often recommended) |
| School-age (5-17 years) | Varicella, Hepatitis A, HPV, Meningococcal Conjugate Vaccine, Flu shot (annual) |
This table provides a general overview. Specific requirements may vary based on location and individual camp policies. It’s essential to confirm the precise vaccination requirements with the specific summer camp.
Reasons Behind Tightening Vaccination Rules
Summer camps are vital for children’s social and developmental growth. However, the increasing number of unvaccinated children attending these camps raises significant concerns about potential health risks. This necessitates a closer look at the rationale behind tightening vaccination policies, focusing on the potential for outbreaks, the prevalence of vaccine-preventable diseases, and the crucial role of herd immunity.Protecting children from preventable illnesses is paramount.
This is particularly true in shared environments like summer camps where close contact and rapid transmission of infectious diseases are more likely.
Potential Health Risks of Unvaccinated Children
The presence of unvaccinated children in a summer camp environment exposes others to preventable diseases. Measles, whooping cough, and other illnesses can spread rapidly among children who haven’t received the necessary vaccinations. Unvaccinated children are not only at risk themselves but also pose a significant threat to their peers, particularly those with compromised immune systems. Infectious diseases can have severe consequences, including hospitalization, long-term health complications, and even death.
Increasing Prevalence of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases
The recent resurgence of vaccine-preventable diseases highlights the importance of vaccination. Cases of measles, for example, have been on the rise in certain parts of the world. This resurgence underscores the need for maintaining high vaccination rates to prevent the spread of these diseases and protect vulnerable populations.
Factors Driving Concerns About Unvaccinated Children
Several factors contribute to concerns about unvaccinated children attending summer camps. The potential for outbreaks in close-contact settings like camps, the vulnerability of those with weakened immune systems, and the ethical considerations surrounding the rights of other children to a safe environment are all significant issues.
Potential for Outbreaks in Summer Camp Settings
Summer camps provide an environment conducive to the rapid spread of infectious diseases. Close proximity, shared activities, and limited opportunities for isolation all contribute to the risk of outbreaks. The potential impact of an outbreak on the entire camp community, with its potential to disrupt activities and lead to extensive quarantines, is a key concern. Historical examples of large outbreaks in similar settings demonstrate the devastating consequences of insufficient vaccination coverage.
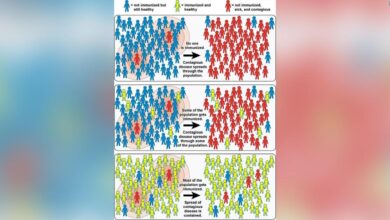
Importance of Vaccination in Maintaining Herd Immunity
Herd immunity protects the entire community, not just those who are vaccinated. When a high percentage of the population is vaccinated, the spread of contagious diseases is significantly reduced, effectively shielding those who cannot be vaccinated (due to medical reasons) or who have not yet developed immunity. This collective protection is crucial for maintaining a healthy community and preventing outbreaks.
Potential Benefits of Mandatory Vaccination Policies
| Policy Benefit | Detailed Explanation |
|---|---|
| Reduced Risk of Outbreaks | Mandatory vaccination policies significantly reduce the likelihood of large-scale outbreaks in summer camp settings, safeguarding the health of all children. |
| Protection of Vulnerable Populations | Vaccinated individuals shield those who cannot be vaccinated or are at a higher risk of severe illness. |
| Maintenance of Herd Immunity | High vaccination rates maintain herd immunity, preventing the widespread transmission of vaccine-preventable diseases, benefiting the entire community. |
| Public Health Preservation | By minimizing the risk of disease transmission, mandatory vaccination policies support the overall health of the community. |
| Enhanced Safety and Well-being | Creating a safer and healthier environment for all children, regardless of their vaccination status. |
Impact of the New Rules on Summer Camps
Summer camps across the country are adapting to stricter vaccination policies, and the ripple effect is already being felt. These new mandates are poised to significantly alter the landscape of the summer camp experience, impacting everything from enrollment numbers to financial viability. The changes necessitate careful consideration of potential challenges for both camps and families.The tightening of vaccination requirements for summer camps will undoubtedly have a profound impact on enrollment and camp operations.
The new policies will force camps to reassess their current practices, implement new procedures, and possibly face significant financial implications. This shift demands proactive adaptation and careful planning.
Potential Impact on Enrollment Numbers
The stricter vaccination policies will likely affect enrollment numbers. Families with unvaccinated children may opt to seek alternative summer activities, leading to a decrease in enrollment for some camps. This effect is already being seen in some areas, as parents weigh the costs and benefits of complying with the new requirements. A drop in enrollment could strain camp budgets, requiring cost-cutting measures or innovative strategies to attract new campers.
Camp Adaptation Strategies
Many camps are actively adapting to these new rules. Some are proactively communicating with families, clarifying the requirements, and offering support. Others are exploring alternative vaccination documentation processes, such as accepting records from healthcare providers outside the immediate area. These proactive measures will be crucial for maintaining enrollment levels. One example is a renowned science camp that is partnering with local healthcare clinics to offer on-site vaccination clinics to ease the process for families.
Financial Implications for Camps
The tightening of vaccination policies will undoubtedly have financial implications for summer camps. Decreased enrollment could lead to a reduction in revenue, forcing camps to cut costs or potentially raise prices for remaining campers. The cost of administering the vaccination clinics, educating families, and potentially adjusting facilities will all contribute to the financial strain. For example, a small, independent camp might face a significant challenge in covering the costs associated with providing on-site vaccination services.
Impact on Different Types of Camps, Summer camps tightening rules on vaccinations
The impact of vaccination requirements will vary across different types of summer camps. Residential camps, which often have a higher density of campers and staff, may face a greater need for vaccination-related adjustments than day camps. Furthermore, specialized camps, such as those focusing on children with specific needs, might encounter unique challenges in accommodating the new requirements. This is especially true if these camps have a high percentage of campers or staff from specific regions or communities where vaccination rates might be lower.
Challenges for Families with Unvaccinated Children
Families with unvaccinated children may encounter significant challenges. They might face difficulty finding alternative summer activities or incur additional expenses related to vaccinations. Some might be required to take additional time off from work or other commitments to ensure their children can obtain necessary vaccinations. These challenges highlight the need for support systems and flexible solutions for these families.
Potential Financial Burden on Families
| Vaccination Type | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|
| Measles, Mumps, Rubella (MMR) | $50-$150 |
| Varicella (Chickenpox) | $50-$100 |
| Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis (DTaP) | $30-$70 |
| Polio | $15-$35 |
| Influenza (Flu) | $30-$50 |
Note: Costs can vary depending on the location, healthcare provider, and insurance coverage.
The table above illustrates the potential cost of vaccinations. These costs, while sometimes covered by insurance, can represent a significant burden for families with limited resources. Furthermore, the cost of obtaining the necessary documentation to comply with the requirements may also add to the overall expenses.
Public Response to the Tightening of Rules

Summer camp vaccination policies are sparking heated debates, and the public response reflects a wide spectrum of opinions. Parents, campers, and community members are weighing the benefits of increased safety against concerns about individual liberties and potential drawbacks to camp operations. The discussions often center on the perceived risks and benefits, and the role of personal choice in public health.
Varying Perspectives on Vaccination Policies
Public opinion on the new vaccination policies is sharply divided. Proponents emphasize the importance of herd immunity and disease prevention, particularly in the vulnerable population of children. Conversely, opponents often raise concerns about individual autonomy and the potential for adverse reactions to vaccines. This divergence in perspectives underscores the complexity of the issue.
Arguments in Favor of Stricter Requirements
Proponents of stricter vaccination requirements frequently highlight the significant public health benefits of herd immunity. By preventing the spread of infectious diseases, mandatory vaccination policies protect not only those who are vaccinated but also those who cannot be vaccinated for medical reasons. This approach also ensures a safe environment for all participants within the summer camp setting. Public health officials often point to the success of similar vaccination programs in reducing the incidence of preventable diseases.
Arguments Against Stricter Requirements
Opponents of stricter requirements often emphasize individual rights and the freedom of choice regarding medical decisions. They raise concerns about potential adverse reactions to vaccines and argue that mandatory vaccination policies can disproportionately impact families who have conscientious or religious objections. Concerns about potential legal challenges and the financial burden on families are also often voiced. Some argue that the risks of vaccine side effects may outweigh the benefits of herd immunity, particularly in cases of rare but serious reactions.
Public Discussions and Debates
Online forums, social media platforms, and local news outlets have become battlegrounds for the vaccination debate. Parents share personal stories and opinions, and heated discussions erupt regarding the safety and effectiveness of vaccines. The intensity of these online debates often obscures nuanced perspectives and factual information. Local town hall meetings and community forums have also become venues for public discourse, often characterized by differing views and passionate exchanges.
Role of Social Media in Shaping Public Opinion
Social media plays a significant role in shaping public opinion on vaccination policies. Viral posts, often lacking scientific backing, can quickly spread misinformation and fuel public anxieties. This creates an environment where emotions and personal opinions often outweigh objective facts. The rapid dissemination of information on social media platforms requires critical evaluation of sources and factual verification.
Data on Public Support/Opposition
Reliable data on public support or opposition to these policies is not readily available in a centralized format. Public opinion polls conducted on this topic are often inconsistent in their methodology and results, making it challenging to draw definitive conclusions. The limited data available suggests a substantial division in public opinion.
Summary of Viewpoints
| Viewpoint | Key Arguments | Potential Concerns |
|---|---|---|
| Pro-Vaccination | Herd immunity, disease prevention, public health benefits | Potential for adverse reactions, financial burden on families |
| Anti-Vaccination | Individual rights, freedom of choice, potential vaccine side effects | Risk to vulnerable populations, decreased herd immunity |
Legal and Ethical Considerations
The tightening of vaccination policies in summer camps raises complex legal and ethical questions, particularly regarding parental rights, public health, and the balance between individual freedoms and community well-being. These considerations demand careful scrutiny to ensure the policies are both effective and ethically justifiable.The legal landscape surrounding mandatory vaccination is varied and nuanced, differing significantly between jurisdictions. Navigating these complexities is crucial for understanding the implications of these policies.
Legal Frameworks Surrounding Mandatory Vaccination Policies
Different jurisdictions have varying legal frameworks governing mandatory vaccination. These frameworks often reflect the specific priorities and legal traditions of each region. Understanding these legal distinctions is essential for comprehending the nuances of mandatory vaccination policies. Some jurisdictions have broad public health powers that allow for mandatory vaccination policies for certain populations, while others may have more limited or specific provisions.
Ethical Considerations Involved in Mandatory Vaccination Requirements
Mandatory vaccination policies raise several ethical dilemmas. One major concern is the potential infringement on parental autonomy and the right to make decisions regarding their children’s health. Balancing individual rights with the broader public health goal of disease prevention is a critical ethical consideration. The potential for discrimination and unequal access to healthcare based on socioeconomic factors also poses an ethical concern.
Rights of Parents to Make Decisions Regarding Their Children’s Health
The right of parents to make decisions regarding their children’s health is a fundamental principle in many legal systems. However, this right is not absolute and may be limited by public health concerns, particularly in the context of contagious diseases. Parents have a moral and legal obligation to ensure their children’s well-being, but this does not always translate into unfettered decision-making power on matters impacting public health.
Legal Precedents and Court Cases Related to Mandatory Vaccination
Numerous court cases have addressed the issue of mandatory vaccination. These cases have often focused on the balance between individual liberties and public health concerns. Some precedents have upheld mandatory vaccination policies, while others have struck them down, depending on the specific legal framework and the circumstances of each case. The varying interpretations of the law by different courts illustrate the complexity of the issue.
Comparison of Vaccination Policies Across Different Jurisdictions
Vaccination policies vary significantly across jurisdictions, reflecting differences in legal frameworks, cultural norms, and public health priorities. Comparing these policies provides insights into the diverse approaches to protecting public health and balancing individual rights. The variations highlight the challenges in creating a uniform approach to vaccination policies across different legal contexts.
Summer camps are definitely tightening their vaccination rules, which is a big deal for families. It’s a tricky situation, but hopefully, these new rules will help keep everyone safe. Thinking about the mental health benefits of summer, checking out Healthline’s picks for the 15 best mindfulness gifts healthlines picks for the 15 best mindfulness gifts might offer some peaceful solutions for stress and anxiety, which are very relevant to these changing camp policies.
Ultimately, these rules are designed to keep the campers healthy and happy during the summer season.
Key Legal and Ethical Arguments for and Against the Tightening of Vaccination Rules
| Argument | Justification |
|---|---|
| For Tightening | Protecting vulnerable populations, especially infants and those with compromised immune systems, from infectious diseases. Maintaining herd immunity to prevent outbreaks. |
| Public health is a shared responsibility, and individuals have a duty to contribute to the well-being of the community. | |
| Stricter policies can act as a deterrent to the spread of preventable diseases. | |
| Against Tightening | Potential infringement on parental autonomy and the right to make decisions regarding children’s health. |
| Risk of stigmatization and discrimination against families with differing beliefs. | |
| Potential for unequal access to healthcare based on socioeconomic factors. | |
| Limited evidence demonstrating a significant correlation between tighter vaccination rules and reduced disease transmission in certain populations. |
Alternative Solutions and Strategies

Summer camp vaccination policies are evolving, creating a complex interplay between public health concerns and parental rights. Finding a balance that prioritizes safety while respecting individual choices is crucial. This necessitates exploring alternative strategies beyond mandatory vaccination policies. These approaches aim to foster a healthy environment for all campers while accommodating the diverse needs of families.
Alternative Approaches to Ensuring Health and Safety
Several alternative approaches can complement vaccination policies to ensure the health and safety of all campers. These methods prioritize preventative measures, educational outreach, and personalized support for families. Flexible approaches allow for accommodating diverse needs and perspectives.
Summer camps are cracking down on vaccination requirements, which is understandable given the current health climate. But while that’s happening, exciting advancements like a potential patch for peanut allergies, as detailed in this fascinating article, patch for peanut allergies shows promise , offer a glimmer of hope for managing food allergies. This could significantly impact the future of summer camp safety protocols, especially for children with allergies.
Ultimately, keeping kids safe and healthy is the priority, whether it’s through vaccinations or innovative treatments like this patch.
- Enhanced Hygiene and Sanitation Protocols: Rigorous cleaning and disinfection schedules, handwashing stations, and readily available hand sanitizer are essential for minimizing the spread of illnesses, regardless of vaccination status. Regularly disinfecting common areas and equipment is critical to mitigate risk. For example, increased frequency of cleaning and disinfecting in communal areas like dining halls and play areas can significantly reduce the risk of infectious disease transmission.
Summer camps are tightening vaccination rules, which is causing a lot of anxiety for families. Navigating these changes can feel overwhelming, but remember that 6 ways to stay calm while dealing with uncertainty can help you manage this stressful situation. Ultimately, staying informed and prepared will help families adapt to these new vaccination requirements for the summer camp season.
- Comprehensive Health Screening and Monitoring: Implementing robust health screening procedures, including symptom checks and temperature readings, can aid in early identification of potential illnesses. Regular monitoring of camper health, with prompt response to any concerning symptoms, helps contain potential outbreaks.
- Increased Vaccination Education and Outreach Programs: Comprehensive vaccination education programs, delivered in an accessible and engaging manner, can help families understand the benefits of vaccination for their child’s health and the community’s well-being. Engaging community leaders, healthcare professionals, and parents in educational initiatives can significantly impact vaccination rates. These programs should focus on dispelling misinformation and emphasizing the safety and effectiveness of vaccines.
Addressing the Needs of Families with Unvaccinated Children
Understanding and addressing the needs of families with unvaccinated children is crucial for maintaining a balanced approach. These strategies involve providing support and resources while emphasizing the importance of health and safety.
- Providing Resources for Vaccination: Offering financial assistance or discounted vaccination services can help families who may face barriers to vaccination. Partnerships with local health clinics or community organizations can streamline access to affordable vaccination services.
- Individualized Health Plans: Allowing for individualized health plans, developed in consultation with healthcare providers, for children with specific health concerns can create a safe environment for all campers. These plans can Artikel the necessary precautions and accommodations to protect both the child and the wider community. This approach acknowledges the diverse circumstances and health conditions of individual campers.
- Promoting Open Communication and Collaboration: Establishing clear communication channels between camp staff, parents, and healthcare providers is essential. Open dialogue fosters trust and allows for collaborative solutions to address the health concerns of unvaccinated children.
Innovative Solutions for Balancing Health Concerns with Parental Rights
Balancing health concerns with parental rights requires innovative approaches that respect individual choices while ensuring the safety of the community.
- Developing Clear and Transparent Policies: Implementing transparent policies regarding vaccination requirements and alternative options fosters trust and understanding. Clearly outlining the reasoning behind vaccination policies and the rationale for alternative solutions is essential. This creates a more inclusive and equitable environment for all families.
- Providing Educational Resources: Offering access to a wide range of educational resources, including articles, videos, and interactive tools, can equip families with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions. Providing multiple perspectives and viewpoints on vaccination can empower families to make decisions aligned with their values and beliefs.
- Creating a Supportive Community Environment: Creating a supportive community environment that values diversity of opinion and promotes respectful dialogue can contribute to a positive and productive atmosphere. Open communication and mutual understanding can facilitate the acceptance of different viewpoints and foster a safe environment for all campers.
Alternative Strategies and Potential Effectiveness
| Alternative Strategy | Potential Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Hygiene and Sanitation Protocols | High – Reduces transmission of illness regardless of vaccination status. |
| Comprehensive Health Screening and Monitoring | Medium – Aids in early identification of illnesses, allowing for prompt intervention. |
| Vaccination Education and Outreach | High – Increases understanding and acceptance of vaccination, potentially influencing future vaccination decisions. |
| Financial Assistance for Vaccination | Medium – Can help families overcome financial barriers to vaccination. |
| Individualized Health Plans | High – Addresses individual needs, promotes safety and inclusivity. |
| Open Communication and Collaboration | High – Fosters trust and mutual understanding, leading to more effective solutions. |
Future Trends and Projections: Summer Camps Tightening Rules On Vaccinations
Summer camp vaccination policies are rapidly evolving, reflecting broader societal shifts in public health and individual freedoms. The recent tightening of vaccination rules has sparked considerable debate, raising questions about the future trajectory of these policies. Understanding these potential developments is crucial for stakeholders in the summer camp industry and the broader community.
Projected Future of Vaccination Policies
The future of vaccination policies in summer camps will likely be shaped by several interconnected factors. The ongoing evolution of COVID-19, the emergence of new infectious diseases, and public health recommendations will play a significant role. Further, legislative actions at the local, state, and national levels could introduce new mandates or relax existing ones. The ongoing debate about individual rights versus public health considerations will continue to influence the development of these policies.
Potential Legislative Changes
Legislative changes regarding vaccination requirements for summer camps could emerge in response to evolving public health data, lobbying efforts from various stakeholders, and changing societal attitudes. Some states may introduce stricter mandates, potentially requiring vaccinations for a broader range of illnesses. Conversely, other jurisdictions might relax or eliminate existing requirements. The political landscape and the public’s perception of the efficacy and safety of vaccines will heavily influence these legislative shifts.
Role of Technology in Monitoring and Enforcement
Technology is poised to play an increasingly significant role in monitoring and enforcing vaccination policies. Digital vaccination records, coupled with streamlined reporting systems, will enable camps to efficiently verify compliance. This will also allow for faster identification and response to potential outbreaks. Automated systems for tracking vaccination status and reporting requirements can enhance administrative efficiency and reduce the potential for errors.
This technology may also integrate with existing camp management software, streamlining administrative tasks.
Emerging Trends in Public Health and Vaccination Policies
Emerging trends in public health and vaccination policies include a greater emphasis on personalized medicine and tailored vaccination schedules. Additionally, there’s a growing awareness of the importance of vaccine hesitancy and how to address it effectively. Furthermore, the role of community engagement in shaping vaccination policies will become increasingly important. Understanding and addressing the underlying reasons behind vaccine hesitancy and misinformation will become critical to successful implementation of vaccination policies.
Potential Scenarios for Vaccination Policies in the Coming Years
| Scenario | Vaccination Policy | Driving Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1: Continued Strict Requirements | Maintenance of stringent vaccination requirements for a broad range of illnesses, including potential new additions. | Continued concerns about the spread of infectious diseases, legislative support for public health measures. |
| Scenario 2: Relaxation of Existing Requirements | Reduction in required vaccinations, possibly focusing on a limited set of illnesses. | Shifting public sentiment towards personal autonomy, legislative pushback against stringent mandates. |
| Scenario 3: Targeted Vaccination Policies | Implementation of vaccination policies that vary based on the location, demographics, and specific health risks of the community served by the summer camp. | Focus on community health disparities, individualized health care approaches, and evidence-based practices. |
| Scenario 4: Hybrid Approach | Implementation of policies that combine stricter requirements for certain high-risk illnesses with more flexible approaches for others. | Balancing the need for public health protection with individual rights, adaptation to evolving health data and scientific consensus. |
Closing Notes
In conclusion, the tightening of vaccination rules in summer camps presents a complex issue with numerous factors at play. From historical trends in vaccination requirements to the potential financial burden on families and camps, the debate raises important questions about public health, individual liberties, and the responsibility of institutions to ensure a safe environment for all campers. The future of summer camp vaccination policies hinges on finding a balance between public health priorities and individual rights, requiring ongoing dialogue and potentially innovative solutions.