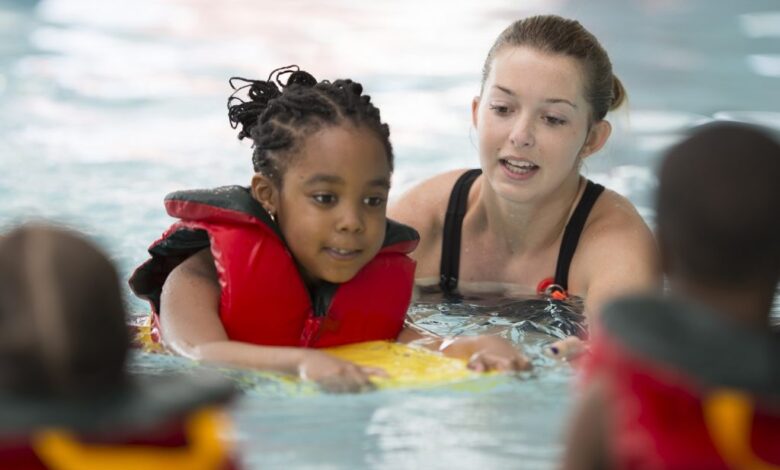
Swimming for children with asthma can be a fantastic activity, offering a safe and effective exercise option. It’s a fun way to stay healthy, but it requires careful consideration. This guide explores the benefits, safety precautions, and modifications needed to ensure a positive swimming experience for children with asthma.
This comprehensive guide covers everything from understanding the impact of asthma on physical activity to creating a safe swimming environment, adapting swimming programs, and monitoring progress. We’ll also delve into nutrition, hydration, and equipment considerations, making sure you have all the tools to help your child thrive in the water.
Introduction to Swimming for Children with Asthma
Swimming offers numerous benefits for children’s overall health, including cardiovascular fitness, muscle strengthening, and improved respiratory function. It’s a low-impact exercise that can be particularly beneficial for children with various health conditions, including asthma. However, proper adaptation is crucial to ensure safety and effectiveness.Asthma, a chronic respiratory condition, can significantly impact children’s physical activity. Symptoms like wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath can limit participation in strenuous exercises.
Therefore, adapting activities to suit the child’s specific needs and abilities is essential for fostering their physical development and preventing exacerbations.
Benefits of Swimming for Children’s Overall Health
Swimming is a comprehensive exercise that engages multiple muscle groups, promoting strength and endurance. It also improves cardiovascular health, leading to better heart function and overall well-being. Additionally, the buoyancy of water can reduce stress on joints, making it a suitable exercise option for children with various physical limitations.
Swimming as a Safe and Effective Exercise Option for Children with Asthma
Swimming, when appropriately adapted, can be a remarkably safe and effective exercise option for children with asthma. The controlled environment and consistent water temperature can help regulate breathing and minimize triggers. Furthermore, the rhythmic nature of swimming can aid in relaxation and reduce stress. Children can maintain a consistent effort without the rapid fluctuations in exertion common in other forms of exercise, making it more manageable for those with asthma.
It is crucial, however, to ensure that swimming is tailored to the child’s specific needs and abilities, and to have proper supervision and monitoring in place.
Adapting Swimming for Children with Asthma
Implementing appropriate adaptations is key to ensuring a safe and effective swimming experience for children with asthma. This involves adjusting the intensity and duration of the sessions, as well as the environment. Supervision by trained personnel and the availability of asthma medication and emergency support are vital.
Comparison of Swimming with Other Exercise Options for Children with Asthma
| Exercise | Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Swimming | Low impact, controlled environment, promotes respiratory function, good for cardiovascular health, rhythmic nature. | Requires access to a pool, may require specific adaptations depending on the child’s condition, need for supervision. |
| Running | Excellent for cardiovascular health, accessible. | High impact, can trigger asthma symptoms due to exertion, and environmental factors. |
| Cycling | Good for cardiovascular health, moderate intensity. | May not be suitable for all children with asthma, depending on individual needs. |
| Team Sports | Social interaction, team spirit. | Exertion levels can vary, potential for exposure to triggers, often less controlled environment. |
Swimming provides a safe and effective exercise option for children with asthma, with its low-impact nature, controlled environment, and potential to improve respiratory function.
Safety Considerations for Swimming
Swimming can be a fantastic activity for children, promoting physical fitness and enjoyment. However, children with asthma require specific precautions to ensure a safe and enjoyable experience. Understanding the potential risks and implementing appropriate safety measures is crucial for minimizing the risk of asthma attacks during and after swimming.Swimming, while generally beneficial, can present unique challenges for children with asthma.
Factors like the environment, exertion levels, and specific triggers can significantly impact their respiratory health. Therefore, careful planning and proactive measures are essential to maintain a safe and positive swimming experience.
Potential Risks Associated with Swimming
Children with asthma may experience increased respiratory symptoms during or after swimming due to various factors. Cold water, chlorine, or other irritants in the water can trigger bronchospasms. Exertion during swimming can also strain the respiratory system, potentially leading to asthma attacks. Furthermore, exposure to airborne irritants like mold or mildew in certain swimming environments can exacerbate asthma symptoms.
These risks highlight the importance of careful preparation and supervision.
Importance of Proper Supervision and Monitoring
Constant supervision is paramount for children with asthma during swimming sessions. A designated adult should closely monitor the child’s breathing and overall condition. Regular checks for signs of distress, such as wheezing, coughing, or shortness of breath, are essential. Early intervention can prevent an asthma attack from escalating. Immediate action, including administering prescribed medication, is critical if symptoms arise.
Precautions in Different Swimming Environments
Swimming environments vary significantly, demanding different precautions. In a pool, the chlorine content can be a major trigger. Children with asthma should be closely monitored, especially during periods of increased exertion or exposure to chlorine. Open water presents different challenges. Unpredictable weather conditions, currents, and potential exposure to allergens in the surrounding environment require extra vigilance.
Parents must be acutely aware of the potential risks and take necessary precautions.
Necessary Precautions Checklist
This checklist Artikels essential safety measures before, during, and after swimming for children with asthma:
- Before Swimming: Administer prescribed medication as directed. Assess the child’s current asthma control. Ensure the child has appropriate swimwear and a towel.
- During Swimming: Maintain constant supervision. Keep an inhaler readily available. Monitor the child’s breathing and skin color. Encourage rest periods, especially during periods of intense activity.
- After Swimming: Monitor the child’s breathing for any signs of worsening symptoms. Encourage the child to warm up and dry off promptly to avoid chilling. Administer medication as needed.
Asthma Triggers to Avoid During Swimming
Specific triggers can exacerbate asthma symptoms during swimming. Children with asthma should avoid swimming in environments with high concentrations of chlorine, mold, or mildew. Exposure to irritants like dust or pollen should also be minimized. Furthermore, children should avoid swimming when they are already experiencing cold symptoms, as this can worsen their respiratory condition. Understanding these triggers can significantly reduce the risk of asthma attacks.
Modifications and Adaptations for Swimming
Swimming can be a fantastic activity for children, but it’s crucial to adapt the experience for those with asthma. Proper modifications and careful management of asthma triggers can make swimming a safe and enjoyable experience. Understanding how to adjust activities, medication use, and recognizing symptoms is key to a positive swimming experience.
Strategies for Modifying Swimming Activities
Modifying swimming activities involves several key strategies. First, starting with shorter periods of swimming and gradually increasing duration is vital. This allows the child’s body to adapt and prevents overexertion. Secondly, providing frequent rest breaks during swimming sessions is important. These breaks allow the child’s breathing to return to normal, preventing the buildup of symptoms.
Thirdly, ensuring the pool environment is comfortable and free from irritants is also critical. Avoiding chlorine-related irritants or other environmental triggers will significantly reduce the risk of asthma attacks. Finally, monitoring the child’s response to swimming activities and adjusting as needed is paramount. This proactive approach ensures that swimming remains enjoyable and safe.
Role of Medication and Inhalers in Managing Asthma
Asthma medication and inhalers play a critical role in managing asthma during swimming. Children with asthma should always carry their prescribed inhalers with them to the pool. Inhalers, especially those providing quick-relief medication, should be readily available for use during or after swimming. It is essential to understand that inhalers are not a guarantee against attacks, and they should be used in conjunction with the child’s regular asthma treatment plan.
Knowing the specific types of medication a child is on and the correct dosage is vital. This will aid in effectively managing asthma symptoms during and after swimming.
Adjusting Swimming Intensity and Duration
Adjusting swimming intensity and duration based on the child’s condition is crucial. Starting with shorter durations and lower intensity activities is essential. Swimming laps or engaging in longer periods of intense exercise may not be appropriate initially. The intensity should be gradually increased based on the child’s tolerance and response. It’s important to have a clear plan for modifying intensity and duration, which should be adjusted based on the child’s individual needs.
Recognizing and Responding to Asthma Symptoms
Recognizing and responding promptly to asthma symptoms during swimming is critical. Symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, coughing, chest tightness, or rapid breathing should be immediately addressed. If symptoms arise, the child should stop swimming immediately and use their inhaler as prescribed. If symptoms persist or worsen, seeking immediate medical attention is crucial. This proactive approach will help to prevent severe asthma attacks.
Swimming Strokes and Suitability for Children with Asthma
| Swimming Stroke | Exertion Level | Suitability for Children with Asthma |
|---|---|---|
| Backstroke | Moderate | Generally suitable, provides a relatively less strenuous activity |
| Breaststroke | Moderate to High | May be suitable with modifications, potentially higher exertion than backstroke |
| Butterfly | High | Generally less suitable due to high exertion and increased demand on respiratory system |
| Freestyle | High | Generally less suitable due to high exertion and increased demand on respiratory system |
The table above provides a general guideline for different swimming strokes and their suitability for children with asthma. The exertion level associated with each stroke can impact the child’s ability to manage their asthma symptoms. Modifying the intensity and duration of each stroke based on the child’s specific needs is vital.
Swimming Programs and Resources
Swimming is a fantastic activity for children, offering numerous physical and mental benefits. However, for children with asthma, careful planning and appropriate resources are crucial to ensure a safe and enjoyable experience. This section explores various swimming programs tailored for children with asthma, highlighting the importance of educational resources and different approaches to instruction.Many swimming programs can be adapted to meet the needs of children with asthma.
These programs often prioritize careful monitoring, medication administration, and understanding of asthma triggers. Educational resources are essential for both parents and children, providing valuable knowledge about asthma management and swimming safety.
Swimming Programs for Children with Asthma
Swimming programs designed for children with asthma typically involve a phased approach. Initial sessions often focus on acclimatization to the pool environment, building tolerance to water, and gradual introduction to swimming techniques. Experienced instructors are critical in these programs, ensuring they are familiar with asthma management protocols and able to recognize and respond to potential issues. These programs frequently include components like recognizing asthma symptoms, using inhalers correctly, and understanding the importance of hydration.
Educational Resources for Parents and Children
Educational resources play a vital role in empowering both parents and children with the knowledge and skills necessary for safe swimming. These resources can take many forms, including informative websites, brochures, and videos. These resources emphasize the importance of proper medication administration, recognizing asthma triggers in the pool environment, and understanding the signs of an asthma attack. They often provide practical tips for managing asthma during swimming activities, including pre-swimming warm-up routines and post-swimming relaxation techniques.
For example, the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America (AAFA) offers comprehensive resources for both parents and children on managing asthma and its impact on various activities, including swimming.
Comparing and Contrasting Approaches to Swimming Instruction
Different swimming programs may employ various approaches to teaching children with asthma. Some programs might focus on a slow, incremental approach, introducing techniques gradually and emphasizing relaxation. Other programs might emphasize a more structured, intensive approach, incorporating specific exercises and drills. Crucially, all programs should prioritize safety and allow for individual adjustments based on the child’s specific needs and asthma management plan.
Consistent communication between the swimming instructor and the child’s healthcare provider is essential for a successful program.
Reputable Organizations Offering Support
Numerous organizations provide valuable support and guidance for children with asthma and their families. The American Lung Association (ALA) and the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America (AAFA) offer valuable resources and information about managing asthma. These organizations often host workshops, support groups, and educational materials for parents and children. These groups can provide a valuable network of support and help families feel more confident in managing asthma during swimming.
Online Resources for Practical Advice and Guidance
Several online resources provide practical advice and guidance for parents of children with asthma who are interested in swimming. These resources offer valuable information, including videos demonstrating proper inhaler use and detailed explanations of asthma management strategies. A good example is the website of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), which offers valuable information about asthma and its management, including precautions for engaging in activities like swimming.
The websites of reputable medical organizations also often provide useful resources, such as educational materials and FAQs related to asthma and swimming.
- Websites: Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America (AAFA), American Lung Association (ALA), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- Videos: YouTube channels featuring asthma educators, or educational videos produced by reputable organizations like the ALA and AAFA, may offer practical demonstrations on managing asthma while swimming.
Swimming and Exercise for Children with Asthma: Swimming For Children With Asthma
Introducing swimming to children with asthma can be a rewarding experience, fostering physical development and enjoyment while managing potential risks. Proper guidance and gradual progression are key to ensuring a safe and enjoyable swimming experience for these children. A personalized approach, tailored to individual needs and breathing patterns, is crucial for maximizing benefits and minimizing any adverse effects.Understanding the importance of gradual progression and careful monitoring is paramount.
Swimming involves exertion and varying water temperatures, which can impact a child’s respiratory system. Implementing strategies for motivation and engagement helps children develop a positive association with swimming, creating a lifelong enjoyment of the sport.
Swimming is a fantastic activity for kids, but if your child has asthma, you need to be extra cautious. Proper hand hygiene is crucial, and knowing how to choose a safe hand sanitizer is key. For example, checking the ingredients and ensuring it’s child-friendly is vital, and how to tell if the hand sanitizer you’re buying is safe is a great resource for parents.
Ultimately, safe swimming practices are essential to keep your child healthy and enjoying the water.
Introducing Swimming to Children with Asthma: A Step-by-Step Guide
A gradual introduction is essential for children with asthma. Begin with short, supervised sessions in a familiar environment, focusing on water acclimation and basic aquatic skills. This approach allows for monitoring of breathing and exertion levels, minimizing potential triggers.
Swimming is a fantastic activity for kids, especially those with asthma. Proper breathing techniques are key, and it can actually help strengthen lung function. Learning to navigate the water safely, and developing a love of the aquatic world, can be surprisingly beneficial. Interestingly, Peruvian cuisine, particularly the work of Franco Noriega, Franco Noriega Peru cooking , emphasizes fresh, vibrant flavors that might inspire new approaches to healthy meals, which can indirectly contribute to a child’s overall well-being.
Ultimately, swimming offers a fun and accessible way to improve respiratory health for kids with asthma.
- Initial Sessions: Focus on water safety and comfort. Use a shallow end and provide support and encouragement. Short sessions (10-15 minutes) are sufficient. Ensure a calm and supportive environment.
- Building Endurance: Gradually increase the duration of sessions and incorporate basic water movements like kicking and arm strokes. Observe for signs of fatigue or difficulty breathing and adjust accordingly.
- Skill Development: Introduce more complex skills, such as floating and basic strokes. Maintain short sessions and provide ample rest periods. Focus on proper breathing techniques within the water.
Gradual Progression in Swimming Activities
Gradual progression is crucial for children with asthma. Avoid pushing the child beyond their capabilities. Observe for signs of distress, such as increased breathing rate, wheezing, or chest tightness. Adjust the intensity and duration of sessions based on the child’s response. Consistency is key to achieving sustainable progress.
- Monitoring Rest Periods: Incorporate regular rest periods between activities to allow the child’s respiratory system to recover. Encourage deep breaths and relaxation techniques during these breaks.
- Varying Difficulty: Alternate between periods of high and low intensity activities. Swimming involves variable exertion levels, and the child needs to adjust accordingly. Ensure that the child’s efforts are not beyond their comfort zone.
- Adapting to Individual Needs: Recognize that children react differently. Be flexible and adaptable, modifying the plan as needed to accommodate individual needs and progress.
Monitoring Breathing and Exertion Levels
Constant monitoring of the child’s breathing and exertion levels is essential. Look for signs of difficulty breathing, such as wheezing, rapid breathing, or chest tightness. Adjust the activity level and rest periods as needed.
- Recognizing Signs of Distress: Familiarize yourself with the specific signs that indicate the child is experiencing difficulty, such as increased breathing rate, wheezing, or chest tightness. Promptly address any signs of distress.
- Adjusting Intensity and Duration: Be prepared to reduce the intensity or duration of the swimming session if the child shows signs of exertion. Prioritize the child’s comfort and well-being.
- Importance of Hydration: Ensure the child drinks plenty of water before, during, and after swimming sessions to maintain hydration. Hydration is vital for overall health and athletic performance.
Motivating and Engaging Children in Swimming
Creating a positive and supportive environment is key to motivating children with asthma to participate in swimming. Celebrate small successes and focus on the enjoyment of the activity. Highlight the benefits of swimming, such as improved fitness and social interaction.
- Positive Reinforcement: Praise and reward the child for effort and progress, regardless of the outcome. Focus on the child’s effort and perseverance, fostering a positive attitude towards swimming.
- Making Swimming Fun: Incorporate games and activities to make swimming more engaging. Use positive language and encouraging words.
- Teamwork and Encouragement: Encourage participation with peers. Provide support and encouragement from other swimmers and coaches.
Stages of Swimming Lessons and Adjustments for Children with Asthma
The following table Artikels the different stages of swimming lessons and the corresponding adjustments for children with asthma.
| Stage | Description | Asthma Adjustments |
|---|---|---|
| Beginner | Water acclimation, basic safety | Short sessions, frequent rest breaks, close monitoring for signs of distress. |
| Intermediate | Introduction of basic strokes, kicking | Gradual increase in duration and intensity, monitoring exertion levels, individualised pace. |
| Advanced | Complex strokes, endurance training | Careful monitoring of breathing, adjust pace based on response, incorporate more rest periods. |
Swimming Environment and Equipment
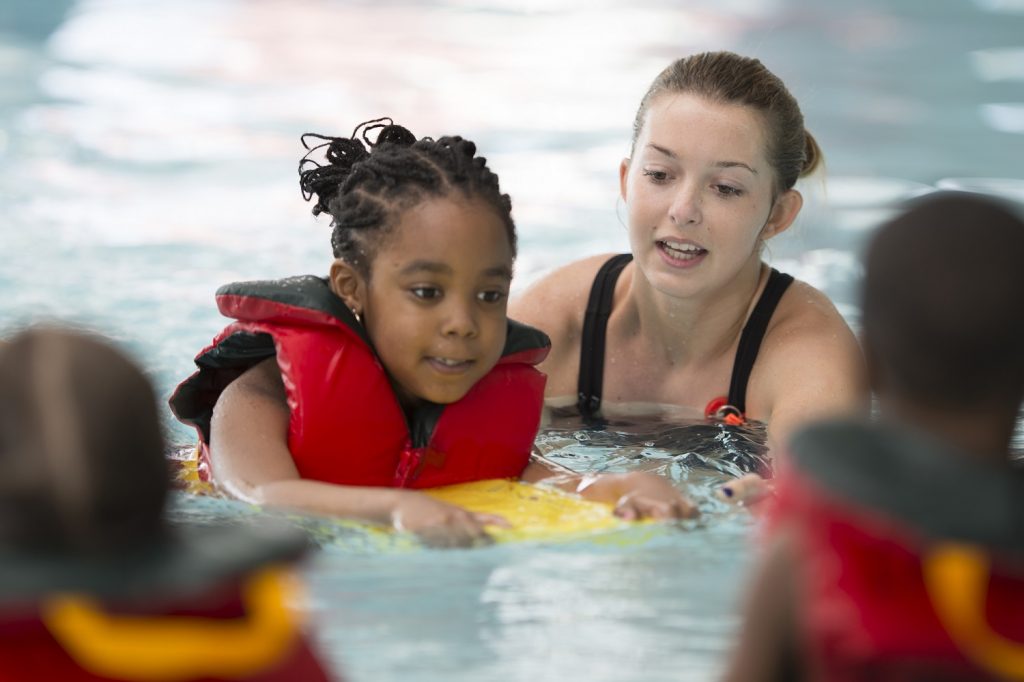

Swimming is a fantastic activity for children, but it’s crucial to ensure a safe and supportive environment, especially for those with asthma. Proper pool conditions, equipment, and attire can significantly impact a child’s comfort and well-being during their swim sessions. This section delves into the specifics of creating an optimal swimming experience for children with asthma.The ideal swimming environment for children with asthma prioritizes factors that minimize respiratory irritation and discomfort.
This includes careful consideration of pool water temperature, chemical levels, air quality, and the overall atmosphere within the pool complex. A well-managed pool environment can significantly improve the swimming experience for children with asthma, allowing them to fully enjoy the activity.
Ideal Pool Conditions
Maintaining optimal pool conditions is essential for children with asthma. Warm water temperatures, typically above 80°F (27°C), are often recommended, as they can reduce respiratory irritation. A well-maintained pH balance, ideally between 7.2 and 7.8, is crucial. Furthermore, ensuring adequate circulation and filtration to remove impurities is important to keep the water clean. Proper ventilation in the pool area, minimizing airborne irritants, is equally vital.
Swimming is a fantastic activity for kids with asthma, offering a low-impact workout that strengthens their lungs. However, as the weather turns colder, finding suitable winter activities for kids can be tricky. Luckily, exploring winter activities for kids can help you discover fun alternatives, while also keeping an eye on the health benefits of water activities like swimming.
Ultimately, swimming remains a great choice, even during the colder months, for children with asthma.
Air Quality in Swimming Pools
Air quality within the pool complex plays a significant role in the swimming experience for children with asthma. Pools should be well-ventilated to prevent the accumulation of chlorine fumes or other potentially irritating substances. Monitoring chlorine levels is essential. High levels of chlorine can exacerbate asthma symptoms in sensitive individuals. Regular checks and adjustments to chlorine levels can help mitigate potential issues.
Air quality is equally important outside the pool area, particularly during changing weather conditions or high pollen seasons.
Swimming Equipment Suitability
The choice of swimming equipment can affect a child’s swimming experience. For example, swim caps and goggles should be made of breathable materials to avoid irritation. Tight-fitting or poorly-ventilated swimsuits can lead to overheating and discomfort, potentially triggering asthma symptoms. Consider choosing materials that allow for proper airflow and ventilation. Lightweight and quick-drying swimsuits are recommended to prevent overheating during prolonged swimming sessions.
Lightweight swim caps are also recommended to prevent heat build-up.
Swimming Attire Selection
Selecting the appropriate swimming attire is crucial for a comfortable and safe swimming experience. Materials such as chlorine-resistant fabrics and quick-drying materials are recommended to minimize skin irritation. Choosing swimsuits that are not too tight or restrictive is vital to allow for proper breathing and prevent overheating. Swimsuits should be breathable to prevent excessive heat build-up.
Pool Chemicals and Their Impact
Certain pool chemicals can exacerbate asthma symptoms. Excessive chlorine levels, for example, can irritate the airways, triggering coughing and wheezing in susceptible individuals. Bromine, another common pool disinfectant, can also cause respiratory issues in some people. Monitoring and maintaining appropriate levels of pool chemicals is essential for ensuring a safe swimming environment. Exposure to certain cleaning agents used in the pool area, such as strong acids or bleaches, should also be avoided.
Testing the water regularly to ensure proper chemical levels is critical. A pool attendant or lifeguard should be available to address any chemical concerns immediately.
Nutrition and Hydration Before and After Swimming

Fueling your child’s body properly is crucial for both their swimming performance and overall health, especially if they have asthma. Proper nutrition before and after swimming helps maintain energy levels, supports respiratory function, and minimizes the risk of asthma triggers. Hydration plays a vital role in keeping airways clear and preventing dehydration, a common factor that can exacerbate asthma symptoms.Understanding the relationship between nutrition, hydration, and asthma is essential for supporting a child’s well-being during and after swimming.
A balanced approach to nutrition and hydration can help minimize asthma symptoms and maximize enjoyment of the activity.
Importance of Pre-Swimming Nutrition
Adequate fuel before swimming is vital for maintaining energy levels throughout the workout. A balanced meal or snack containing complex carbohydrates provides sustained energy, preventing fatigue and potential asthma flare-ups. Avoiding sugary snacks or overly processed foods before swimming is important.
Healthy Snack Choices Before Swimming
Choosing the right snacks before swimming is key to supporting a smooth and enjoyable experience. These snacks should be easily digestible and provide sustained energy.
- Whole-grain crackers with a small amount of nut butter: Provides a good balance of carbohydrates and protein for sustained energy.
- A small bowl of oatmeal with fruit: Oatmeal is a complex carbohydrate source, and fruit provides vitamins and minerals. Be sure to avoid overly acidic fruits that might trigger discomfort.
- A small portion of whole-wheat toast with avocado: Provides healthy fats, protein, and carbohydrates for sustained energy.
- Plain yogurt with berries: A good source of protein and probiotics, alongside the antioxidants and vitamins from berries.
Hydration Before and After Swimming
Maintaining adequate hydration is essential for respiratory health. Dehydration can worsen asthma symptoms by increasing airway inflammation.
- Encourage drinking water throughout the day, particularly before, during, and after swimming.
- Offer water, diluted fruit juices, or electrolyte drinks to aid in hydration.
- Avoid sugary drinks, as they can lead to a rapid rise and subsequent crash in blood sugar, which may worsen asthma symptoms in some individuals.
Post-Swimming Nutrition
Post-swimming nutrition helps replenish energy stores and aids in recovery. A meal or snack should contain a balance of protein and carbohydrates to support muscle repair and replenish glycogen stores.
Avoiding Food Triggers
Certain foods can trigger asthma symptoms in some individuals. It is crucial to identify potential triggers and avoid them.
- Common food triggers include dairy products, nuts, eggs, soy, wheat, and certain fruits.
- Consult with a pediatrician or registered dietitian to identify specific food triggers and create a personalized dietary plan to avoid them.
Nutritious and Easily Digestible Foods
Choosing foods that are both nutritious and easily digestible is important for children with asthma.
- Lean meats, poultry, fish, and beans provide protein for muscle repair.
- Whole grains like brown rice and quinoa are good sources of complex carbohydrates.
- Fruits and vegetables provide vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Milk and yogurt (if tolerated) provide calcium and protein.
Monitoring and Evaluating Swimming Progress
Swimming for children with asthma requires careful monitoring to ensure both enjoyment and safety. Regular evaluation of progress is crucial for adapting the program and ensuring the child’s well-being. This involves tracking breathing patterns, exertion levels, and overall participation, all while respecting the child’s comfort and limitations.
Breathing and Exertion Monitoring Strategies, Swimming for children with asthma
Monitoring a child’s breathing and exertion levels during and after swimming is essential. This involves observing their respiratory rate and effort, noting any changes in color (e.g., bluish tint), and listening for wheezing or other unusual sounds. Pay close attention to their heart rate and whether they seem overly fatigued or short of breath. Using a simple visual scale, such as a 1-5 rating, can help in documenting the intensity of their exertion.
A rating of 1 could signify minimal exertion, while a 5 could represent maximum exertion.
Assessing Enjoyment and Participation
Evaluating the child’s enjoyment and participation in swimming activities is just as important as monitoring their physical responses. Observe their facial expressions, body language, and interactions with others. Do they actively participate in drills and games? Do they appear enthusiastic or hesitant? Open communication with the child is key to understanding their feelings about the swimming sessions.
Asking them directly how they feel about the activity can provide valuable insight.
Tracking Progress and Making Adjustments
Regularly tracking progress is vital to making informed adjustments to the swimming program. This involves documenting the dates of swimming sessions, the activities performed, and any observed symptoms. This data can help identify patterns, trends, and areas where adjustments might be necessary. A well-maintained record can also aid in communication between the child’s caregivers, the swim instructor, and any medical professionals involved.
If the child is struggling, the program can be modified or adjusted to meet their individual needs.
Swimming Progress Log
This table provides a template for documenting swimming sessions and related health concerns.
| Date | Activity | Breathing Rate (breaths/minute) | Exertion Level (1-5) | Symptoms | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024-08-15 | Warm-up drills | 18 | 2 | None | Child participated actively |
| 2024-08-15 | Backstroke practice | 22 | 3 | Mild shortness of breath | Instructor adjusted the pace and rest periods |
| 2024-08-16 | Breaststroke practice | 20 | 2 | None | Child seemed more comfortable |
Swimming Session Log Template
This template provides a structure for recording swimming sessions and associated health information.
“Detailed records are crucial for identifying patterns, adjusting the program, and ensuring the child’s well-being.”
| Date | Time | Activity | Breathing Rate (breaths/minute) | Exertion Level (1-5) | Symptoms | Comments ||—|—|—|—|—|—|—|| | | | | | | |
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, swimming can be a rewarding experience for children with asthma, provided proper precautions and modifications are in place. This guide has highlighted the importance of safety, tailored programs, and ongoing monitoring to ensure a positive and healthy swimming journey. Remember, a proactive approach and a supportive environment are key to making swimming a safe and enjoyable activity for your child.